Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- White spots on the nails, reasons for what to do, white spots on the nails and folk signs
- Available methods for rapidly increasing blood leukocytes
- Nail and skin fungus will not resist the coffee grounds
- Crocus furniture exhibition. Furniture exhibitions
- Owl tattoo on arm value
- The biggest members in the world
- Fractures of the phalanges of the foot photo
- What is “bad” and “good” cholesterol
- What to do if the skin around the nails dries
- The safest natural varnishes list
Advertising
| Fracture of the base of the phalanx. Phalangeal fractures |
The mechanism of injury at the turn of the main phalanx:Most often the mechanism of injury at the turn of the nail phalanx straight: compression, crush. Clinical symptoms of fracture of the phalanx:
Diagnosis of fracture of the phalanx:X-ray clarify the nature of the fracture: the separation of tuberosity, the pearl of the body of the nail phalanx, the longitudinal fracture of the nail phalanx. 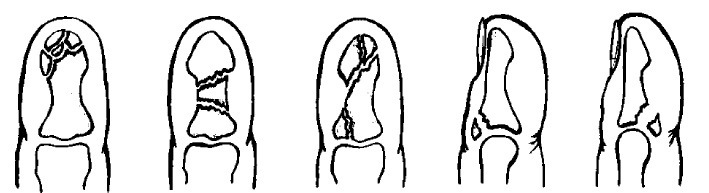 Treatment of a nail phalanx fracture:TO conservative treatment Fracture of the nail phalanx refers to immobilization with a plaster cast in the position of moderate flexion of the finger for up to 3 weeks. During this period, the true fusion of fragments does not occur, but disappears pain syndrome, abnormal mobility of fragments, due to the formation of scar tissue. Restoration of bone structure occurs within 3–3.5 months. In the presence of an open fracture, even with the crush of soft tissues, it should be limited to anesthesia, toilet wounds, stopping bleeding and immobilization. After 2-3 days in the tissues, blood flow will improve and a good result can be obtained. Attitude to the nail plate should be careful. Particular attention is paid to the restoration nail bed. Even a delaminated plate should be laid in place and fixed with 1-2 seams to the soft tissues. 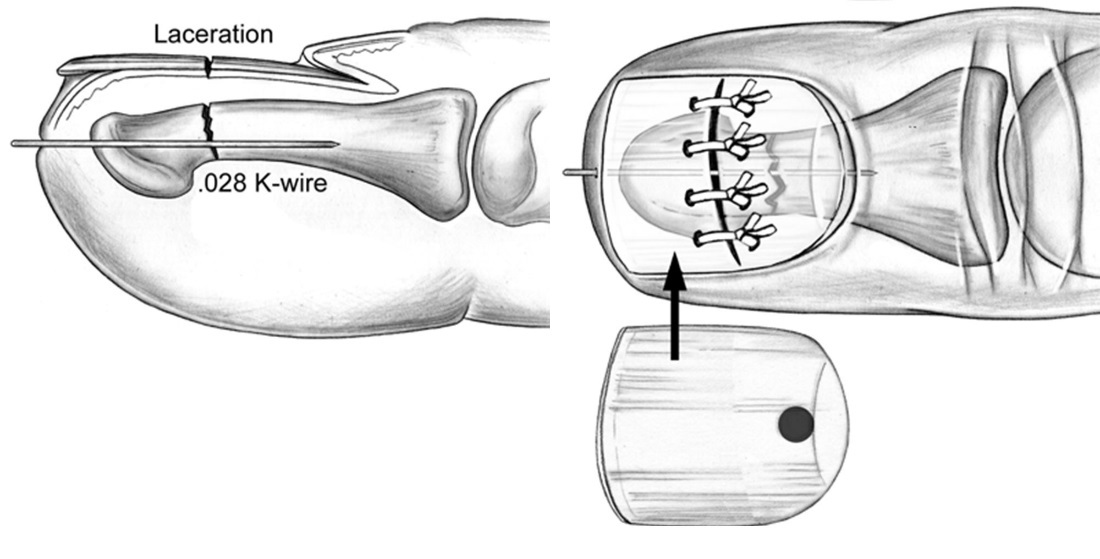 Fractures of the middle phalanges of the fingersThe mechanism of injury at the turn of the middle phalanges of the fingers:As a rule, at the fracture of the middle phalanges of the fingers, the mechanism of injury is direct. The determining factor in the displacement of fragments is the thrust of the legs of the surface flexor of the finger. 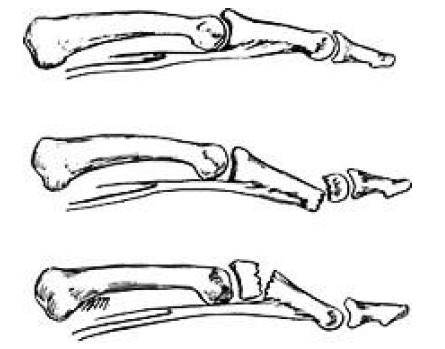 Diagnosis of fracture of the middle phalanges of the fingers:X-ray The survey specifies the diagnosis and the nature of the displacement of fragments. Treatment of fractures of the middle phalanges of the fingers:Closed reposition - thrust for a finger with simultaneous pressure on bony protrusions. To hold the fragments of the finger give the position of moderate flexion in the joints. Immobilization: aluminum tire, plaster splints or circular plaster cast. Unstable fractures are fixed by holding one or two spokes. The first signs of adhesion occur in 3-4 weeks. Scars immobilize breaking, while the pain disappears. A stiffened callus forms in 2–2.5 months. Restriction of movements in the joints of the finger can last up to 6–8 months. In some cases, with open and comminuted fractures, as well as intraarticular fractures with a large number of small fragments, skeletal traction may be the method of choice. Fractures of the main phalanges of the fingersThe mechanism of injury at the turn of the main phalanges of the fingers:The injury mechanism is usually straightforward. The displacement of the fragments determines the direction of the wormlike and interosseous muscles, which tend to bring together the fragments, therefore the typical displacement is at an angle open to the back side. The main phalanxes on ¾ of their circumference are enclosed in a tight case formed by tendons. Treatment of the main phalanges of the fingers is often accompanied by restriction of movements due to cicatricial fusion of the tendons with callus. Treatment of fractures of the main phalanges of the fingers:Closed reposition perform traction method. You have to put considerable effort to stretch the fragments and match them in the correct position. It is known that the deviation of the axis of the finger at 5º leads to the cross of the fingers when they are bent. Therefore, an important element of the reposition is the elimination of rotational and axial displacements. The best way retention of fragments is the holding of two mutually intersecting spokes