Sections of the site
Editor's Choice:
- Codes for GTA: San Andreas
- Prayer deceased brother from sister
- Why God allows suffering, illness and war and t
- Children's poem. Bookshelf - V. Vysotsky - Children's children's poems
- Why is it important to read the holy gospel and how to do it?
- Kazan Icon of the Mother of God
- Thank you very much for your attention
- Several interesting statements of the holy fathers about post
- Akathist Healer Great Panteleimonu on the health of sorrising
- Sunday, Sunday Day Orthodoxy Resurrection
Advertising
| The causes and symptoms of the disease of the ENT organs. Acute inflammatory diseases of the pharynx treatment methods of the throat |
|
Sharp inflammatory diseases Things and Glows Acute inflammation of the pharynx sharp inflammation of the nasopharynk TO linen.The main complaints of patients are the unpleasant sensations in the nasopharynx - burning, tingling, dryness, often accumulation of the secrecy of the secret; Headache, localized in the occipital region. Children often have a disruption of breathing and bent. With the predominant localization of the process in the area of \u200b\u200bthe mouth of hearing tubes, there is pain in the ears, a decrease in the hearing of the type of sound engineering. In adults, this disease flows without a sharp deterioration in the overall state, and in children the temperature reaction is significant, in particular, in cases where inflammation applies to the larynx and the trachea. Painful cervical and occipital lymph nodes are increased. Differential diagnosis It should be carried out with diphtheria noodopharygitis (dirty-gray raids are usually visualized; the study of nasopharynk smear usually allows you to clearly establish the diphtheria nature of the lesion); with congenital syphilitic and gonococcal process (here other signs are the following signs - gonorial conjunctivitis, with luece - hepatosplegegaly, characteristic skin changes); With diseases of a wedge-shaped sinus and a lattice labyrinth cell (here, a radiographic study helps to establish the correct diagnosis). Treatment. Carry out infusion into every half of the nose of 2% (for children) and 5% (for adults) of the protargol solution or collargol 3 times a day; In pronounced inflammation, a 0.25% solution of nitric acid silver is poured into the cavity of the nose, and then the vasoconducting droplets. Conducting general anti-inflammatory and antibacterial treatment is justified only with a pronounced temperature reaction and the development of complications. It is shown the appointment of polyvitamins, physiotherapy - quartz on the soles of the feet, UHF to the nose area. Acute inflammation of the octopling (pharyngitis) Clinic. With acute pharyngitis, patients are most often imposed complaints of dryness, fellowship and soreness in the throat. Pain may radiate in the ear when swallowing. With pharyngoscopy, hyperemia and swelling of the oral mucosa are determined, an increase and bright hyperemia of lymphoid granules located on the rear wall of the pharynx. The pronounced forms of acute pharyngitis are accompanied by an increase in regional lymph nodes, in children in some cases - a temperature response. The process can be distributed both up (involving the nasopharynk, the mouth of the hearingpipes) and down (on the mucous membrane of the larynx and the trachea). Transition B. chronic forms It is usually due to the continuing impact of the pathogenic factor (professional harm, chronic somatic pathology). Differential diagnosis In children, they spend with a hymealic pharyngitis, syphilitic defeat. In adults it is necessary to consider pharyngitis (in the case of its non-infectious genesis) as a manifestation of the exacerbation of chronic somatic pathology, primarily the disease of the gastrointestinal tract (since the pharynx is a kind of "mirror", which reflects the problems in the organs below). Treatment It consists in excluding irritating food, the use of inhalation and pulverizations of warm alkaline and antibacterial solutions, common reaction The body shows the purpose of paracetamol, as well as a rich drink of a liquid rich in vitamin C. With a pronounced edema, the purpose of antihistamine preparations is shown. Angina Among the clinicians, it is customary to divide all available forms of an angino on vulgar (banal) and atypical .. Vulgar (banal) angina Vulgar (banal) angins are mainly recognized by pharyngoscopic features. For vulgar angins, the presence of four common features: 1) the pronounced symptoms of general intoxication of the body; 2) pathological changes in palatine almonds; 3) the duration of the process is not more than 7 days; 4) Bacterial or viral infection as a primary factor in etiology. Distinguish between their forms: Catarial angina It begins acutely, burning, perfense, a small pain when swallowing. In case of inspection, the tissue of almonds, the edges of the sky, almonds are spilled, the almonds are increased in the amount, places are covered with a film of the mucous-purulent exudate. Dry language, covered. Regional lymphouoslas are moderately increased. Follicular angina It is usually begins sharply with an increase in body temperature up to 38-39 0 s, sharp throat pain, increasing when swallowing, general phenomena of intoxication are more pronounced - headache, sometimes pain in the lower back, fever, chills, general weakness. In the blood of pronounced inflammatory changes - neutrophilee to 12-15 thousand, moderate roded shift to the left, eosinophilia, SE reaches 30-40 mm / h. Regional lymph nodes are increased and painful. With pharyngoscopy - spilled hyperemia and infiltration of a soft sky and a mudget, an increase and hyperemia of palatal almonds, numerous magic follicles are determined on their surface, which are usually revealed for 2-3 days from the beginning of the disease. Lacooner aneg It takes more hard. In case of inspection on the hyperemic surface of the sky, almonds, yellowish-white raids are observed, easily removable with a spatula, two-way localization. Incixing phenomena are more pronounced. Fibrinic (fibrinic-film) ahinka It is a type of two previous anneas and develops when the burst follicle follicles or fibrinous raids form a film. Here it is necessary to conduct a differential diagnosis with diphtheritic damage (based on the data of the bacteriological examination of the smear). Treatment. The basis of rational treatment of angin consists of compliance with the gentle regime, local and general therapy. In the first days, the bed regime is required, the allocation of individual dishes, care products; Hospitalization in the infectious department is necessary only in severe and diagnostically obscure cases of the disease. Food should be soft, unprazing, nutritious, abundant drink will contribute to disintellation. When appointing medicinal preparations The complexity of the approach is necessary. The basis of treatment is antibiotic therapy (the advantage is given to antibiotics wide spectrum Actions - semi-synthetic penicillins, macrolides, cephalosporins), course 5 days. The purpose of antihistamine preparations will help to stop the phenomena of edema, which mainly provokes pain syndrome. With pronounced intoxication, it is necessary to monitor the condition of cardiovascular and respiratory systems. In terms of local treatment, it is advisable to use drugs that provide local anti-inflammatory, anesthetic and antiseptic effect (septol, streptils, neo-angine). Rinsing with preparations that have a comprehensive action (OCI, Texetidine) are also highly effective. Phlegmonous angina (inttenonzillar abscess) is relatively rare, usually as a consequence of the purulent melting of the almond section; This defeat is usually one-sided. In this case, the almond is hyperemic, increased, the surface of it is tense, palpation is painful. Small inttenzillary abscesses usually revealed spontaneously and can proceed asymptomatic, but mostly it takes place in the breakthrough of the mouth to the oral cavity, the parapesillar abscess clinic is developing in paratrozillary cells. The treatment consists of a wide autopsy of the abscess, with recurrence, tonsillectomy is shown. Herpety angina develops mainly in young children, highly docking, and usually applies airborne, less likely - fecal-oral. Caused by adenoviruses, influenza virus, coke virus. The disease begins sharply, from fever up to 38-40 0 s, pain in the throat when swallowing, head and muscle pain develops, it is also vomiting and diarrhea as signs of general intoxication. With pharyngoscopy - in the field of soft sky, spilled hyperemia, on the entire surface of the oral mucosa, there are small reddish bubbles that are resolved after 3-4 days. To atypical angina applies first of all angina Simanovsky-Wenzan (The pathogen is the symbiosis of the spindle-shaped stick and spirochetes of the oral cavity), the basis for setting the correct diagnosis here is the microbiological storing of the smear. The