Sections of the site
Editor's Choice:
- Codes for GTA: San Andreas
- Prayer deceased brother from sister
- Why God allows suffering, illness and war and t
- Children's poem. Bookshelf - V. Vysotsky - Children's children's poems
- Why is it important to read the holy gospel and how to do it?
- Kazan Icon of the Mother of God
- Thank you very much for your attention
- Several interesting statements of the holy fathers about post
- Akathist Healer Great Panteleimonu on the health of sorrising
- Sunday, Sunday Day Orthodoxy Resurrection
Advertising
| Pathological processes in the throat - species, causes of the occurrence, methods of treatment. Chronic banal tracheitis of pharynx and larynx diseases: species and symptoms |
|
The most common diseases among adults and children are diseases of the ENT organs, namely larynx and pharynx. They develop mainly in the autumn-winter period when immunity is reduced and the frequency of colds and respiratory diseases increases. Diseases of pharynx and larynx: species and symptomsPathology of pharynx and larynx - one of the most common and deliver a large discomfort. Lor disease can flow in acute and chronic form. The diseases of the pharynx and larynx include:
Diseases are developing when viruses and bacteria are evolving. The following factors can provoke the development of these diseases: supercooling, inflammatory processes in nearby fabrics, endocrine diseases, gastrointestinal diseases, etc. Principles of drug treatment
After identifying the cause and type of disease, treatment is assigned:
Therapeutic therapy also involves the use of vitamin and mineral complexes, immunomodulator. Throughout the entire treatment period, more fluid should be used, eat to take in a rubber and warm form. Application of antibiotics: whether they need
Most often, the treatment of diseases of the pharynx and larynx consists of antibacterial therapy. Pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis, virus nature epiglotte is treated without using antibiotics. However, if a bacterial infection is joined, the pathology proceeds very hard. It is possible to develop serious complications. Antibiotics for diseases of the pharynx and larynx are prescribed in the following cases:
It is important to know that the improper use and selection of antibiotics can provoke the development of a chronic form, so it is forbidden to use antibiotics. From antibacterial drugs prescribe:
Antibiotics choose depending on the type of pathogenic microorganisms. Inhalation as a method of treatment
Inhalation therapy is one of the methods of treating diseases of the pharynx, larynx and respiratory organs. After the inhalation, the inflammatory process decreases, the pharynx is softened, the mucus dies and the pain decreases. Thanks to the nebulaizer, the drug is sprayed into small particles and penetrates all corners of the pharynx, almonds. When used as a solution, mineral water, anti-inflammatory agents (tincture of eucalyptus, Rotokan, etc.), antiseptics (, etc.), immunomodulators (, interferon, etc.) can be used as a solution. If there is no nebulizer, you can make steam inhalations. For steam inhalations can be used medicinal herbs, soda, etc. Recipes steam inhalation at home:
Inhalations are pronounced therapeutic effectHowever, before conducting, you should consult with your doctor. Rinse throat: how to perform a procedure
For rinsing, you can use both drugs and healing plants. Of medicines You can use:
Popular and long known is saline (on a glass of water a teaspoon salt and a little soda). If there is no allergies to iodine, then 3 drops of iodine can be added to the solution. The most common I. effective recipes For rinse throat:
The procedure should be performed no more than 5 times a day after eating in 30 minutes. After it, do not eat for an hour. Folk treatments
Inflammatory processes in the throat and larynx can be eliminated only with the help of medication methods. Reduce symptoms of laryngitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis and other pathologies of pharynx and larynx will help folk methods. Popular recipes for the treatment of nasopharynx diseases:
Folk methods with regular use reduce the error and pain, which significantly facilitates the state of the patient.
Inflammation of the mucosa of the rear wall of the pharynx can lead to peritonzillary abscess. The infection extends to nearby organs, provoking the development of pharyngitis and laryngitis. Usually it is provoked by streptococci. If the cause of acute pharyngitis is hemolytic Strelkokok Groups A, it provokes the development of articular rheumatism. With a decrease in immunity, viral pneumonia is possible.To avoid unpleasant consequences and possible complications, It is necessary to turn to and not to delay the treatment. Under the term "sickness of the throat" in everyday life, most often implies the ENT diseases of the pharynx (department of digestive and respiratory systems, which informs the nasal cavity, the oral cavity and the larynx). As in the case of other organs, the sickness of the throat may be a consequence of infection (viral, bacterial or fungal) - both acute and chronic, various injuries, harmful external influences (caustic and toxic substances, dust, tobacco smoke). ClassificationENT-Diseases of the throat can be divided into acute inflammatory, chronic inflammatory and complications. Diseases of the larynx and throat also include hypertrophy of the sky and pharyngeal almonds, foreign bodies, injuries and burns of the pharynx. Consider their details separately. SymptomaticsAcute inflammatory diseasesThis group includes acute pharyngitis and various angina, almost the most frequent throat disease in children.