across the fracture line. The needles are removed after 3-4 weeks, further immobilization is carried out with a plaster cast, without fixing the nail phalanx. It is necessary for the prevention of tendon adhesion with surrounding tissues and callus. Literature: Traumatology and orthopedics: / ed. V.V. Lashkovsky. - 2014. In case of fractures of the toes, the affected area may not heal for a long time. And with improper handling and treatment, the finger can lose its shape and flexibility. What are the causes, symptoms of a toe fracture and what to do about it? Causes of Toe FractureInjury or injury to the feet (stuck toe) or as a result of a heavy object falling on the toes may result in broken phalanxes of the toes. The location of the fingers (in the front of the foot) make them the most vulnerable part of the foot for fractures and injuries. Long-lasting movements, such as in some sporting events, can lead to a broken finger, which can be called stress or microcracks at the fracture site. If your finger hurts near the nail, then the reasons may lie in the systemic illness of the body. Thus, pain can be caused by arthrosis, arthritis or malfunction of the cardiovascular system. Of course, in this case we are talking about discomfortthat occur throughout the nail phalanx of the finger (or even a few), and not about localized foci of inflammation. Such pains can equally often occur in both the toes and hands. For vascular diseases, however, it is more characteristic of the defeat of the toes. In this case, the skin on them may turn white or get a bluish tint. Diabetes can also be the reason why it hurts near the nail on the arm or leg. This is a fairly common syndrome for people who suffer from this disease. Additionally, it may be accompanied by burning sensation and sufficient severe itching in the feet, cracks and inflammations on the skin of the feet and hands. Ingrown nailA toe fracture is a fairly common injury. Most of the cases of these injuries are traumatic fractures that arise as a result of tightening the legs, during compression and hitting the toes. There are also pathological fractures of the toes. In this case, the fracture is the result of the negative effects of certain diseases that significantly reduce the level of strength. bone tissue: osteomyelitis, osteoporosis, hyperparathyroidism and others. Fracture of the phalanx of the toe can be closed and open, without displacement or with displacement, complete and incomplete, as well as localized on the main, nail or middle phalanx, or simply to be combined. Nature has arranged the structure of the fingers so that it can easily happen. bone fracture simultaneously in several places. It is precisely the location of the injury that directly affects these or other violations of the integrity of the bone. Fracture of the toes of the photo scare us, but not all cases carry a danger to the human body. Fractured toe symptomsBruised toe symptomsBruised toe symptoms have a wide variety, and are very unpleasant. There are several degrees of contusion. In light situations of injury, the subcutaneous tissue and the skin itself are injured. Patients complain sharp pain and progressive swelling. The general condition remains unchanged. For heavier bruises, hemorrhage is noted. soft tissue (hematoma) accompanied by impaired motor function. A similar incident could hurt nail plate (read about nail bruise), which, as a rule, disappears and is updated on a new nail. After a few hours, the pain syndrome gradually subsides, and the swelling grows. If the skin or subcutaneous tissue is injured during the contusion, the hematoma will immediately be felt. When a patient has a severe toe injury, which damages the deeper layers of the skin, the hematoma will only be visible from the outside on the second or third day. Especially nasty bruise thumb legs, because for its full recovery takes much more time. The intensity of the signs of a broken finger In almost all cases, subject to this The main feature of the fracture of the big toe Transportation of the patient should be carried out in a prone position or sitting, with a raised leg. To do this, put a small cushion under the thigh and lower leg. The patient improves the venous outflow of blood from the damaged foot, as a result, soft tissue swelling and pain reduction is reduced. The appointment of painkillers to the patient is mandatory for any type of bone