differential diagnosis of such anneas should be carried out with the diphtheria of the pharynx, syphilis of all stages, tuberculous lesion of the almonds, systemic diseases of the blood-forming organs, which are accompanied by the formation of necrotic masses in the field of almonds, with tumors of tonsils. Angina Naso-cell almonds (acute adenoitis) is mainly found in children, which is associated with the growth of this almond in childhood. The causative agent can be both a virus and microorganism. In older children, with acute adenoy, there is a slight disorder of the general condition, the subfebilitation, the first symptom is the feeling of burning in the nasopharynk, and then the disease occurs as acute rhinitis, i.e. The difficulty of nasal breathing, watery, mucous membranes, and subsequently purulent discharge from the nose appear. Pains in the ears, bellows, in some cases it is possible to join the acute average otitis. With pharyngoscopy and rear rososcopy, the bright hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the rear wall of the pharynx is observed, according to which the mucous-purulent discharge flows from the nasophary. The nasopharynk almond is increased in size, it is hypered, it has point or solid raids on its surface. In early age children, acute adenoiditis begins suddenly with an increase in body temperature to 40 0 \u200b\u200bC, often with pronounced inxication-vomiting, liquid stool, symptoms of brain shell irritation. After 1-2 days, the difficulty of nasal respiration appears, discharge from the nose, an increase in regional lymph nodes. Complications of adenoiditis - catarrhal or purulent average otitis, retrofaring the abscess, the suppuration of regional lymph nodes. Differential diagnosis in children are carried out with children's infectious diseases, in which inflammation is possible in the nasopharynxal almond. Treatment, the general and local, spend on the same principles as with an angina, acute rhinestone. At heart age it is necessary to prescribe vesseloring drops into the nose before each feeding. The following are less frequent angns. Defeating side rollers - Usually combined with acute adenoiditis or occurs after the operation of tonsillectomy. For this species, angina is characterized by the appearance at the beginning of the development of the pain in the throat with irradiation in the ears. For angina Tubar Almonds (which is also basically noted during acute inflammatory diseases of the pharynx) a typical sign, along with sore throat, irradiating in the ears, is the labeling of the ears. The correct diagnosis is easy to install at rear rososcopy. Angina of the paternal almonds It is found mainly in the middle and old age, and the painfulness is characteristic of tongue and its palpation. Diagnostics are carried out with a laryngoscopic examination. It is important to remember that such terrible complications of the paternal sore throat, as swelling and stenosis of the larynx, are sometimes observed the glossite and phlegmon bottom of the oral cavity. For a general practitioner, it is important to correctly and promptly recognize the local complications of an angino, requiring consultations and treatment of an otorinolangologist specialist. This is first paratonzillitwhich develops a few days after the exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis or an angina. The process is most often localized in the front or front upper Department Between the capsule of the sky almond and the upper part of the front sky alignment. His rear localization is between almond and rear handle, bottom - between the lower pole and the side wall of the pharynx, the lateral - between the middle of the almond and the side wall of the pharynx. A typical clinic is the emergence of one-sided pain when swallowing, which with the development of the process becomes constant in nature and is sharply intensified when swallowing. Trices arises - the tonic spasm of chewing muscles, the speech becomes bent and an alignant. As a result of regional cervical lymphadenitis, pain reaction occurs when head turns. The transition of paraphalitis from the edema, the infiltrative phase in the absced usually occurs on the 3-4 days. On the 4-5th day, an independent opening of an abscess can occur - either into the oral cavity, or into parafaring aleacional space, which leads to the development of severe complication - parapharing. At the beginning of the disease before the abscess breakthrough with pharyngoscopy, the asymmetry of the 13th, due to the protrusion, most often of the superdalist area, hyperemia and infiltration of these tissues are noted. In the area of \u200b\u200bthe greatest protrusion, it is often possible to see thinning and yellowish edema - the place of the smoking breakthrough of the pus. In obscure cases, the diagnostic puncture is carried out. Differential diagnostics are carried out with diphtheria (however, for this infection, triumph is uncharactertene and often there are raids) and scarletina, in which the characteristic rash is developing, as well as indications of typical epidanamnez. Tumor lesions of the pharynx usually flow without increasing temperature and strong pain in the throat. In the face of inflammation, which also flows without increasing the temperature and severe throat pain. In the face of inflammation, which also flows without a trismity, there are spilled hyperemia and swelling with a brilliant background of the mucous membrane on the mucous membrane with a glittering background, and bubbles are poured on the soft sky. Paragonzillitis treatment In the stage of infiltration and abscess, surgical is the opening of an ulotnik, regular emptying, according to the testimony - abscess-tonsillectomy. The scheme of complex treatment of purulent pathology is presented earlier. Pilot abscessIt is usually found in small children due to the fact that the retrofaring (inseignant) space is filled with loose connective tissue with lymph nodes, as expressed in childhood. After 4-5 years, these lymph nodes are reduced. Symptomatics - Pain in swallowing, which, however, do not achieve such an extent as with paratonic abscess. In young children, these pains cause strong anxiety, a weakness, cry, sleep impairment, etc. Small patients refuse their breasts, cough, jerk milk through the nose, which is very soon entails a nutrition. Further symptoms depend on the reactivity of the body and the localization of the abscess. When it is located in the nasopharynk to the fore, there are breathing disorders, cyanosis appears, inspiratory retraction chest, the voice acquires a nasal shade. With a low position of the cap abscess, a narrowing of the entrance to the larynx is developing with an increasing respiratory impairment, which has a snoring character, which can later lead to the phenomena. With an even lower abscess location, symptoms of the esophagus and trachea appear. When viewing the oz, you can see a round or oval pillow-like swelling of the rear wall of the pharynx located on one (side) side and giving fluctuation. If the abscess is in the nasopharynk or closer to the entrance to the larynx, then it is unavailable by direct ferris, it is possible to identify it only at rear rososcopy or laryngoscopy, or palpatorially. With secondary plug abscesses, changes from the spine are joined to these symptoms, the impossibility of turning the head to the sides, the rigidity of the nape. Diagnostic valuable palpator examination. Differential diagnosis is carried out with a retrofaring tumor tumor (for example, lipoma), here the puncture will help properly diagnose. Treatmentsurgical. Parafaringeal abscessThis type of abscess is a relatively rare complication of the inflammatory process in the almond or near-chain tissue. The most commonly occurred parafaringeal abscess as a complication of paratronzillary abscess. There is a picture of a long non-permitted paratronzillic abscess, when or did not occur in the spontaneous opening of an ulcer, or incoming incoming, or it did not lead to the desired result. The overall condition of the patient continues to deteriorate. High temperatures holds, leukocytosis increases in the blood, ESP increases. In pharyitingoscopy, there is a decrease in the swelling and protrusion of a soft sky in some cases, but the proportion of the side wall of the pharynx in the almond region appears. Protecting in the parafaring land area accompany changes from the neck. Along with increased and painful with palpation with lymphatic nodes, a more diffuse and painful swelling appears in the field of the angle of the lower jaw (both at the angle of the lower jaw and in the region of the mesh). If the specified swelling against the background of the degradation of the general condition of the patient is joined by pain in the course of the vascular beam, then it is necessary to think about the beginning of the development of the septic process. Occonditional abscess, not timely opened, entails further