Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- Technology and step-by-step instructions for nail gel: steps, rules, process
- White spots on the nails, reasons for what to do, white spots on the nails and folk signs
- Available methods for rapidly increasing blood leukocytes
- Nail and skin fungus will not resist the coffee grounds
- Crocus furniture exhibition. Furniture exhibitions
- Owl tattoo on arm value
- The biggest members in the world
- Fractures of the phalanges of the foot photo
- What is “bad” and “good” cholesterol
- What to do if the skin around the nails dries
Advertising
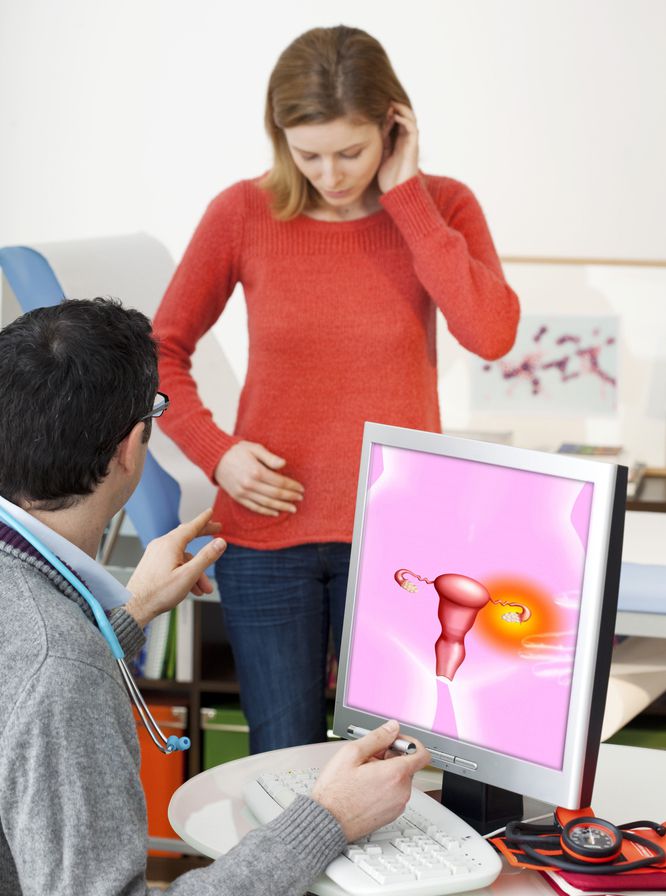
| Follicular cyst sizes dangerous. Can I get pregnant? Characteristic symptoms of cysts. |
|
Ovarian cyst may occur unexpectedly, without causing any problems. There are about 40 types of these neoplasms. Most cysts appear as a result of hormonal disorders - as a rule, after several menstrual cycles, they disappear themselves. Sometimes, however, the cyst stubbornly remains in its place and begins to grow, posing a threat to the health of the woman. What are ovarian cysts and why do they come?There are two categories: organic and functional. While organic cysts affect older women. These cysts do not return, in most cases are benign, but potentially carcinogenic. How to find out if I have ovarian cystsSurgical treatment of ovarian cysts. What is ovarian cysts? Most women have some kind of ovarian cyst at some point in their life. They usually appear in the reproductive age of women and are rarely malignant.Following the link http://nmed.org/lechenie-kisty-yaichnika-bez-operacii.html, you will learn what an ovarian cyst is, what are its first symptoms, and how to treat folk remedies. In the meantime, we will provide you with basic information regarding this ailment. Why ovarian cyst appears?The neoplasm in the area of the ovary is formed mainly due to the inhibition of the follicular rupture. This happens when the follicle does not receive an egg, or its cells die. When there is no ovulation, the follicle continues to grow and fluid accumulates in the middle of it. After some time, it is converted into an ovarian cyst. The reason for this most often becomes a hormonal imbalance. However, there are other reasons why an ovarian cyst occurs: They can be defined as “bags” filled with fluid that appear inside the ovaries or on their surface. The ovaries are located on both sides of the uterus and usually an egg is extracted every month so that it can be fertilized. These types of cysts are called follicular, usually do not get sick and disappear spontaneously. Another common ovarian cyst is the corpus luteum, which occurs when the follicle opens and the fluid collects inside. It also usually disappears, but sometimes it can grow and cause pain and bleeding. These two ovarian cysts, the follicular and corpus luteum, are functional, that is, they occur in the normal process of the menstrual cycle.