fracture, including damage to the toes. Most often, non-narcotic analgesics (analgin, paracetamol, pentalgin) and anti-inflammatory drugs (nimesil, ibuprofen) are prescribed to the patient. Fracture of the toe is immobilized only in case of suspected displacement of bone fragments. In other situations, the immobilization of the toe is not justified, because this manipulation can cause pain in a person. A damaged toe is gently fixed to the tire with bandages. The doctor can use as a tire a plank or plates that are pre-wound with two layers of fabric and placed on the left and right of the finger. It relieves swelling very well, reduces hematoma and pain sensations applying cold to the foot. The doctor may use an ice pack or a bag of crushed ice for this purpose. An ice pack can be applied for 10-15 minutes, and then removed for 2-3 minutes. TreatmentIn principle, any person can provide first aid. First you need immobilize the foot, that is, immobilize it. After removing the shoes, you must bandage the damaged limb with a sterile bandage if there is a wound. This is done in order not to bring the infection there. Then you need to find any solid object that would act as a tire, and pin it to the foot. You just need to remember that when dressing a wound, your hands should be clean. As a result of such actions, the wound will not be damaged again by bone fragments, and the pain should be reduced. Treatment of fractures depending on their typeWhen treating a toe fracture, its location must be considered:
How to diagnose a toe fractureThe traumatologist will certainly interview the victim in order to clarify how the finger was injured. At the same time, an inspection of the foot is carried out, which makes it possible to identify the relative and absolute signs of a fracture. The accuracy of the diagnosis is confirmed by x-ray examination. The picture gives the doctor a picture of the position of the bone fragments.
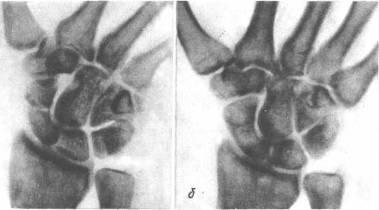
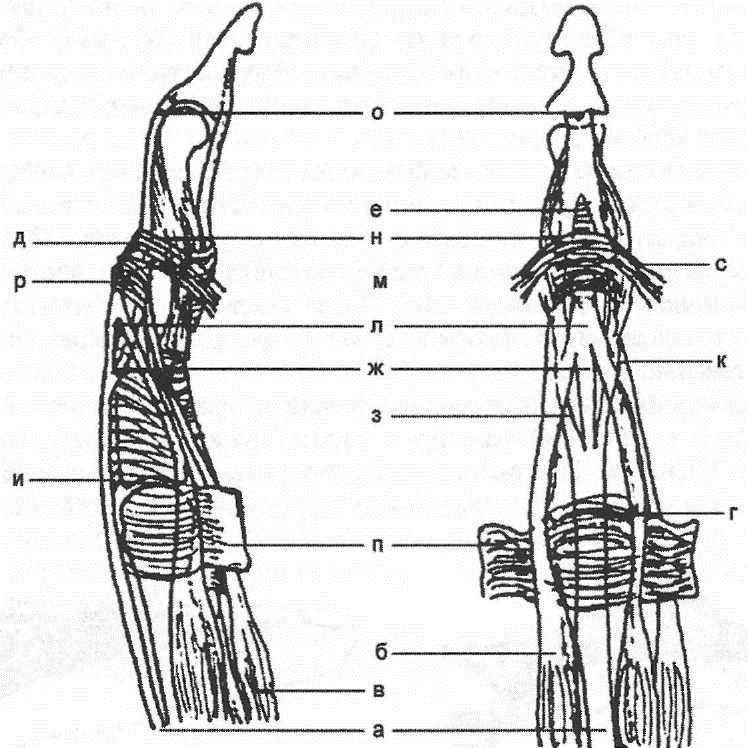
Volgograd State Medical University Department of Traumatology, orthopedics of field surgery, with a course of traumatology and orthopedics HFC Essay on the topic: "Injuries brush." Completed: 5th year student faculty of Medicine 13 groups Pavlenko A.V. Volgograd 2013 1. Brush damage 1.1 Fracture base brushes 1.2 Fracture diaphysis brush 1.3 Fracture of the metacarpal bones 1.4 Fractal phalanx fracture 2. Clinic 3. Treatment 4. Damage to the flexor tendons of the fingers 5. Damage to the extensor flexor tendons 6. Damage to the ligaments of the joints of the fingers 7. Physiotherapy at various stages of outpatient rehabilitation treatment of patients with hand bone fractures. 8. Treatment of the effects of the combined injuries of the tendons and nerves of the forearm and hand. 9. References. 1. Brush damageBoth isolated and combined damage to the bones, tendons, and muscles of the hand are observed. Dislocations of the bones of the wrist are rarely observed. Perilunar dislocations of the hand are most common (the dislocation line runs distal to the lunate bone), sometimes combined with scaphoid fractures. A slight deviation of the hand to the elbow side is determined; II, III and IV, the fingers are bent, their extension is painful. In the early stages it is possible to reduce the dislocation with the subsequent imposition of a plaster splint. In case of dislocations of high prescription, the reduction is performed promptly. Often there is a dislocation in the metacarpophalangeal joint of the first finger. At the same time, periarticular tissues are often infringed between the articular surfaces. Deformation of the joint and flexion of the finger are noted. With complete dislocation of the I finger, the main phalanx is at a right angle to the I metacarpal, with incomplete dislocation, this angle is obtuse (Fig. 1). Fig. 1 Rear dislocation 1 finger brush Reduction of dislocation carried out under local anesthesia. Having seized a finger, it is stretched and at the same time over-extended, and then the finger is bent in the direction of the palm. Put a plaster splint on the forearm, hand and finger, which is fixed in the position of easy bending. Fractures of the bones of the wrist are rarely observed, more often than others there is a fracture of the scaphoid, which occurs mainly when falling on an outstretched arm (Fig. 2). From the first row of wrist bones, the navicular bone, having an arcuate shape, is the longest. It takes the greatest part in the formation of the wrist joint. Its distal surface is concave, prosimalnaya - convex.
