Birch - perhaps the most "Russian" of all types of trees. It is difficult to imagine a plant as praised by the classics of all generations. This is not surprising: the rare grace and power, combined in her image, inspire people to work. But, in addition, it is also a very valuable representative of forests, giving not only wood. Today we will talk more about these beauties, find out what kind of common and rare birch there are.
Birch is one of the most common plants in our country. There are about a hundred species of birch trees growing not only in Russia, but also in the forests of North America and all of Europe. All varieties of birch trees can be divided into two large groups:
- trees (their height varies within 30-50 meters, and the trunk width can reach 1.5 meters);
- shrubs (large, small and creeping species).
- Wood. Birch flesh has a high degree of strength, which allows it to be used for the production of plywood products.
- Caps are growths that can form on birch roots, trunks or branches. In the section, the cap has a very interesting pattern, which after processing allows it to be used for the manufacture of various handicrafts.
- Tar is a special substance extracted from this tree by dry distillation. It is used in medicine, as a rule, as part of various ointments or tar soap.
- Paint. At a certain processing, a yellow dye can be obtained from the plant leaves.
- Pyltsenos. fishery, as it is an important pollen.
- Birch bark is the top layer of bark, which is distinguished by its strength and durability (due to the resins in the composition). Used as a combustible substance or material for various handicrafts.
- Birch sap, which is extracted in the spring, is very useful. It is used both in raw form and as a component. various decoctions and syrups. In addition, birch sap can be used for feeding beekeepers.
- The medicine . Broths and infusions from different parts of birch are used in medicine as diuretics, bactericidal or antipyretic drugs. Next, we will try to find out what kind of birch species exist.
Popular species
As mentioned earlier, there are a large number of species of birch trees. Today we will talk about some of the most popular ones.

Hung
The most common variety of birch in Russia is hanging. It looks like a tree, up to 3 meters in height with smooth white bark. In young trees, it is noticeable that the upper layer of the bark is easily stratified. The “birch retirees” can see deep gray furrows penetrating the entire upper layer of the bark. The barrel of this variety is quite flexible, straight with hanging branches, wedge-shaped leaves and earrings.
The average lifespan of this tree can range from 100 to 120 years. The tree becomes “grown up” by the age of 8, then the color of the bark also changes: it turns white from brown. It is also worth noting that the hanging birch becomes in old age, the young representatives of the species have the usual straight branches.

This plant is distributed throughout the country, but most often it can be found in the central regions and in Western Siberia. Due to its unpretentiousness, it is able to grow in various climatic regions: it is found both in the tundra and in the steppe. Birch grows quickly enough, occupying any free piece of land, displacing other tree species.
This plant is widely used in human activities. So, resinous birch trees are almost collected in early spring, immediately after that young leaves are collected. Birch bark is usually collected from the middle part of a growing tree or fallen tree. In early spring, birch sap is also mined, which, due to its composition (water, special chemical elements and organic compounds), has a mass of useful properties. It is known that from one hectare of hanging birch you can get up to 10 tons of juice. All year round and collect chaga (medicinal fungus, which chose as their residence just the trunks of this type of trees).

Dwarf
Dwarf birch its appearance is much more like a low-growing branched shrub than a familiar tree. Its other name “Yernik” seems to emphasize the predilection of this bush for the formation of thickets. It grows in the north of Russia, as well as in Europe, Canada and China. It can be found in the Alps or in the mountainous stretches of Scotland. In our country, it can most often be found on the territory of Yakutia, Chukotka, Kamchatka or the Amur Region. This is understandable, because this plant prefers mountainous or marshy terrain, damp soil.
Dwarf birch is a shrub whose growth usually does not exceed 2-2.5 meters. The trunk of a dwarf-type current is smooth, but the foliage is small (up to 2 centimeters), with a darker upper part. The branches are usually straight. The bark is not the usual white, but brownish-brown. It is important to note that this shrub grows very slowly, but at the same time is one of the most frost-resistant in the world. In economic activities, little is applied: only in the northern tribes is it used as fuel or reindeer food.

Karelian
Karelian birch is a variety of short trees, characterized by the presence of a strange growth on the trunk (burl) and a patterned very beautiful sawn wood. It grows, as the name implies, in Karelia, but not only. This type of birch is found in other territories of Russia, as well as in Lithuania. This species is further divided into three varieties: short, medium height, tall.
When processing wood gives dark brown and yellowish shades. The unusual pattern of wood allows the use of Karelian tree for the manufacture of dishes, boxes, vases, watches and any other souvenirs.

Paper
Paper birch is a fairly powerful tree, whose growth reaches 30 meters. It got its name because of the wide dense bark, which, being in young pink, eventually turns white. The leaves of this tree are quite large, reaching a length of 10 centimeters. The plant is very unpretentious, can grow in any soil, with any lighting.
Cherry
North American species of birch. It is a tree, up to 25 meters high. Young plants have a wide pyramidal crown, which with age begins to hang, forming a ball. The bark of an unusual dark color (mostly cherry or red hues). It has rather large leaves, up to 12 centimeters long, pubescent along the veins perimeter. In spring, the tree blooms profusely, releasing a large number of long earrings. The tree grows fast enough, lives long. Prefers deep wet bud.
Yellow
This is a large tree, reaching 30 meters in height. Homeland is North America (hence the other name - American birch). It has a very interesting color of the bark, which can be either light orange or gray or reddish-brown. The leaves are also large: up to 12 centimeters. The plant is very tenacious, fast growing. Prefers moist, but drained soil. Quietly can live up to 300 years.
Small-leaved
A relatively small tree (up to 15 meters), can often grow as a gnarled shrub. Distributed in the desert valleys, rivers and marshes of Western Siberia, Altai or Mongolia. The bark is yellowish gray or even pink. The leaves are quite small.
Fluffy
Low tree, different 15-meter white trunk and a wide crown, which is formed by branches directed strictly upwards. The leaves are shiny, small (up to 6 centimeters). Immediately after the formation of foliage gummy, very fragrant. The plant tolerates darkening and swampy soil.

Far East
Perhaps the most enduring plant in this group. It is a slender straight tree with a 30-meter trunk and a spreading crown. Very shade tolerant. Young plants, for example, cannot develop at all if they are not in the shade. Prefers foothills. Far Eastern birch can be found in Primorye, Khabarovsk Territory, as well as in the expanses of China and North Korea.
Differs in the presence of a shaggy wide trunk covered with light yellowish bark. The leaves are oval, large and dense. This type of birch can live to 80-100 years.
Woolly
This is a representative of the flora of the mountains and mountain glades, dark coniferous forests of Eastern Siberia, the Far East of Russia and Korea. It is a 15-meter tree with a large number of fluffy buds. The leaves are wide, up to 9 centimeters, covered with a soft edge along the lower veins.
Rare species
There are rare species of birch trees. This is, above all, a squat birch, a Dahurian, a Schmidt tree, a red one, a far away, and a Hermann birch. We will talk about them in more detail.
From the video "Birch species" you will learn a lot about this plant.
Squat
Another deciduous fluffy plant from a large family of birch. Most often it can be found in the marshy areas of Western Europe, Mongolia and in the European part of Russia. The plant is a shrub in height from 1 to 1.5 meters. The branches are straight, the leaves are quite small (up to 3.5 centimeters). The bark of birches of this species is smooth, often dark or brown. Squat birch is listed in the Red Book of several regions and republics of Russia. This plant is used in medicine as a component of certain types of drugs.

Daurskaya
High plant (height up to 25 meters), for the growth of which requires a lot of light and moisture. Daur or Korean birch grows in the Far East, Mongolia, China, Korea and Japan. It is noted that the places of its growth can be considered very successful for agriculture.