Depending on its origin, ovarian cyst can be benign or malignant. There are single and multiple cysts (polycystic). The tumor may appear on the surface of the right or left ovary. Another type of ovarian cysts, not so often, is organic, which is not caused by the normal functioning of the ovary. They can be of several types: teratomas, endometriomas, cystadenomas, etc. some are born, for example, teratomas and others appear over the years, many times without a reason that causes them. What symptoms cause ovarian cysts?In many cases, ovarian cysts are usually painless, but sometimes they can give symptoms such as. Pain in the lower abdomen that can spread to the back or legs Pain in the pelvic region during and after a period Pain during intercourse Nausea, vomiting or marked tenderness in the chest Abdominal swelling Pressure in the rectum or rectum Bladder, feeling that he cannot empty it at all. If you feel a sudden and severe pain in the pelvis or abdomen, or if fever and vomiting accompany you, it is important that you go to a doctor or emergency room. Depending on the structure, there are the following types of ovarian cysts:
The most common type is the first. It is not difficult to treat the follicular cyst of the ovary, because the disease is considered the most "harmless." In most cases, the follicular cyst itself resolves through several menstrual cycles. If this does not happen, the doctor may prescribe hormones that normalize the activity of the patient's ovary. How are ovarian cysts detected?As we have said, most ovarian cysts do not cause symptoms, therefore it is recommended to conduct periodic gynecological examinations to find them. Your gynecologist will be able to detect a cyst by probing the ovaries during manual examination of the pelvis. If you think that a cyst exists, the diagnosis is usually completed by laparoscopy, a technique that allows you to see the contents of the abdomen and pelvis with a tiny video camera, a laparoscope. Other tests, such as ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging or blood tests, can also be performed. Symptoms and diagnosis of the diseaseIn most cases, the cyst is a benign tumor. Sometimes, however, because of its size or location, it causes various diseases. Therefore, it is very important to detect the disease in time and begin treatment of the ovary. A large cyst can be felt by touch. If you are under the skin in the area of the left or right ovary thickening, you see a small lump, then you need to go to the doctor immediately and begin treatment. What is the correct treatment?Early diagnosis of cysts is important in order to monitor them or, if necessary, quickly remove them. In many cases, surgery is not required. Ovarian cysts will be monitored with periodic checks, waiting for them to go away on their own. In some cases, if they cause pain or if your gynecologist deems it necessary, a laparoscopic surgery will be performed, in which Dr. Javier del Pozo, a partner of our clinic, is a national and international standard. However, a small cyst may not give any symptoms, and the patient does not know about her presence. Usually, a woman learns about her illness by chance, during an x-ray, ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. A large ovarian cyst can cause discomfort as a result of its pressure on vital organs and body structures. In this case, the patient feels a strong pain in the abdomen. You can contact us and we will notify you about it without any obligation. Your problem has a solution, do not wait anymore. I was diagnosed with ovarian cyst. . A cyst is a sac filled with fluid or semi-solid material that develops near or within the ovary. Ovarian cysts can be functional or organic. Functional cysts are relatively common and common during the reproductive age of women. A few days before ovulation, the follicle develops, but during ovulation, the follicle does not break and does not release the egg, so the fluid remains inside and forms a cyst. Among the symptoms of ovarian cyst are also worth mentioning:
Sometimes an ovarian cyst leads to alopecia - that is, baldness. In this case, you will need urgent treatment with hormonal drugs, as well as procedures to restore healthy hair. These functional or physiological ovarian cysts usually disappear within 8-12 weeks without treatment. They should be distinguished from organic cysts, which do not disappear spontaneously, usually increase in size and can cause twisting, rupture or bleeding with subsequent pain. In this case, the treatment is performed surgically by laparoscopy. It is usually recommended to limit the same physical activity until you know the characteristics of the cyst. In the case of teratoma or dermoid cyst, exercise can cause torsion with subsequent pain, which will require surgical treatment through laparoscopy. TreatmentAny treatment always begins with tests. The basic test in the diagnosis of patients with suspected ovarian cyst is a gynecological examination, abdominal ultrasound or vaginal ultrasound. They make it possible to determine the level of development of the neoplasm and to begin an adequate treatment. If cancer is suspected, the doctor will