Fig.2. Fracture of the navicular bone of the hand: but- before treatment; 6 -after Clinical signs that can suspect a fracture are painfulness at pressure in the area of the projection of the navicular bone and during passive movements in the wrist joint, swelling in the area of this joint. The diagnosis confirms the X-ray examination. At the turn of the navicular bone impose plaster cast, fixing the wrist for 3-6 months. In case of an incomplete fracture of the navicular bone, surgical intervention is indicated. In the case of fractures of the other bones of the wrist, a similar treatment is performed. Fractures of the metacarpal bones are quite common, especially fracture of the first metacarpal bone. It is most common among fractures of the metacarpal bones and most often in men. The injury mechanism is a direct blow with a bent first finger on a hard object. Allocate: base fractures fractures of the diaphysis (middle part) of the first metacarpal bone. Fracture base Fracture of the base of the first metacarpal are intraarticular and extraarticular or transverse. The patient complains of pain in the area of the fracture. The first finger is bent and pressed to the palm. Usually there is a pronounced swelling and swelling in the area of damage. When probing for a fracture, pain sharply increases and fragments can be palpated in the “anatomical snuffbox” area. If a small triangular fragment of the first metacarpal bone remains in place, and the bone is dislocated towards the radius, such a fracture is called a Bennett fracture (Fig. 3). Fig. 3 Bennett's Fracture Fracture with dislocation, but chipped, called Roland's fracture. The diagnosis is clarified by x-rays in two projections Treatment. Of great importance is the exact comparison of bone fragments, which must be carried out as soon as possible, not later than the second day after the fracture. A one-time comparison of fragments is carried out under local anesthesia, if successful, a plaster cast is applied with the obligatory gripping of the entire first finger under the control of an X-ray. If re-displacement occurs, it is necessary to impose skeletal traction for up to 3 weeks or perform surgical treatment. Fragments are fixed with one or two spokes for 3 weeks. After that, the needles are removed, and the plaster cast is left up to 5 weeks. Then prescribe physiotherapy and physical therapy. Fracture diaphysis brush Fracture of the diaphysis - the body of the first metacarpal bone is rare, since the bone is quite mobile. The injury mechanism is usually a direct blow to the bone. Fracture can be with or without offset. The patient is worried about pain in the area of injury, aggravated by the movement of the first finger, with the load on the first finger. Treatment. In the absence of signs of bias on X-rays, a plaster cast is applied from the middle third of the forearm to the base of the fingers, but the first finger should be completely immobilized for one month. Complete mapping of fragments is usually not achieved, since a small angular deformation of the bone does not affect its function. With a large displacement of fragments carry out simultaneous comparison of fragments, followed by the imposition of a plaster cast. Very rarely have to resort to surgical treatment and fixation of fragments using the spokes. Fracture of the metacarpal bones Fractures of the second, third, fourth, and fifth metacarpal bones are less common. They arise under the influence of a direct injury to the hand and less frequently when struck with a fist or when falling onto a fist. Often there are fractures of not one, but several metacarpal bones. The displacement of fragments may be insignificant, since the metacarpal bones are fixed to each other by ligaments and muscles. But more often, especially in case of multiple fractures, fragments are displaced along the length at an angle open to the palmar or back of the hand. The patient complains of pain in the hand, palms, aggravated when trying to squeeze the brush into a fist. To determine the location of the fracture, the patient is pulled over the finger, with a fracture of the corresponding metacarpal bone, the pain increases dramatically. The diagnosis is clarified by X-ray images (Fig. 4).
