Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- Technology and step-by-step instructions for nail gel: steps, rules, process
- White spots on the nails, reasons for what to do, white spots on the nails and folk signs
- Available methods for rapidly increasing blood leukocytes
- Nail and skin fungus will not resist the coffee grounds
- Crocus furniture exhibition. Furniture exhibitions
- Owl tattoo on arm value
- The biggest members in the world
- Fractures of the phalanges of the foot photo
- What is “bad” and “good” cholesterol
- What to do if the skin around the nails dries
Advertising
| Interpretation of the complete blood count |
|
In the procedure of general clinical blood examination (this is how scientifically called “a sheet with analyzes”) is not difficult. Why do you need itWhat are we for? A physician must assess the condition of our body when we address it with health complaints. And the specialist makes this assessment on the basis of hemoglobin content in erythrocytes, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, leukocyte formula. To make the final verdict, the doctor compares the results of the tests with the normal values - the characteristic of "healthy" blood. Inconsistencies associated with an increase in the percentage of any type of cells in the blood indicate states whose names are formed by adding the endings "-s", "-oz" or "-c" to the name of the corresponding cell shape. For example, neutrophilia, eosinophilia, erythrocytosis. The decrease in the percentage indicators of cells is indicated by the addition to their names of the ending "-penia" - neutropenia, eosinopenia. How to prepare for taking bloodMirSovetov remind you what you need to pay attention to the results of the analyzes were as accurate as possible. Finger blood is taken on an empty stomach in the morning - this means that after the last meal, about 10 hours should pass. Before going to the clinic, you can drink some water (, coffee, dairy products - taboo). If you drank alcohol the day before, it is best to forget about visiting the laboratory for a few days. In addition, one day before the procedure it is not necessary to engage in intensive physical exercise, to go to the bath. What do the numbers say Hemoglobin (Hgb) occupies about 95% of red blood cell proteins. His main mission is to carry oxygen. The hemoglobin content in the blood varies by sex: the norm for men is 130-160 g / l, for women - 120-140 g / l. An increase in hemoglobin concentration indicates the following conditions:
The decline is observed when:
Red blood cells (RBC) - bags with hemoglobin carrying oxygen or carbon dioxide. The norm for men is 4.0-5.0х10-12 / l, for women - 3.7-4.7 x 10 ^ 12 / l. Symptom of erythrocytosis - an increase in the number of red blood cells. Erythrocytosis, depending on the indicators, is divided into primary and secondary. Indicators from 8.0-12.0 x 10 ^ 12 / l and more indicate primary erythrocythemia, which in many cases occurs against the background of one form of leukemia (benign blood disease) - erythremia. A secondary increase (very high rates) in the percentage of red blood cells indicates:
Reducing the concentration of red blood cells is observed when:
The blood also contains young forms of red blood cells - reticulocytes. Their rate is 0.2-1.2% of the total number of red blood cells. Their number reflects the speed of the bone marrow, where new red blood cells reproduce.  Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) - in a healthy person, it is normally kept within 1-10 mm / hour (men) and 2-15 mm / hour (women). It should be noted that the ESR indicators may vary under the influence of a number of physiological causes (food intake - up to 25 mm / hour, menstruation or pregnancy - up to 45 mm / hour). There is nothing good to expect from the increase in ESR, it indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. It can be:
In addition, an increase in ESR can also be caused by non-inflammatory conditions:
The decrease in ESR is observed when:
Leukocytes (WBC). These white blood cells protect our bodies from various uninvited guests - viruses and bacteria. They are larger than red blood cells, but much smaller in number than them. Norm - 4.0-9.0 x 10 ^ 9 / l. With an increased level of leukocytes, they speak of leukocytosis, taking into account its shape. Physiological leukocytosis can be observed in completely healthy people as a reaction to certain natural conditions (the last trimester of pregnancy, the last day before menstruation, during breastfeeding, after hot baths, a few hours after meals). Pathological Leukocytosis points primarily to:
A decrease in the number of leukocytes (leukopenia) is a sign of poor production of young leukocytes in the bone marrow. It is observed at:
Platelets (PLT) - The smallest cellular blood plate, but no less important. Normal coagulability of blood and elasticity of vessels depends on their normal amount. A sufficient content of platelets is expressed in the formula 180-320 x 10 ^ 9 / l. Thrombocytopenia always signals the following alarm conditions:
Thrombocytosis also signals the presence of chronic inflammatory processes in the body, acute infectionsabout the growth of malignant tumors. After reviewing the above information, you can easily navigate in the indicators of your own blood count, but remember that the doctor must prescribe the treatment, regardless of your knowledge. Antibodies are special compounds of the protein class, they are produced by the immune system. Their active production begins immediately after ingestion of pathogenic microorganisms. In addition to the search for antibodies to Giardia antigens, an indicator such as avidity is measured. However, not every laboratory has the ability to conduct research of this type. This indicator reveals the strength of the compounds between antigens and antibodies. With it, you can get an approximate period of infection, which is very important for the appointment of high-quality therapy. DecryptionAn important point after the analysis of the vein is its further correct decoding. The indicator for the diagnosis is the rate that exists in medicine for each type of immunoglobulin. Diagnostics of immunofermental type takes into account not only quantitative indicators, but also qualitative. The latter can only show whether the analysis is negative or positive. It is also important to take into account the total lamblia antibodies. Their detection does not always indicate a one hundred percent positive result of the study. IgG immunoglobulins are often present for some time after infection. Giardiasis can be established, provided that the IgM antibody positivity coefficient is in the range 1-2, and IgG class immunoglobulins are not detected at all. If KP is more than two, this indicates an acute form of lesion, in which the detection of cysts is possible. When IgG does not go beyond the boundaries of the two, and class M is not detected, this can speak directly about the long course of infection, at which active reproduction of microorganisms does not occur. With the help of laboratory analysis it is possible to detect antibodies to Giardia in the blood of a patient. Their presence will help identify the invasion of early stage and immediately begin treatment. The production of antibodies in the blood is produced by the immune system, provided that pathogenic microorganisms enter the body and their active vital activity. There are many options. blood test. Blood is taken for various purposes, to obtain indicators of the level of various elements in the blood, as well as other related processes. Accurate blood test will help in time to establish what is wrong in the body and will prompt the doctor what measures need to be taken to improve your condition. Blood test It also helps to control the effects of drugs on the body. So let's take a closer look at what types of blood tests exist and how they are decrypted. General (clinical) blood test: decoding and meaning of all indicatorsGeneral blood analysis (other name "clinical blood test") - This is one of the most common laboratory tests. It allows you to evaluate information for the diagnosis of many diseases, as well as to trace the dynamics of recovery during treatment, which is prescribed by the doctor. In the number of indicators that reveals clinical blood testinclude the following ( decoding of a clinical blood test): Hb-hemoglobin (a decrease in its level is observed in anemia; an increase in erythrocytosis) / normal 12.20 - 18.10 G / DL; Leukocyte formula: EOS - eosinophils: a direct indicator of high sensitivity of the body. The increase in their number indicates the presence of allergies, hay fever, eczema. A decrease in the number of eosinophils is observed under stressful organisms caused by severe bacterial infections, as well as in the treatment of the adrenal cortex with hormones / normal 0.00-0.70 K / blockquote, 0-7%; ESR - erythrocyte sedimentation rate (increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), as a rule, indicates the presence of inflammatory or neoplastic processes in the body) / normal 5-20 mm / hour; What is a biochemical blood test?Any change in the biochemical composition of blood is a signal that one of the organs does not cope with its function as it is necessary.