prescribe a blood test or a CT scan. Your hormonal drug - like a cystYour hormonal Like a cyst. . The ovoid follicular cyst is a thin circular wall with a smooth surface and fluid content, the amount of 2 to 7 cm in diameter or more, found in one of the tissues of the ovary. Sometimes these cysts can be several, but they are all single-chamber, without septa. This cyst is formed from a folded follicle. The follicle is a vial with clear content, in which the first half of the oocytes of the menstrual cycle matures under the action of hormones. The most active hormone in the first half of the menstrual cycle are pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone and estrogen secreted by the ovaries. As the egg cell matures, the follicle is released from the ovary, this time called ovulation. In some cases, the follicle is broken and the egg remains in the ovary. This is known as anovulatory menstrual cycle. The method of treatment of ovarian cysts depends on its type. For example, if you have a small follicular cyst of the left or right ovary, the gynecologist may recommend only your control. But if the specialist believes that it is necessary to start a drug or surgery, do not postpone this matter indefinitely, and in any case do not refuse therapy. Why? Because a cyst can be the first sign of ovarian cancer, carry a risk of rupture or put pressure on other organs, preventing their proper functioning. Neoplasms sometimes also require pharmacological treatment - hormones, antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs. Since the follicle does not burst and the follicular cyst, it can be both hormonally active and inactive. The reason for the formation of follicular cysts are usually hormonal imbalances and inflammatory diseases female reproductive organs. This is typical for women of childbearing age and before menopause. After treatment of infertility, multiple bilateral cysts may occur. Girls under 15 years of follicular cysts make up at least one third of all ovarian cysts and tumors that are found in this age group. Now more about each method Hormone therapyThis method is used for large ovarian cysts. The doctor prescribes certain hormones in strict quantities to reduce the size of the tumor. This facilitates its subsequent removal with the lowest possible surgical intervention in women of reproductive age. Treatment with hormones requires careful monitoring of an ovarian cyst. If the doctor suspects that it may be cancerous, the use of certain hormones is not recommended due to the possibility of accelerating the growth of malignant cells. Follicular cysts are found even in the ovaries of the fetus and newborn. How do follicular cysts work? Manifestations of follicular cysts largely depend on their hormonal activity and the presence of female gynecological disease. In cases where a follicular cyst exhibits hormonal activity, proliferation of the uterus mucous membrane, uterine bleeding occurs, the girls note premature puberty. When patients have more cysts can complain of pain in the lower abdomen. If hormonally inactive follicular cysts of a woman are usually not aware of their existence, they are detected by chance during an ultrasound and disappear on their own within a few months. The most common complication of ovarian follicular cysts, especially in children, is the torsion cyst of the leg, which can cause a rupture of its wall and subsequent contents of the abscess intestine with the development of peritonitis. This complication begins acutely, often after physical exertion or a sudden change in body position. LaparoscopyLaparoscopy is prescribed when there is complete certainty that the ovarian cyst is not malignant. This treatment can only be used by women under the age of 50 years. The essence of laparoscopy is the surgical penetration to the ovary region through the bottom of the navel. The size of the incision is very small. Then in abdominal cavity carbon dioxide is injected to increase the amount of free space for handling. It also allows you to accurately separate the organ that was operated on. Next, a special probe (laparoscope) is introduced, which will allow to monitor the tissues in the ovary region. Following the laparoscope, the instruments necessary to remove the tumor are placed in the abdominal cavity. Pain in the lower abdomen, which extends to the perineum, thigh, lumbar region, often accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Body temperature during the first few hours usually remains normal. Sometimes the pain subsides quickly, and the unsurpassed screening leg cysts do not affect the condition of the woman. If peritonitis begins, heatthere is severe pain in the abdomen. Diagnosis of ovarian follicular cysts. If the follicular cyst is large enough, it was discovered during a gynecological obstetric procedure: it was felt in the form of a smooth, round, dense, sedentary, elastic formation, usually without pain. The first step in laparoscopic removal of an ovarian neoplasm is to create a groove under the area where there is a cyst. Using forceps, the doctor cuts the top layer of the ovary. Then the tumor is removed with a scalpel or coagulated with