complications: sepsis is most often found due to involvement in the internal jugular vein process. With an abscess in the parafaring-plane space, the process may propagate up to the base of the skull. Distribution of the process of the book leads to mediastinitis. An purulent parotitis may also occur due to a breakthrough in the bed of the parole. Treatment Parafaringent abscess only surgical. Gundy Angina - acute inflammation Lamfadenoid tissue of the larynx (in the field of scrambled-haired folds, intersperpalotic space, in morganic ventricles, pear sinus and individual follicles). The disease can develop as a result of injury (in particular, foreign bodies), as well as the complication of ARVI. The patient complains of pain when swallowing, pain when changing the position of the head, dry throat. The phenomena of general intoxication are expressed moderately. Regional lymphadenitis is determined, usually one-sided. With laryngoscopy, hyperemia and infiltration of the mucous membrane of the larynx on one side or a limited area are revealed. Upon the protracted flow of the process, the formation of abscesses in the location of lymphoid fabric is possible. Treatment is the same as in acute catarrhal laryngitis, but in severe cases it is necessary to appoint massive antibiotic therapy. With significant stenosis, the imposition of tracheostas is shown. The patient must observe the regime that is gentle by the diet, useful alkaline inhalations. Anti-inflammatory therapy includes the introduction into the body of sulfanimamides, antibiotics; Mandatory use of antihistamine drugs. Laryngitis sharp catarrhal laryngitisAcute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx can be observed both as an independent disease (cold, too hot or cold food), chemical or mechanical stimuli (nicotine, alcohol, dusty and smoky air), professional harm, for example, excessive voice tension (strong cry, loud command ), and with common diseases, such as measles, cough, influenza, typhoid, rheumatism, etc. Clinical acute laryngitis is manifested by the occurrence of hoarseness, perversions, sore throats, the patient worries dry cough. Violation voices is expressed in varying degrees of dysfony, right up to Afony. The diagnosis of acute laryngitis is not difficult to deliver, based on the anamnesis, symptoms and characteristic hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the larynx. Differential diagnosis should be carried out with a false criterion (in children) and the damage to the larynx during diphtheria, tuberculosis, syphilis. The treatment must first provide for a strict voice regime, a diet with a restriction of acute, hot, cold food, alcohol, smoking. Highly efficient inhalations with antibiotic solution (fuzafungin 2 inhars 4 times a day), with the predominance of the edema component over inflammatory, it is advisable to appoint inhalations with hydrocortisone or the use of inhaler of the beclometazone of dipropionate 2 inhale 3 times a day, antihistamines are also used from local treatment - infusion In the larynx vegetable oil (peach, olive), hydrocortisone suspension. Phlegmonous (infiltrative-purulent) laryngitisFlegmonous (infiltrative-purulent) Larygitis is relatively rarely either due to injury, or after the infectious disease (in children - cortex and scarlatine). The pathological process is involved with a submembricted layer, less often - muscular and bunding apparatus of the larynx. Patients complain of a sharp pain when swallowing, especially at the location of the infiltration in the field of the epiglotter and the damage-shaped cartilage. Regional lymphadenitis is palpable. With laryngoscopy, hyperemia and infiltration of the mucous membrane of the larynx, an increase in the scope of the affected area, sometimes with the areas of necrosis are revealed. There is a limitation of mobility of larynx elements. A total inflammatory response is expressed. Treatment is carried out in the hospital, taking into account the severity of the picture. With increasing phenomena, the stenosis is carried out by tracheostomy. Complex therapy is necessary with the inclusion of antibiotics, antihistamine drugs, according to indications - Mukolithics. In the presence of abscess, its treatment is only surgical in a specialized hospital. Hondroperichondrite cartilage laryngesThe emergence of this pathology is associated with the infection of the cartilage and the superior to the skeleton of the larynx as a result of its injury (including after surgery). As a result of the suffered inflammation, necrosis of cartilage tissue may occur, the scarring, which leads to the deformation of the organ and the narrowing of its lumen. The clinical picture is determined by the localization of the inflammatory process and the degree of its development, during laryngoscopy, a hyperemic area is revealed with thickening to be tissues, their infiltration, often with the formation of a fistula. In addition to massive antibiotic therapy and hyposensibilization, physiotherapeutic treatment is a majority treatment - UV, UHF, microwave, ionogalvanization for larynx with calcium chloride, potassium iodide. The treatment of chondroperichondrites of the larynx must be carried out under a specialized hospital. Podskaya LarygitSupporting laryngitis (false croup) is a type of acute catarrhal laryngitis, developing in a swinging space. It is observed in children aged 2-5 years against the background of acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose or pharynx. Clinic False cereal is quite characteristic - the disease is developing suddenly among the night, the bout of the cough. Breathing becomes whistling, sharply difficult, expressed inspiratory shortness of breath. Nails and visible mucousse acquire a cyanotic shade. In case of inspection, there is an increase in soft tissues of the yapper, above and connectible spaces. The attack lasts from a few minutes to half an hour, after which the profuse sweat and the improvement of the state appears, the child falls asleep. Diagnostics is based on the clinical picture of the disease and data of laryngoscopy in cases where it is possible to perform. Differential diagnosis is carried out with true (diphtheria) crop. In the latter case, the suffocation develops gradually and does not debut acute rinoparyitis. Regional lymphadenitis is expressed. Typical manifestations - dirty gray raids in the throat and larynx. It is necessary to train parents of children who have similar states, a certain tactics of behavior. Usually these are children prone to laryngospasm suffering in diathesis. LEGAL EVENTS - Moisturizing and air ventilation in the room where the child is located; It is recommended to give warm milk, "Borjomi". Use distracting tools: on the neck mustard pieces, hot foot baths (no more than 3-5 minutes). In efficiency shows the imposition of tracheostas. Highland swelling It is not an independent disease, but only one of the manifestations of many pathological processes. Maudan's swelling is inflammatory and disgraining. The inflammatory swelling of the larynx may accompany the following pathological processes: Gunted angina, phlegmonous laryngitis, abscess of the nastestrian, native processes in the throat, lateral inclusive and capped spaces, in the region cervical department Spine, the root of the tongue and soft tissues of the oral cavity. One of the frequent causes of the larynx swelling are injuries - firearms, stupid, stitching, cutting, thermal, chemical, foreign bodies. The traumatic swelling of the larynx can develop in response to surgical intervention in the larynx and neck, as a result of long-lasting top tracheobronchoscopy, due to long-term and traumatic larynx intubation, after radiation therapy for diseases of the neck organs. The abnormal swelling of the larynx as a manifestation of allergies occurs when idisincasia to some food products, medicinal and cosmetic drugs. This can also include angioemical swelling of Quinka, in which the swelling of the larynx is combined with edema and neck. Highland swelling can develop with diseases of the cardiovascular system, accompanied by the insufficiency of blood circulation II-III degree; Diseases of kidneys, liver cirrhosis, cachexia. Treatment in the swelling of the larynx is aimed at treating the main disease that led to the edema and includes dihydration, hyposensitizing and sedatives. First of all, the following appointments are appropriate with the inflammatory nature of the larynx swelling: 1) antibacterial therapy parenterally (pre-clarifying the portability of drugs; 2) a solution of semicolound 0.25% 2 ml in the muscle 2 times a day; Calcium gluconate solution is 10% intramuscularly depending on the degree of edema severity; 20 ml of 40% glucose solution, 5 ml of solution ascorbic acid intravenously drip 1 time per day; Rutin 0.02 g inside 3 times a day; 3) hot (42-45 0 c) foot baths for 5 minutes; 4) warming compress on the neck or mustard plants for 10-15 min 1-2 times