It has an original openwork crown: in young animals - pinkish or red, in adult plants - dark gray, brown. The detached layers of birch bark do not fall off, but remain hanging on the trunk. The leaves are oval dark green. Coal is commonly produced from Daurian birch, and its wood is used to make all kinds of handicrafts.
Birch Schmidt
It is also called iron birch. The plant can reach a height of 20 meters. Differs widely nizkopasazhennoy crown, which can begin at 8 meters. The bark of the tree is usually dark, gray or brown. It grows on the territory of the rocky regions of Primorye, in China and Japan. This type of birch loves light. Under good conditions, the life of this species of birch can go up to 400 years.
Red
Red birch, as its name implies, is distinguished by the unusual color of the bark, ranging from red to yellow and gray. This is a short tree, about 5 meters tall. It grows only on the territory of Kazakhstan and is on the verge of extinction.
Dalekarlieskaya
Very beautiful plant with small thin foliage and long weeping branches. A fairly frost-resistant plant growing in the European part of Russia and the Scandinavian Peninsula.
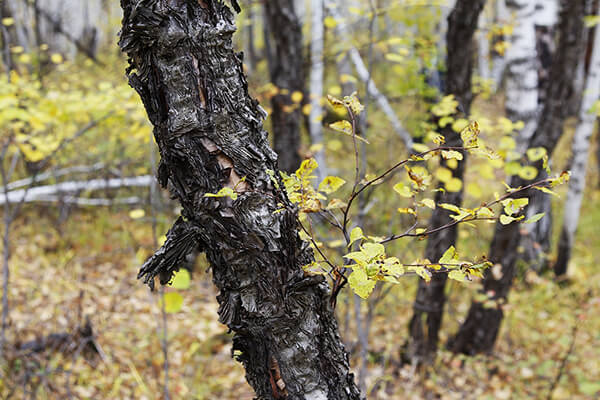

Birch Erman
Tree 15-20 meters in height with a spreading crown. The bark of this species of birch trees is distinguished by a dark gray, brown, and sometimes yellowish color. The leaves are quite large (up to 14 centimeters). The upper half of the leaf is usually dark green, and the lower half is light. This tree is very soilless, can grow on rocky surfaces. Distributed in the territory of Kamchatka, the coast of the Sea of Okhotsk, the Kuriles, in the eastern part of Russia and Japan. Used in the manufacture of coal or decorative handicrafts.
Photo Gallery
Photo 1. Dahur variety of birch Photo 2. Karelian birch
Birches grow not only in Eurasia, but also in North America (Canada, in the USA - only in the northern part of it). As for our continent, the species of this tree is found in the flora of Asia (its eastern part) - Russia, China, Japan and western Europe - in Belarus, Ukraine, the countries of the Caucasus. Here there are such species: Woolly Birch, Hanging Birch, Yellow Birch and so on. Where the birch also grows: in the tundra (in the form of a dwarf tree or shrub, the species is called dwarf Birch), in the steppes and mountains (Radze Birch), Siberia (White Birch, Black Birch) and even in the Arctic.
Birch thickets enter the European part of Eurasia, it is found in countries such as Romania, Moldova, Poland, Finland, etc., trees are part of deciduous and mixed forests or even form separate birch groves.
Birch species in North America
As in Eurasia, various types of birch grow on sandy soils and go far into the Arctic. In Canada, there are common species: Black Birch, Cherry Birch, warty Birch.
Birch hanging or warty - Betula pendula Roth (Betula verrucosa Ehrh.) Is a tree from the birch family. This low tree grows slowly, but reaches an amazing age for birches - up to three hundred years. Apparently, “cherry” it is named for the similarity of the trunk with the trunks of old cherries - they are just as dark and there is no bark on them at all. Its leaves are not at all like the leaves of our ordinary birch trees, they are more likely similar to the leaves of some distant relative of birch trees like a hornbeam, and this is absolutely true. Scientists believe that it is black birch - the ancestral group of the entire broad genus, and their descendants acquired the white trunks much later, after moving to the mountains. The fruits of black birch are also unusual - they resemble more cones of coniferous trees than catkins. Black birch wood is extremely hard, it was used even for the manufacture of machine parts, which, combined with slow growth, led to catastrophic consequences. So, in our Far East has become a rare species and is listed in the Red Book birch schmidt (B. schmidtii), and in the USA, V. uber, who had previously lived in the mountainous Pennsylvania of Pennsylvania, disappeared completely into the wild nature and is now preserved only in botanical gardens. It is clear that if there are already adult birch trees on the plot, then there is no problem in choosing one or another species and variety. If there are no birches, and you only decided to plant them on the plot, then keep in mind that their diversity is now extremely large. The size of the species and varieties sold varies from 70 cm in height (!) To 20-25 meters, the size of a leaf is from 8 mm in diameter to huge leaves for birch - 15 cm long, the color of the bark is not always white, and may be brown, yellow, black, beige and sometimes even pinkish. Some plants have autumn color; some - no, some grow quickly, some slowly, some turn into spectacular tapeworms, and some are quite slender and require landing only in a group. In some species, the decorative characteristics are such that they are read only from close range (flaking bark, heavily rugged leaves, etc.) and they, respectively, require planting only next to the observer. In some, on the contrary, the entire decorative effect is noticeable only from a distance (crown shape, its openwork ...) and they need to be planted at a distance equal to at least two or three tree heights. But not all are going to plant decorative forms and varieties of birch, some express a desire to plant the most common, already described above birch hanging or fluffy. First of all, remember about their final dimensions, which significantly exceed the size of their varietal counterparts. When they are already there, this is one thing, but when choosing to land, you need to think carefully.
| Birch warty or hanging -AT. verrucosa Ehrh. = V. pendula Roth
Distributed throughout the European part of Russia and beyond the Urals to the Ob River. Heliophilous mesophyte, microtherm, mesotrophe, edificator of indigenous small-leaved forests of Western and Central Siberia, anthropogenically progressive unstable edificator of temporary secondary communities on burns and cuttings and assektator of coniferous and deciduous forests. One of the most popular birch trees, without which gardening does not do in Russia.
Betula pendula "Youngii"
Photo EDSR.
|