Blood for biochemical analysis is taken from the cubital vein. Before taking the analysis, the patient is recommended not to eat - in this case, the result will be the most reliable. Overall decoding of biochemical analysis of blood represents the following groups of indicators: - squirrels; What is a blood test for hCG (a blood test for pregnancy)?The abbreviation HCG means "human chorionic gonadotropin." This is a hormone that appears in a woman’s body during pregnancy. HCG analysis (he blood test for pregnancy) can be carried out on the third day after the delay of menstruation. Below are the indicators that are normal in different periods of pregnancy. RW blood test: for syphilisTo detect this venereal disease at an early stage, 10 ml of blood is taken from a patient on an empty stomach for a Wasserman reaction. A negative reaction to syphilis is hemolysis - the process of destruction of red blood cells. If hemolysis is not observed, then the degree of reaction is evaluated. It determines the stage of the disease. RW blood test aims to diagnose syphilis as early as possible. What is PSA blood test?"PSA" stands for "prostate specific antigen." Blood test for PSA helps to diagnose the pathology of the prostate gland. High level PSA can be a signal of prostate cancer, prostatitis or adenoma. Here are some indications for conducting blood test for PSA: - observation of the prostate diseases against the background of the treatment; The upper limit of the PSA level is considered to be 2.5 - 3 ng / ml. However, for different age categories this indicator may vary. Blood test for hormones: indications forHormones are substances in our body that are responsible for all physiological and even emotional processes in the body. Blood test for hormones will tell you in what condition the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and sex glands are located. It will also help the doctor to choose the best. drug treatmentwhich will not break your hormonal balance. To get the most accurate test result for hormones important: - refrain from iodine-containing food; Blood test for tumor markersTumor markers are proteins that are produced by cells of various tumors. In the presence of a tumor, special substances are produced that are very different from the normal substances of the body, and their number in the blood is very large. Blood test for tumor markers reveals the content of precisely such substances. This is primarily: - AFP; Timely detection of tumor markers can help prevent the development of cancer. Blood test for sugarEach person’s blood contains a certain amount of sugar. Its level is always maintained at the same level in a natural way. Sugar is the main source of energy for the whole body. However, elevated sugar levels may indicate a number of endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus). Blood test for sugar It is considered satisfactory if the sugar level is within: - adults: 3.88 - 6.38 mmol / l; Blood test for sugar surrenders strictly on an empty stomach. Blood test for tuberculosis: is there such a test?As such, separate blood test for tuberculosis does not exist. To identify this disease, you can use the standard clinical blood test. As a rule, a large number of platelets in the blood indicates tuberculosis. Predisposition to tuberculosis is usually detected by the MANTU reaction. Blood test for HIV infectionThe blood for this analysis is taken from a vein. HIV is known to be treatable. This suggests that the detection of the disease at an early stage will help avoid the consequences that may lead to the development of an incurable disease. Blood test for HIV It is rendered anonymously and is recommended to everyone who has sex with different partners, uses the same hygienic equipment with HIV-infected people and in other cases of possible risk of acquiring HIV infection. International normalized attitude: blood test INRAnticoagulants are used in the treatment of diseases that are associated with the formation of blood clots in the veins: - thrombophlebitis, Blood test INR allows the physician to monitor the effectiveness of the action of drugs in these diseases. Do you want to pass blood tests in Moscow?It is no secret that patients are primarily interested in the accuracy and reliability of the analysis results. Our main task is the high accuracy of laboratory studies. We achieve this by: - the most modern equipment; Blood tests in our clinic - the best solution for laboratory research in Moscow. All analyzes in one place, quickly and accurately. Your health is our primary concern. Hepatitis - liver disease, which is based on inflammatory processes caused by various viruses or toxins. This disease is dangerous with complications such as cirrhosis, liver failure, and even liver cancer. Timely detection of hepatitis is key to proper treatment and restoration of liver function. Hepatitis is one of the most common diseases in the world, and every year the number of people suffering from this disease increases by 20-50%. There are more than 500 million carriers of the hepatitis virus in the world. The most common varieties are hepatitis B and C. Every year, about 600 thousand people die from complications of hepatitis B, while hepatitis C takes the lives of more than 350 thousand cases. Approximately 10-25% of infected people develop cirrhosis and liver cancer. Interesting Facts:
The reaction of the body to hepatitis viruses (the concept of antigens and antibodies)Most common cause the occurrence of hepatitis is the ingestion of a virus capable of affecting liver tissue.A virus is an infectious agent that infects cells of living organisms. It consists of a protein coat (capsid) surrounding the genetic material of the virus (DNA or RNA). In some cases, the virus envelope is protected by a fat layer (supercapsid). Some elements of the virus envelope are recognized by the body as foreign particles. Such elements are called antigens. Most often, antigens are proteins, but sometimes these can be complexes in which polysaccharides or lipids are attached to proteins. In response to their hit the immune system produces specific molecules called antibodies. These are immunoglobulins that can circulate freely in the blood as well as be associated with B-lymphocytes. They are the most important component of the body's immunity. Antibodies are not only able to recognize foreign particles entering our bodies, they also participate in the binding and removal of these particles. For each antigen, there is a specific antibody that recognizes and binds only to this antigen. It is for this reason that antigens and antibodies play a special role in the diagnosis various diseases. Their presence in the blood indicates the presence in the body and the degree of activity of various infections. What is PCR? Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - one of the methods laboratory diagnosisaimed at the identification and analysis of certain sections of DNA. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - one of the methods laboratory diagnosisaimed at the identification and analysis of certain sections of DNA. The vital activity of all living things, including viruses and bacteria, is based on genetic information called DNA or RNA. It consists of areas located in a strict and unique order. genes. Allows you to selectively reproduce certain genes for the purpose of their analysis and decoding. Since the genetic information of each organism is unique, such an analysis with the highest accuracy determines the specific characteristics of the analyzed genetic information. Practical application of the PCR method:
How to detect hepatitis? Hepatitis is dangerous because it may be asymptomatic for a long time. Therefore, you should not wait for the first signs of the disease, you should periodically conduct tests to identify this disease. Hepatitis is dangerous because it may be asymptomatic for a long time. Therefore, you should not wait for the first signs of the disease, you should periodically conduct tests to identify this disease. Laboratory studies are essential in the diagnosis of hepatitis. They are the detection of specific antigens and antibodies in the human body, as well as viral genetic information. The biochemical composition of the blood can change significantly in the presence of liver disease, so do not neglect such an important analysis as liver tests. Hepatitis tests:
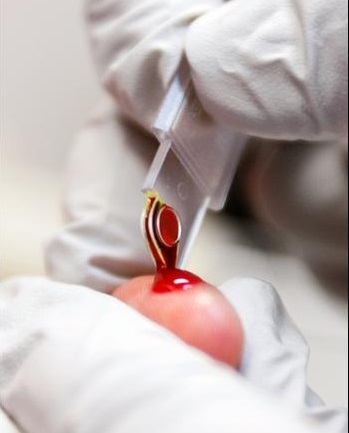
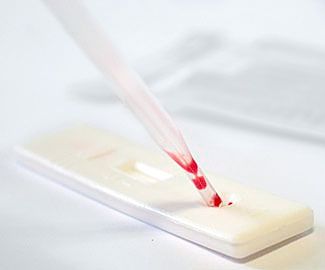
The rapid test kit includes a test strip in a sealed package, a napkin with a disinfectant solution, a finger pricking scarifier, a pipette for taking a blood sample from a finger (one or two drops is enough) and a chemical to dilute a blood sample.
Chronic Hepatitis B The cause of chronic hepatitis B is the hepatitis B virus, which contains antigens in its structure, which are characteristic only of this virus. In response to their appearance in the body, the immune system creates specific antibodies, indicating not only the presence but also the activity of the virus. For this reason, antigens and antibodies are major markers of this disease. An important role is also played by the analysis of PCR to identify the genetic material of the virus in the body. The cause of chronic hepatitis B is the hepatitis B virus, which contains antigens in its structure, which are characteristic only of this virus. In response to their appearance in the body, the immune system creates specific antibodies, indicating not only the presence but also the activity of the virus. For this reason, antigens and antibodies are major markers of this disease. An important role is also played by the analysis of PCR to identify the genetic material of the virus in the body. Markers of chronic hepatitis B:
Along with the identification of hepatitis B markers, a biochemical blood test is performed, including mandatory liver tests. The composition of the blood provides important information about the state of the liver, its functionality and the extent of liver damage to the virus.
Chronic Hepatitis C Chronic hepatitis C is caused by liver damage by the hepatitis C virus. Its peculiarity is the fact that the genetic information of this virus is not contained in the DNA, like in most viruses, but in RNA, which gives it a high mutation capacity. This property represents a major obstacle to the creation of a vaccine, as well as to the formation of antibodies in the body against this virus. Chronic hepatitis C is caused by liver damage by the hepatitis C virus. Its peculiarity is the fact that the genetic information of this virus is not contained in the DNA, like in most viruses, but in RNA, which gives it a high mutation capacity. This property represents a major obstacle to the creation of a vaccine, as well as to the formation of antibodies in the body against this virus. Markers of chronic hepatitis C:
Detection of antibodies in the blood indicates that the virus is present in the body, and a type of antibody helps to determine the degree of activity of the virus.