a day; 5) With the cough, the occurrence of crusts and thick sputum - expectorant and diluting wets of the means (carbocyusein, acetylcysteine). Inhalation: 1 chimotrypsin vial + 1 ephedrine + 15 ml 0.9% sodium chloride solution, breathe 2 times a day to 10 minutes. Treatment should always be carried out in a hospital, since when increasing the difficulty of breathing through the larynx may require tracheostomy. Acute tracheitis . Typically, the disease begins with acute catarrhal rhinitis and naphorgitis and quickly applies to the book, covering the trachea, often and large bronchi. In other cases, large bronchi is involved simultaneously with the trachea. In this case, the clinical picture acquires the character acute tracheobronchita . The most characteristic clinical sign of acute banal tracheite is cough, especially strongly disturbing the patient at night and in the morning. With a pronounced inflammatory process, for example, influencing hemorrhagic trachelieThe cough is of a painful fitful character and is accompanied by a stupid slandering pain in Zeva and beast. Due to the pain with deep breath, patients are trying to limit the depth of respiratory movements, which is why the breathing is expected to compensate for the oxygen deficiency. The overall state of adults suffers a little, sometimes there is a subfebilitation, headache, a sense of breakdown, pain in the whole body. In children, the clinical picture proceeds sharply with an increase in body temperature up to 39 ° C. Dyspnea usually does not happen, with the exception of sharp heavy generalized Viral lesions of the SDP, in which there are pronounced general intoxication, a violation of cardiac activity, the oppression of the respiratory center. The wet at the beginning of the disease is scarce, it is difficult to find it, which is explained by the stage of "dry" catarrhal inflammation. Gradually, it acquires mucous-purulent character, becomes more abundant and is more easily separated. Cough ceases to cause unpleasant scrubbing pains, the general condition improves. With ordinary clinical flow And in a timely manner, the disease is completed within 1-2 weeks. Under adverse conditions, non-compliance with the prescribed regime, a non-time-started treatment and other negative factors, recovery is delayed and the process can go to the chronic stage. Diagnostics the acute banal trachea of \u200b\u200bdifficulties does not cause, especially in cases of seasonal colds or flu epidemics. The diagnosis is established on the basis of a typical clinical picture and characteristic symptoms of catarrhal inflammation of the tracheal mucosa. Difficulties occur during influenza toxic forms when the inflammation of the respiratory tract should be differentiated with pneumonia. Treatment almost identical to such with acute laryngitis. The prevention of complications in the pronounced forms of tracheoobronichite are great importance, for which the patient is prescribed antibacterial, immunomodulatory, a lining treatment with intensive vitamin (A, E, C) and disinfecting therapy. Preventive measures are particularly relevant on dusty production and in periods of influenza epidemics. Chronic banal tracheitisChronic tracheitis is a systemic disease that is addictive to one degree or another airways- Disease is a predominantly adult population of large industrial cities, people of harmful productions and abusing bad habits. Chronic tracheobronchites can act as complications of children's infections (measles, diphtheria, cough, etc.), the clinical flow of which was accompanied by sharp tracheitis and bronchitis. Symptoms and clinical current. The main symptom of chronic tracheite is a cough, stronger in the night and morning. This cough is especially painful with a cluster of sputum in the area of \u200b\u200bkarins, drying into dense crusts. With the development of an atrophic process, in which only the surface layer of the mucous membrane is affected, the cough reflex persists, however, with deeper atrophic phenomena, breathtaking and nerve endings, cough severity decreases. The course of the disease is long, alternating with periods of remission and exacerbation. Diagnosis install using fibroscopy. However, the reason for the occurrence of this disease often remains unknown, with the exception of cases when it occurs in people of harmful professions. Treatment determined by the form of inflammation. With a hypertrophic trachea, accompanied by the release of mucous-purulent sputum, the inhalation of antibiotics is used, the selection of which is carried out on the basis of the antibioticogram, blowing at the moment of inhalation of the binding powders. In atrophic processes in the trachea, vitamin oils are instilled (carotoline, rosehip oil and sea buckthorn). Corks are removed by infusion in the trachea solutions of proteolytic enzymes. Basically, the treatment corresponds to those in banal laryngitis. The inflammatory diseases of the esophagus include: Acute esophagitis. Chronic esophagitis. Reflux Ezophagitis. The peptic ulcer of the esophagus. The last two diseases are the result of a systematic irritation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus with an acidic content of the stomach, causing inflammation and dystrophy of tissues. Acute esophagitis.Acute acute esophagites arise as a result of an acute bacterial or viral infection. They do not have practical significance during the disease and disappear along with other signs of the disease, if they do not acquire an independent chronic flow. Acute esophagitis can be: Catarrhal esophagitis. Hemorrhagic esophagitis. Purulent esophagitis (abscess and phlegmon of the esophagus). The reasons for the occurrence of acute esophagitis are a chemical burn (exfoliative esophagitis) or injury (zakost, wound when swallowing acute items, bones). Clinical picture acute esophagitis. Patients complain with acute esophagitis for pain behind the sternum, amplifying when swallowing, sometimes dysphagia. The disease occurs sharply. It is also accompanied by other signs inherent in the main process. With influenza - this is an increase in temperature, headache, pain in the sip, etc. With a chemical burn there are guidelines for reception inside alkali or acid, traces of a chemical burn on the oral mucosa are found in the throat. The abscess or phlegmon of the esophagus is characterized by severe pain behind the sternum when swallowing, the difficulty of swallowing dense food, while the warm and liquid food in it is not delayed. Signs of infection and intoxication appear - an increase in body temperature, leukocytosis in the blood, ESP increased, has a place of proteinuria. X-ray study It allows you to detect an infiltrate that causes some delay in the food lump, to establish its localization and degree of damage to the wall of the esophagus. Ezophagoscopy: mucosa in the field of infiltrate hyperemic, edema. With a careful study, it is possible to find the opposition - fish bone or acute bone, stuck in the fabric of the esophagus. With the help of tongs foreign body extracting. The edge of the device is possible to try the density of infiltrate. If the abscess matured, the tissue of a soft consistency is revealed in the center. Diffuse Ezophagitis accompanied by hyperemia and swelling mucous. It is covered with a white and gray raid, easy to bleed. Erosions have an irregular shape, more often the longitudinal, covered with a gray raid. Peristalistics saved. Acute esophagitis can occur without consequences. After chemical burn, powerful scars develop, causing the esophagus narrowing. Acute and chronic diseases of the pharynx Adenoids. This is the growth of nasopharynk almond. It occurs between the ages of 2 to 15 years, by 20 years begin to atrophy. Inflammation of adenoid tissue is called adenoiditis. There are three degrees of increasing adenoids:
Symptoms:
Diagnostics:
1 method - conservative treatment. It is carried out at 1 and 2 degrees of increasing adenoids and during the period of inflammatory processes in the nasal cavity. 2 way - operational treatment - adenotomy. It is conducted in the hospital, the tool is adenot. Indications for surgery: 3 degree, 2 degree in frequent colds and otitis and the absence of effect from conservative treatment, 1 degree in case of hearing impairment. Care B. postoperative period:
The main complications of adenoids and adenoiditis: a decrease in hearing, the development of chronic rhinitis, deformation of the facial skeleton and a bite disruption. 1. Hypertrophy of palatal almonds. The increase can be three degrees, but inflammatory process There is no almonds. Almonds can interfere with breathing, food, rebuilding. For the third degree of increment, the operation is carried out - tonsillotomy - partial cutting of palatal almonds. A tonsillet is cut off part of the almonds serving beyond the limits of the sky. 2. Acute pharyngitis. This is an acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rear wall of the pharynx.