Betula pendula "Purpurea"
Photos by Anna Petrovichev
|

Betula pendula carelica "Nana"
Photos by Anna Petrovichev
|
Tree up to 20 m tall, with openwork, irregular crown and smooth, white, exfoliating bark. In adult trees, the lower part of the trunk is covered with a powerful blackish crust, with deep cracks; this is what distinguishes it from most birch trees. The branches are mostly hanging, young shoots are warty. The leaves are rhombic, bare, up to 7 cm, resinous, sticky in youth. Earrings wilted. The fruit is an oblong-elliptical, winged nutlet. It grows fast, hardy, undemanding to the soil, very light-requiring, drought-resistant. In the culture for a long time. Seed germination is high. Cuttings rooted weakly.  Betula pendula "Artopurpurea" Betula pendula "Artopurpurea"
Photo of Kirill Tkachenko
Growing dynamics of birch (fluffy similar indicators): Living up to 100-120 years, in height continues to grow up to 50-60 years, in thickness up to 80 years. During this period, the growth rate changes so in the first 5-6 years the height growth is moderate, subsequently it increases significantly and, starting from about 10 years, reaches 75-90 cm per year. The final size is about 20 m in height. Keep in mind that also somewhere from 20 years old it begins to bear fruit, and birch is a pioneer breed. This means that it throws out a great multitude of seeds right into the vacated territories (for example, after a forest fire, and in the garden after digging the plot), thereby occupying an area and not letting anyone else germinate. And only then in the process of competition from these seedlings there are only a few plants that continue to grow in the territory free from other species. In fact, this is not such a problem, since the seedlings are quite easily pulled out. Partly the growth of large birches can be limited. Despite the fact that in the domestic literature the possibility of cutting birch is often excluded at all, it is still possible. Often birch trees are cut in the Scandinavian countries. They cut off the tip and part of the side branches. As a result, the crown thickens, the size of the plant decreases. However, this can be done only with plants that are in the stage of active growth, that is, they are only young plants (stem diameter up to 15-20 cm). If you cut off old birch in a similar way, then you will have a bare trunk on the plot. But the young have some problem with pruning. Crohn thickens and looks spectacular only in summer, but when the foliage flies around, we see a not very beautiful arrangement of skeletal branches (unnatural). So if this is a dacha, then there are no problems, and if the house is for year-round living, it makes sense to think well. Many people still remember birch when they start talking about roof gardens. Everyone remembers the young birch trees growing on the walls of the destroyed temples and the roofs of old estates. But we must understand that it is precisely because of its pioneering nature, about which we have already spoken above, that a birch sows with millions of seeds dilapidated buildings. Of this million, a very small percentage of seeds penetrate the slits, even less into those slits where moisture gets, some of the remaining ones die, as there is water, but there is no substrate. In the substrate and with the seedling water they begin to develop, but even less remain after the first winter, when many die from freezing of the root system. And so year after year. Did anyone see an adult tree on the wall or roof? If he saw it, then this is the case for a million, and there is no guarantee that the birch you purchased in the garden center, solemnly hoisted on the roof, will be identical to the one remaining of a million. It has several forms, of which the most decorative: pyramid (f. fastigiata) - with a narrow pyramidal crown; mourning (f. tristis) - with very thin weeping branches that form a rounded crown; cabin boy (f. Youngii) - with an irregular, picturesque crown, with thin drooping twigs; purple (f. purpurea) - with purple leaves; var. carelica (Merckl.) Haemet-ahti - bp Karelian. A tree that has six forms of growth - from creeping to straight-barred. Protected in reserves. Occurs within the range of the main species from Belarus and to the north. Cultivated in botanical gardens and grown in nurseries. In GBS since 1949, 5 samples (35 copies) were grown from seeds obtained from St. Petersburg and Karelia. In the arboretum trees, height from 4 m to 18 m. Plant, bloom and bear fruit in the same time frame as the species. Full winter hardiness. Seed germination is low. Cuttings are not rooted. Beautiful park tree, spectacular in single and group plantings on the lawn. Karelian birch does not have a special external beauty, but its bizarrely wavy wood is strikingly beautiful. In fact, Karelian birch - not even separate form the main species, and the result of infection with a certain type of fungus, which occurs at a young age. Although the mushroom does not kill such a tree, it turns into a giant “witch broom”. Unfortunately, there is the difficulty of breeding Karelian birch - and this is one of the problems of its distribution. Otherwise, she would have long been firmly seated in our gardens. When trying to sow, you have to wait a long time to reject a non-form (some have more than 10 years). One of the most successful methods of vaccination, and now still and not very widespread method of microclonal reproduction. "Youngii". The height depends largely on the height of the grafting, but often not more than 2-4 m. It has an umbrella-shaped crown. The main branches are spreading or curved. The terminal branches are very thin and drooping, the crown is of the wrong shape. Plants develop very differently and can to meet both very picturesque specimens and those that look extremely unnatural. Due to its size it is good for a small garden. It is often found in culture in European botanical gardens. In GBS since 1973, 1 sample (1 copy) is grown from planting material obtained from Kiev. At the age of 16 you ota 8.6 m, a trunk diameter of 13 cm. The plant grows, flowers and fruits in the same time frame as the appearance. Temp growth medium. hardiness complete. The germination of seeds is high. "Aurea". This slow-growing tree up to 10 m high has very beautiful shiny golden-yellow leaves. Their coloring is especially bright in spring and early summer, and later they turn greenish-yellow. Autumn color does not have. Flowers - Earrings yellow color, appear in May. Crohn openwork with falling branches, white trunk. It grows quite slowly. "Crispa". Tree up to 10-15 m. Slender, graceful tree with hanging branches and deeply dissected leaves that turn yellow in autumn. Sometimes it is considered a synonym for the form of" Dalekarlika ", but the latter is not as weeping as this. "Fastigata". The tree up to 10 m. Has a columnar crown shape, especially in youth. With age, the crown fluffs somewhat, but retains its vertical structure. All its branches are directed almost upwards, since they are at an acute angle to the trunk. "Golden Cloud". Tree up to 10 m high with leaves of rich yellow color, when blooming with a peach-orange shade. Leaves often burn in the sun and can suffer from a disease in which they fall prematurely. "Gracilis". The tree is up to 10-15 m high. The shape is very similar to the shape of" Lacyniata ", but has smaller, delicate, delicate, deeply dissected leaves and a very weeping crown shape. In general, among all the cut leaf forms, the most open, light and air. "Laciniata". Tree up to 15 m. Tree with an open crown, drooping shoots and rather deeply dissected leaves. It grows slower than the main species. In severe winters, annual shoots freeze slightly. "Purpurea"This is a slow-growing tree up to 10 m high with purple leaves, hanging shoots and a fairly loose crown. Dark purple leaf color is especially evident in early summer. The plant looks unusual because of the contrast of white stem and dark leaf color. In autumn, the leaves do not change color. The crown is narrow, smaller than the original species. In the crown often return shoots appear with ordinary green leaves that need to be removed. Single-handedly, the plants look extremely slender and it is better to use them in groups of 3 pieces. In GBS since 1959. 1 bratz (7 specimens.) grown from seedlings obtained from the Netherlands. Currently, the height is 15 m, the trunk diameter is 14 cm. The plant grows, blossoms and fruits at the same time as the species. The average growth rate. Winter hardiness is average (in severe winters partially frosted over.) 15% of rooted cuttings. There are more varieties " Nigra"and" Bibor"- also with dark purple leaves. Both of these forms originated from the Purpurea b. and are in many ways similar to it. However, their leaves are of a much more saturated color and at the same time more resistant, not so green in the middle - end of summer, as a form of Purpurea. "Tristis". The tree is up to 8-10 m high. It has a very weeping crown shape. The branches are thin, lowered vertically, hang almost to the ground and can have a length of up to several meters. In autumn, the leaves become yellow. "Trost "s Dwarf". Tree up to 1.5 - 2 m. A tree or shrub with slender twisting shoots, which is important and rare for birch dwarfs, white bark and strongly dissected leaves. A slow-growing openwork plant. A very good option for a small-sized garden.

