Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- Technology and step-by-step instructions for nail gel: steps, rules, process
- White spots on the nails, reasons for what to do, white spots on the nails and folk signs
- Available methods for rapidly increasing blood leukocytes
- Nail and skin fungus will not resist the coffee grounds
- Crocus furniture exhibition. Furniture exhibitions
- Owl tattoo on arm value
- The biggest members in the world
- Fractures of the phalanges of the toes of the photo
- What is “bad” and “good” cholesterol
- What to do if the skin around the nails dries
Advertising
| Worm invasions in children part. Infection with intestinal worms is manifested in this way. Folk remedies for worms |
|
The main route of infection is fecal-oral. This means that the eggs of the worm are out of the feces. They can be in the soil, animal hair, vegetables, berries, fruits, any surfaces. The mechanism is the simplest: they ate an unwashed apple; they stroked the cat on the street, and then they put unwashed hands to their lips (there are thousands of examples of this kind). There are species that are infected through non-fried fish, meat, game. To a lesser extent, but quite real - through the water, receiving unboiled water from a reservoir, well. In the body, the eggs / larvae of the worm can die under the influence of gastric juice. But this applies more to adults (with a strong immunity), in infants, the imperfection of the gastrointestinal tract makes it more likely that they will survive. And then they go all the way of their development.
The above symptoms may also apply to other diseases, therefore the appropriate diagnosis is required. Most characteristic symptoms helminth infections:
Symptoms in infants:
Worms are transmitted to children under one year by parents, other relatives or medical staff, i.e. people who do not care much about their own hygiene. Fetal infection is also not excluded. Diagnostics Self-diagnosis, even if it seems to you that all the symptoms on the face, will not work. An experienced doctor will necessarily resort to laboratory diagnosis. To confirm or disprove the hypothesis, research is required or fragments of (whole) pinworms. The specialist will evaluate the appearance of the feces, as well as microscopy them.
How to cure worms in a childIt is important to understand! For the treatment of helminthic invasion, there are many drugs, but, unfortunately, many of them have a number of side effects. Reception is strictly contraindicated in small children. That is why the appointment of drugs for worms should be dealt with exclusively by a qualified doctor. He, taking into account the results of the tests, will determine the optimal therapy. Self-selection of drugs is strictly prohibited. What is prescribed against worms for childrenThe list of effective remedies for treatment includes not only antihelminthic drugs of wide and directed action, but also vitamins, as well. Vitamin complexes and probiotics are necessary for the normalization of intestinal microflora, restoration of the level of lost amino acids, nutrients, salts and minerals. Antihistamines help to normalize the immune system.
Often parents, having learned that their children have symptoms of helminthic invasion, panic. It would seem that the child’s worms may appear from if he lives in normal conditions, eats only food prepared by the caring hands of his mother or grandmother, is under constant adult supervision outside, has no contact with domestic cats, dogs and even more with wild animals ? However, there are many more sources of infection than you can imagine, therefore even the most well-groomed babies are not insured against such invasions. About twenty types of sheets are most common in children. There are:
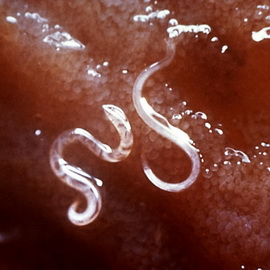
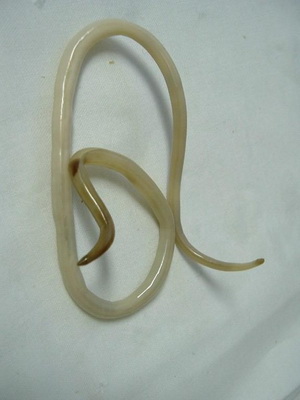
All varieties of worms in children can develop cyclically when they are in one host (obligate helminths), others (optional) go through the development cycle in humans only in the first stage. Infection with some worms occurs through self-infection or from person to person. Most often find worms in children aged from three to twelve years. These photos show what the worms are in children:
Where do the worms in the child's body come from (with video)Not a single organ and not a single human tissue is insured against the possibility of damage by one or another helminth. In this case, the intestinal wall is damaged, point hemorrhages are formed on it. Some types of helminths (for example, ankylostoma) feed on spilled blood, causing it in humans. Children are subject to helminthic invasions to a much greater extent than adults. Where do worms come from in children and how to prevent their appearance in the intestines? The settlement of helminths is facilitated by communication with pets, playing in the sand, swimming in ponds, eating unwashed vegetables and fruits. Having settled in the intestines, the helminths slowly poison the body of the small host. From there, they can later migrate almost throughout the body, especially if the child. There are some travelers larvae that throughout life cycle they spread throughout all organs and systems, sometimes penetrating into tissues and causing permanent damage to their functions. Therefore, long-term infection with banal worms can be fatal. As is known, the human child belongs to the number of immature, and the relative duration of its maturation as compared with other representatives of the mammalian class is extremely long. One would expect that the level of development of the child’s digestive tract compared to adults is very low, but in reality this is not the case. Although at the time of the birth of a child, the development of various parts of his digestive system is not fully completed, the intestine and liver of the fetus function from 3-4 months of intrauterine life, secreting digestive juices and bile. The stomach and pancreas lag a little in their development, and their digestive function begins to be determined only in a six-month fetus. Surprisingly, the activity of the digestive tract in the fetus is quite active. The fruit, starting from 3-4 months, makes swallowing movements, swallowing the amniotic fluid containing proteins, sugars, urea, minerals and hormones. Swallowed amniotic fluid passes through the stomach into the intestine and is absorbed. Only a part of the contents of the stomach and intestines is not absorbed and forms meconium - the original feces. The stomach of the newborn, located in the left hypochondrium, has a cylindrical shape. His muscular layer is poorly developed, the entrance to the stomach is wide, and this largely contributes to the regurgitation of food. During the first year of life, the child’s stomach is horizontal. From the moment the child begins to walk, the stomach gradually assumes an upright position. The mucous membrane is thick, with mild folds and a dense network of blood vessels. The muscular layer is developed moderately. The secretory glands of the child's stomach produce the same digestive juices as in an adult, only their activity is much lower. Digestion in the stomach of incoming food in infants occurs at low acidity, since the secretory cells of the mucous membrane produce an insufficient amount of hydrochloric acid. Protein digestion is facilitated by enzymes contained in the gastric juice — chymosin, gastrixin, pepsin, and others. Partially digested food from the stomach enters duodenum, where It can be said that the intestine consists of two tubes inserted one into the other, one tube (outer) consists of the muscular layer, the other (inner) consists of the mucous membrane. Both tubes can slide one against the other due to the loose submucosal layer facilitating movement. In the submucosal layer are blood vessels and nerves. Functions of the layers of the intestinal wall are different: the mucous membrane is involved in the absorption of nutrients and digestion, the muscular membrane performs the motor function. The muscles of the intestinal wall constantly run through wavy contractions, which serve to promote food in the process of its digestion. Such muscle contractions are called intestinal motility. The inner surface of the small intestine is covered with the smallest finger-like outgrowths - villi, due to which the area of the small intestine is increased many times, which contributes to the most complete absorption of nutrients. Villi are involved in an important process - parietal digestion in the intestine, as they contain the smallest digestive glands. It is the parietal digestion that is most developed in children (in adults, abdominal). This is the final stage of digestion. In the large intestine is the absorption of water, minerals and drugs. Partially in it can occur and the digestion of nutrients from the small intestine along with enzymes. By the time of birth digestive tract the baby is sterile, but after a few hours, various microorganisms appear in it that get there with the air and from the moment they start feeding. The distribution of normal microflora in different parts of the digestive tract is not the same. Normal microflora in the oral cavity and large intestine is plentiful and varied. There are practically no microorganisms in the stomach and the upper parts of the small intestine, which is explained by the inhibitory effect of acidic gastric juice on them. The composition of the microflora of the large intestine largely depends on the nature of the nutrition of the child. The microflora in the intestine performs a number of specific functions. Thus, E. coli and enterococcus, together with bifidus bacteria, inhibit the growth of pathogenic and putrefactive bacteria; it synthesizes group B vitamins (B1, B2, B6, etc.) and vitamin K. At the same time, the normal intestinal microflora itself is sensitive to various adverse effects, in particular to antibiotics, if they are used improperly and uncontrolledly, as well as to other drugs, including antihelminthic drugs. Uncontrolled use drugs can lead to various diseases gastrointestinal tract. In these cases, the number of bifidobacteria, enterococci and non-pathogenic Escherichia coli sharply decreases, or they disappear completely, and at the same time various pathogenic and putrefactive microorganisms develop, sharply disturbing the normal functioning of the intestine, poisoning the body with toxins, which further aggravates the primary disease.