Clinical manifestations:
With pharyitingoscopy: hyperemia, swelling, mucous-purulent discarded on the rear wall of the pharynx. The infection can cover the nasopharynk and descend to the lower respiratory tract. Treatment: Elimination of annoying factors, gentle diet, warm drink, rinse throat, irrigation with solutions ("Kameton", "Inhalipte"), inhalation, oroseptics ("Faringosept", "Septol"), lubrication of the rear wall of the throat with lugol and oil solutions, Warming compresses, FTL. 3. Chronic pharyngitis. This is a chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rear wall of the pharynx. It is divided into 3 types: catarrhal or simple, hypertrophic and atrophic.
Clinical manifestations:
With pharyngoscopy:
Clinical manifestations:
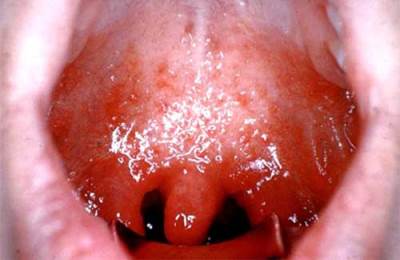
With pharyngoscopy: a sharp blowout of one almond, the displacement of a soft sky and tongue (asymmetry of the language) in a healthy side, hyperemia of the mucous membrane, rotten smell of mouth. Different in the course of two stages: infiltration and abscess. Treatment: - Wide spectrum antibiotics:
During the ripening of the abscess, an autopsy is made (local anesthesia - irrigation with a solution of lidocaine) at the site of the greatest protrusion using a scalpel and washing the cavity by antiseptics. In the following days, the edges of the wound are diluted and washed. Paraphalitis patients are put on dispensary accounting with a diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis and should receive preventive treatment. When repeated paraphalids, almonds are removed (tonsillectomy operation). Chronic tonsillitis. This is chronic inflammation of the skynote almonds. It is more common in middle-aged children and adults up to 40 years. The cause of chronic tonsillitis is: an infectious-allergic process caused by staphylococci, streptococci, adenoviruses, herpes virus, chlamydia, toxoplasmas. Pre-providing factors:
Classification:
Clinical manifestations are divided into local manifestations and common. Complaints: Throat pain in the morning, dry, tingling, feeling of the foreign body in the throat, nasty smell From the mouth, a history of frequent angina. Local manifestations with pharyngoscopy:
General manifestations:
A compensated or simple form is the presence of complaints and local manifestations. Decompensated or toxic-allergic form - the presence of local signs and general manifestations. Chronic tonsillitis may have conjugate diseases (general etiological factor) - rheumatism, arthritis, heart disease, urinary system, etc. Treatment. All patients with chronic tonsillitis should be on dispensary accounting. Treatment is divided into conservative and surgical. Conservative treatment includes local and common. Local treatment:
General treatment.
Such treatment is carried out 2-3 times a year. In the absence of the effect of conservative treatment and the presence of frequent exacerbations of the disease is shown surgery - Tonsilectomy is a complete removal of cessing almonds, is carried out in patients with chronic decompensated tonsillitis. Contraindication for tonsillectomy are:
In this case, high-scoring treatment is carried out - cryotherapy or galvanokauksky. Preparation of patients with tonsilctomectomy operation includes: blood test for clotting and platelet content, examination internal organs, Sanation of foci of infection. Before the operation, a medical sister measures blood pressure, pulse, watches the patient not to take food. The operation is carried out under local anesthesia using a special toolkit. Care for patients in the postoperative period includes:
Important prophylactic work: identification of persons with chronic tonsillitis, their dispensary observation and treatment, good hygienic conditions Labor and others. Factors. Angry is an acute infectious disease with the local lesion of the lymphoid tissue of the sky almonds. Inflammation may occur in other almonds pharynx. Pathogenic microorganisms, more often beta hemolytic streptococcus, staphylococci, adenoviruses. Less often the causative agent are mushrooms, spirochetes, etc. Path transmission infection:
Pre-providing factors: supercooling, almond injuries, the structure of almonds, hereditary predisposition, inflammatory processes in the nasophaling and nasal cavity. Classification: more often meet - catarrhal, follicular, lacunar, fibrinous. Less often meet - herpetic, phlegmous, fungal. List of references
In children. In the structure of the pharynx, 3 departments are distinguished: the nasopharynx, the rotogling and the aluminum. Pathological processes occurring in the throat are also divided depending on localization. With acute viral or bacterial inflammation, the mucous membrane of all pharynx departments is affected. In chronic pathology, the mucosa of one anatomical department is usually affected. EtiologyThe reason for the acute inflammation of the pharynx is infection:In more rare cases, respiratory syncitial virus, and human immunodeficiency become pathogens.
An annoying factors contributing to the development of the disease include:
The main factors provoking the disease include the following:
ClassificationFaringite is classified for two main forms - acute and chronic.
By origin, pharyngitis is classified for types:
By the nature of the defeat and morphological changes:
SymptomaticsBasic clinical sign Acute pharyngitis is the pain in the throat, increasing when coughing. Often the appearance of pain is preceded and the response that persists within a few days. The larger the swelling of the mucous membrane, the pain is more intense. Strong pain puts into ears and causes refusal of patients from food. After the formation of persistent owl syndrome A painful, dry, "scratching" throat appears. General symptoms of pharyngitis are: the deterioration of the general condition, weakness, malaise, fast fatigue, fever. These signs of intoxication are preserved within three days and gradually pass.
The ENT doctor on the examination of the patient detects hyperemia of the rear wall of the pharynx with the sections of the mucous-purulent plaque, as well as the swelling of the sky, almonds and tongues. The submandibular and cervical lymph nodes are painful and enlarged in most patients. Pharisingoscopy makes it possible to detect the inflamed mucosa of the rear wall of the pharynx with characteristic manifestations - hyperemia, edema, lymphoid granules on the mucous membrane. Gonococcal Farriangit - Symptom of urogenital gonorrhea, and in some cases - independent pathology. Gonorrheal pharyngitis develops after an unprotected orogenital act with an infected person. In most cases, pathology proceeds asymptomatic and is revealed by chance with a microbiological study. In some patients, classical symptoms of pharyngitis are developing. On the hyperemic and edema mucosa of the rotogling appear sections with Allergic pharyngitis - Inflammation of the pharynx, developing after the allergen hitting the mucous membrane. As allergens, dust, pollen, pet wool, feather, drugs, food, chemicals used in everyday life and manufacturing are used. All symptoms of allergic pharyngitis are associated with swelling of the mucous pharynx. The disease is manifested local signs - dry, sharp, elevated. In addition to the symptoms of the inflammation of the pharynx, nasal is concluded, and other signs associated with the effects of allergen to the upper respiratory tract. If it is not eliminated in time, then sharp pharyngitis can go into chronic.
Local signs of catarrhal inflammation:
Patients become irritable, they have a dream and normal rhythm of life.
In adults, some forms of chronic pharyngitis may differ by morphological changes and clinical signs.
Features of inflammation pharynx in childhoodPharyngitis - pathology, quite often affecting children's organismflowing in various forms and is often a manifestation of other disease - adenoiditis, tonsillitis. To avoid heavy complications and the transition of the disease in an atrophic or subatrophic shape, sick children are forbidden during the week to go outside to crude weather and soar the throat. Soda rinsings also do not recommend children with chronic pharyngitis, since the soda dries the mucous membrane, which can provoke the development of severe complications. To identify pathology in kids is quite difficult. This is due to low-rise clinical manifestations that do not allow to identify the disease "to the eye". After listening to the complaint, the specialist inspects the chiffs of the child. The rotogling with a given disease is red, sweeping, swollen with the presence of the mucous membrane or purulent discharge, the rear wall of the grainy with point hemorrhages or bubbles filled with blood. Key complaints of a child:
Local signs are saved a couple of days and gradually disappear. Temperature of the body is subfebrile or normal. Children is usually painful to swallow saliva than food.