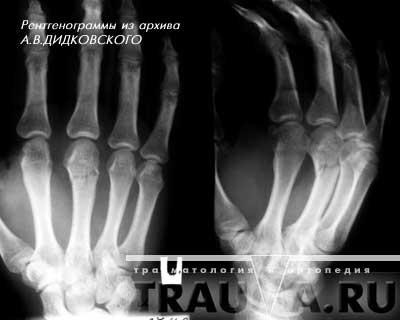
Fig. 4 Fracture of the head 3 metacarpal bones with a slight displacement, in two projections Treatment. If no displacement is detected, a plaster cast is applied from the upper third of the forearm to the base of the fingers, with the mandatory full grip of the finger, corresponding to which the metacarpal bone is broken. The term of immobilization is one month. In the presence of displacement, a one-stage comparison of fragments is carried out manually, followed by the imposition of a plaster cast for one month. Sometimes fragments still can not be compared, in this case is carried out surgery with fixation of fragments using knitting needles or mini-plates. Fractal phalanx fracture Fracture of the phalanges of the fingers is more common in adults. In terms of frequency, it stands on the I place among other hand fractures. According to S. Bunnel statistics (1956), it accounts for 50% of all hand fractures, 5.4% for all skeletal fractures. There is an isolated fracture of one phalanx and multiple phalanxes of several fingers or several phalanges of one finger. According to B.K-Babich (1960), E.V. Usoltseva (1961), multiple fracture occurs in 20-29% of cases in relation to all fractures of the phalanges of the fingers. Caused by direct injury. The most frequently observed fracture of the proximal and middle phalanges, at least - distal. Restoration of the function of a damaged hand is, first of all, the restoration of anatomical relationships, without which it is impossible to resume movements with your fingers. The mechanism of injuries is most often direct (a blow to the fingers, a drop of heavy objects on the hand). Fractures of the phalanges, especially the main one, can also occur in the case of an indirect injury - a sharp over-flexion, twisting of the finger. The nail is most often injured, the main phalanx is more rare and even less often. II finger is most often damaged, followed by III, and then the rest. Quite often several fingers are injured at once. Fractures may be periarticular, intraarticular, and diaphyseal. Fractures of the nail phalanx are usually comminuted.
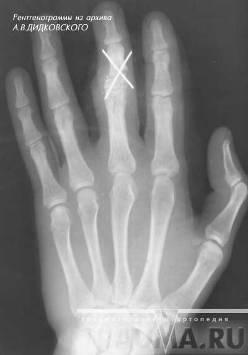
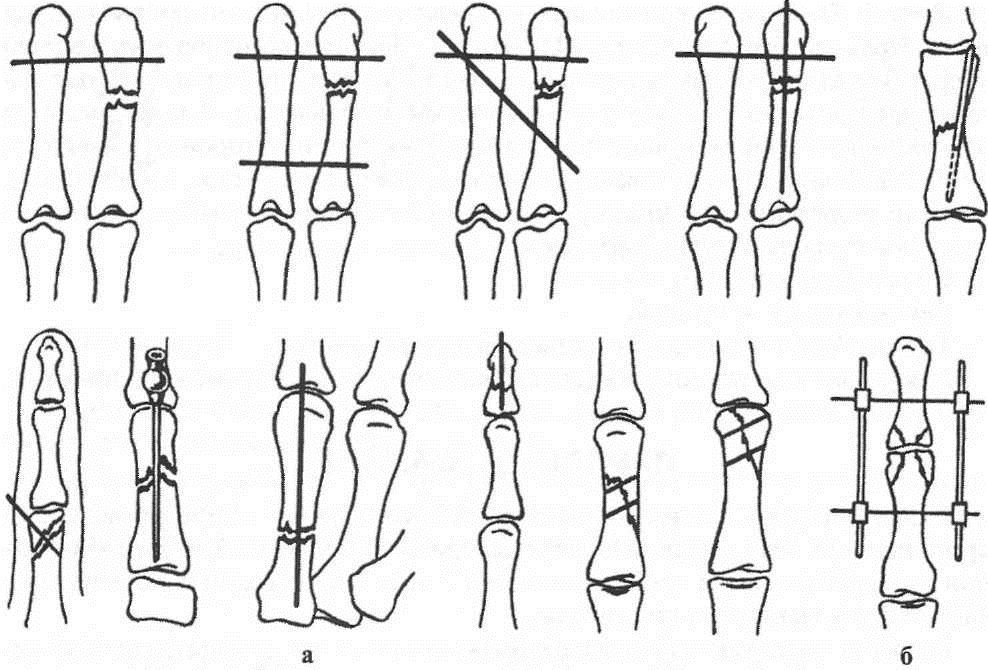
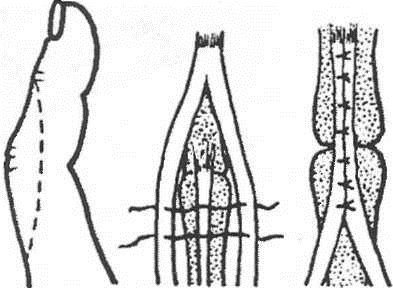
Fig.5 Fracture of the base of the middle phalanx of 3 fingers with offset osteosynthesis of the spokes. Of the phalanges, the nail is most often damaged, then the proximal and middle, more often without displacement of fragments. In case of marginal fractures, immobilization with a plaster Longuet lasts 1-1 1/2 weeks, with fractures of the nail phalanx, the nail acts as a splint. Reposition of fragments produced by stretching along the axis of the finger while simultaneously giving it a functionally advantageous position. Immobilization is carried out with two plaster splints (palmar and dorsal) from the tip of the finger to the upper third of the forearm (Fig. 1). With intraarticular fractures, shorter periods are required (up to 2 weeks), with periarticular - up to 3 weeks, with diaphyseal fractures - up to 4-5 weeks. Fractures of the proximal phalanx grow together faster than fractures of the middle. Fig. one.Therapeutic immobilization in case of fractures of the phalanges of the fingers of the hand: a - plaster splint; b - Böhler's tire; c - rear simulated tire Rehabilitation - 1-3 weeks. Surgical treatmentshown in fractures of the metacarpal bones and phalanges with a tendency to secondary displacement. Fragments are compared and fixed with needles percutaneously (Fig. 2). Immobilization is carried out with plaster Longuet on the palmar surface for 4 weeks. Spokes removed after 3-4 weeks. With intraarticular and periarticular fractures of the phalanges with displacement of fragments, a distraction apparatus is used.
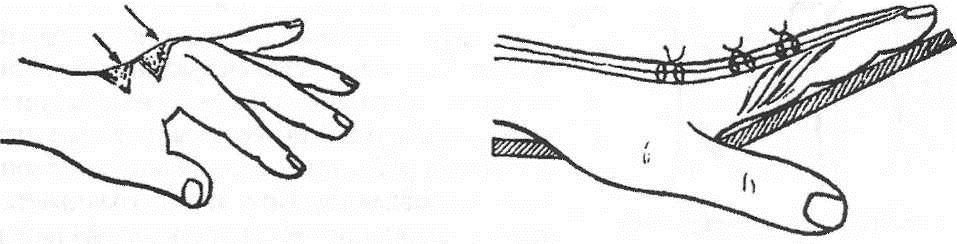