The implementation of the processes of digestion in the small intestine is possible only with the direct participation of the pancreas and liver. The functional activity of the pancreas is closely related to the functioning of the liver, which plays an important role in almost all types of metabolism in the body. The bile produced by the liver and the bile acids it contains stimulate the secretion of digestive juices by the pancreas, and also participate in the digestion of fats. Functional maturity of the liver reaches, like the pancreas, by 6–9 years of age. Watch the video "Worms in children", which shows the main ways of infection with worms: Why do worms appear in the intestines of a child?The most common helminthic invasions in children are enterobiasis (pinworm infection) and ascariasis (caused by ascaris). Symptoms of worms in young children: signs of the appearance of worm infestationThe main sign of the appearance of worms in a child is itching in the area anus and perineum, aggravated at night during sleep. Sometimes it is so pronounced that the child's sleep is disturbed. Itching is intolerable, and the child combs the skin. In this case, helminth eggs are under the nails. With a long course of the disease, the child’s fatigue increases, a decrease in mood is noted, it becomes capricious, unbalanced, the work of the gastrointestinal tract is disturbed. Often in children with worms in the intestine, the level of hemoglobin in the blood decreases, the immune system is weakened. Another sign of a worm infestation in a child may be such an allergic reaction as skin rashes, as well as runny nose and coughing fits. Sometimes the general condition of the child is disturbed, headaches, dizziness, nausea appear. On the symptoms of the appearance of worms in young children, you can talk in the event that the baby becomes nervous, easily excitable. Nervous tics may occur. With ascariasis, a strong paroxysmal cough may disturb. Sometimes worms are long in the body, not showing themselves. In this case, neither the parents nor the child themselves know about them. However, when exposure to the body of adverse factors (such as stress, reduced immunity, poor ecology, etc.), they are activated. Here you can see photos of different types of worms in children:
Ways of infecting children with worms
Helminths affecting the human body are divided into two large groups or into two types: flat and roundworms. Flat or round worms are called the shape of their bodies. The type of flatworms, in turn, is divided into the class of trematodes (flukes) and cestodes ( tapeworms). Roundworms are otherwise called nematodes. How can a child get worms? Infection of children with worms (invasion) occurs when eggs or larvae of worms enter the body. Worm eggs enter the environment from the feces of infected people and animals. They have microscopic dimensions, are very resistant to various influences and can maintain viability outside the body for a long time (in the soil, on the surface of objects or products, in the folds of linen, on the skin). When helminth eggs get into oral cavity baby, they pass, partially breaking down, through the acidic, aggressive environment of the stomach for them and are activated in the intestine, where there are favorable conditions for the development of adults from eggs. Infants and preschool children are particularly susceptible to helminthic invasions, since they still have imperfect protective barriers of the gastrointestinal tract. Simply put, the child swallows the eggs of worms when he puts dirty hands into his mouth, toys, eats unwashed fruit, etc. A baby may become infected at home, on a visit or kindergarten in contact with contaminated surfaces or objects (outdoor shoes, the floor in the hallway, toys, common areas), on the street (picking up any objects, playing in the sandbox or on the ground), as well as contact with animals (especially stray or home) who are on the street). The probability of the appearance of worms is very high if the rules of elementary hygiene are not followed (unwashed hands, eating unwashed vegetables and fruits, eating raw water from natural water bodies, etc.).
How to determine the presence of worms in a child: manifestations of helminthic invasion
How to understand that the child has worms, and what symptoms indicate infection? If a baby develops signs such as drooling, nausea, loss of appetite or abnormal increase in it (the child constantly asks for food), cramping abdominal pain that occurs regardless of food intake, upset stools (diarrhea, constipation), fatigue, frequent headaches pain or dizziness, pallor and blue under the eyes, if the child often suffers from a cold, has a rash on the skin, then the likelihood of helminthic invasion is very high. Some related phenomena can also indirectly confirm the presence of worms: persistent intestinal dysbiosis (often with the suppression of normal Escherichia coli), low hemoglobin, increased eosinophil count, increased ESR in the general blood count. Often, worms lead to the "allergization" of the body, and then come to the fore skin manifestations in the form of atopic dermatitis, neurodermatitis, "diathesis". As a rule, these are persistent, difficult to symptomatic treatment of the condition, which, however, quickly disappear after specific antihelminthic treatment. Diagnosis of helminthic invasions
In cases of increased risk of infection with worms (contact with animals, playing with a child on the ground or in open sandboxes, if a child is accustomed to taking things in the mouth, biting his nails or licking his fingers, etc.), it is advisable to undergo an in-depth examination, including, in addition to a three-time analysis of feces , special blood tests that detect antibodies to helminths. In the presence of allergic manifestations of unknown origin, an increase in the number of eosinophils in the blood test, persistent intestinal dysbacteriosis, it is desirable to donate blood for the determination of Ig E and Ig G immunoglobulins for ascaris and other helminths. You can check for worms in pets. It is imperative that you pass an analysis of feces for dysbacteriosis: if the level of normal E. coli is significantly lower than normal, then the probability that the child has worms is about 85%. How to determine if the child has worms?
It will be useful to remind you that scraping enterobiosis (if suspicion falls on pinworms) should be taken in the morning without undermining the child, because the purpose of this analysis is to detect worms eggs laid overnight on the skin. That is why it makes sense to go to the clinic just after that night, during which the baby slept restlessly. How often in our time can we hear from parents that their son or daughter is allergic to certain foods, plants, dust, and so on. It seems that every second child is allergic. Meanwhile, the cause of allergies (more precisely, the reason that in everyday life is called allergies) can be the same worms. Worms - roundworms or pinworms, or protozoa - giardia or chlamydia, captured a child's body, poison it with products of their vital activity. As a result of intoxication on the skin, rashes or other manifestations may appear that adults take for allergies.
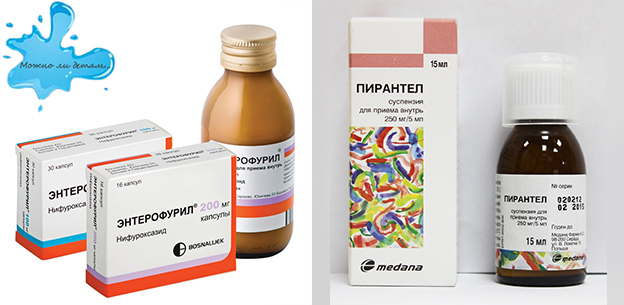
It is not so difficult to get rid of worms, and a child enrolled in the ranks of allergy sufferers will probably experience limitations all his life and be treated for a non-existent disease. It may well be that, having expelled uninvited guests from the child’s body, you will not find a trace of past allergies in the future. In the following sections of the article you will learn what the worms are dangerous for a child. How to understand that a child has worms: symptoms of enterobiosisThe source of helminthiasis is a sick person. Infection occurs through the ingestion of eggs through the mouth and swallowing with saliva. Self-infection is also possible when combing the perianal area; eggs can get into the mouth from the skin of the hands. The main clinical symptom is perianal itching, abdominal pain, increased stool. The main diagnosis is the detection of pinworm eggs in a scraping from the perianal area, or the detection of female worms on the surface of feces. To cure it is enough to ensure the sanitary and hygienic standards in the care of the body, clothing, housing. To remove the worms from the child as soon as possible, the treatment is carried out with drugs like "Verlux", "Pirantel" and others according to the established scheme. To remove worms in children and prevent reinfection, it is necessary to wash the child, to lubricate dry skin near the anus with petroleum jelly or baby cream, and to put on thick underwear at night. In the morning the pants are washed, scalded with boiling water, and the bedding is either changed or ironed; the family members must be examined. Control tests for enterobiasis are carried out on the 10th and 30th day. Special dietary treatment for enterobiasis is not carried out. How to find out that the child has worms: symptoms of ascariasis
The larvae leave the eggs in the small intestine, they penetrate into the blood capillaries, piercing the intestinal wall, and can get into any organs: liver, lungs, brain. The larvae feed on serum and red blood cells. From the lungs, the larvae penetrate through the alveoli into the respiratory tract, along with mucous secretions enter the intestine and reach sexual maturity after 70 days. Ascaris lives about one year, after which it dies and is removed mechanically with feces out. During the development of the larvae, the main symptom is allergic manifestations due to metabolic products or disintegration of the larvae. Another group clinical manifestations associated with the appearance of eosinophilic infiltrates in the intestinal wall, lungs, and other organs. Clinical manifestations may also be related by mechanical action. In places of perforation of the larvae in the internal organs hemorrhages may occur. Roundworm in the intestinal lumen are located freely, resting against the ends of the intestinal wall. They move freely and can penetrate the stomach, esophagus, pharynx, and even the frontal sinuses. A serious condition occurs when ascaris penetrates the pancreas and liver. This can cause abscesses of various organs. Sometimes a cluster of ascaris in the intestinal lumen can cause mechanical obstruction. Manifestations of ascariasis depend on the intensity of the invasion of worms and their location. How to determine the presence of worms in a child in this case? In the first phase (migration), the symptoms are scanty, expressed malaise, cough, discharge of mucopurulent sputum, which may have an orange color and an admixture of blood. Increased body temperature, dry rales are heard in the lungs. Hemorrhages and various rashes may appear on the skin. Radiographically in the lungs are determined by various infiltrates. From the side of the blood pronounced eosinophilia. With a massive invasion, appetite decreases, weight loss, abdominal pain is noted, intelligence decreases in children, they lag behind in psychomotor development. There are symptoms of the nervous system: dizziness, fatigue, restless sleep,. There may be photophobia, dilated pupils. In the first phase of the disease, the presence of ascaris larvae in sputum and specific antibodies in the blood is detected. In the clinical period, the main method is the study of feces for the presence of ascaris. In the early phase, an elevated blood eosinophil content is determined.