Biochemical analysis of blood helps to determine the extent of liver damage and its functionality.
Chronic Hepatitis D The hepatitis D virus is not independent, and its activity in the body depends on the presence of the hepatitis B virus. Nevertheless, it is considered one of the most infectious and hard flowing forms of hepatitis. As in the case of hepatitis C, its genetic material is represented by an RNA chain, which makes it easy to change, creating new forms of the virus. The hepatitis D virus is not independent, and its activity in the body depends on the presence of the hepatitis B virus. Nevertheless, it is considered one of the most infectious and hard flowing forms of hepatitis. As in the case of hepatitis C, its genetic material is represented by an RNA chain, which makes it easy to change, creating new forms of the virus. Markers of chronic hepatitis D:
Anti-HDV IgMappear within a month after infection and indicate a high activity of the virus, an acute form of the disease or exacerbation chronic process and ineffective treatment. This is a bad sign, foreshadowing an unfavorable outcome of the disease. Anti-HDV IgGindicate the presence of the virus in the body and persist throughout life. High rates indicate a chronic disease, and low - about an earlier illness. Hepatitis B Markersare a mandatory analysis in cases of suspected hepatitis D, since the hepatitis D virus can only be active in its presence. These markers will help determine the activity of the hepatitis B virus in the body and the nature of the course of the disease. Hepatic tests (biochemical blood test) Toxic hepatitisToxic hepatitis - inflammatory disease caused by the damaging effects of toxins on the liver cells. The role of toxins is played by various medications, industrial poisons, inedible plants and mushrooms, pesticides, etc. It is incredibly difficult to distinguish toxic hepatitis from other liver diseases, therefore the diagnosis of this disease is very voluminous and long-term.Hepatic tests (biochemical blood test)
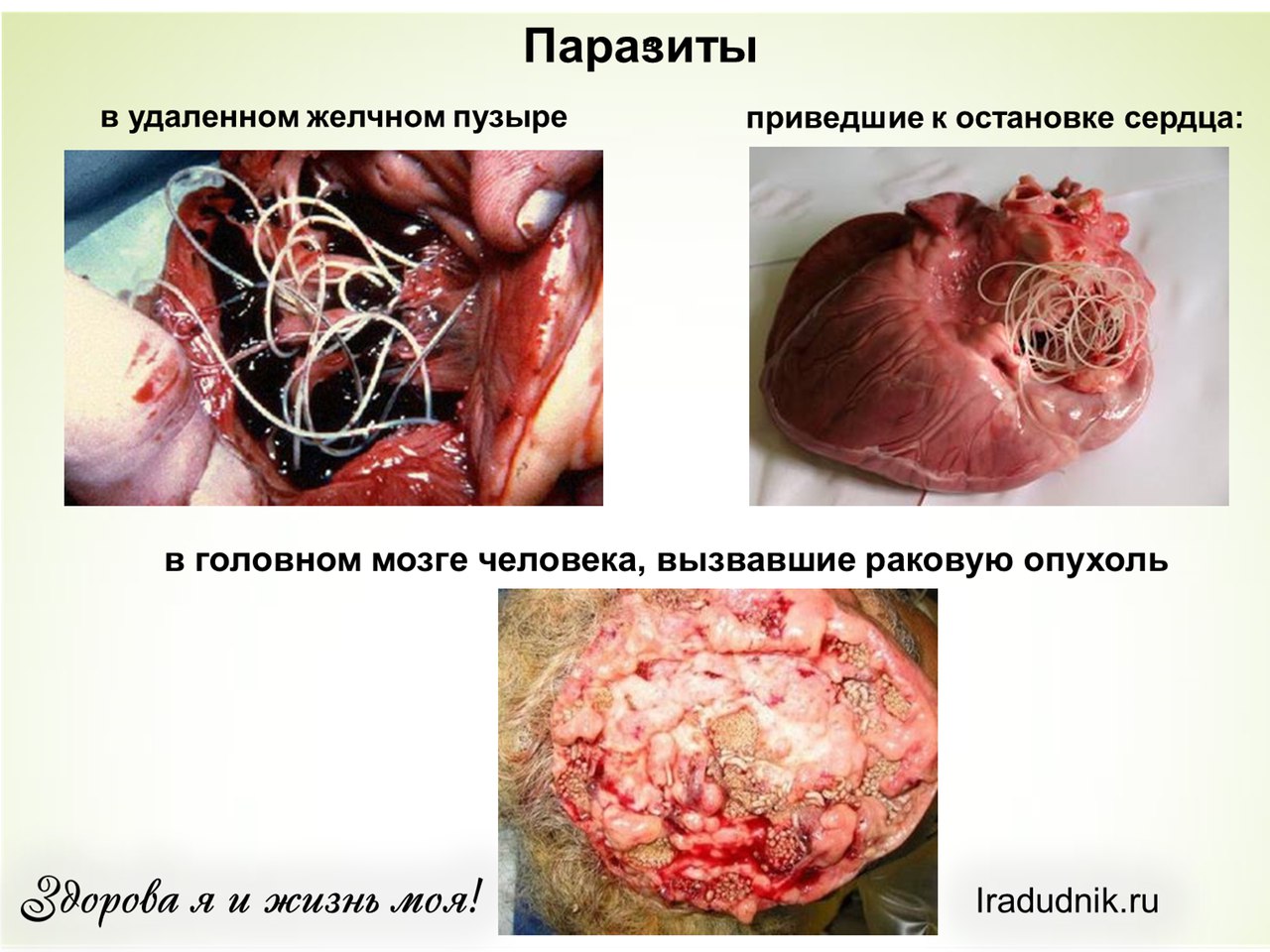
Some of them immediately begin to act aggressively and destroy the body. A part - for the time being, acts imperceptibly until their number becomes such that the carrier organism can no longer withstand and the person dies. Look at the photo. These are the organs of specific people. It is a pity that their lives ended tragically ...