Fig. 2Transosseous fixation of the fingers and phalanges with the spokes of the fingers: a - the needles (options); b - distraction external apparatus Damage to the ligaments of the finger jointsThe reasons.Damage to the lateral ligaments occurs as a result of a sharp deviation of the finger at the level of the joint (kick, fall, "breaking off"). Often the ligaments are partially broken, a complete rupture leads to instability of the joint. The ligaments of the proximal interphalangeal and I metacarpophalangeal joints are mainly damaged. Signs:pain and swelling in the area of the joint, restriction of movement, lateral mobility. Specify the diagnosis of point palpation bellied probe or the end of the match. To exclude the separation of the bone fragment, it is necessary to make radiographs in two projections. When the ulnar lateral ligament of the metacarpophalangeal joint of the first finger of the first finger breaks, the swelling may be insignificant. There is pain when moving the finger in the radial direction, reducing the grip force. Damage to the ligament may be over, or comes separation from the place of attachment to the proximal phalanx. Treatment.Local cooling, immobilization of a finger in a half-bent position on a cotton-gauze roller. The imposition of a simulated plaster splint on the palm of the finger to the middle third of the forearm. Flexion in the joint to an angle of 150 °. UHF-therapy is prescribed as a decongestant. The term of immobilization - 10-14 days, then - light thermal procedures ILFC. Immobilization of the first finger is carried out in the position of slight bending and elbow adduction, for a period of 3-4 weeks. With the phenomena of complete rupture of the ligament or tearing it off, early surgical treatment is shown (suture, plastic) under the conditions of a specialized medical institution. After the operation - immobilization with plaster Longuet also for 3-4 weeks. Rehabilitation - 2-3 weeks. Disability is restored after 1-1 1/2 months. Damage to the extensor flexor tendonsFeatures of anatomy are presented on fig. 3
Fig. 3The structure of the dorsal aponeurosis: a - tendon of the common extensor; b - intercostal muscle tendon; in - a tendon of worm-shaped muscles; d - spiral fibers; d - retinacular ligaments; e - triangular cords; W - central tape; h - side tapes; and - a portion of aponeurosis to the base of the proximal phalanx; K - medial strips of the interosseous and worm-shaped muscles tendons; l - the average portion of aponeurosis; m - the lateral strips of the tendons of the interosseous and worm-like muscles; n - lateral portions of aponeurosis; o - the final part of the tendon-aponeurotic stretching; n - transverse mepristal ligaments; p - transverse portion of the reticular ligament Damage to the extensor flexor tendons and hand are 0.6-0.8% of all fresh injuries. From 9 to 11.5% of patients are hospitalized. Open damage is 80.7%, closed damage - 19.3%. Causes of open extensor tendon damage:
Causes of closed extensor tendon injuries:
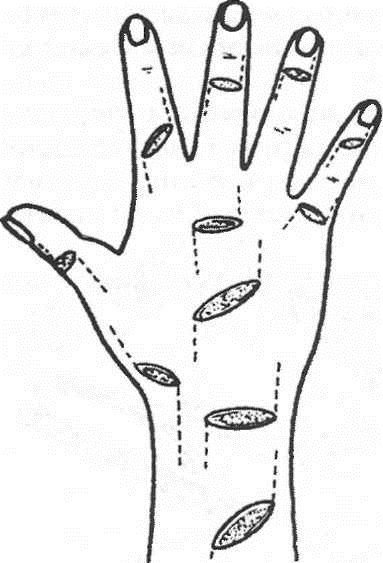
The subcutaneous tendon rupture of the long extensor of the first finger is described in 1891 by Sander under the name “paralysis of drummers”. In the army drummers with a long load on the hand in the position of the back flexion develops chronic tendovaginitis, which causes degeneration of the tendon and, as a result, its spontaneous rupture. Another reason for the subcutaneous rupture of the tendon of the long extensor of the first finger is microtraumatization after a fracture of the radial bone in a typical place. Diagnosticsfresh open injuries of the extensor tendons presents no particular difficulty. Localization of wounds on the dorsum of fingers and hand should alert the doctor, who will pay special attention to the study of motor function. Damage to the extensor tendons, depending on the zone of damage, is accompanied by characteristic dysfunction (Fig. 4).
Fig. four. 1st zone - zone of the distal interphalangeal joint to the upper third of the middle phalanx - loss of the function of extension of the distal phalanx of the finger. Treatmentoperative - extensor tendon stitching. When the extensor tendon is damaged at the level of its attachment to the distal phalange, a transosseous suture is used. After the operation, the distal phalanx is fixed in the position of extension with a needle held through the distal interphalangeal joint for 5 weeks. 2nd zone - the base of the middle phalanx, proximal interphalangeal joint and the main phalanx - loss of the function of extension of the middle phalanx of the second to fifth fingers. When the central extensor bundle is damaged, its lateral bundles are displaced to the palmar side and begin to unbend the distal phalange, the middle phalange takes the flexion position, and the distal one - the extension. Treatmentoperative - stitching the central bundle of the extensor tendon, restoring the connection of the lateral bundles with the central one. When all three beams of the extensor apparatus are damaged, a primary suture is applied with a separate restoration of each bundle. After surgery - immobilization for 4 weeks. After the suture is applied to the tendon and immobilized for the period of adhesion, extensor contracture of the joints develops, which requires prolonged rehabilitation. The 3rd zone - the zone of the metacarpophalangeal joints and the metacarpus - the loss of the function of the extension of the main phalanx (Fig. 5).