Prevention is the prevention of environmental pollution by faeces. A thorough washing of vegetables and fruits before meals and in the preparation of salads is recommended. To prevent worming of the environment with helminths, it is recommended to identify and treat persons infected with ascaris, examination of children in preschool institutions and in grades 1-4. Dietary treatment is auxiliary due to the frequent occurrence of iron deficiency anemia and protein deficiency. Milk, butter, eggs are included in the diet of children; it is useful to include wheat porridge with yellow pumpkin, strawberries, raspberries, bananas, walnuts, watermelon, dogrose, beetroot, fruits of mountain ash, infusion of nettle leaves. Leaf or nettle roots in the form of infusion is used for anemia as a means of increasing the hemoglobin content and increasing the number of red blood cells. What are the dangerous worms for a child: trichocephalosis, teniarinhoz and defillobotriozThe source of the invasion is a sick person. The larvae enter the human digestive tract with contaminated food, water, vegetables and berries grown on contaminated soils. Signs of the disease. Patients develop fatigue, general malaise, dizziness, restless sleep, abdominal pain, usually in the right iliac region, alternating constipation and diarrhea. An attack of appendicular colic may occur, if the whipworm is located in the appendix, appendicitis may develop when an infection is attached. It is also possible the development of moderate anemia, severe eosinophilia. The diagnosis is determined by finding the eggs of the claw in feces and on the basis of clinical manifestations. The treatment is carried out in the hospital with the use of mebenlazole, disfeil, naphtomol and other means. Apply and the introduction of oxygen. The main measure of prevention of invasion is the prevention of environmental pollution by faeces, the use of unwashed vegetables and fruits is unacceptable. Diet with whipwash is of secondary importance and is assigned to correct nutrition in case of anemia and. The main thing - the elimination of the main reason - the expulsion vlasoglav. Diagnosis is based on the detection of segments and worm eggs in fecal masses, as well as spontaneous discharge of segments outside the defecation. The treatment is carried out with a pheno or an extract of a male fern.
Signs of the disease. In humans, the tapeworm, by virtue of its magnitude, causes:
The incubation period is up to 60 days. The manifest and hidden forms of invasion are distinguished. The disease usually develops gradually. There are symptoms of the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, pain in the stomach, all over the stomach, there are signs of asthenoneurotic syndrome, weakness, general malaise, dizziness. There is B12-deficient anemia, the main symptoms of which are:
With a recent invasion, eosinophilia is expressed. The severity of anemia depends on the nature of nutrition of the patient. The diagnosis is confirmed on the basis of history, stay in the epidemic focus, the allocation of parts of worms with feces, the presence of B12-dependent anemia.
Dietary treatment is important, although the main thing is the expulsion of the tapeworm. In addition to the introduction of vitamin B12, a hepatic diet is prescribed. Delivery of the missing vitamin B12 is carried out by assigning various dishes from the liver. Liver therapy is prescribed for 2-3 weeks under the control of a blood test. After normalization of blood, increase of hemoglobin, erythrocytes, liver dishes are constantly included in the child's diet. Characteristic of this group of helminths cestodes is that these worms have a head, equipped with special attachment bodies, their body has the form of a tape. These worms are characterized by the presence of hermaphroditism, they have both feminine and masculine elements, so they self-fertilize the eggs of the worm. Usually the body of the worm consists of segments; the length of tapeworms can reach several meters. How to get rid of worms in children with drugsRepeated self-infection if personal hygiene rules are not followed makes it difficult to treat helminth infections. Therefore, it is necessary to re-examine the child after treatment, and sometimes a second course of treatment. Currently, there are a large number of medicines that can quickly and effectively get rid of worms. Antihelminthic properties have onions, garlic, pumpkin seeds, wormwood, St. John's wort, tansy, male fern, walnut. Begin treatment as early as possible. Antihelminthic drugs are selected depending on the specific type of worms. First, do not treat yourself and do not treat your children, without consulting an experienced doctor. Uncontrolled use of drugs can cause you irreparable harm. And secondly, such treatment, even under the supervision of a physician, can be effective only when the diagnosis is precisely known. To make the diagnosis is extremely difficult. We have already talked about this above. Here and expensive research, and the blurring of symptoms, and other interfering factors.
How to remove worms in children homeopathic medicines
When starting a homeopathic treatment, remember that for a quarter of an hour before and after taking the medicine, you should refrain from consuming any strong smell (for example, garlic), strong drinks, chewing gum, or smoking. All this can neutralize the effect of the drug. From the table below you will find out the name of the pills recommended for children to get rid of worms. Prevention of helminthic invasions in children
Remember: prevention of the appearance of worms in children and the observance of hygienic measures significantly reduces the risk of helminth infection. Article read 3 268 times (a). Worm infestation is a common disease that occurs in people of any gender and age. It is often called the "dirty hands disease", because most often it is problems with personal hygiene that lead to defeat. The symptoms of helminthic invasion can manifest themselves in different ways, and therefore the disease is divided into acute and chronic.  Symptoms of helminthic invasions often vary depending on what kind of worm has settled in the body. Most often the cause of the disease are roundworms. It is possible to notice the infection process in about a week, since at this point the migration phase of the larvae begins.
These signs are easily confused with an allergic reaction and diseases of the respiratory system, such as bronchitis and pneumonia. It is possible to determine that treatment is required for helminthic invasion by ascaris using lung X-rays, since accumulations of infiltrates will be seen in the picture. In case the worms spread through the intestines, it is possible to isolate more specific signs:
Symptoms of pinworm spreadA person infected with pinworms will mostly feel the same symptoms as in the case of ascaris, but the nervous system will be affected. The patient will become more irritable, he will start having problems with sleep.
At a certain point, pinworm eggs can be seen in the feces with the naked eye, but until this point they cannot be detected with a standard analysis. The fact is that this type of worms does not reproduce in the intestines. Signs of Trichinella DevelopmentIf trichinella is in the human body, the disease will occur in three main phases.  The effects of flatworm activityIf a person picked up flatworms, sort of bull snake - after a month and a half, he will have the following symptoms: Wide tapeworm - another common pathogen of helminthiasis among flatworms. It causes diphyllobothriasis, which is very difficult to notice. Sometimes people experience dizziness, and fever and nausea occur only in the later stages. At this time, skin rashes and red spots on the mucous membranes of the mouth may develop. Symptoms of defeat by trematodesAmong flatworms, a large group of trematode flukes stands out. Once in the blood, they reach many organs, such as the lungs or liver, and can also settle in the pancreas or intestines. Because of the breadth of the spread, the symptoms are very variable. Within a few days, the worms will get used to the new host organism, and then begin to actively proliferate.
Features of children's worm infestationNote! Street animals often use children's sandboxes as a toilet, so it is very easy to get worms in such places. Among the symptoms of worm infestation in children, there is a lack of appetite, pallor and problems with sleep. In addition, you should pay attention to gastrointestinal disorders, increased temperature and itching of the anus. Consequences and possible complicationsWith timely diagnosis, curing invasion is not difficult, so the serious consequences of the disease are already a relic of the past. However, infecting children can cause developmental delays, both in terms of psychology and physical data.