electricity. The second method is especially recommended for women of childbearing age, who in the future plan to have children, and in which the cyst has a small size. Ultrasound can be considered as the only circular chamber of formation with a uniform content and with thin walls. Treatment of ovarian follicular cysts. Identification of follicular cysts was observed and treated conservatively after two or three months. To speed up reabsorption, he uses potassium iodide electrophoresis, hormones, anti-inflammatory treatment. If, despite the treatment, the cyst increases in size, which is removed. In addition, the indication for surgical removal of cysts is a larger follicular diameter, increased mobility, torsion or bleeding in the cyst, an abscess, and a suspicion of a malignant tumor. The next step of the operation is the separation of the cyst from the ovarian tissue. To do this, use rinsing. saline or suction method. After that, the cyst is cut from the surface of the ovary with scissors. Additionally, the doctor coagulates the wound with an electric shock to minimize the risk of bleeding. After the cyst has separated from the surface of the ovary, it is removed from the abdominal cavity. Surgery to remove a follicular cyst is usually performed laparoscopically, through small incisions, when the body is inserted into special tools and used to remove the cyst. Symptoms and Causes Diagnosis Treatment Drugs The clinical picture. . Hyperandrogenism is the most common endocrine disorder in women of childbearing age. Male sex hormones or androgens in women are mainly produced by the adrenal glands and ovaries. However, from peripheral tissues, such as adipose tissue and skin, it also depends on the level of androgens in the body, since they play a role in the transformation of more powerful androgens. Laparoscopic surgery is less invasive than conventional surgery. Complications are extremely rare, the recovery period is short, and the procedure leaves almost no traces on the skin. This technique is suitable for the treatment of follicular and dermoid ovarian cysts. Classic surgery (laparotomy)Ovarian cyst, which was defined as a cancerous lesion, or which is of considerable size, requires removal by the traditional method. This treatment is called laparotomy. Hyperandrogenism or an excess of androgens can affect various tissues and organs, causing a number of disorders, including acne, hirsutism, virilization and dysfunction of the reproductive system. Sources and types of male sex hormones in women. The glands of the endocrine system produce a total of five types of androgens: testosterone, dehydroepiandrosteronsulphate, dehydroepiandrosterone, androstenedione and androstenediol. Testosterone and its biologically active form - dihydrotestosterone - the only androgen that can provide a direct androgenic effect. The size and nature of the ovarian neoplasm affects the choice of options for surgery. A cyst of considerable size that does not show signs of malignancy is removed by cutting the transverse suprapubic zone and emptying the contents. If an ovarian cyst has a malignant nature, then it must be eliminated with a longitudinal incision. Androgens are produced by the ovaries. . The ovaries produce 25% of testosterone circulating in a woman’s blood. Its dependent secretion of luteinizing hormone, which, in turn, prescribes the anterior pituitary gland. Androgens are produced by the adrenal glands. . They produce 50% and 25% testosterone androstenedione. The secret of adrenal secretion does not depend on adrenocorticotropic hormone, which is produced in the anterior pituitary gland. In the adrenal glands, estrogen and prolactin can also be affected. Peripheral testosterone conversion. . Skin, adipose tissue, liver and organs genitourinary system also affect the level of testosterone in the blood. Androgen metabolism. . Of all circulating androgens in the blood, only testosterone and dihydrotestosterone can activate androgen receptors. In women of childbearing age, 25% of testosterone is found in the adrenal glands, and the same in the ovaries. The balance of testosterone produced by the conversion of androstenedione and other androgens into peripheral tissues. Typically, 80% of testosterone is associated with sex hormones that bind globulin, 19% with albumin and 1% testosterone, which circulates freely in the bloodstream. If the cyst has reached such a size that it cannot be removed through a skin incision, then the doctor uses a puncture. First, an incision is made in the area of the ovary, then the contents are sucked off with a special tool. After the ovarian cyst shrinks in size, it can be freely removed from the abdominal cavity. If the ovarian cyst has become a malignant tumor and has metastasized, then, together with the neoplasm, the uterus and its appendages will need to be removed. In some cases, however, doctors restrict the removal of a single ovary. In this case, the woman has a chance to become pregnant if she starts an effective restorative treatment after the operation. Folk remediesIf you have an ovarian cyst, do not rush to have surgery. At first, it is best to try treatment with folk remedies.