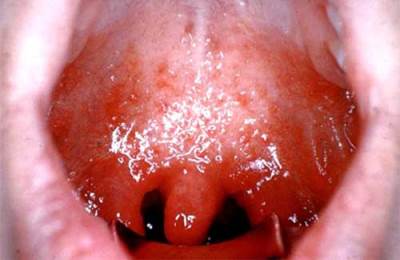
Acute pharyngitis - acute inflammation The mucous membrane of the pharynx, developing due to the impact of microorganisms or harmful factors Environmental, such as smoking, alcohol, etc. In this disease, the patient is most often complaining about the feeling of burning, dryness, sore throat, suffocation, sensations are described as "com in the throat". Temperature is usually either pain. Angina is a common acute infectious-allergic disease, developing with the damage to the lymphoid tissue of the pharyngeal ring. The reason most often serves a beta hemolytic streptococcus group A. An angine embodiment is isolated (catarrhal, follicular and lacunar), atypical forms, as well as specific angins with some infectious diseases and blood diseases.
- Most light form, characterized by pain and frang in the throat, a sense of "coma", minor pain when swallowing and slightly raising Temperatures. Follicular angina - Leaks harder with severe pain, irradiating in the ear, headache, weakness, sometimes vomiting, suffocate. Temperature can rise to 39 ° C. Lacooner is the most severe of banal forms. All almonds are covered with a raid, the lacuna is filled with a yellowish-white rode, and pains are also observed when swallowing, fever and symptoms of intoxication, including the feeling of "coma in the throat".
With phenomena, angina proceed:
It is possible to attach fungal infection. A separate form of angina is angina Simanovsky-Plata-Wensen. It causes a symbiosis of the spherose-like bacterium and the spirochki of the oral cavity, leading to the development of greenish plaque, the feelings of "coma" in the throat, rotten smell of mouth and high temperatures.
Anglets can proceed with complications, such as paratronzylitis, para- and retrofaring towing abscesses. Paraathonzillitis is the inflammation of the osindal fiber, manifested in a strong increase in temperature to 39-40 ° C, the impossibility of eating and smoothing saliva due to very strong pain, "Coma in the throat", choking; Also characterized by trisms - a symptom in which a person cannot fully open the mouth due to the tonic spasm of chewing muscles. In the cavity of the mouth in the projection of the almond, a major escape is revealed. Parafaringeal abscess is the suppuration of parafaring tape, and the refractoryal - plug. The symptoms are largely similar to paratronzillite (except for characteristic swelling), the differential diagnosis should be carried out by an ENT doctor. Hypertrophy AlmondsUnder this term implies the growth of lymphadendic tissue. Most often there are hypertrophic processes in the sky and pharyngeal almonds.
Children with such a disease do not sleep well, coughing at night, some of this may develop neuropsychiatric disorders. Chronic inflammatory diseasesRelated to them chronic forms pharyngitis and tonsillitis. Chronic pharyngit - Inflammation of the mucous pharynx - arises due to not enough effective treatment acute forms. Catarial, hypertrophic (side and granular) and atrophic forms are found.
Patients complain of sadness, allocation, tickness, "com" in the throat, suffocation, feeling foreign bodies, laying the ears. Temperature may not rise. Often to swallow something they need a sip of water. Chronic tonsillitis - persistent infectious-allergic disease with local manifestations in the form of inflammation of almonds. Most often arises as a complication of other infectious processes (such as angina and caries).
In a toxic-allergic form, symptoms of intoxication and allergyization are added to the angles, conjugate diseases are often found, such as rheumatism, glomerulonephritis, polyarthritis, endocarditis and others. Foreign bodies, injuries and burn burnsForeign bodies most often fall into the throat when talking or laughter during food, as well as children during games. Sometimes the ingredients in the elderly are dentures. Patients complain on com in throat, pain and breathing and swallowing.
The burning of the throat is the external and internal, penetrating and imperriburing, isolated and combined, blind and through. The symptoms most often are bleeding, respiratory disorders, speech, difficulty swallowing because of the "coma", suffocation, expressed by pain syndrome. Burns can develop with thermal and chemical lesions of the throat wall. Thermal burns more often causes the effects of temperatures - getting hot food and beverage, less often hot air or steam. Chemical burns occur when exposed to hydrochloric, acetic, nitric acids, caustic soda or potassium.