Diagnosis of the disease
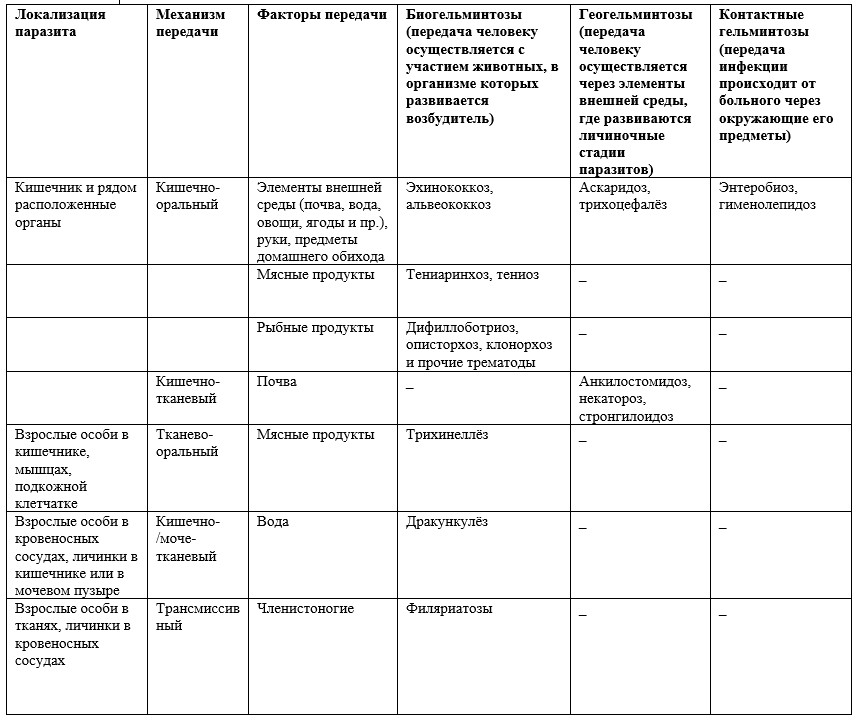
How to deal with defeat?Depending on the severity and complications that have arisen, in addition to direct infection, it is necessary to fight diseases of the lungs and heart, and sometimes genitourinary system. During treatment, it is important to monitor hygiene and disinfect the place of stay, to prevent re-infection. How to prevent infection?It is difficult to doubt the need to wash vegetables, fruits, herbs and berries. If you can, it is better to pour the product with boiling water. In addition, preventive measures include:  In order to protect against worms invasion, it is necessary to monitor soil contamination and the treatment of sick people, but these preventive measures belong to the public level, and individuals can practically do nothing in this respect. However, the rules of personal hygiene and cooking products are usually sufficient to prevent helminthic invasion. Helminthiasis in children is a rather acute problem in the modern world, because not only doctors of narrow specialties, but also employees of the medical district service, as well as employees of children's school and preschool institutions are involved in it. Helminths in children and adults are mainly classified into two types: roundworms and flatworms. The type of roundworms is a class of roundworms (nematodes), a type of flatworms are classes of tape (cestodes) worms and flukes (trematodes). Most frequent species helminth infections in children are roundworms, among which are leading and. This is due to the ease and speed of transmission in the case of enterobiasis and the long-term viability of Ascaris eggs, which can live for three or more years in the soil. Trematodosis and are rare diseases that are characterized by natural foci, as well as food habits. Usually, children become infected more often than adults, and their disease is much more serious. As a rule, this is due to the immature immune system children, and the lack of regular personal hygiene habits. Table 1 - The prevalence of helminths in the Russian FederationEpidemiological classification of human helminthiases (E.S. Leikina)
Table 2 - Epidemiological classification of human helminthiases (E.S. Leikina). To view the table click on it. Pathogenesis of invasionsIn response to such allergens, the baby's body produces antibodies that trigger a huge cascade of reactions leading to various manifestations in varying degrees. Of course, it is not always necessary to consider an allergic reaction as something harmful or harmful. This kind of protective mechanism was developed in the process of evolution by our body. Among the less dangerous allergic reactions may be an increase in eosinophilic cells in the blood, rash-type urticaria, the most dangerous include angioedema, anaphylactic shock, growth of lymphoid tissue with a possible tumor process. Inflammation in the organs leads to disorders of the digestive system, pain, growth of lymphoid elements of the body. In the late period of invasion, biology, life expectancy, the habitat of the worm in the body are of particular importance in the development of pathological processes. Worms have not only allergic, but also mechanical and toxic effects, they become agents of pathogenic microorganisms, consume nutrients and beneficial trace elements from the human intestine. The mechanical effect of helminths depends on the method of their attachment in the body. and flukes have special suckers, which, attached to the shell, impair circulation and promote inflammation. Hookworms with teeth are inserted into the membrane, and due to the release of a special substance, blood clotting is delayed, leading to bleeding. Pinworms and dwarf chainers gouge through the intestinal wall and penetrate deep into it. The toxic effect is associated with the release of metabolic products that cause the destruction of red blood cells, paralyzing the walls of blood vessels, which leads to hemorrhages. Also, these substances reduce the content of hydrochloric acid in the gastric juice, which helps to reduce the body's resistance to microbes that enter the child’s body, for example, with food. Traumatization of mucous membranes, bile ducts, blood vessels and skin by mature individuals or their larvae contribute to the penetration of dangerous or conditionally dangerous microbes into the body. Also, waste products of worms alter the composition of the natural intestinal microflora, leading to dysbiosis and increasing the formation of atypical copies of natural bacteria, which can then reduce the immune defense mechanisms of the child. Clinical manifestations of infection in childrenDue to the diversity of the pathogenetic mechanisms of action of worms on the body, the symptoms of helminthic invasions (worms) in children are diverse, sometimes masquerading as other infectious or surgical diseases. Also, the diverse symptoms of helminthiasis are caused by the presence in the body of the child not only of the adult, but also of the larvae. Symptoms of intoxicationIntoxication syndrome is caused by exposure to enzymes and other substances that produce helminths in the process of life. The manifestations of intoxication syndrome include appetite disorders (decrease to complete absence), rapid weight loss or sudden weight loss, physical development, dizziness, excessive sweating, reduced attention (the child seems to be “not here”), increased salivation (up to the appearance of harmful habits in the form of spitting), weakness and general poor health. This also includes compensatory enlargement of the liver and spleen in response to the introduction of the larvae and their toxins. General intoxication syndrome is characteristic of all helminth infections, however, most often it accompanies. Skin lesions
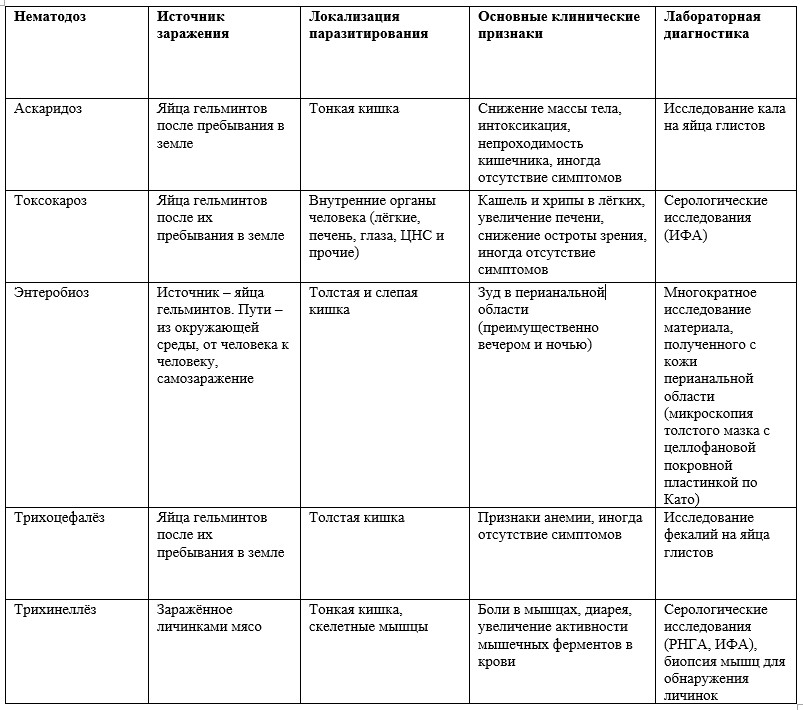
Usually, skin lesions appear with a variety of rash such as urticaria, focal dermatitis, blistering rashes, which can lead to peeling in the future. Also referred to skin lesions itching (for example, with enterobiasis). Intolerable itching can cause the child to constantly scratch the affected area, which can later lead to the addition of a microbial infection with the formation of pustular eruptions (pyoderma), which include furuncle, hydradenitis, impetigo. Exanthema syndrome is characteristic of ascariasis, toxocariasis, enterobiosis, hookworm, rarely - for cysticercosis of the skin, opisthorchiasis. Gastrointestinal symptomsThis syndrome includes the so-called dyspeptic symptoms. The appearance of such symptoms is due to both mechanical (due to tissue damage) and toxic (due to excretory function) the effect of helminths on the body. Dyspeptic symptoms include nausea, vomiting, which does not always depend on food intake, frequent or persistent diarrhea (sometimes with mucus or blood), less often constipation, heartburn, belching, painful bloating, discomfort when swallowing, pain during movement of the tongue ( with trichinosis). Such violations of the adequate activity of the digestive system will certainly lead to a deterioration of mood, decreased appetite, and, consequently, to a