With the accession of secondary infection and the development of complications (angina or adenoiditis), general symptoms with severe intoxication begins to grow.
Pharyngitis during pregnancyFarrygit, like any other disease, is a dangerous for the body of a pregnant woman and creates many inconvenience associated with the inability to use the usual treatments. The disease is manifested in pregnant women by classic local signs, subfebrile temperature, lymphadenitis, voice hoarse, an adsadous cough. Faringitis often complicates the course of pregnancy. In the absence of adequate treatment in the early deadlines, it can lead to miscarriage, and in later - to premature birth. DiagnosticsThe diagnosis of pharyngitis includes the instrumental examination of the patient - pharyngoscopy, immunodiagnostics, microbiological research of the separated nasopharynx, determination in streptococcal antigens. If the first suspicions appear on the inflammation of the pharynx, it is necessary to inspect it. Inspection of the pharynx is a simple procedure, often conducted at home and does not require special skills or skills. The patient must be brought to the light and the spoon handle to press on the central part of the tongue. It is necessary to control the depth of the spoon promotion so as not to provoke vomiting. In patients, the mucosa is injected and sweeping. If the disease is accompanied by fever, it is necessary to consult a doctor, since the symptoms of pharyngitis are in many ways similar to the nickname clinic. Acute - Grozny Pathology, often leading to a difficult complication. Distinctive signs of angina in children are:
Differential diagnosis of pharyngitis is carried out with laryngitis and tonsillitis. Inflammation of the pharynx and larynxFaringitis - disease with localization pathological process On the mucous membrane of the pharynx. It manifests itself local inflammatory signs And general symptoms of intoxication - fatigue, fatigue, decrease in performance, headache. Pathology complicates the flow of rhinitis and ORVI. The inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the larynx and voice ligaments of bacterial or viral origin is called. Local symptoms of laryngitis: malfunction, hoarseness ,. System features include: fever, pain in muscles and joints, malaise, weakness. Besides infectious factors The causes of laryngitis are: overvoltage of voice ligaments, larynx injuries and their consequences.
The inflammation of the pharynx and larynx differ in the localization of the pathological process, etiology and pathogenesis. Larygitis therapy in most cases is carried out using antibiotics, and in the treatment of pharyngitis, they are practically not used. Both pathologies are ORVI satellites and make themselves to know from the very beginning of the disease. Inflammation of pharynx and almondsTonsillitis - Acute infectious and inflammatory pathology, striking the mucous membrane of the sky almonds. Called an angina the conditionally pathogenic bacteria of the drip group of infection - streptococci and staphylococci transmitted by air drip from a sick person. In more rare cases, there are no viruses, fungi and even chlamydia. Angina complicates the course of respiratory infections. Inflammation of the pharynx and almonds are manifested by similar clinical signs. With pharyngite - Morning sore throat, hyperemia and swelling of mucous membranes, burning and dryness, shakes, comes in the throat. General signs Inxications are weakly expressed or there are no no. For - the pain in the throat is more intense, Therapeutic principles used in the damage to the pharynx and inflammation of almonds differ significantly. In acute tonsillitis, antibiotics are prescribed, and in chronic - surgical intervention. With pharyngitis usually use antiseptic solutions For rinsing, aerosols, inhalation, abundant drink. TreatmentTreatment of acute pharyngitisIn acute pharyngitis, hospitalization is not conducted and patients are treated at home. The prognosis is favorable: recovery occurs in about 7 days. Treatment of pathology includes:
Treatment of chronic pharyngitaBegin treatment of chronic pharyngitis is necessary with eliminating causal factors and adverse conditions that slow down the process of recovery. During the exacerbation, the use of local antibacterial drugs is shown. Systemic antibiotic therapy is carried out only if there are pronounced symptoms of the disease and signs of intoxication. Pathology with severe trophic changes in the mucosa is poorly amenable to therapy, and atrophic pharyngitis is not completely curable. Basic principles of treatment:
Addition to the medical therapy of chronic pharyngitis can be with funds folk Medicine. ethnoscienceDecorations and drugs of medicinal herbs are widely used to treat acute pharyngitis. They are used for the broods of the sore throat or for inhalations.  Phytotherapy
Treatment of pharyngitis in childrenTreatment of pathology in children spend at home. The main therapeutic measures for pharyngitis: 
If, after carrying out all the measures described at home, the child's condition deteriorates, and the body temperature grows, it is necessary to consult a doctor. Treatment of pharyngitis in pregnant womenAll pregnant women who have pain in the throat must visit the specialist. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable because it is about preserving the health and life of a woman and the future child. Specialist, given the features of the disease and the state of a pregnant woman, will determine the cause of pathology and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Therapeutic events in pregnant women are in compliance with the basic principles:
Folk medicine funds used to treat pharyngitis in pregnant women - propolis, honey, garlic, phytotherapy. PreventionSimple rules will help to prevent the development of the disease:  Complications of pharyngita
Streptococcal pharyngitis is complicated by the formation manifested by one-sided symptoms: swelling of soft tissues, pain and erythema. With pharyngitis, the infection applies to the descending way, which leads to the development of inflammation of the larynx, trachea and bronchi. In addition to laryngitis, and in patients with a protracted strength of streptococcal inflammation of the pharynx, articular rheumatism occurs. The main complication of pharyngitis is the overall decrease in the quality of life. For those who are associated with the need to speak, this disease becomes a real problem. A long-term flow inflammation leads to a change in voice timbre.