B.pendula var. carelica
Photo EDSR.
|

B.pendula cv. Trost "s Dwart
|

B.pendula "Purpurea"
Photos of Andrei Sedov
|
|
 Paper birch -AT. papyrifera Marsh. Paper birch -AT. papyrifera Marsh.
Eastern and Central North America. It grows in all types of forests, swamps and river valleys. More unpretentious than B. pendula. Heliophilous mesophyte, mezoterm, microtroph. In culture, it is found widely in Europe, Asia and North America. A powerful tree up to 30 m tall, with a broad dense crown. The bark of the trunk is bright white, in young trees it is pinkish, it is easy to peel off with leaf-like, transverse stripes. The paper name has received the name for bark whiteness. The old birch bark exfoliates from the trunks in huge chunks, really resembling sheets of thin paper. Young shoots are fluffy, later naked, dark brown, shiny. Leaves ovate, large (up to 10 cm long). In GBS since 1965, 6 samples (22 copies) were grown from seeds obtained from botanical gardens in the USA and Canada. At 27 years old, height is 10.7 m, trunk diameter is 27.8 cm. Plant grows from the second half of April to the beginning of October. The growth rate is high. It blooms in late April. The fruits ripen in October. Full winter hardiness. Seed germination is high. It is frost-resistant, it is unpretentious to the soils, but it is more moisture-loving and shade-tolerant than warty birch. Despite the great similarity, both birches are so different from each other that they can land in joint groups. Interesting for park construction in single, group and aleynyh landings. In culture since 1750. var. subcordata(Rydb.) Sarg. - B. b. half heart shaped. Tree up to 7 m tall. North and Central North America. Grows in mixture with other breeds. Heliophilous mesophyte, mesotrophe, microtherm. In the culture is rare. In GBS since 1953, 2 samples (5 copies) were grown from seeds obtained from St. Petersburg and Lausanne. At age 40, height 17.4 m, trunk diameter 24 cm. Plant grows from mid-April to late September-early October. The growth rate is average. It blooms from 5 years in the middle of May. Fruits in 11 years, the fruits ripen in mid-August. Full winter hardiness. Cuttings rooted weakly. Photo of Kirill Tkachenko
|
 Cherry birch - V. lenta L. Cherry birch - V. lenta L.
Very decorative North American look. East North America. It grows in the mountains in a mixture with other hardwoods, is found on rocky habitats. Prefers deep, moist, well-aerated soil. Heliophilous mesophyte, mesotrophe, micro mezoterm. In a culture in Europe, North America. Tree up to 25 m tall, in youth with a pyramidal crown, in adult plants - with a rounded, with hanging branches. The bark of the trunk is dark, cherry-red (hence the name “cherry”). Young shoots slightly pubescent, later naked, red-brown. Its oblong-ovate, large, beautiful leaves are remarkable (12 x 5.5 cm). In their youth, they are silky, pubescent, adults - bright green above, shiny, dull green below, pubescent along the veins; in autumn they become reddish-yellow, very showy. In spring, it draws attention to itself with abundant, long, stapled earrings. This low tree grows slowly, but reaches an amazing age for birches - up to three hundred years. In GBS since 1957, 7 samples (18 copies) were grown from seeds obtained from the botanical gardens of the USA, Canada, Kiev and natural habitats. At the age of 24, trees growing in a bushy manner reach a height of 7.3 m, a crown diameter of 370 cm. Plant grows from mid-April to late September-early October. The growth rate is average. It blooms from 8 years old in the second half of May. Fruits in 8 years, the fruits ripen in October. Winter hardiness is average (in severe winters it is partially frost-covered). Seed germination is good. In youth it grows quickly, prefers deep, moist, well-drained soil. Durable. It can be recommended for widespread use in the alleys, single and group plantings from the latitude of St. Petersburg. In culture since 1759. Photo EDSR.
|
 Birch is far away -AT. dalecarlica L. =Betula pendula var. dalecarlica Birch is far away -AT. dalecarlica L. =Betula pendula var. dalecarlica Some botanists consider it as a dissected leaf form of warty birch [" Laciniata" or " Dalecarlica"- far away from the birch tree], Homeland Scandinavian Peninsula, in a culture of a single across the European part of Russia. It grows in mixture with other hardwoods. Heliophilic microtherm, mesophyte. Widely cultivated in gardens, often found in landscaping European cities. Once found in Central Sweden near the city of Uppsala. Dalecarlian birch is the plant emblem of the Swedish province of Dalarna, where the great scientist Karl Linnaeus lived and worked. It was in this province in 1523 that the uprising began against the occupying Danes, which ended victoriously by 1536. When choosing such a symbol, apparently, it was not done without the heritage of the ancestors - after all, the rune of the Berkan (which means “birch” in Old Swedish) in the Scandinavian sign system is a powerful ward of hearth.  A beautiful tree up to 20 m tall, similar in appearance to a birch, weeping, but differs from it in deeply dissected leaves with unequal-toothed edges. The plant grows in terms of normal birch. Hardy It reproduces by budding with an awakening or dormant kidney, grafting with a cutting, during seed reproduction a large splitting of characters is noted. A beautiful tree up to 20 m tall, similar in appearance to a birch, weeping, but differs from it in deeply dissected leaves with unequal-toothed edges. The plant grows in terms of normal birch. Hardy It reproduces by budding with an awakening or dormant kidney, grafting with a cutting, during seed reproduction a large splitting of characters is noted.
In GBS since 1953, 2 samples (4 copies) were grown from cuttings obtained from the nursery of the city of Zheleznodorozhny (Moscow region). Trees, height 6 m, trunk diameter 8 m. Planted in the same time as the species. The growth rate is average. Does not bloom. Winter hardiness is high. Rooted cuttings of 100% without special treatment. Very decorative, can be used in landscaping to create decorative groups. It has graceful decorative form (f. gracilis) - with weeping branches and smaller and thinly dissected leaves than the typical form. It is used in a single landing at critical points of partners. Nowadays, the forms “Crisp” and “Dalekliklika” are often considered synonymous, but the true “Dalekarlika” is rare and differs from “Crisp” by deeper-cut leaves and practically non-crybing branches. Photos by Anna Petrovichev
|
 Dahurian birch, or black -AT. davurica Pall. =B. nigra Dahurian birch, or black -AT. davurica Pall. =B. nigra It grows throughout the Far East, in Mongolia, North China, Japan, Korea. It is considered an indicator of soil suitability for farming. Protected in reserves. It grows in the lower part of the mountain slopes on deep and wet soils as an admixture in deciduous forests. Heliophilous mesophyte, mesotrophe, micro mesotrophe, stable assektator. In a culture in the botanical gardens of Europe and the Far East.  Tree up to 25 m tall with a widely spreading openwork crown. It is easily distinguished from other species by the original bark: in young trees, it is pinkish or even slightly reddish, in old trees it is dark gray, sometimes even black-brown, cracking along. Birch bark periodically exfoliates and partially falls off, part of it remains hanging in scraps, giving the impression of curliness. This attracts attention, but the tree should grow near the observer: the walkway, benches, porch, and so on. From a distance of even one height, this sign is already difficult to distinguish. Tree up to 25 m tall with a widely spreading openwork crown. It is easily distinguished from other species by the original bark: in young trees, it is pinkish or even slightly reddish, in old trees it is dark gray, sometimes even black-brown, cracking along. Birch bark periodically exfoliates and partially falls off, part of it remains hanging in scraps, giving the impression of curliness. This attracts attention, but the tree should grow near the observer: the walkway, benches, porch, and so on. From a distance of even one height, this sign is already difficult to distinguish.
The leaves are oval, dark green, in autumn - yellow-brown. It blooms after the blooming of the leaves. The vegetation period is shorter than other birch trees. In GBS since 1955, 5 samples (40 copies) were grown from seeds obtained from Dnepropetrovsk and natural habitats. At 34, height is 11.5 m, trunk diameter is 26.6 cm. Plant grows from 28.IV ± 5 to 5.X ± 8. The growth rate is average. Blossoms from 8.V to 12.V. Fruits ripen 16.X. Full winter hardiness. Rooted cuttings of 100% in the processing of 0.01% solution of IMC for 16 hours Very light-requiring and demanding on the soil, but less demanding on soil moisture. Poor pruning and transplanting, suffers from soil compaction. Deserves wide use in order to diversify the range of parks and forest parks. Looks good in clean and group piercing on brightly lit areas. In culture since 1883. Photo left EDSR.
Photo right Knyazheva Valery
|
 Yellow birch, or the american - V. lutea Michx. Yellow birch, or the american - V. lutea Michx. Originally from North America. It is decorative with large sizes (up to 30 m), with an interesting color of bark - silver-gray or light orange, on old trunks - reddish-brown and a form of a leaf similar to hornbeam leaves, up to 12 cm long, in the autumn of a peculiar yellow color. The speed of growth and shade tolerance are average. Hardy Prefers moist but well-drained soil. Lives up to 300 years. Suitable for single, group and aleynyh landings to the south of St. Petersburg, with the exception of the arid south-east and subtropics. In the Asian part of Russia can be used in the south of Western Siberia and the south of the Far East. In culture since 1767. Photo EDSR.
|
| Small-leaved birch -AT. microphylla Bunge
It grows in the desert valleys of mountain rivers and swamps of Western Siberia, Altai, Mongolia. Protected in reserves. Occurs along the desert steppe valleys of mountain rivers. Tree up to 4-5 m tall, often low and gnarled, growing as a shrub. The decorative feature of the species is yellowish-gray, sometimes pink bark, small leaves and a peculiar shape of the crown. Vegetation enters later than other species. It can be recommended for landscaping parks and forest parks in the form of single or group plantings, especially good along the banks of reservoirs. In GBS since 1964, 5 samples (9 copies) were grown from seeds obtained from botanical gardens. At age 17, height is 5.6 m, trunk diameter is 9.8 cm. Plant grows from O1.V ± 9 to O8.X ± 14 for 160 days. The growth rate is average. It blooms from 09.V110 to 19.V113 for 10 days. Fruits ripen 14.VIII ± 35 days. Full winter hardiness. Seed germination is low. Rooted cuttings of 16% in the processing of a 0.01% solution of IMC for 16 hours
|
| Birch useful -AT. utilis The whitest birch grows not in Europe, not in Siberia, or even in America.  Betula utilis var. "Jacquemontii
" Betula utilis var. "Jacquemontii
"
Photo of Kirill Tkachenko
In the skies of the Eastern Gim Alai, near the glaciers of the highest peaks of the planet, above the border of rhododendron thickets and coniferous forests grow birch trees with such white trunks, that without leaves they look like the breeches of the giants emanated from the wind. This birch is useful [V. utilis), and it justifies its name - at an altitude of more than 4500 m above sea level there are practically no other large trees, and it is this single species that provides the Nepalese and Bhutanese mountain dwellers with fuel and building material. Himalayan birch is strikingly beautiful with its huge leaves - they reach the size of a human palm, and in autumn they turn bright yellow and stick to the branches for quite a long time. Unfortunately, this birch is rarely available for sale, with the possible exception of the variety " Doorenbos", obtained in the Dutch nursery of the same name. In contrast to the natural species, which is characterized, in general, a straight trunk," Doorenbos"rather resembles Karelian birch - in adulthood it is not a single-stem tree, but a huge bush. The useful birch grows surprisingly quickly (a five to six-year-old plant can grow up to one and a half meters per year] and is completely winter-hardy in the latitude of Moscow, which, of course, makes its distribution in the gardens very desirable.
|
 Fluffy birch -AT. pubescens Ehrh. Fluffy birch -AT. pubescens Ehrh.
Europe, Western Siberia, Kazakhstan. Protected in reserves. It grows in dampish forests, outskirts of marshes, lakeshores, can form a crumbling on the border of the tundra and forest-tundra, is rarely found in the highlands. Restorative, light-loving mesophyte (but tolerates abundant and stagnant moisture), microtherm, mesotrophe, edificator of indigenous birch forests along the forest border in the northern part of the range and in the forest steppe, as well as in swampy habitats, anthropogenically progressive unstable, of temporal phytocenoses. assektator indigenous coniferous and deciduous forests. In culture, it is often found in botanical gardens and sometimes in the landscaping of settlements. Tree up to 15 m tall, with a pure white trunk that does not form a dark crust at the base; with a broad, egg-shaped crown formed upwardly directed branches. The bark of young branches is smooth, reddish-brown, later pure white. Young shoots are fluffy. The leaves are shiny, ovate or rhombic, up to 6 cm, sticky and fragrant when young. Unlike warty birch, ripe seeds are kept in earrings for a long time. In terms of ecology, it is close to it, but less demanding on the light, it tolerates shading better, marshy the soil, is more frost-resistant and further spread to the north. In culture since 1789. Forms natural plantations in the territory of GBS. At the expositions of the arboretum since 1954, 3 samples (7 copies) were grown from seeds obtained from Kiev, Lipetsk LSOS and Tashkent. At 39 years old, height 17.5 m, trunk diameter 30 cm. Plant grows from 27.V17 to 10.X ± 6 for 166 days. The growth rate is average. Blossoms from 9.V ± 5 to 14.V ± 3 for 6 days. Fruits ripen 3.1X ± 22. Full winter hardiness. Seed germination is average. Cuttings rooted weakly. It has a number of decorative forms: pyramidal (f. fastigiata), eggplant (f. ovalis); rhombolic (f. rombifolia), nettle-leaved (f. urticifolia). There is a purple-leaved form " Atropurpurea"but it is less common. "Urticifolia". In culture in the collections of botanical gardens of Europe. In the GBS since 1969, 1 sample (1 copy) was grown from seeds obtained from Germany. At 24, height was 7.4 m, trunk diameter was 6 cm. It grows in the same time frame , as the species. The growth rate is average. It does not bloom. Winter resistance is low. Photo of Cheban Elena
|