Usually abdominal pain provoke roundworm, nematode and tapeworm. Often with such an unpleasant symptom faced by people who often travel the world and eat exotic food.
It is no secret that the skin reflects the internal state of the body. Any problems with internal organs, including toxic damage to the walls of the stomach, will certainly affect the skin condition, causing a number of related problems.
A couple of years ago, the medical community believed that unpleasant smell from the mouth is formed precisely in the oral cavity. Banal "unpleasant smell" from the mouth develops into a serious illness. Perhaps now you will take a fresh look at the state of your body and understand the causes of your ailments. Do not bear the pain and do not wait for the unpleasant symptoms to disappear by themselves. Periodically conduct antiparasitic program. It is important that it be productive, simple, accessible and exclusively using natural remedies (herbal fees and tinctures). It is precisely such programs that I offer to my clients. One of them |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Read: |
|---|
New
- Sequence of procedures
- The program of intensive moisturizing of the skin on cosmetics bark
- What you need for acrylic powder
- What does owl mascot mean
- Analyzes for pancreatitis: what research should be done and what indicators show
- Owl - a talisman to attract money and good luck
- What bird screams at night with a kitten's voice?
- Cholesterol and stress
- Manicure at home
- Effective facial


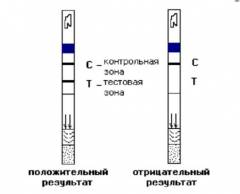
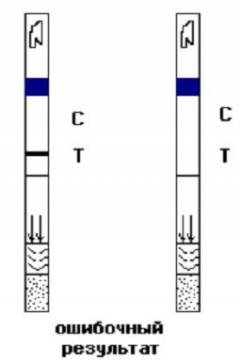
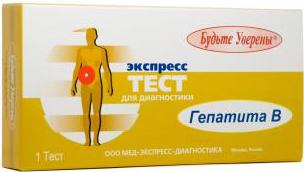 Nowadays, they are gaining more and more popularity. rapid tests for hepatitis, which allows to quickly and reliably determine the presence in the blood of hepatitis markers at home. They are a set of test strips impregnated with a chemical that changes its color when it comes into contact with a particular hepatitis marker. Such tests are quite simple to use, and the accuracy of the results reaches 99%.
Nowadays, they are gaining more and more popularity. rapid tests for hepatitis, which allows to quickly and reliably determine the presence in the blood of hepatitis markers at home. They are a set of test strips impregnated with a chemical that changes its color when it comes into contact with a particular hepatitis marker. Such tests are quite simple to use, and the accuracy of the results reaches 99%.