Fig. five. Treatmentoperative - stitching of the extensor tendon, immobilization with a plaster Longuet from fingertips to the middle third of the forearm for 4-5 weeks. The 4th zone - the zone from the wrist joint to the transition of the tendons into the muscles on the forearm - loss of the function of the extension of the fingers and hand. Treatmentoperational. When revision of the wound to mobilize the extensor tendons near the wrist joint, it is necessary to cut the dorsal ligament of the wrist and the fibrous channels of the tendons that are damaged. Each tendon is sewn separately. The back ligament of the wrist is restored with lengthening. Fibrous channels do not restore. Produce immobilization plaster Longuet for 4 weeks. Diagnosis, clinical presentation and treatment of fresh closed injuries of extensor flexor tendons.Subcutaneous (closed) damage to the extensor tendons of the fingers is observed in typical locations - the long extensor of the first finger at the level of the third fibrous canal of the wrist; three phalangeal fingers - at the level of the distal and proximal interphalangeal joints. With a fresh subcutaneous rupture of the tendon of the long extensor of the first finger at the level of the carpal joint, the function of extension of the distal phalanx is lost; The stabilization function of these joints is lost: the finger droops and loses the function of the grip. Treatmentoperational. The most effective method of transposition of the tendons of the extensor of the II finger on the extensor I. Fresh subcutaneous ruptures of the extensor tendons of the second to fifth fingers at the level of the distal phalanx with the separation of the bone fragment and at the level of the distal interphalangeal joint are accompanied by a loss of the function of the nail phalanx. Due to the tendon of the deep flexor, the nail phalanx is in the forced position of flexion. Treatment of fresh subcutaneous ruptures of the extensor tendons of the II — V fingers is conservative. For closed tendon adhesions, the distal phalanx is fixed in the extension or over-extension position with various tires for 5 weeks. or fixation is made with a Kirschner needle through the distal interphalangeal joint. With fresh subcutaneous detachment of extensor tendons with a bone fragment with a significant diastasis, surgical treatment is indicated. Fresh subcutaneous rupture of the central part of the extensor apparatus at the level of the proximal interphalangeal joint is accompanied by restriction of the extension of the middle phalanx, moderate edema. With proper diagnosis in fresh cases, the finger is fixed in the position of extension of the middle phalanx and moderate distal flexion. In this position of the finger, the worm-like and interosseous muscles are most relaxed, and the lateral bundles are shifted to the central bundle of the extensor apparatus. Immobilization lasts 5 weeks. (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6 Prostate extensor tendon damage.A large variety of secondary deformities of the hand with chronic injuries of the extensor tendons is caused by a violation of the complex biomechanics of the flexor-extensor apparatus of the fingers. Damage in the 1st zone appears in two types of finger deformation. 1. If the extensor tendon is completely damaged at the level of the distal interphalangeal joint, the extension function of the distal phalanx is lost. Under the influence of the tension of the tendon of the deep flexor, a persistent flexion contracture of the distal phalanx is formed. This deformation is called the "thumb-hammer." A similar deformation occurs when the extensor tendon is detached with a fragment of the distal phalanx. 