 Birch is ribbed or Far Eastern -AT. costata Trautv. Birch is ribbed or Far Eastern -AT. costata Trautv.
Most suitable for harsh growing conditions. One of the distinguishing features of this species - exceptional shade tolerance. Young plants can only develop in the shade. In culture it is very rare, but it can certainly be recommended for parks and forest parks. The shaggy trunk, covered with brilliant light yellow bark, the peculiar shape of the crown give it an original look throughout the year. A common breed of foothills, companion conifer of the Khabarovsk and Primorsky Territories, Northeast China and North Korea. It grows in deciduous and mixed mountain forests. Mesophyte shade tolerant, microtherm, microtroph, assector of cedar-broadleaf and cedar-birch forests. In the collections of botanical gardens in Europe, rarely in North America, the Far East and East Asia. Straight slender tree up to 30 m tall, with a spreading piercing crown. The largest birch of the Far East. Lives in favorable conditions up to 80-100 years. Shoots in youth shortly pubescent. The leaves are oblong-oval, with a strongly elongated pointed, dense, dark green, strongly pubescent in the period of blooming. In the autumn period are painted in a variety of yellow tones. In the GBS since 1970, 2 samples (11 copies) were grown from seeds brought from natural habitats. At 31, height is 12.2 m, trunk diameter is 22 cm. Plant grows from 28.IV16 to 25.1X ± 16 for 150 days. The growth rate is average. It blooms from 14.V to 16.V18 for 3 days. Fruits ripen 18.VIII. Full winter hardiness. Seed germination is low. Cuttings are not rooted. Demanding on soil moisture and air. It tolerates urban conditions, does not tolerate soil compaction, painfully reacts to pruning and transplanting. It can be recommended for landscape groups mixed with cedar and other conifers. It is very effective in combination with the Far Eastern maples: false-fibold, small-leaved, Manchurian. In culture since 1880. Photo EDSR.
|
 Wool birch -AT. lanata (Regel) V. Vassil. Wool birch -AT. lanata (Regel) V. Vassil.
The representative of the mountain slopes, gaps, clarified places of dark coniferous forests of the subalpine belt of Eastern Siberia, the Far East and Korea. In forest phytocenoses. Heliophilous mesophyte, mesotrophe, micro mezoterm. In the culture of rare. Completely different from our birch tree, up to 15 m tall. Notable is the presence of pubescence on young twigs, as well as woolly or even felt-pubescent buds. The earrings are upwards directed. The leaves are broadly oval, up to 9 cm, from above along the veins with diffusely hairy. It belongs to the most cold-resistant deciduous species. By decorative and silvicultural properties similar to stone birch. Recommended for use in single and group plantings of gardens and parks. In GBS since 1967, 2 samples (8 copies) were grown from seeds brought from natural habitats; there are plants from the reproduction of GBS. At 38, height is 8.5 m, crown diameter is 450 cm. It grows from early May to early September. The growth rate is average. Blossoms in May. Not fruitful. Full winter hardiness. Cut poorly. Photo of Kravchenko Cyril
|
 Birch Erman, or stone -AT. ermanii Cham. Birch Erman, or stone -AT. ermanii Cham.
It is naturally distributed in Kamchatka, the Commander Islands, Sakhalin, the coast of the Sea of Okhotsk, the Kuriles, and Japan. Protected in reserves. It grows in mountain forests, forming clean birch forests on strongly stony slopes or in the subalpine zone. Heliophilous, restorative mesophyte, microtherm, mesotrophe, edificator of park birch forests and assektator stand of coniferous-deciduous forests. In a culture in the botanical gardens of St. Petersburg, Moscow, Vladivostok, Arkhangelsk. Tree up to 15 m tall, with a widely spread crown. The bark of the trunk is variously cracking, dark gray, brownish, chestnut gray or yellow-gray, often hanging on the trunks and branches with rags. Shoots densely warty. Ovate leaves (14 x 10 cm), dark green above, paler below. Very hardy, undemanding to the soil. It received its second name for its ability to grow on stony places where other birches do not grow. In GBS since 1951, 7 samples (15 copies) were grown from seeds and living plants brought from natural habitats, as well as from seeds obtained from Lipetsk LSOS. At 22, height is 19.3 m, trunk diameter is 38 cm. Plant grows from 27.IV ± 6 to 5.X ± 8 for 161 days. Growth rate is slow. It blooms from age 16 from 12.V to 13.V13 for 2-3 days. Fruit ripening was observed on 16.IX. Rooted cuttings of 8% in the processing of 0.01% solution of IMC for 16 hours As a very original plant can be used in single and group plantings. In culture since 1880. Photo EDSR.
|
Location:
prefers sunny or slightly shaded places, but there are also quite shade-tolerant ones (B. woolly, ribbed, yellow). Landing:
when planting, the distance between the plants is at least 3–4 m. The soil mixture consists of leafy soil, peat and sand (2: 1: 2). Sand drainage with a layer of 15 cm is desirable. Planting is done in early spring at the age not older than 5-7 years, more adults are planted in winter, with a frozen clod; during the autumn planting a great fall occurs. When planting birches, there is one very important mandatory rule - in no case should the root neck of a seedling be buried. If it turns out to be at least a little below the level of the soil / the tree will suffer for several years, then it will still die. The fact is that in this case, mycorrhiza completely dies on birch roots, and without their cohabitants, the birch mushrooms cannot exist. For the same reason, birch trees do not tolerate the spreading of soil over the roots of mature trees and the rise of the groundwater level (the latter is less concerned with the original bog species - the fluffy birch, but it is rather rarely grown). Of course, in the early years, the seedlings should be watered as needed, but later not only the majority of “black” birches tolerate the drought, but even the birch is fluffy. But on the fertilizer of the soil it is worth thinking, again, only in the case of “black” birches, very demanding of this. The best fertilizer will be adding leafy land directly during planting. Well, for white-trunched birches you should not worry about it at all - everything you need will be delivered to these plants by symbiotic mushrooms.
Care:
Top dressing. In early spring, before the leaves appear, and at the end of spring, trees are fed: 1 kg of mullein, 10 g of urea, 15 g of ammonium nitrate are taken to a bucket of water. 10- to 20-year-old plants require 30 liters of solution, in 30 and more years - 50 liters.
Watering. Mandatory during landing and three or four days after it.
Loosening, multiplying. The soil is loosened to a depth of 3 cm during weeding. Mulching pristvolny circles with peat, peat compost, wood chips layer of 8-12 cm.
Haircut, trimming. In the spring cut dry branches.
Protection against diseases and pests. Pipe-beetles damage young shoots and leaves. It is recommended to collect and burn the affected leaves, and pristvolny circles - to dig over. Caterpillars of the silkworm-nun and bucephalus of the chickens eat the leaves leaving only the veins. Caterpillars shake, and plants treated with insecticides. May beetles and their larvae eat roots. Recommended soil digging and selection of birch larvae are susceptible to many fungal diseases, especially tinder fungi that destroy wood. It should be removed. Anti-rust is sprayed with fungicides, for example, copper oxychloride (0.4%).
Preparing for the winter.Cover pristvolny circles at especially valuable decorative forms planted in the fall.  Betula utilis var. occidentalis Betula utilis var. occidentalis
Photo of Tatiana Shakhmanova
Reproduction:
to plant one of our common birch trees, it is enough to dig up a small seedling on some abandoned field, but with the reproduction of exotic species, everything is much more complicated. If the varieties of warty birch, in particular, this applies to super-weeping and dissected-leaf forms, nurseries are now being supplied in rather large quantities, then the reproduction of other species will most likely have to be handled by the gardeners themselves, and with this it will be a lot of trouble. The fact is that birch trees are completely unable to reproduce in the simplest and most familiar way to us - grafting, and growing from seed and grafting remain the ways to obtain new plants. Birches are propagated by sowing seeds collected during the browning of earrings. Germination of 90%. further quickly falls. It is better to plant immediately after harvesting or in late autumn. Birches are well renewed, giving interesting decorative multiple forms. Dried to air-dry condition (humidity 7-14%), seeds are stored in hermetically sealed containers, plastic bags or paper bags in a refrigerator or dry unheated room. At the same time germination lasts 1 - 2 years. Laboratory germination depends on the species. Sowing in the fall or early spring. Freshly picked seeds are light-sensitive: they germinate in the dark at 15 - 32 ° С. At 15 ° and below with. sprout only after lighting. After dry storage before sowing stratification is necessary at 1–1 0 ° for 2–3 months or the treatment of gib-berellic acid at a concentration of 100 mg / l for 24 hours. Discontinued s. germinate at 12 - 25 °. Sowing with. superficial in well prepared grooves or ridges with compaction with. to sowing substrate. Crops are mulched with fine sawdust, peat, humus, sand or black soil, covered with shields or straw by 50 - 70% before germination. During this period, the crops are watered daily until the substrate is completely saturated with moisture, weeds are removed in a timely manner, and the lighting and the rate of irrigation are adjusted depending on the temperature and humidity of the air. Although birches massively colonize abandoned land, fires and felling, their tiny seedlings are very picky at the beginning of the conditions of life. First of all, most birches in the very young age need plenty of sunlight. Even insignificant shading by weeds turns out to be fatal for them, and they germinate only lying on the surface of the soil - they cannot be buried. Therefore, if you decide to sow some birch, it should be done in a box with soil specially steamed from the weeds, and then you have to water the whole spring carefully, but very carefully, with tiny sprouts. But starting from mid-summer, when the plant reaches five centimeters, you can already stop worrying about them and transplant them into a “little school” with a clear conscience. However, the above procedure applies only to “white” birches. “Black,” as typical forest dwellers, require less light, but their seedlings barely barely grow in the first year (despite the fact that their seedlings are several times larger than those of “white”] and are completely unstable to the slightest drought. Rapid growth begins with them only in the second or third year. Another method of breeding birch is grafting. This is the only way to propagate their varieties, but this requires considerable skill. It is necessary to adjust the time of the operation very precisely - the leaves should start to unfold on the rootstock, and the graft should be kept completely at rest (in the refrigerator at a temperature of about zero]. Apparently, the beginning and middle of May will be the best time for inoculation of birches. The vaccine itself is produced by cutting with one or two kidneys in a “split”, “in the butt” manner and the like: in other words, so that the rootstock is thicker than a scion. It is important to gently graft and protect them from excessive evaporation (for example, placing them in a new plastic bag). One Even with such tricks, the percentage of successful vaccinations is insignificant, it is higher only in cool greenhouses with constantly high air humidity. Worse than that, it turns out that it is almost impossible to graft black birch onto a white one or vice versa — the relationship of these groups affects. In our area, the only way to reproduce such dark beauties as cherry or Dahurian birch, is painstaking cultivation from seeds. Using:
are among the best park trees and highly desirable in gardens and alleys plantings, but always on the lawn. Decorative openwork crown, bright colored bark, light green foliage in the spring and golden yellow in the fall. Suitable for all types of landings, especially in combination with mountain ash, willows, oaks, lindens, maples, beech trees, bird cherries, as well as against the background of coniferous species. When planting birch trees, its neighborhood should be taken into account as an “ochleasyvatel”, especially birch trees with thin hanging branches, from which conifers especially suffer. Partners
: under hanging birch, it is always better to grow herbs and plants than under fluffy. In the latter, the crown is denser, the crowns of individual trees touching. But there are a number of plants, albeit not so many, that could be used under it. The limiting factors here are shade and dryness. Among woody plants one could use common hazel and its varieties, calligod and its varieties, snow growers in the assortment, some spireas (albeit to the detriment of abundant flowering), tree karagana and its varieties as ground-cover and winding along supports, tree clapper and virgin five-leaf grapes of smaller size than usual, but there will grow white and its varieties, some hawthorn and Tatar honeysuckle, padubolithic mahony and Chubushnik (though not so abundantly flowering), not bad bushes, but not much bilno-blooming, will give silver roe, shrubby, it is good to use alpine currant and mountain ash in the assortment, Chinese junipers, forms and varieties of common spruce, thawed western and other plants. The list of perennials - even more. The limiting factor is the same - dry shadow. Well even if they are not the most demanding of fertility. materials used:
Sergey Kuptsov "Such Different Birches" // "Garden and Garden" - 2007 - No. 6
Alexander Sapelin "Birch, White Friend" // "The Bulletin of the Florist" - 2008 - №23
|
Botanical name: Warty birch (Betula verrucosa), hung. Birch genus, Birch family.
Homeland birch wart: Far East.
Lighting: photophilous.
The soil: well fertilized.
Watering: abundant.
Maximum tree height: 30 m.
Tree's average lifespan: up to 120 years.
Landing: seeds.
Warty birch: tree description
Warty birch is a deciduous tree about 25–30 m high. Young individuals differ in brown bark, which becomes white by 8 years. Older plants have cracks in the lower part of the trunk, the bark acquires a black color. Birch wood has a yellowish-white shade, it is quite dense and heavy. The branches are covered with resinous glands - warts, from which the birch got its name "wart". Young branches are pulled down, this gives the crown a distinctive look, hence its second name is hanging.
Birch wart leaf
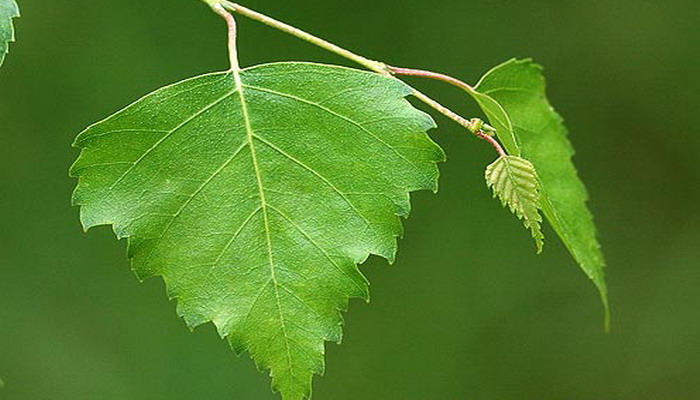