delay in the physical and mental development of the child. Injuries to the gastrointestinal tract are to some extent characteristic of all helminth infections. Stomach acheMore often pain syndrome associated with the development of an adult worm. Abdominal pain occurs due to the fact that the worm passes the so-called ileocecal valve, or Bauhinia, which separates the small and large intestines. Also, pain can be associated with the process of increasing the spleen and liver, because the capsule of these organs is rich in receptors and gives you a sensation of pain when stretched. Another pain can occur during the migration of larvae, when they pierce the walls of blood vessels, stomach, and other organs. Pain syndrome in children has no clear localization. Most often, the pain spreads to the entire abdomen. This is due to the fact that the abdominal wall itself is very rich in receptors, including pain. Since children are small, all organs are much closer to each other than adults. Due to such close proximity, stimulation of some receptors quickly spreads to neighboring ones, gradually covering the entire abdomen. Pain syndrome is characteristic of all helminthiasis, less often manifested in the defeat of pinworms. Neurological signsAlso, damage to the nervous system can be toxic and organic when the worm secretes a neurotoxic substance or when a migratory larva enters the brain or spinal cord. In this case, children have meningeal symptoms characteristic of meningococcal infections (neck stiffness, Babinsky, Kerniga, and other symptoms), loss of consciousness, epileptic seizures, memory loss, hallucinations, delusions, photophobia, gait disorders due to root damage spinal cord, goose bumps and tingling in the limbs (parasthesia), cooling of the limbs due to impaired nervous regulation of blood vessels, increased intracranial pressure, vomiting, not bringing relief. Affections of the nervous system are most often characteristic of ascariasis, toxocariasis, spinal cord and brain. AnemiaAnemic syndrome is a frequent companion of helminth infections in both children and adults. It occurs as a result of damage to the worms of the vascular walls and the absorption of red blood cells and other substances directly from the blood, as well as from the host food bolus. Most often, the defeat of worms leads to hypochromic iron deficiency anemia. However, the appearance of signs of vitamin B12-folic acid deficiency anemia (megaloblastic, pernicious) indicates a wide lesion that cannot produce these vitamins on its own, and therefore absorbs them from the host intestine. In severe cases, shortness of breath with the usual physical exertion, abnormal heart function (increased heartbeat, blood pressure, abnormal tones and noise in the heart), irritability, decreased physical activity, epileptic seizures and loss of consciousness appear, appetite, stool are disturbed, Gunther's glossitis (insult to the tongue), insomnia, hallucinations, delirium occur with pernicious anemia. Reduced hemoglobin with iron deficiency anemia less than 50 g / l can lead to heart failure in a child. Manifestations of anemia are most often characteristic of teniasis and teniarinhosis, diphyllobothriasis, ankilostomiasis, enterobiosis, ascariasis, and trichocephalosis. Hematologic changesThis syndrome includes changes observed in the blood test. In mild cases of the manifestation of the disease, these changes are not noticeable to the patient and pass on their own during treatment. Changes in the blood are usually of a general infectious nature, therefore it is impossible to recognize the causative agent by analyzing only blood. Usually, changes in the blood accompany the early phase of the disease, and in the uncomplicated chronic phase they can completely disappear. In severe cases, changes in the blood may be associated with damage to specific organs. The changes found in the study of blood include: an increase in eosinophils (not typical for trichocephalosis), abnormal blood cells, an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, an increase or decrease in leukocytes, a decrease in hemoglobin, a decrease in vitamins B1, B6, B12, A, C, a decrease in iron , copper, an increase in various fractions of bilirubin, an increase in liver cell enzymes (AlAT, AsAT), an increase in alpha-amylase. Hematological syndrome is inherent in all helminths, however, because of the above reasons, it can not be detected. The defeat of other organs and systemsThe migration of the larvae of some helminths can cause damage to the respiratory tract, which can lead to pneumonia, bronchopneumonia, bronchitis (sometimes obstructive), influenza-like diseases, asphyxiation, purulent pleurisy. Such diseases are manifested by an increase in temperature, cough, general malaise, shortness of breath, hemoptysis, decreased activity, delayed psychophysical development, suffocation, wheezing and wheezing, hoarseness, chest pains. Lung lesions are most often characteristic of ascariasis, toxocariasis, trichinosis, ankilostomiasis, pulmonary cysticercosis, and echinococcosis of the lungs. Damage to the liver, biliary tract, pancreas can be the result of the migration of both larvae and adults. Lesions of these organs can be manifested by abdominal pain, enlargement of the liver and spleen (hepatomegaly and splenomegaly), jaundice, tenderness in the liver, temperature, lack of appetite, delayed development, nausea vomiting, impaired stool. Such phenomena are characteristic of fascioliasis, opisthorchiasis, echinococcosis, alveococcosis, hymenolepiasis, trichinosis, rarely enterobiosis, ascariasis. Eye damage is manifested by a decrease in visual acuity, periorbital edema, strabismus, pain during eye movement, conjunctivitis, uveitis, retinitis. These changes are characteristic of toxocariasis, trichinosis, eye cysticercosis. Lesions of the urogenital system are characteristic of enterobiasis and are secondary changes. Severe itching can lead to combing and the appearance of pustules on the skin, insomnia, irritability, urine. Boys can engage in masturbation, girls - masturbation, which can lead to a breakthrough of the hymen. The pinworms crawling out of the anus can crawl into the girls' vagina, also causing itching and infection, leading to vaginitis. Sometimes the presence of vaginitis contributes to the formulation of an incorrect diagnosis, long and futile treatment. The defeat of the heart muscle is characteristic of toxocariasis, trichinosis, cardiac cysticercosis, echinococcosis. Cardiac disorders are manifested by rhythm disturbances, heart failure, high blood pressure. In severe cases, such phenomena are fatal. Sometimes the symptoms of helminth infestation in children are manifested by pain in the muscles and joints. The characteristics of the main nematodosis are given in the table below.
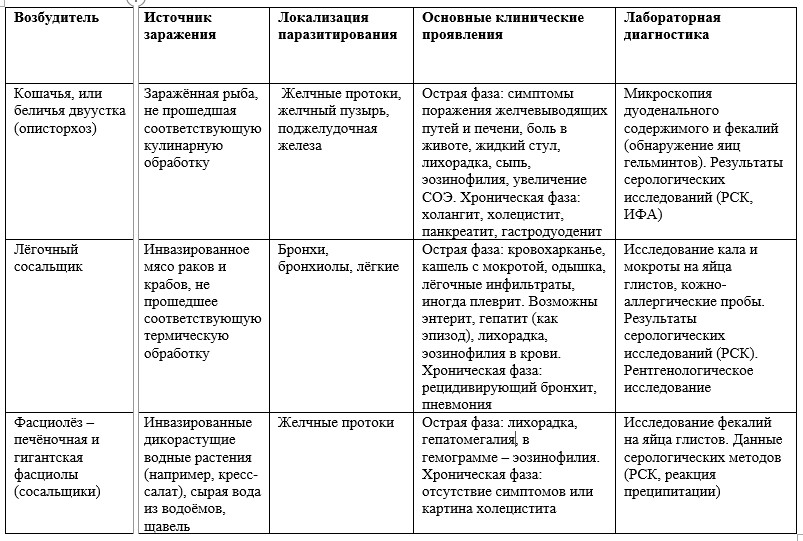
Table 3 - Epidemiology, clinical presentation and diagnosis of major nematodoses in the territory of the Russian Federation. To view the table click on it. In the following table, we tried to combine data on the epidemiology, clinical picture and diagnosis of the main trematodosis.