Discussions: Joseph addison With exercise and temperance, most people can do without medicine. Follicular cyst of the ovary is called a neoplasm of benign etiology. It is formed from the dominant follicle, which, when ripe, did not reach the fallopian tube due to the lack of ovulation in the next cycle. The tumor is one-sided, consists of a single-chamber cavity with fluid, often serous contents. It can reach up to 9.5 cm in size. Despite such a large volume, ordinary cysts break through the membrane and leave the organ at a size of about 3 cm. In this case, the final maturation of the follicle does not occur. Causes of follicular ovarian cystThe disease has no age. It can occur in girls during puberty and in premenopausal women. There is a theory that the main factor influencing the formation of tumors is the activity of the brain at the subcortical level. Stressful situations or nervous tension causes the activity of the nerve centers responsible for hormonal balance, and its work is disturbed. As additional causes of follicular benign neoplasmhormonal imbalance, can be identified:
There are symptoms of follicular ovarian cyst in the treatment of infertility, while taking hormonal drugs. This condition appears as by-effect during ovulation overstimulation for early conception in preparation for IVF. Symptoms of the diseaseThe formation of this neoplasm may be asymptomatic, and the woman then learns about its presence only during the ultrasound examination. Feelings largely depend on the general condition, concomitant gynecological diseases different etiology and size of the tumor. In girls, their periodic occurrence can be assumed in early puberty. Women in reproductive age with hormonal disturbances may have the following symptoms:
For some reason, it is believed that the right ovary neoplasms occur more often than the left. Perhaps, such a theoretical opinion was formed because the right ovary is located at the junction of the main aorta and the renal artery, respectively, its blood supply is enhanced. In practice, this theory was not confirmed. But since the tumor from this side is symptomatic in terms of inflammation of the appendix, the attention of the right ovary is greater. Even the question was considered separately whether it is possible to become pregnant with a follicular cyst of the right ovary? The chances of conception are the same, no matter where the neoplasm occurs, left or right, for any reason. Follicular cyst and pregnancy
When a pathology appears in one of the ovaries, it is excluded from the reproduction process for this cycle. Usually the follicle resolves within 2 months, but there may be cases requiring medical intervention when the follicles are in the body for a long time and continue to grow. But getting pregnant is possible if the follicle matures in a paired ovary in the next menstrual cycle. The appearance of a neoplasm during pregnancy is considered as a medical case. Throughout this period, women have increased progesterone production, which gives rise to the formation of the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum and can degenerate into a follicle. The normal functioning of the hormonal system blocks rebirth due to the production of prolactin, and new follicles do not mature. But sometimes nature fails and follicles form. A rupture of a neoplasm during pregnancy can occur due to the pressure of an enlarged uterus, so a woman is put on special control. What is dangerous follicular neoplasmYou can ask a reasonable question: why start the treatment of a follicular cyst, if it itself resolves late or early? The presence of tumors is dangerous, as it can cause serious complications:
Torn follicles and internal bleeding are eliminated only by operational methods. Treatment of follicular cystWhen a recurrent follicle is detected, which reaches a large size and causes suffering to the patient, the examination is carried out first. During it, concomitant diseases causing growth of the neoplasm are established, and appropriate treatment is carried out. Directly for cupping growth of the follicle are assigned:
If the neoplasm is enlarged, surgical treatment may be required. Laparoscopic operations are usually performed, during which the cyst is exfoliated and the walls are sutured, or ovarian resection is performed - excision of the damaged area. When ovarian apoplexy, rupture of the follicle, emergency operations are usually performed openly with a scalpel. But in most cases, doctors take an observant position without prescribing medicines, which always have significant side effects on the general condition of the patient. As ancillary measures that contribute to the regression of the follicular cyst, treatment with folk and homeopathic remedies is recommended. For the treatment of folk remedies follicular ovarian cysts are used the following recipes:
When treating a follicular cyst, one should not forget about a positive attitude. To improve health and mood, it is necessary to balance the mode of work and rest, to eat right, to allocate time to do your favorite thing. Improve brain activity pleasant meetings and walks in the fresh air. Intensive exercise and sex will have to be postponed. |
| Read: |
|---|
New
- Sequence of procedures
- The program of intensive moisturizing of the skin on cosmetics bark
- What you need for acrylic powder
- What does owl mascot mean
- Analyzes for pancreatitis: what research should be done and what indicators show
- Owl - a talisman to attract money and good luck
- What bird screams at night with a kitten's voice?
- Cholesterol and stress
- Manicure at home
- Effective facial