The leaves are alternate, long-petiolate, have a triangular-diamond shape, with a wedge-shaped base, smooth, 3.5-7 cm long, 2-5 cm wide. The edges of the leaves are dvukozubchatye. Wart birch leaf has a weak aroma and astringent taste.
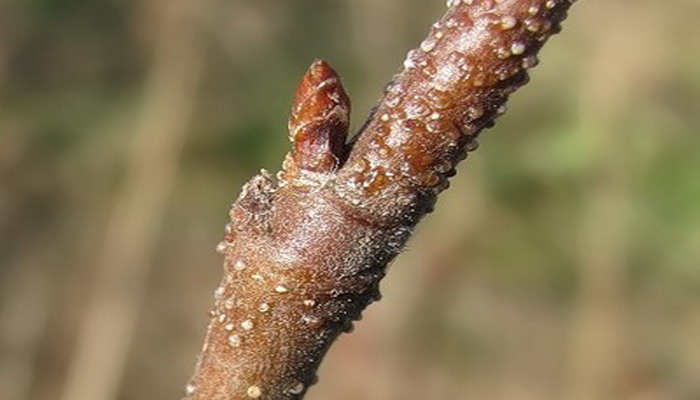

Kidney sessile. The flowers are small, inconspicuous, do not possess decorative value. Collected in same-sex tassels - earrings: at the ends of the branches are stamens, oblong, cylindrical in shape, 6-10 cm long, yellow; on shortened lateral branches - pistillate, cylindrical, directed upwards, 2-3 cm long, green.
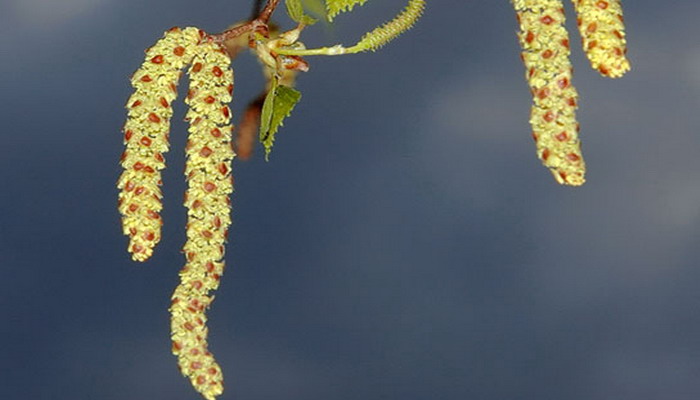

The wart birch blossoms from April to May.
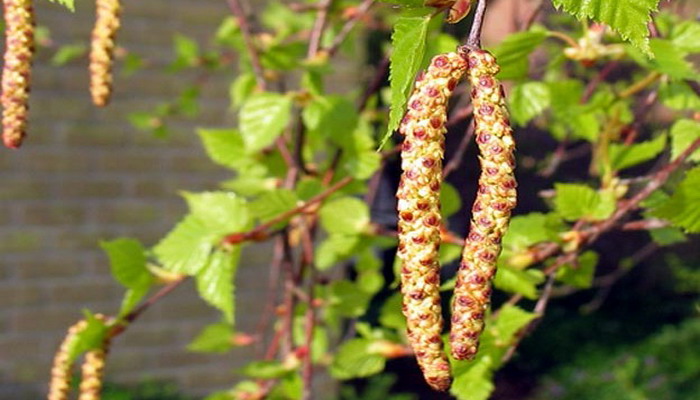