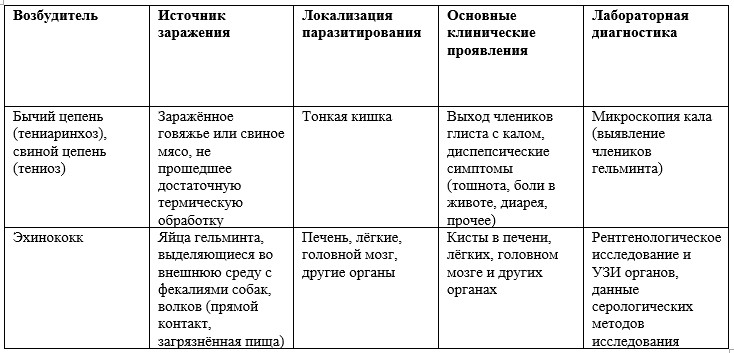
Table 4 - Epidemiology, clinical presentation and diagnosis of the main trematodoses in the territory of the Russian Federation. To view the table click on it. Characteristics of the leading tsestodoz are shown in table 5.
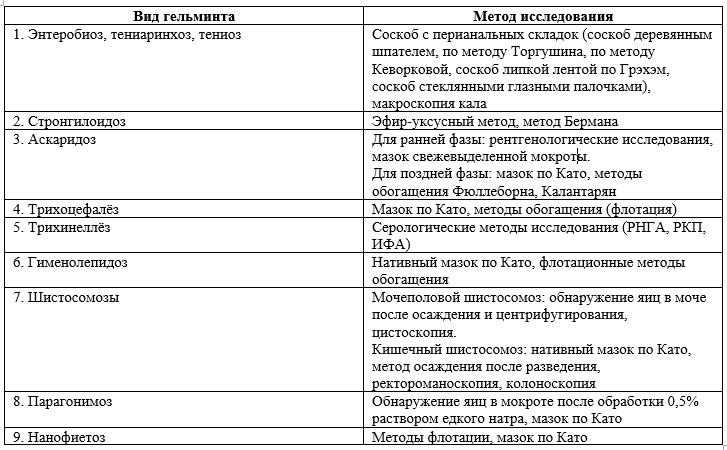
Table 5 - Epidemiology, clinical presentation and diagnosis of the main cestodiasis. To view the table click on it. Diagnostic methodsIn the diagnosis of helminthiasis in children, it is usually never limited to one method of research, because it is not always possible to identify the eggs or larvae of specific helminths that live in the human intestine. Macroscopic examinations (mainly for differential diagnosis of bovine and porcine chains in combination with a survey) and microscopic examinations, which are divided into simple, complex and special methods, are usually used to study feces. Simple microscopic methods for the diagnosis of helminthic invasions in children and adults include the native smear, the Schulman twist method, the Kato thick smear method with cellophane. The complex microscopic methods include the flotation method (effective for detecting dwarf chain, whipworm, hookworm, ascaris, wide tapeworm eggs), sedimentation-sedimentation methods (used to determine wide spectrum helminths). Special microscopic methods are used for certain types of worms and are presented in the table below.
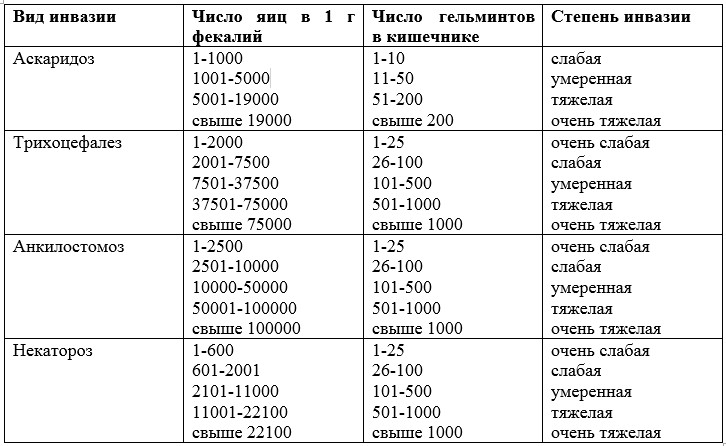
Table 6 - Methods for the diagnosis of individual helminth infections, taking into account the characteristics of invasion Also in the diagnosis of helminthiasis, sputum examination (paragonimiasis, ascariasis, schistosomiasis, echinococcosis), blood examination (filariasis), urinalysis (schistosomiasis, echinococcus larvae, eggs of other helminths that fall on the perineum), muscle biopsy specimens (trichinellosis method), are used. for trichinella detection). Quantitative research methods are used to determine the strength of damage, assess the effectiveness of anthelmintic drugs, determine the quality of deworming, control preventive measures. There are two main quantitative methods: Stoll and Krasilnikov-Volkova.
Table 7 - Intensity of invasion depending on the number of helminth eggs in 1 g of feces. To view the table click on it. Serological methods are used for diagnosis and screening, based on the detection of specific antibodies in the serum. The most significant serological research methods:
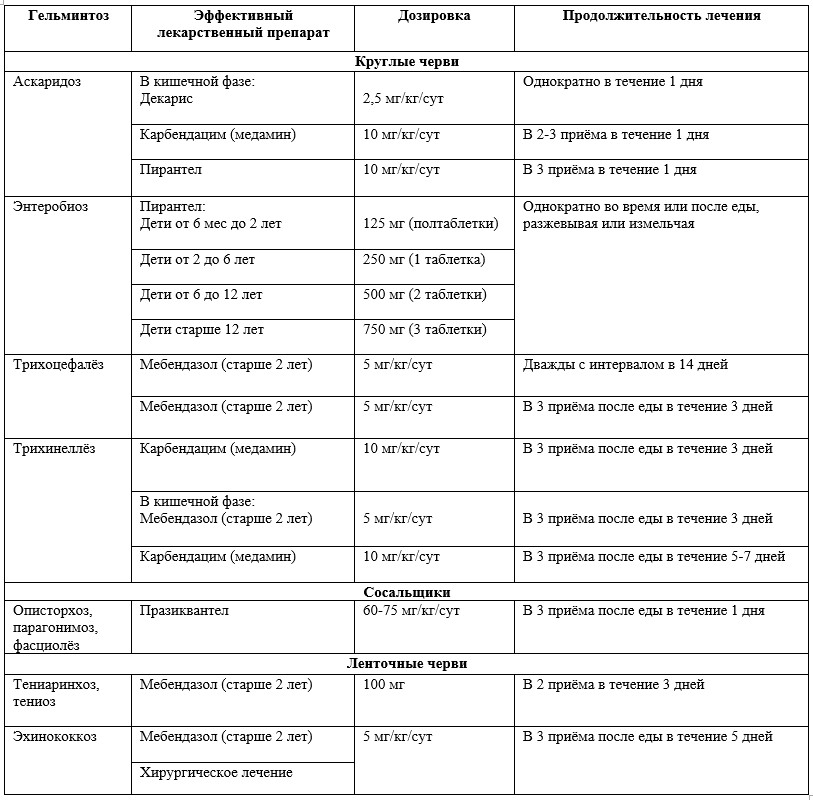
Methods of interviewing children may be difficult due to age because of the shyness of the child. Features of treatment in childhoodTreatment of worms in children is carried out as an outpatient (at home), with a mild course of the disease, and in the hospital with a severe course of worm infestation. The dosage of anthelmintic drugs is selected based on the type of helminth, age and body weight of children. There are no tablets and suspensions immediately from all worms !!! In the treatment of helminthiasis in children, the following are commonly used. anthelmintic drugs (see table below).