Video: Pain in the throat in a child, "Dr. Komarovsky"
10419 0 Foreign bodiesForeign bodies often fall into the throat during food (fish and meat bones) or by chance (coins, toys, particles of cereals of cereals, dentures, nails, pins, etc.). The probability of foreign bodies ingredients increases in senior people when using dentures (cease to control the food lump).Often the throat foreign bodies are observed in children who put various items in the mouth. In countries with a hot climate, a throat can be detected by living foreign bodies (leeches), which fall inside as a result of the use of water from contaminated reservoirs. Acute foreign bodies are most often stuck in the field of passage of the food lump: skydress, the root of the tongue, the side walls of the pharynx, valkeules, pear pockets. Large foreign bodies (coins, toys, rings from the nipples) remain in the gear part of the pharynx, before entering the esophagus. The presence of a foreign body is manifested in the throat an unpleasant feeling and crucial pain In a certain place during swallowing. In the presence of large foreign bodies, which are at the entrance to the esophagus, in addition to the sensation of the foreign body, it is difficult to swallowing, and some affected - and breathing. If there is a foreign body in the throat there is a savory enhancement. The survey of patients with foreign bodies should be started with pharyngoscopy. If the foreign body is not detected during pharyngoscopy, it is necessary to carry out an indirect hypoparianoscopy, during which it is possible to see the foreign body in the area of \u200b\u200bthe tongue almond, Valkel, the sneak-shaped cartilage or the walls of the pear-shaped pocket. Large bodies are clearly visible in the gentle part of the pharynx. One of the signs of the presence of a foreign body in the area of \u200b\u200bthe pear-like pocket may be a delay in halves (salivary lake). Foaming saliva, swelling of the mucous membrane and difficulty breathing give reason to suspect the foreign body of the Gunding pharynx. Patients often swallow stale bread crusts to remove the foreign body, while it penetrates the depth of the tissues or breaks. In this case, a finger study of the oral and gentle part of the pharynx should be carried out, in which you can try to take a deep foreign body. In the presence of suspicion of the metallic foreign body, radiography is performed. The detected foreign body can be removed by capturing it with tweezers or Corncang. If the foreign body is in the guttan part of the pharynx, they conduct local anesthesia by irrigating the mucous membrane of the pharynx 2% diene solution or 10% lidocaine solution. The removal of the foreign body from the gentle portion of the pharynx is carried out during indirect or (rarely) direct hypoparianoscopy. Timely removal of the foreign body prevents the development of complications. If the foreign body remains, the inflammation of the walls of the pharynx develops, the infection can spread to the adjacent fiber. In this case, the inclusive abscess and other complications are developing. Possible imaginary foreign bodies of the pharynx. Such patients turn to different doctors with a complaint that they were suppressed by a foreign body for several months or years ago. So far, they feel pain, as well as the presence of a foreign body, which is capable of moving. During an objective examination, any changes in the throat are not marked. The general condition of the patients is not violated. These patients are sick of various neurosis (neurotic, psychstore, etc.). They are very hard to convince them that they have no foreign bodies. EtiologyInsulated acute pharyngitis may occur after a common or local hypothermia, from the reception of acute food, in the workers who have just begun to work in harmful chemical enterprises.Clinical pictureIn most patients, the general condition is almost not impaired. Body temperature is normal or subfebrile. Only in children it can reach high numbers. Patients complain about the sensations of dryness, turning and sore throat, which are enhanced during swallowing and can be given to the ear. Sometimes there are sensations of laying. There are no hearing deterioration due to the ecremia of the mucous membrane of the hearing pipes. The throat pain decreases after the use of warm, non-irritating dishes.The pharyngoscopic pattern is characterized by the presence of mucous-purulent discharge on the rear wall of the pharynx, hyperemia and edema of the mucous membrane, which are moving from the walls of the pharynx to the rear pavements and the tongue. Lymphaded follicles of the rear wall of the pharynx hyperemic, elapsed, enlarged, clearly act under the mucous membrane (Fig. 117). Regional lymph nodes may increase.
TreatmentIt is necessary to exclude food, irritating the mucous membrane of the pharynx. Even without treatment after 3-5 days, recovery comes. Inhalation or pulveryization of the pharynx with alkaline solutions, 5% solution of albacid or antibiotics can be carried out. Assign aerosols (Kameton, Inhalipt, Propazole, Ingakamuf, etc.), sucking tablets (Falimint, Faringosept), disinfectants (furacilin, ethanidine lactate, infusions medicinal plants). Only at high body temperatures are prescribed antibiotics and antibody drugs.Chronic pharyngitChronic pharyngitis is a common disease. More than 30% of patients who add to Lor Cabinets Polyclinic, sick chronic pharyngitis of different shapes.EtiologyChronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx is a polyethological disease. Very often, chronic pharyngitis develops in workers who work with harmful chemicals, in conditions of dusting industrial premises. Considerable role is played acute food, Harmful habits (smoking, alcohol abuse), as well as a violation of nasal respiration, the presence of chronic infection in the surrounding organs (chronic rhinitis, is shining, chronic tonsillitis, chronic pathology of the oral cavity).Chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx supports chronic diseases of the digestive channel (chronic gastritis, enteritis, colitis), liver, pancreas, uterus and its appendages, endocrine system (diabetes, hyperthyroidism). Very often, chronic pharyngitis occurs in patients with different neurosis, and the symptomatology of chronic pharyngitis worsens the course of neurosis. Clinical pictureDistinguish chronic catarrhal, hypertrophic and atrophic pharyngitis.Chronic catarrhal pharyngitisPatients complain about the feeling of the foreign body in the throat, the separation of mucus, as well as heartburn. Hyperemic, elapsed mucous membrane is covered with astringent mucous-flints. Often the chronic inflammatory process goes to the rear pacifices, tongue. Some patients have a sharply elastic, the increased tongue is lowered into the harvested pharynx department, so they can only sleep in a certain position. Sometimes the mucous membrane of the pharynx acquires a gray shade or is covered with spots, which indicates severe vasomotor disorders.Chronic hypertrophic pharyngitisPatients are concerned about the blurred pain in the throat, the need to constantly pull the thick mucus. The pharyngoscopic picture is different. The mucous membrane of the pharynx is hypersed, thickened, covered with islets thick mucus. In the rear wall of the pharynx, increased, hyperemic and elapsed lymphadendic formations are noticeable and elongated formation. In this case, suspected the presence of granular pharyngitis.If there are late hypertrophic pharyngitis, there is hypertrophy of lymphadenoid tissue on the side walls of the pharynx in the form of continuous elongated formations of red. Often these two forms in one patient are combined. Sharp hypertrophy of the granules, side rollers and pagan almonds are sometimes observed in persons who have ceased to be removed almonds. With the exacerbation of the process on hypertrophied lymphaded formations, it is possible to see the yellowish and whitish points (ventilated follicles) or a white fibrinous flare. Chronic atrophic pharyngitisPatients complain of dryness, heartburn, alluring and the formation of dry crusts in the throat. Especially all is manifested in the morning. As a result of a long conversation, the throat dries, so the patient is forced to drink a sip of water. With pharyngoscopy, it is revealed that the mucous membrane of the pharynx is sharply sophisticated, the grid of blood vessels is shouted through it. The surface of the pharynx is covered with a thin layer of transparent dried discharge, giving the so-called lacquer shine. In the launched cases, the dry mucous membrane is covered with greenish or yellow crusts. Sometimes, if there are such crusts, patients do not complain about anything.It happens that the patients make a lot of complaints, including pain in the throat, and with pharyngoscopy, humidity is determined, unchanged mucous membrane. In this case, we are talking about parathesides of the pharynx. TreatmentFirst of all, it is necessary to eliminate factors supporting a chronic inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the pharynx: professional harm, smoking, alcohol. The diet must be gentle. It should be actively treated with a disease of the digestive channel, the appendages of the uterus, endocrine pathology, restore the nasal respiration, eliminate the focus of infection in the adjacent organs, treat the neurosis.Alkaline solutions in the form of inhalation, irrigation, rinsing are locally applied. On the mucous membrane of the pharynx in the aggravation stage affects anti-inflammatory drugs. In recent years, irradiation of the rear wall of the pharynx by helium-neon laser is used to treat chronic atrophic pharyngitis. Effective is the cryosium on the mucous membrane of the pharynx with all forms of chronic pharyngitis, especially hypertrophic. DI. Zabolotnaya, Yu.V. Mitin, S.B. Smesaping, Yu.V. Deev Under the term "sickness of the throat" in everyday life, most often implies the ENT diseases of the pharynx (department of digestive and respiratory systems, which informs the nasal cavity, the oral cavity and the larynx). As in the case of other organs, the sickness of the throat may be a consequence of infection (viral, bacterial or fungal) - both acute and chronic, various injuries, harmful external influences (caustic and toxic substances, dust, tobacco smoke). ClassificationENT-Diseases of the throat can be divided into acute inflammatory, chronic inflammatory and complications. Diseases of the larynx and throat also include hypertrophy of the sky and pharyngeal almonds, foreign bodies, injuries and burns of the pharynx. Consider their details separately. SymptomaticsAcute inflammatory diseasesThis group includes acute pharyngitis and various angina, almost the most frequent throat disease in children.