Fruits - small winged nuts, ripen in late summer - early autumn. It begins to bear fruit from 10 years, in planting - from 20-25 years.
Deciduous tree birch warty: root system
The warty birch tree has a strong root system, which, depending on the growing conditions, can be superficial or go deep.
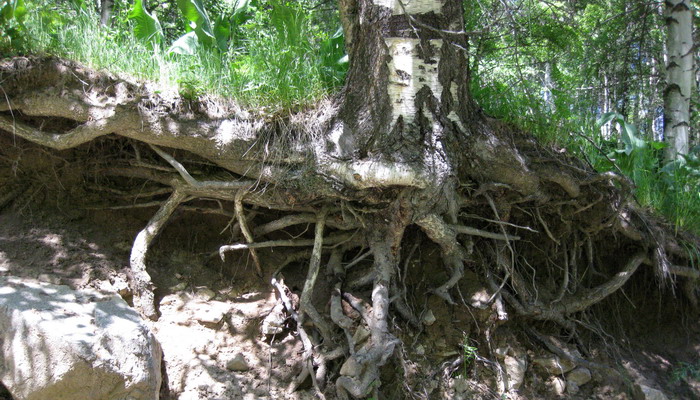

Taproot dies quickly, lateral roots develop at an accelerated rate and overgrow with biciform small roots. Root system lies almost on the surface of the earth, so the plant requires intensive watering, especially on hot, dry days.
Cap on the trunk of a wart birch is a very common phenomenon and a distinctive feature of the tree. This growth has a coarser and more dense wood than the wood of the tree itself. A month before the appearance of leaves and flowering, birch sap begins.
The start of juice extraction occurs in March, the most heavy discharge birch sap observed in late April, lasts 15-20 days. Birch sap has a pleasant sweet taste and healthy properties.
Propagation of wart birch
Birch is warty, hung multiplied by seeds. Seeds are sown when the earrings are brown, immediately after harvest, in late autumn or spring.

The seeds left for spring sowing are stored in a closed container. When sowing, they are lightly sprinkled with earth, leveled. On the surface of the ridge stack straw or thin branches through which produce watering. After spitting up the seedlings, the coating is removed, the seedlings are shaded with shields. The wart birch is restored by pneumos shoots formed after the death of young trees.
Plant seedlings
Warting birch seedlings are transplanted in early spring, at the age of trees not older than 5-7 years, since older seedlings take root worse.

Larger plants are planted in winter with a large frozen clod. The distance between the trees is 3-4 m. Soil mixture:.
Fruits of wart birch
In open places, the tree begins to bear fruit from 10-12 years. In plantations, from 20-25 years.
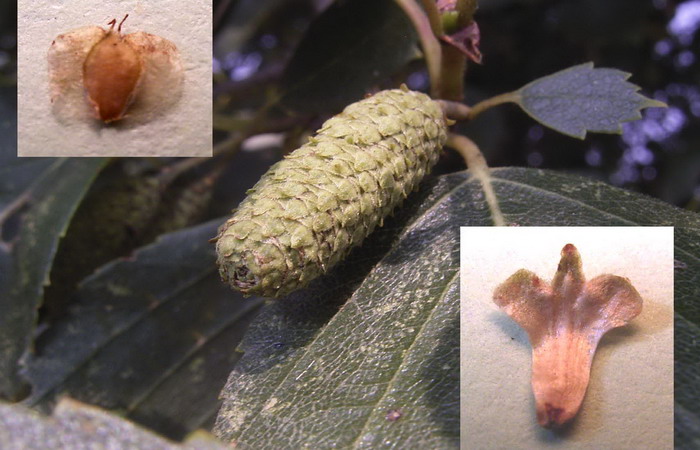

The birch fruit is a small, flattened nut with two webbed wings. Tree fructifies annually and quite abundantly. Fruits ripen in July, earrings are revealed after the seeds ripen. One part of the seed falls on the soil in the fall, the other in the spring. Seeds germinate on an empty, non-vegetated surface of the earth. Prefer a soil rich in minerals and. Thickets of grass and moss prevent the emergence of shoots. When the wind is strong, the seeds of a birch are carried to a distance of up to 100 m from the mother tree. Fruits are not opened.
Spread of wart birch
Wart birch is widespread in North America, Europe, North Africa, Western and Central Asia. In the mountains rises to a height of 2100-2500 m above sea level.
Prefers areas with a temperate climate. In Russia is one of the most common trees. Most often grows in the European part, Western Siberia, Altai and the Caucasus.
Birch forests are formed on the site of reforested or burnt forests, often coniferous. Since birch is very light-loving, it is quickly supplanted by other more shade-tolerant and large trees. It grows in deciduous and mixed forests, steppes and forest-steppe areas.
It grows in forests, as an admixture to the bulk of other trees in light areas. Birch stands are found in gardens and parks.
Birch Fasgiata: tree description
 Birch warty Fastygiata (Betula pendula Fastigiata) is a type of hanging birch. Crohn narrow, kolonovidnaya. Its height reaches 20 m, width up to 5 m. The branches are directed upwards. The leaves and trunk are the same as those of wart birch. The leaves do not fall off for a long time, keep on the branches until late autumn. The root system is powerful, windproof. The height of the birch tree is about 10 m. The diameter of the crown is 2 m. It grows quickly, the annual growth is 40 cm in height. Lifespan up to 100 years. Flowers, flat, green, irregular in shape, 1 cm long. The leaves are diamond-shaped, bright green, in autumn yellow from 3 to 7 cm.
Birch warty Fastygiata (Betula pendula Fastigiata) is a type of hanging birch. Crohn narrow, kolonovidnaya. Its height reaches 20 m, width up to 5 m. The branches are directed upwards. The leaves and trunk are the same as those of wart birch. The leaves do not fall off for a long time, keep on the branches until late autumn. The root system is powerful, windproof. The height of the birch tree is about 10 m. The diameter of the crown is 2 m. It grows quickly, the annual growth is 40 cm in height. Lifespan up to 100 years. Flowers, flat, green, irregular in shape, 1 cm long. The leaves are diamond-shaped, bright green, in autumn yellow from 3 to 7 cm.
Birch hanging wart Fasghiata has a decorative trunk and a beautiful crown. Used in single landings and in groups, to create alleys and parks. Light-requiring, drought-resistant, not whimsical to the soil. Winter hardiness is high. The root system is superficial.

Planting is done in open areas or partial shade. Soil mix: turfy ground, peat, sand. Top dressing is necessary in early spring before the appearance of the leaves and in the late spring. Nitrogen-containing fertilizers are used: ammonia, urea, ammonium nitrate. In the fall of mineral fertilizers, nitroammofosk. Watering is required after planting and during dry periods. Loosening to a depth of 3 cm to control weeds and saturate the earth with oxygen. Pruning drying branches is carried out in the spring.
Tree pests: birch sapwood, bucephalus crested hen, pipe beetle, cockchafer, silkworm nun.
Application of birch wart in industry and in everyday life
The warty birch tree, the photo of which is located above, is quite in demand in industrial production. Due to the strength, elasticity and ease of processing, birch is used as a material for the manufacture of furniture. It is fairly easy to polish and grind, furniture from its array has a pleasant golden hue. Birch produces plywood, fence board, toys, skis, coal, souvenirs and much more. During the processing of birch wood, methyl alcohol, acetic acid, and turpentine are obtained from it. It is used in medicine and the manufacture of perfumes.
Many parts of this plant are used in everyday life: bark, wood, bark, birch sap. Quite a long time ago, birch firewood has been used as fuel. They are good because they dry quickly, prick easily and burn for a long time. When burning, they emit much more heat than aspen or pine. Possess healing properties. When burned, they fill the room with a special aroma that disinfects the air and has a beneficial effect on the respiratory tract, thereby preventing colds.
The use of birch wart in medicine
AT traditional medicine plant leaves are used. Their infusion is an effective diaphoretic and diuretic agent. Fresh leaves are doused with boiling water and used as compresses for rheumatism and polyarthritis. To strengthen and grow hair make infusions and decoctions of birch leaves and buds. Birch sap serves as a tonic. It is rich in vitamins, minerals and trace elements. Contains tannins, aromatic substances, sugar, malic acid.
In traditional (scientific) medicine, birch wood is widely used. Birch charcoal is obtained from it in the form of Karben tablets, which helps with food poisoning, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, with increased acidity, fermentation and flatulence.