Table 8 - Treatment regimens for major helminth infections in children Dekaris inhibits the biochemical processes of respiration, causes paralysis of muscle cells ascaris, causes their death. Sometimes decaris is used not only for the destruction of ascaris, but also for other roundworms (hookworms, necators, whipworm, pinworms). Side effects of this drug are very rare and do not require separate treatment. It is necessary to appoint with caution to pregnant women. Carbendacim paralyzes the muscle cells of roundworms, after which they become unable to remain in the intestine. The drug is applicable when invaded by ascaris, pinworms, hookworms and whipworm. Tablets are usually crushed or chewed, and then washed down with a glass of water. Undesirable effects are expressed by nausea, weakness and allergic reactions. Contraindications include allergic reactions with the first use of the drug or to its components, as well as pregnancy. Pyrantel blocks the transmission of nerve impulses to muscle cells in roundworms, facilitating their detachment from the intestinal wall. Suitable for pinworms, ascaris, hookworms, necators. This anthelmintic drug is prescribed with caution to children up to two years. Side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, dizziness, weakness, confusion, rash, fever. Contraindications include hypersensitivity to the pyrantel. Despite the listed side effects as far as possible, Pyrantel is well tolerated by patients, and the dosing regimen makes the drug one of the most convenient and often prescribed. Pyrantel produces in the form of a suspension or worms tablets for children and adults. Mebendazole violates the use of glucose by worms, inhibits the formation of proteins and energy sources in worms. Is an effective remedy for, echinococcosis, teniasis and mixed helminthiasis. Contraindications: children up to two years, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, allergic reactions to the first use of the drug, pregnancy, liver failure. From side effects emit dizziness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, allergic reactions (rash, angioedema). Praziquantel is a drug of a wide spectrum of action, causes a persistent contraction of the muscle cells of the worm and paralysis of its muscles, after which a part of it is digested in the intestine, and a part goes out with feces. Let's apply at infection by flukes, lazerzami and tsepny, and also at cysticercosis. Contraindications are allergic reactions to the components. Caution is prescribed to children under 4 years. Side effect drug is reduced to nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, lethargy, fever, excessive sweatingrash, itching. In severe cases, various anti-helminth drugs are added to the treatment, reducing the intensity various symptoms. These can be no-shpa, papazol, tsuercal, prednisone, dexamethasone, linex and others, whose dosages are selected depending on the severity of specific phenomena, age and body weight of the child. Do not treat the child for worms on their own, without the supervision of the attending physician. Folk remedies for wormsMany adults are ashamed to go to the doctor for help in detecting worms in a child because they have remorse because they could not properly follow their children and teach them basic hygiene. Some adults do not trust modern medicine from worms, thinking that their danger is much higher than beneficial effectwhich they can render. Therefore, most parents are trying to remove the worms from the child independently, resorting to the means of traditional medicine. However, despite the fact that folk remedies for worms have been used by our ancestors for centuries, they do not take into account the individuality of the case, do not take into account the sensitivity to the components used for treatment, their tolerance by the child, do not provide for concomitant diseases in children. Also, many recipes use not one component, but several at once, the interaction of which turns such a recipe into a real poison. The most commonly used folk remedies in the fight against worms in a child are wormwood decoction for oral administration, enema with a decoction of wormwood, pumpkin seeds. The danger of such treatment of worms at home without the supervision of a physician is as follows. Wormwood can accumulate substances such as molybdenum, selenium and bromine, from which their concentration in the body becomes greater. Exceeding the recommended dosage is very detrimental to the human body as a whole. First, the excess concentration of trace elements in wormwood leads to toxic poisoning.
Wormwood poison the nervous system of both adults and children. In case of poisoning, irritability, hallucinations, convulsions and even seizures may appear. Secondly, coumarin contained in wormwood, can in a number of chemical bonds turn into dicoumarin, which causes bleeding. Therefore, wormwood, even in standard dosages, is contraindicated for anemia of any origin, which is quite a frequent companion of many helminth infections. Thirdly, wormwood can also cause various allergic reactions. Evidence of the use of wormwood just as an anthelmintic drug is missing. Next, consider the possibility of using enemas. First, the effect of enemas is based on the temperature of the injected fluid. So a warm liquid (from 36º to 40º С) promotes the absorption of substances contained in the enema, while a cold fluid (slightly less than room temperature or room temperature) stimulates intestinal motility. Secondly, the standard volume of fluid injected during the enema does not penetrate further into the rectum and sigmoid colon. Thus, the injected liquid or solution in no way can reach the small intestine - the main place of residence of the most frequently recorded helminth infections. Solutions used in folk recipesusually cooled to room temperature. The use of enemas such a temperature will increase only the intestinal peristalsis. Yes, some part small worms or segments larger, due to increased peristalsis and increased coarse separation out of the rectum. However, the habitat and maturation of worms is most often the small intestine, to which the enema does not extend. Therefore, the main part round worms or the head of tapeworms will remain in the intestines, and the cure will not come. In addition, the worms have a powerful fixation device, which provides them with a fairly tight attachment to the intestinal mucosa. Since peristalsis in the intestines is carried out daily, and at times it increases independently (on the nature of food, for example), then to detach worms, such a strong peristalsis is necessary, which will be unbearable for a child more than for worms. If, however, apply warmed decoctions of wormwood, the absorption of substances can lead to both poisoning and damage to the colon mucosa. Such enemas can cause even more damage in view of the fact that the mucous membrane of the rectum is much thinner than the same stomach lining. The action of active substances entails the appearance of microcracks and the addition of various bacterial infections.
Due to the fact that the symptoms of helminthic invasion are usually non-specific, they are often confused with surgical diseases that require emergency aid. Thus, in self-diagnostics, helminthic lesions can be confused with acute appendicitis. For children with appendicitis, enemas are contraindicated in general, since they can increase the pressure on the inflamed process, which can lead to its rupture and peritonitis in the future. Next, let's talk about pumpkin seeds. This is one of the most popular folk remedies for getting rid of worms and for good reason. The active substance of pumpkin seeds is cucurbitin., the amount of which in the vegetable ranges from 0.1-0.4% (depending on the variety of pumpkin). The greatest amount of cucurbitas is contained not in the seed itself, but in a thin green layer between the skin and the seed. When cleaning seeds, most of this layer is simply lost.
Treatment with pumpkin seeds is quite effective, but to a lesser extent than with anthelmintic drugs (for comparison, the effectiveness of pumpkin seeds is estimated to be within 60%, pharmaceutical preparations - about 90-95%). However, the use of untreated seeds is fraught with exacerbations of various gastrointestinal diseases, abdominal pain, diarrhea, appendicitis.
Differential diagnosisSince the incidence of helminth infections in children is quite high, there is a need to examine the child’s feces for worms eggs in all cases of unclear deterioration of health, loss of appetite, decreased activity, dizziness, headaches, irritability, poor sleep, nausea, and vomiting. tummy Helminth infections are distinguished from other infectious diseases, however, sometimes they need to be distinguished from diseases requiring urgent surgical care (acute appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, acute cholecystitis and others), chronic diseases of the digestive system (gastritis, ulcerative colitis, and others). In some cases, it is worthwhile to suspect helminthiasis in the presence of meningeal symptoms (appearing during meningitis) and epileptic seizures. In cases of anemia of any origin, feces are examined for helminth eggs, especially in those areas where diphyllobothriasis is common. With chronic liver diseases, they try to differentiate echinococcosis, alveococcosis, less often - fascioliasis and opisthorchiasis. Preventive actionsThe system of prophylactic anthelmintic measures:
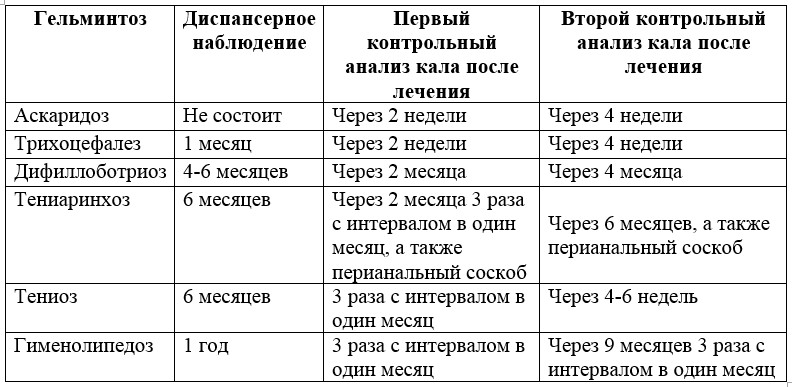
In endemic areas, it is necessary to conduct mass surveys of people for the presence of worms, take into account all the sick in one area, conduct mass anthelminthic treatment, establish a dispensary observation of the sick people after the treatment. When children enter children’s institutions, hospitals, children's camps and sanatoria, they should also be examined. Fecal examinations should be carried out using several research methods. All preschool institutions should investigate to establish availability at least once a year. Ill children are put on the dispensary account under the supervision of the district children's doctor and the doctor of the school and kindergarten.