Acute pharyngitis - acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx, developing due to the impact of microorganisms or harmful factors Environmental, such as smoking, alcohol, etc. In this disease, the patient is most often complaining about the feeling of burning, dryness, sore throat, suffocation, sensations are described as "com in the throat". Temperature is usually either pain. Angina is a common acute infectious-allergic disease, developing with the damage to the lymphoid tissue of the pharyngeal ring. The reason most often serves a beta hemolytic streptococcus group A. An angine embodiment is isolated (catarrhal, follicular and lacunar), atypical forms, as well as specific angins with some infectious diseases and blood diseases.
- the easiest form is characterized by pain and frank in the throat, a sense of "coma", minor pain when swallowing and slightly raising Temperatures. Follicular angina - Leaks harder with severe pain, irradiating in the ear, headache, weakness, sometimes vomiting, suffocate. Temperature can rise to 39 ° C. Lacooner is the most severe of banal forms. All almonds are covered with a raid, the lacuna is filled with a yellowish-white rode, and pains are also observed when swallowing, fever and symptoms of intoxication, including the feeling of "coma in the throat".
With phenomena, angina proceed:
It is possible to attach fungal infection. A separate form of angina is angina Simanovsky-Plata-Wensen. It causes a symbiosis of the spherose-like bacterium and the spirochki of the oral cavity, leading to the development of greenish plaque, the feelings of "coma" in the throat, rotten smell of mouth and high temperatures.
Anglets can proceed with complications, such as paratronzylitis, para- and retrofaring towing abscesses. Paratonzillitis is the inflammation of the osindal fiber, manifested in a strong temperature increase of up to 39-40 ° C, the impossibility of meals and smooth saliva due to very strong pain, "coma in throat", suffocation; Also characterized by trisms - a symptom in which a person cannot fully open the mouth due to the tonic spasm of chewing muscles. In the cavity of the mouth in the projection of the almond, a major escape is revealed. Parafaringeal abscess is the suppuration of parafaring tape, and the refractoryal - plug. The symptoms are largely similar to paratronzillite (except for characteristic swelling), the differential diagnosis should be carried out by an ENT doctor. Hypertrophy AlmondsUnder this term implies the growth of lymphadendic tissue. Most often there are hypertrophic processes in the sky and pharyngeal almonds.
Children with such a disease do not sleep well, coughing at night, some of this may develop neuropsychiatric disorders. Chronic inflammatory diseasesThese include chronic forms of pharyngitis and tonsillitis. Chronic pharyngit - Inflammation of the mucous pharynx - arises due to not enough effective treatment acute forms. Catarial, hypertrophic (side and granular) and atrophic forms are found.
Patients complain about sickness, allocating, tickling, "com" in the throat, suffocation, a feeling of a foreign body, laying the ears. Temperature may not rise. Often to swallow something they need a sip of water. Chronic tonsillitis - persistent infectious-allergic disease with local manifestations in the form of inflammation of almonds. Most often arises as a complication of other infectious processes (such as angina and caries).
In a toxic-allergic form, symptoms of intoxication and allergyization are added to the angles, conjugate diseases are often found, such as rheumatism, glomerulonephritis, polyarthritis, endocarditis and others. Foreign bodies, injuries and burn burnsForeign bodies most often fall into the throat when talking or laughter during food, as well as children during games. Sometimes the ingredients in the elderly are dentures. Patients complain on com in throat, pain and breathing and swallowing.
The burning of the throat is the external and internal, penetrating and imperriburing, isolated and combined, blind and through. The symptoms most often are bleeding, respiratory disorders, speech, difficulty swallowing because of the "coma", suffocation, expressed by pain syndrome. Burns can develop with thermal and chemical lesions of the throat wall. Thermal burns more often causes the effects of temperatures - getting hot food and beverage, less often hot air or steam. Chemical burns occur when exposed to hydrochloric, acetic, nitric acids, caustic soda or potassium.
The burns are most often accompanied by pain, salivation, general intoxication. Because of the numerous complications of burn burns are a vital state.
TreatmentThe treatment of acute pharyngitis is usually carried out outpatient, he is prescribed the therapist or an ENT doctor. It includes rinsing with antiseptics (chlorophyptom, infusion of chamomile), aerosols (Phasex), desensitizing and immunostimulating drugs. Antibiotics are rarely appointed.
Banal angins are usually treated with an outpatient ENT doctor, in difficult cases - in the hospital. Antibiotics are prescribed from a group of penicillins, antihistamines (TAVEGIT, TELFAST), inhalation of bioparox, rinsing and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Treatment infectious diseases and blood diseases, accompanied by the phenomena of an angina, should not hold an ENT, but an infectious hematologist in the respective hospitals.
With the sinks of the Simanovsky-Platie-Wensena, antibiotic therapy of penicillin preparations, a lining and vitaminity therapy; Sange the oral cavity and purify the almonds from necrotic foci.
Paragonzyllitis and other abscesses include antibiotic therapy and mandatory surgical intervention for the rehabilitation of purulent foci. Chronic pharyngitis is treated outpatient an exception to the impact of harmful factors (alcohol, smoking), inhalations, lubrication of the throat Collargol (conducted by the ENT doctor), resorbing caramels with antiseptics (hexalysis, pharyingosept). In the treatment of chronic pharyngitis, both conservative and surgical methods are used. The first implies the washing of Lakun Almonds (10-15 procedures), lubrication of their surface with yodinol or collargol, rinsing and physiotherapy procedures (UHF or microwave therapy). Surgical methods include tonsillectomy. Similar, but less radical method - tonsillo - or adenotomy, respectively, treat hypertrophy of paternal almonds.
Foreign bodies remove the ENT doctor using special tongs or loops. It is not necessary to remove the foreign body yourself with the help of tweezers, as you can aggravate the process and call asphyxia. Surgical processing of the Russian Academy of Sciences also holds a LOR specialist if required tools and equipment, most often - in the hospital. Treatment of burn burns - a difficult and multistage process, cycling both Lorov and other specialists. Initially, all activities are usually aimed at preserving the life of the patient, then to prevent the formation of adhesions.
In the remote period, the most frequent procedure is a bunning - expanding the loss of the throat to restore its passability. PreventionDiseases of the throat are diverse, therefore their prevention is different. Train safety situations should be avoided, follow the used food and drinks, not to talk during meals. It is also necessary to treat all acute diseases in time, in no case leave the process is unremitted.
It helps to cope with viral and bacterial infections In just two days, it contributes to the activation of immunity and removes toxins from the body, reducing the time of rehabilitation. |
| Read: |
|---|
Popular:
New
- Not lies, but alternative facts: Press Secretary Donald Trump quarreled with the press on the very first day of work in the White House
- Laura Ingrea is the future spokesman for Trump and her Russian children
- Alina Saprykin: "I want to liberate the territory first of all
- Victoria Beckham: the story of the transformation into "sullen non-versa" Victoria Beckham nose
- Marion Cotiyar Figure Parameters
- Horoscope Career for Lev for March
- Virgo - Astroprognosis for December
- Camping in Crimea Minich and Lassi
- Horoscope for June Taurus Horse
- Women Tiger Virgin Tiger Symbols and Talismans




 yellow-gray raid and separate follicles in the form of red grains. Inflammation is often distributed from the pharynx on the almonds, the gum, heaven, the larynx with the development of the corresponding pathologies.
yellow-gray raid and separate follicles in the form of red grains. Inflammation is often distributed from the pharynx on the almonds, the gum, heaven, the larynx with the development of the corresponding pathologies.
 Children who walk little and sleep in a room with dry and warm air fall into the risk group.
Children who walk little and sleep in a room with dry and warm air fall into the risk group.

 in the ears and amplifying after lunch. Almonds are covered with purulent raid. Patients appear
in the ears and amplifying after lunch. Almonds are covered with purulent raid. Patients appear