Birch tar is a part of the well-known ointments of "Konkov", "Vishnevsky" and others used for healing wounds and skin diseases. The bark effectively fights malaria, edema and lung diseases. Made from birch bark and essential oilused for cosmetic purposes. Infusion of birch buds is effective as a choleretic, diuretic, antiseptic, disinfectant. Wart birch sap is a part of the “Biomos” preparation, which serves to heal wounds and burns. Apply juice for the prevention of vitamin deficiency, for colds and skin diseasesfor kidney stones, sexually transmitted diseases, arthritis, rheumatism, for the prevention of caries and how anthelmintic agent. Birch syrup is prescribed instead of glucose.
Wart birch leaves are harvested in May, during the flowering of the tree. Dried in the open air, away from direct sunlight. The shelf life of the treated leaves is 2 years. Birch sap is harvested during sap flow from trees intended for cutting. The collection of buds is carried out at logging sites and tree felling sites. The best period for collection is early spring, the time of bud swelling. The branches cut off in winter are tied up in bunches, held in the sun, so that the buds swell and thresh them.
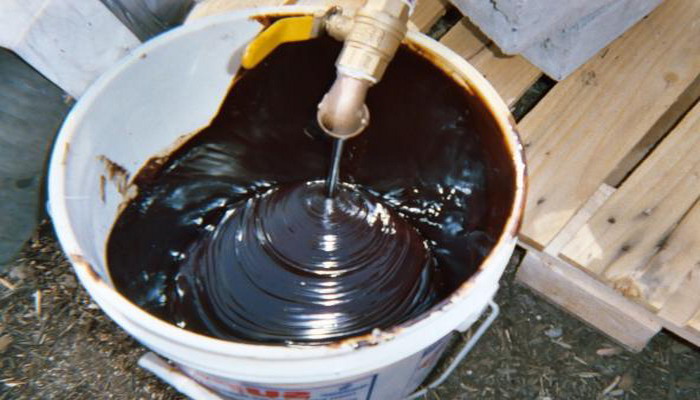
Birch tar
Birch tar found its use for a long time. Its production was previously engaged in tar. Today, tar is produced in industrial production.

The processed bark is packed tightly into the iron boilers and the tar is distilled from it. To prevent a vacuum in the furnace, the bark must be tightly clamped. Filled boilers are closed and heated. One distillation lasts up to 11 hours.
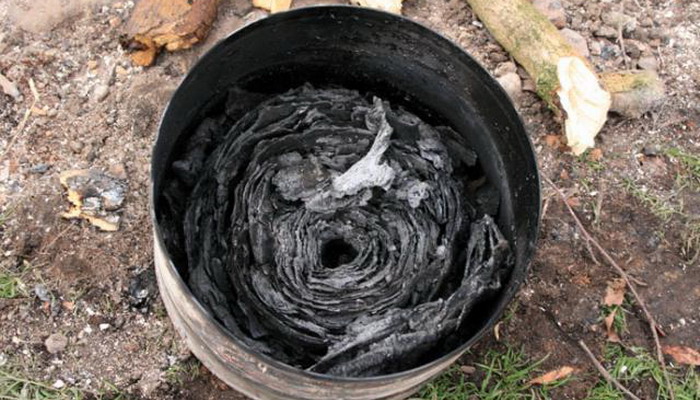
History of birch bark
 In the past, birch bark took an important place in people's lives. It was used in the construction of houses to prevent moisture. Thanks to its antiseptic and water-repellent properties, it protected the home from rotting and mold.
In the past, birch bark took an important place in people's lives. It was used in the construction of houses to prevent moisture. Thanks to its antiseptic and water-repellent properties, it protected the home from rotting and mold.
Birch bark made toys, dishes and many other products used in everyday life and in everyday life. In the peasant hut, all the utensils were made of this material: baskets, tuesa, bags, boxes, salt shakers, and more. From birch bark weaved bast shoes, hats, feet and waders. Sewed out of her clothes. Birch bark toys: rattles, animal figures, balls, small toy boats, children received from an early age.
It was used to create musical instruments: a pipe, horns, zheleek. In addition, birch bark was necessary for writing. Birch bark was the most affordable and cheap material. To make the bark suitable for writing, it was boiled, and then the letters on it were made with sharp bone, and later with a metal rod. Adults wrote letters on bark or created scientific works, children studied writing on it, wrote letters, drew.
Photos of the birch tree are presented below the photo gallery.
Photo gallery: wart birch (click on image to enlarge):






















 Betula pendula "Artopurpurea"
Betula pendula "Artopurpurea" 


 Paper birch -AT. papyrifera Marsh.
Paper birch -AT. papyrifera Marsh.
 Cherry birch - V. lenta L.
Cherry birch - V. lenta L.
 Birch is far away -AT. dalecarlica L. =Betula pendula var. dalecarlica
Birch is far away -AT. dalecarlica L. =Betula pendula var. dalecarlica  A beautiful tree up to 20 m tall, similar in appearance to a birch, weeping, but differs from it in deeply dissected leaves with unequal-toothed edges. The plant grows in terms of normal birch. Hardy It reproduces by budding with an awakening or dormant kidney, grafting with a cutting, during seed reproduction a large splitting of characters is noted.
A beautiful tree up to 20 m tall, similar in appearance to a birch, weeping, but differs from it in deeply dissected leaves with unequal-toothed edges. The plant grows in terms of normal birch. Hardy It reproduces by budding with an awakening or dormant kidney, grafting with a cutting, during seed reproduction a large splitting of characters is noted. Dahurian birch, or black -AT. davurica Pall. =B. nigra
Dahurian birch, or black -AT. davurica Pall. =B. nigra  Tree up to 25 m tall with a widely spreading openwork crown. It is easily distinguished from other species by the original bark: in young trees, it is pinkish or even slightly reddish, in old trees it is dark gray, sometimes even black-brown, cracking along. Birch bark periodically exfoliates and partially falls off, part of it remains hanging in scraps, giving the impression of curliness. This attracts attention, but the tree should grow near the observer: the walkway, benches, porch, and so on. From a distance of even one height, this sign is already difficult to distinguish.
Tree up to 25 m tall with a widely spreading openwork crown. It is easily distinguished from other species by the original bark: in young trees, it is pinkish or even slightly reddish, in old trees it is dark gray, sometimes even black-brown, cracking along. Birch bark periodically exfoliates and partially falls off, part of it remains hanging in scraps, giving the impression of curliness. This attracts attention, but the tree should grow near the observer: the walkway, benches, porch, and so on. From a distance of even one height, this sign is already difficult to distinguish. Yellow birch, or the american - V. lutea Michx.
Yellow birch, or the american - V. lutea Michx. 
 Fluffy birch -AT. pubescens Ehrh.
Fluffy birch -AT. pubescens Ehrh.
 Birch is ribbed or Far Eastern -AT. costata Trautv.
Birch is ribbed or Far Eastern -AT. costata Trautv.
 Wool birch -AT. lanata (Regel) V. Vassil.
Wool birch -AT. lanata (Regel) V. Vassil.
 Birch Erman, or stone -AT. ermanii Cham.
Birch Erman, or stone -AT. ermanii Cham.








 Birch warty Fastygiata (Betula pendula Fastigiata) is a type of hanging birch. Crohn narrow, kolonovidnaya. Its height reaches 20 m, width up to 5 m. The branches are directed upwards. The leaves and trunk are the same as those of wart birch. The leaves do not fall off for a long time, keep on the branches until late autumn. The root system is powerful, windproof. The height of the birch tree is about 10 m. The diameter of the crown is 2 m. It grows quickly, the annual growth is 40 cm in height. Lifespan up to 100 years. Flowers, flat, green, irregular in shape, 1 cm long. The leaves are diamond-shaped, bright green, in autumn yellow from 3 to 7 cm.
Birch warty Fastygiata (Betula pendula Fastigiata) is a type of hanging birch. Crohn narrow, kolonovidnaya. Its height reaches 20 m, width up to 5 m. The branches are directed upwards. The leaves and trunk are the same as those of wart birch. The leaves do not fall off for a long time, keep on the branches until late autumn. The root system is powerful, windproof. The height of the birch tree is about 10 m. The diameter of the crown is 2 m. It grows quickly, the annual growth is 40 cm in height. Lifespan up to 100 years. Flowers, flat, green, irregular in shape, 1 cm long. The leaves are diamond-shaped, bright green, in autumn yellow from 3 to 7 cm.


 In the past, birch bark took an important place in people's lives. It was used in the construction of houses to prevent moisture. Thanks to its antiseptic and water-repellent properties, it protected the home from rotting and mold.
In the past, birch bark took an important place in people's lives. It was used in the construction of houses to prevent moisture. Thanks to its antiseptic and water-repellent properties, it protected the home from rotting and mold.