2. When the extensor tendon is damaged at the level of the middle phalanx proximal to the distal interphalangeal joint, the lateral bundles, having lost contact with the middle phalanx, diverge and shift in the palmar direction. At the same time, active extension of the distal phalanx is lost, it takes the position of flexion. In connection with the violation of the fixation point of the lateral bundles, over time, the function of the central bundle extending the middle phalanx begins to prevail. The latter takes the position of hyperextension. This deformation is called the "swan neck". Treatment of chronic damage to the extensor tendons in the 1st zone is operative. The most important condition is the complete restoration of passive movements in the joint. The most common operation is the formation of scar duplication with a cut or without dissecting it, and fixing the distal interphalangeal joint with a needle. After removing the needles after 5 weeks. after surgery, a course of rehabilitation treatment. With chronic injuries and persistent flexion contracture, arthrodesis of the distal interphalangeal joint is possible in a functionally advantageous position. Chronic damage to the tendon-aponeurotic stretching in the 2nd zone at the level of the proximal interphalangeal joint is accompanied by two main types of deformity. 1. At damage of the central bundle of the extensor tendon, the function of extension of the middle phalanx is lost. The lateral bundles under tension of the worm-like muscles are displaced in the proximal and palmar directions, contributing to the flexion of the middle phalanx and extension of the distal phalanx of the finger. In the gap formed in the extensor aponeurosis, the head of the proximal phalanx moves like a button extending into a loop. There is a typical flexion-hyperextension strain, which received several names: a gap in the form of a loop, the phenomenon of a button loop, triple contracture, Weinstein's double contracture. 2. In case of chronic damage to all three bundles of the tendon extensor apparatus, a flexion installation of the middle phalanx occurs. Re-extension of the distal phalanx does not occur due to damage to the lateral bundles. Treatment of chronic damage to the tendon extensor apparatus at the level of the proximal interphalangeal joint operative. In the preoperative period, in order to eliminate contractures and restore the volume of passive movements, a course of rehabilitation is carried out. Weinstein's operation:after mobilization of the lateral bundles, the tendon-aponeurotic stretching produces their convergence and stitching side-to-side over the proximal interphalangeal joint. In this case, excessive tension of the lateral beams occurs, which can lead to the restriction of flexion of the finger (Fig. 7).
Fig. 7 With chronic injuries of the extensor tendons with dysfunction of the fingers, surgical treatment is indicated. The choice of method surgical treatment depends on the condition of the skin, the presence of scars, deformities and contractures. One common method is the formation of rumen duplicature. AT postoperative period immobilization lasts 4-5 weeks, after which they carry out a course of rehabilitation treatment - application of ozokerite, lidase electrophoresis, massage, exercise therapy on fingers and hand. Traumatology and orthopedics. N.V. Kornilov |
| Read: |
|---|
Popular:
Birch hanging or warty
|
New
- The program of intensive moisturizing of the skin on cosmetics bark
- What you need for acrylic powder
- What does owl mascot mean
- Analyzes for pancreatitis: what research should be done and what indicators show
- Owl - a talisman to attract money and good luck
- What bird screams at night with a kitten's voice?
- Cholesterol and stress
- Manicure at home
- Effective facial
- What is a man after a broken leg?

 The doctor chooses the tactics of treatment depending on the nature of the injury. With an open fracture, there is a risk of wound infection. Such a fracture with improper treatment may be accompanied by suppuration, tetanus and other troubles. That is why injections of antibiotics and tetanus toxoid are done immediately.
The doctor chooses the tactics of treatment depending on the nature of the injury. With an open fracture, there is a risk of wound infection. Such a fracture with improper treatment may be accompanied by suppuration, tetanus and other troubles. That is why injections of antibiotics and tetanus toxoid are done immediately.