The burns are most often accompanied by pain, salivation, general intoxication. Because of the numerous complications of burn burns are a vital state.
TreatmentThe treatment of acute pharyngitis is usually carried out outpatient, he is prescribed the therapist or an ENT doctor. It includes rinsing with antiseptics (chlorophyptom, infusion of chamomile), aerosols (Phasex), desensitizing and immunostimulating drugs. Antibiotics are rarely appointed.
Banal angins are usually treated with an outpatient ENT doctor, in difficult cases - in the hospital. Antibiotics are prescribed from a group of penicillins, antihistamines (TAVEGIT, TELFAST), inhalation of bioparox, rinsing and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Treatment of infectious diseases and diseases of blood, accompanied by the phenomena of an angina should not hold an ENT, but an infectious hematologist in the respective hospitals.
With the sinks of the Simanovsky-Platie-Wensena, antibiotic therapy of penicillin preparations, a lining and vitaminity therapy; Sange the oral cavity and purify the almonds from necrotic foci.
Paragonzyllitis and other abscesses include antibiotic therapy and compulsory surgical intervention For rehabilitation of purulent foci. Chronic pharyngitis is treated outpatient an exception to the impact of harmful factors (alcohol, smoking), inhalations, lubrication of the throat Collargol (conducted by the ENT doctor), resorbing caramels with antiseptics (hexalysis, pharyingosept). In the treatment of chronic pharyngitis, both conservative and surgical methods are used. The first implies the washing of Lakun Almonds (10-15 procedures), lubrication of their surface with yodinol or collargol, rinsing and physiotherapy procedures (UHF or microwave therapy). Surgical methods include tonsillectomy. Similar, but less radical method - tonsillo - or adenotomy, respectively, treat hypertrophy of paternal almonds.
Foreign bodies remove the ENT doctor using special tongs or loops. It is not necessary to remove the foreign body yourself with the help of tweezers, as you can aggravate the process and call asphyxia. Surgical processing of the Russian Academy of Sciences also holds a LOR specialist if required tools and equipment, most often - in the hospital. Treatment of burn burns - a difficult and multistage process, cycling both Lorov and other specialists. Initially, all activities are usually aimed at preserving the life of the patient, then to prevent the formation of adhesions.
In the remote period, the most frequent procedure is a bunning - expanding the loss of the throat to restore its passability. PreventionDiseases of the throat are diverse, therefore their prevention is different. Train safety situations should be avoided, follow the used food and drinks, not to talk during meals. It is also necessary to treat all acute diseases in time, in no case leave the process is unremitted.
It helps to cope with viral and bacterial infections In just two days, it contributes to the activation of immunity and removes toxins from the body, reducing the time of rehabilitation. Absadines, surface injuries with dies with sharp foreign bodies, bone fragments falling with food; Gap soft sweat with an open mouth. Clinical symptoms. Sharp pain, painful swallowing, bleeding, life-threatening in damage to the vessels of the external carotid artery system. Diagnostics. Evaluate the patient's condition, complaints, history; circumstances of injury, objective examination: inspection oral cavity, pharynx (integrity of tissues of mucous, bleeding); Functions of the pharynx (swallowing, difficulty breathing due to reactive edema); Laboratory examination (clinical blood test, taps). Complication of wounds of pharyngeal: Infection of wounds, inflammatory processes, aspiration pneumonia, secondary bleeding from large neck vessels. Gold burns, oral cavity irritating liquidsObjectively: Depending on the degree of lesion, the spilled hyperemia, the expansion of the epithelium with the formation of raids, necrosis of the tissues of the submucms and muscle layers. Gold burns are combined with burns and larynx burns. Foreign bodies GLAKACauses. Often fall with food (fish and chicken bones, husk from seeds), extraneous random items, lack of food intake culture, hasty food; There may be dentures. Clinical signs. Feeling of an extraneous subject in the throat, urge to vomiting, stick pain when swallowing; With large foreign bodies - disruption of breathing, hemoptal, cough, breathing difficulties can be when the leech is hit during bathing in the reservoir. Acute inflammatory diseasesAdenoitisChildren of preschool age are sick. Causes. Infection; disease as a complication of inflammation in the nose and the apparent sinuses; pathogens: staphylococci; Intracellular microorganisms: mycoplasma, chlamydia, rhinoviruses; influenza virus, activation of a banal flora under the influence of cold; Artificial nutrition. Clinical symptoms. Acute start, dryness, burning, at an early age, the difficulty of the act of sucking, headache. Regional lymph nodes submandibular, cervical are increased, painful. Complications: Middle Otitis, sinusitis, recurrences of the disease lead to the hypertrophy of pharyngeal almonds. Acute pharyngitisCauses. Infection; lowering the resistance of the body; preceded rinofaringitis; weather. Objective signs: The temperature is normal, the mucous membrane of the rear and side wall of the pharynx is sharply hyperemic. Angina - acute tonsillitisThe most frequent diseases of the pharynx. Causes. The pathogen: hemolytic streptococcus, staphylococcus, adenovirus. Pre-providing factors: decrease in immunity, supercooling local, general. Angground classification:
With blood diseases (leukemia, monocytosis, agranulocytosis). Primary anginaCatarial anginaClinical symptoms. The easiest form is characterized by local manifestations, the children increase the temperature, the overall state suffers, the pain in the throat, dryness. Objectively: hyperemia of mucous membranes, swelling tonsils, increased, coated with mucous detachable; The submandibular lymph nodes are increased, slightly painful. The course of the disease is up to 5 days. Follicular anginaNetwork almonds are increased, on the surface enlarged jointed follicles, when ripening, revealed, forming white raids on the almond surfaces. Lacooner anegThe pain in the throat lasts until 3 days, in the treatment of phenomenon, inflammation will be stopped on the 7th day. Differential diagnosis - should be distinguished from angina with scarletin, diphtheria, blood diseases. Take into account the epidemic situation. Abscesses GlowParatonzillar abscessCauses. Penetration of infection from the depth of lacun into the okolidalic space with complicated angina; Contributing factors: a decrease in the body's resistance, carious teeth, local hypothermia. Objectively, with pharyngoscopy: hyperemia of the mucous pharynx on the side of the lesion, the voltage of the silicon almond on one side, the asymmetry of the soft nose, painful infiltrate around or almond, the small tongue is eaten. Limph nodes are enlarged and painful. When ripening, spontaneous openings are possible with the release of a significant amount of purulent exudate with an unpleasant odor. Pilot abscessCauses. The spread of infection from the nose, nasopharynk, injuries of the pharynx. Clinical symptoms. Heavy condition. Anxiety, rejection of food. Difficulty breathing, bellows. Clinical symptoms depend on the location of the abscess in lower departments, possibly suffocation, cyanosis. Objectively: with pharyngoscopy on the back wall of the pharynx, a spar-shaped infiltration is determined, hyperemia, pushes the chicken almond and the rear handguard. Young children are informative to palpator research. Differential diagnosis. Pilot abscess must be distinguished from pinch laryngitis, larynx foreign bodies. Complications. Pilot abscesses are dangerous due to aspiration respiratory tract Purulent content with independent opening of an ulcer, death is possible from suffocation, a large infiltrate can close the stroke into the larynx, which will lead to a disruption of breathing up to asphyxia, sepsis. Occonditional abscessCauses. Angina, paratonzillitis, carious teeth, pharynx injuries. Clinical symptoms. The general condition is severe, the difficulty of opening the mouth may be difficult to breathe. With pharyitingoscopy - hyperemia, infiltration on the side surface of the pharynx. Complications: purulent mediastinite. Acute and chronic diseases of the pharynx Adenoids. This is the growth of nasopharynk almond. It occurs between the ages of 2 to 15 years, by 20 years begin to atrophy. Inflammation of adenoid tissue is called adenoiditis. There are three degrees of increasing adenoids:
Symptoms:
Diagnostics:
1 method - conservative treatment. It is carried out at 1 and 2 degrees of increasing adenoids and during the period of inflammatory processes in the nasal cavity. 2 Method - Operational treatment - adenotomy. It is conducted in the hospital, the tool is adenot. Testimony to surgery: 3 degree, 2 degree at frequent colds and otitis and the absence of effect from conservative treatment, 1 degree in violation of hearing. Care B. postoperative period:
The main complications of adenoids and adenoiditis: a decrease in hearing, the development of chronic rhinitis, deformation of the facial skeleton and a bite disruption. 1. Hypertrophy of palatal almonds. An increase can be three degrees, but there is no inflammatory process in almonds. Almonds can interfere with breathing, food, rebuilding. For the third degree of increment, the operation is carried out - tonsillotomy - partial cutting of palatal almonds. A tonsillet is cut off part of the almonds serving beyond the limits of the sky. 2. Acute pharyngitis. This is an acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rear wall of the pharynx.
Clinical manifestations:
With pharyitingoscopy: hyperemia, swelling, mucous-purulent discarded on the rear wall of the pharynx. The infection can cover the nasopharynk and descend to the lower respiratory tract. Treatment: Elimination of annoying factors, gentle diet, warm drink, rinse throat, irrigation with solutions ("Kameton", "Inhalipte"), inhalation, oroseptics ("Faringosept", "Septol"), lubrication of the rear wall of the throat with lugol and oil solutions, Warming compresses, FTL. 3. Chronic pharyngitis. it chronic inflammation The mucous membrane of the rear wall of the pharynx. It is divided into 3 types: catarrhal or simple, hypertrophic and atrophic.
Clinical manifestations:
With pharyngoscopy:
Clinical manifestations:
With pharyngoscopy: a sharp blowout of one almond, the displacement of a soft sky and tongue (asymmetry of the language) in a healthy side, hyperemia of the mucous membrane, rotten smell of mouth. Different in the course of two stages: infiltration and abscess. Treatment: - Antibiotics wide spectrum actions:
During the ripening of the abscess, an autopsy is made (local anesthesia - irrigation with a solution of lidocaine) at the site of the greatest protrusion using a scalpel and washing the cavity by antiseptics. In the following days, the edges of the wound are diluted and washed. Paraphalitis patients are put on dispensary accounting with a diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis and should receive preventive treatment. When repeated paraphalids, almonds are removed (tonsillectomy operation). Chronic tonsillitis. This is chronic inflammation of the skynote almonds. It is more common in middle-aged children and adults up to 40 years. The cause of chronic tonsillitis is: an infectious-allergic process caused by staphylococci, streptococci, adenoviruses, herpes virus, chlamydia, toxoplasmas. Pre-providing factors:
Classification:
Clinical manifestations are divided into local manifestations and common. Complaints: Throat pain in the morning, dry, tingling, feeling of the foreign body in the throat, nasty smell From the mouth, a history of frequent angina. Local manifestations with pharyngoscopy:
General manifestations:
A compensated or simple form is the presence of complaints and local manifestations. Decompensated or toxic-allergic form - availability local signs and general manifestations. Chronic tonsillitis may have conjugate diseases (general etiological factor) - rheumatism, arthritis, heart disease, urinary system, etc. Treatment. All patients with chronic tonsillitis should be on dispensary accounting. Treatment is divided into conservative and surgical. Conservative treatment includes local and common. Local treatment:
General treatment.
Such treatment is carried out 2-3 times a year. In the absence of the effect of conservative treatment and the presence of frequent exacerbations of the disease is shown surgery - Tonsilectomy is a complete removal of cessing almonds, is carried out in patients with chronic decompensated tonsillitis. Contraindication for tonsillectomy are:
In this case, high-scoring treatment is carried out - cryotherapy or galvanokauksky. Preparation of patients with tonsilctomectomy operation includes: blood test for clotting and platelet content, examination internal organs, Sanation of foci of infection. Before the operation, a medical sister measures blood pressure, pulse, watches the patient not to take food. The operation is carried out under local anesthesia using a special toolkit. Care for patients in the postoperative period includes:
Important prophylactic work: identification of persons with chronic tonsillitis, their dispensary observation and treatment, good hygienic conditions Labor and others. Factors. Angina is acute infection With the local lesion of the lymphoid fabric of the sky almonds. Inflammation may occur in other almonds pharynx. Pathogenic microorganisms, more often beta hemolytic streptococcus, staphylococci, adenoviruses. Less often the causative agent are mushrooms, spirochetes, etc. Path transmission infection:
Pre-providing factors: supercooling, almond injuries, the structure of almonds, hereditary predisposition, inflammatory processes in the nasophaling and nasal cavity. Classification: more often meet - catarrhal, follicular, lacunar, fibrinous. Less often meet - herpetic, phlegmous, fungal. List of references
|
| Read: |
|---|
Popular:
New
- Not lies, but alternative facts: Press Secretary Donald Trump quarreled with the press on the very first day of work in the White House
- Laura Ingrea is the future spokesman for Trump and her Russian children
- Alina Saprykin: "I want to liberate the territory first of all
- Victoria Beckham: the story of the transformation into "sullen non-versa" Victoria Beckham nose
- Marion Cotiyar Figure Parameters
- Horoscope Career for Lev for March
- Virgo - Astroprognosis for December
- Camping in Crimea Minich and Lassi
- Horoscope for June Taurus Horse
- Women Tiger Virgin Tiger Symbols and Talismans






 If you do not take measures to treat and eliminate the symptoms of diseases of the pharynx and larynx diseases, it can lead to unpleasant consequences. Acute form of laryngitis can provoke the aggravation of bronchitis
If you do not take measures to treat and eliminate the symptoms of diseases of the pharynx and larynx diseases, it can lead to unpleasant consequences. Acute form of laryngitis can provoke the aggravation of bronchitis