Table 8 - Dispensary observation of children with helminthic invasions Removal of worms in uncomplicated invasions by ascaris and pinworms is allowed to be done on an outpatient basis (at home), and on invasion by tapeworms, chains, whipworm - in the hospital. In order to influence the factors of helminth transmission, it is necessary to introduce various measures to disinfect the environment (soil, edible plants, and others) and household items, in addition to strengthen the veterinary and sanitary inspection. It is necessary to maintain cleanliness and neutralize the land next to the toilets, landfills, monitor the slaughter of livestock. For the prevention of helminthiasis in children, it is strictly necessary to observe simple health measures that will protect the child from infection. Doctors need to explain to adults and children the need for daily wet cleaning of the room where the family lives with the child. It is necessary to wash and, if possible, wash children's toys. It is very important to take care of frequent change of bed and underwear, boil it when washing (enough washing at 90 degrees) and iron with a hot iron. It is necessary to explain to parents that the child’s underwear needs to be changed every day, the panties should be tight, so as not to give the worms or their segments to extend to the nearest parts of the body. Parents before bedtime and after it should wash the child's crotch with warm water and soap. Parents should also teach their children to wash their hands with soap after the street and lavatory. In addition, parents need to monitor the condition of the hands and the length of the nails in the child, as well as gradually accustom him to the elementary rules of personal care. Sick kids need to have their own separate dishes until recovery. If there are more children in the family, they should also be examined for helminthiasis. Often, one of the parents is also affected by helminth, so do not neglect to check for these diseases and in adults, even those who do not live, but are in close contact with sick children. Of the 256 species of helminths in Russia, about 100 have become widespread. Most often, diseases are caused by pinworms, roundworms, whipworms. Every year, half of the country's population becomes infected with pathogens of one of the three main helminth infections (ascariasis, enterobiasis, trichocephalosis). The incidence of echinococcosis and toxocariasis is increasing, especially among the younger generation. Roundworms are ascaris, hookworm, whipworm, pinworm, trichinella, filaria. The most common flatworm - cat fluke and schistosomes. Ribbon worms are most often represented by bovine, pork, dwarf chains, wide tapeworm, echinococcus. Giardiasis is a protozoal disease that unicellular flagellate protozoa causes. Lamblia does not belong to the worms, but there are medicines that simultaneously eliminate helminth infections and giardiasis. The highest risk of infection with worms in long-term and frequently ill children, in large families, in infants with artificial feeding, babies with unformed hygienic skills.
Tapeworms reach a considerable length compared to pinworms and flukes. Cestodes absorb a lot of nutrients, vitamins in the intestines, secrete toxins. Children suffer from digestive disorders, pain, and allergies. Further development of helminthiasis provokes anemia, leads to a decrease in body weight. The main symptoms of giardiasis usually resemble worm infestations: stool disorders, abdominal distension, poor sleep, irritability, and sometimes pain and rash. The most severe conditions in helminth infections are observed in children with poor immunity, immunodeficiency. General signs of helminthic diseases in children are sometimes of the same type. The clinical picture that occurs with different helminth infections can be very similar. There are difficulties, both in determining the species of worms, and in recognizing diseases caused by several groups of helminths. Clinical manifestations of helminthiasis in children
Signs in children with chronic helminthiasis:
The signs listed above are very important for the diagnosis and treatment of helminth infections. It is also necessary to pass feces, blood and other samples for the detection of eggs, larvae, mature worms for laboratory analysis. When enterobiasis is traditionally performed scraping, microhelmintoscopy is used. When teniasis is performed muscle biopsy. Immunological and epidemiological methods are applied. general analysis blood, allergic skin tests, serological reactions. There is a relatively new method for identifying helminthiasis - histological coprology. Stool samples are examined under a microscope after special treatment, fixation and staining with tissue dyes. Thanks to this method, it is possible to detect parts of the bodies of adult cestodes, small nematodes, eggs and larvae. Helminthiasis treatmentThe correct choice of therapeutic methods is possible only after an exact determination of the type of helminth, the phase of the disease. Treatment of helminthiasis in children in pediatrics necessarily takes into account associated diseases. It is known that with running helminthic invasion most often combined diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Drugs for treatment in children of some common helminthiasis and giardiasis
In kindergartens and schools, the family needs early detection of helminthiasis, timely treatment. Among all the anthelmintic drugs for children and adults, mebudenzol and albenadzol are highly effective and are used in multiple helminth infections. During the period of treatment and after it it is necessary to observe hygienic measures. At the end of the therapeutic course should be re-tested. Prevention of helminth infections - types and methodsAccording to the WHO recommendation, chemoprophylaxis can be done in April and November (twice a year). Anti-helminth drugs of a wide spectrum of action are used - mebenadzol and albenadzol, intended for the treatment of the most common helminth infections. Chemoprophylaxis is most needed in at-risk children. The dosage of the drug in this case is the same as in the treatment of helminth infections. It is recommended to examine the worms and deworming pets.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Read: |
|---|
New
- Sequence of procedures
- The program of intensive moisturizing of the skin on cosmetics bark
- What you need for acrylic powder
- What does owl mascot mean
- Analyzes for pancreatitis: what research should be done and what indicators show
- Owl - a talisman to attract money and good luck
- What bird screams at night with a kitten's voice?
- Cholesterol and stress
- Manicure at home
- Effective facial



 Many
Many  Many parents are worried about how to determine if their child has worms. It happens that the mother, examining the feces of her baby, finds live or immobile worms. Most often it is pinworms. In analyzes of feces, eggs of ascaris and other helminths are determined. In this situation, everything is clear and the child should be treated. But more often about the worm infestation in a child has to guess by indirect signs.
Many parents are worried about how to determine if their child has worms. It happens that the mother, examining the feces of her baby, finds live or immobile worms. Most often it is pinworms. In analyzes of feces, eggs of ascaris and other helminths are determined. In this situation, everything is clear and the child should be treated. But more often about the worm infestation in a child has to guess by indirect signs. Diagnosis of helminthic invasions in the feces is rather difficult. This is due to the fact that ascaris eggs or pinworms do not appear in the feces every day, and the smear microscopy technique requires great care. To improve the accuracy of the analysis of feces on the eggs of worms, it is desirable to take at least three days in a row.
Diagnosis of helminthic invasions in the feces is rather difficult. This is due to the fact that ascaris eggs or pinworms do not appear in the feces every day, and the smear microscopy technique requires great care. To improve the accuracy of the analysis of feces on the eggs of worms, it is desirable to take at least three days in a row. Unfortunately, not always worms are visible to the naked eye, and not always feces analyzes show their presence. But there are indirect signs that can be suspected that harmful creatures have settled in the body of your child. So how do you determine that the child has worms?
Unfortunately, not always worms are visible to the naked eye, and not always feces analyzes show their presence. But there are indirect signs that can be suspected that harmful creatures have settled in the body of your child. So how do you determine that the child has worms? Roundworm are round worms. They rank second among helminthic invasions in children. Ascaris worms are spindle-shaped, yellowish-red in color, the back end of the body is crooked. The body of the female is 25–40 cm long, 3–6 mm thick, the length of eggs is 0.4–0.5 mm.
Roundworm are round worms. They rank second among helminthic invasions in children. Ascaris worms are spindle-shaped, yellowish-red in color, the back end of the body is crooked. The body of the female is 25–40 cm long, 3–6 mm thick, the length of eggs is 0.4–0.5 mm.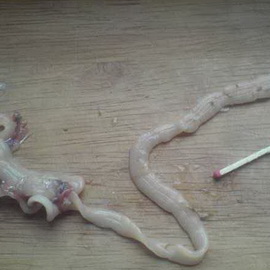 Defillobotrioz. This worm infestation caused by
Defillobotrioz. This worm infestation caused by  Unlike conventional drugs that affect the symptoms of a disease, a homeopathic medicine stimulates the body’s own reserves. Homeopathic medicines, as a rule, have no side effects, they gently and gradually strengthen the human immune system, giving it the strength to fight infection. This is especially important when it comes to treating children.
Unlike conventional drugs that affect the symptoms of a disease, a homeopathic medicine stimulates the body’s own reserves. Homeopathic medicines, as a rule, have no side effects, they gently and gradually strengthen the human immune system, giving it the strength to fight infection. This is especially important when it comes to treating children. In the process, he penetrates
In the process, he penetrates 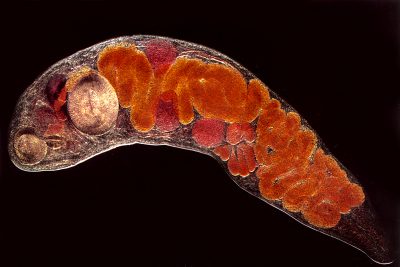 Most often, they place their eggs directly into the venous system, which causes various symptoms, such as:
Most often, they place their eggs directly into the venous system, which causes various symptoms, such as: Long-term lack of treatment gives the worms the opportunity to seriously damage
Long-term lack of treatment gives the worms the opportunity to seriously damage  For the diagnosis used numerous serological studies, such as:
For the diagnosis used numerous serological studies, such as: