Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- Technology and step-by-step instructions for nail gel: steps, rules, process
- White spots on the nails, reasons for what to do, white spots on the nails and folk signs
- Available methods for rapidly increasing blood leukocytes
- Nail and skin fungus will not resist the coffee grounds
- Crocus furniture exhibition. Furniture exhibitions
- Owl tattoo on arm value
- The biggest members in the world
- Fractures of the phalanges of the foot photo
- What is “bad” and “good” cholesterol
- What to do if the skin around the nails dries
Advertising
| Pain in the hands of children causes. Why hurts wrist joint. If the child has a fever |
|
Many parents heard the phrase “Mom, my leg hurts from my baby!”. Most adults do not attach importance to these words, but simply allow the child to rest, because they believe that the crumb is simply tired or tends to attract attention. When a child really feels a pain in his leg, he can easily do the following: 1. Indicate the nature of the pain; The boundary between fatigue and true pain:In order for parents to understand what exactly causes pain in the joint and whether it actually takes place, they need to watch the following for some time: 1. The activity of the child in the process of active games: whether he often stops, whether he wants to leave the game before others, how active he is, whether he is looking for a place to sit down; 2. Does a child often cry for no apparent reason; 3. Has the gait and posture of the child been disturbed; 4. Are there any changes in the size of the joints, especially large ones; 5. The frequency and time of pain; 6. Does the baby hold on to a specific area of the leg or arm; 7. Whether restless his sleep. On the basis of observations and surveys, it is possible to establish an accurate diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribe proper treatment baby Duration and time of pain:The pains that occur in the evening and disappear towards the morning indicate an overstrain of the spine and legs; Pains that occur constantly, regardless of time, accompanied by weakness, weight loss, fever, sweating indicate a chronic inflammatory process in the body. Swelling and pain in the joints:It is very important to examine the painful area to which the child points. The most common symptom is swelling of the joint, which is easily visually diagnosed. Manifested by an increase in the size of the joint. In addition, it becomes hot to the touch, the skin over the joint turns red, the contours become fuzzy. The baby does not make sudden movements, and also resists against touching the affected area. Parents can detect joint edema in this way: lightly push down on it. If there is inflammation, the affected area will resemble the dough. More pronounced signs of inflammation are fever and redness of the joint. Changes in gait and joint pain:With pain in the joints in children, mobility is significantly reduced. Such a manifestation is most noticeable when a baby is walking. The main features are as follows: 1. Slow motion; All the listed signs indicate that the baby does have disorders in the joints, which requires medical intervention. Skin rash and joint pain:When bone and joint pain often can occur and rashes on the skin. If baby chronic inflammation connective tissue, it is likely that he has bluish staining of the area around the eyes, reddish spots in the area of the nose and cheeks, on the hands and fingers. Body temperature and joint pain:If your baby complains of joint pain (a pen-and-leg hurts), then parents should measure his body temperature. It is very important to do this not only when acute pain occurs and the child’s general well-being is impaired. Measure the temperature several times a day in cases where the crumb periodically complains of pain in the joints. This will greatly help the doctor to establish the correct diagnosis and make a treatment plan. Joint pain as important symptoms of serious illness:Joint pain is an important and serious symptom of many diseases. Parents must listen to the baby's complaints and consult a doctor in a timely manner. Painful sensations in the joint may indicate such diseases: This is a disease that is accompanied by the death of bone tissue and is characterized by joint pain. In children, the hip joint (Perthes disease) is most often affected. The main manifestations are as follows: 1. Pain in the knees; In older children, Scheuermann's disease often develops in children. With this disease dies bone spine, especially in the thoracic and lumbar. This is a sluggish progressive disease, the latent period of which lasts up to three years. The main manifestation is extensive pain in the affected areas of the spine, especially while sitting. The back of these children is deformed and takes the form of a semicircle, which is often mistaken for scoliosis. The specialist who treats such babies is an orthopedist. In osteonecrosis, children undergo long-term rehabilitation, aimed at restoring joint function. As a rule, children are not allowed to walk while recovering, which significantly complicates the treatment process, including in the psychological sense. Full body massage is also highly effective. In children with osteonecrosis of the spine, special orthopedic corsets are used. How to diagnose joint pain ?:A preliminary diagnosis of a child who complains of pain in the joints, puts the pediatrician after the examination. Further, such a baby is sent for a comprehensive examination to an orthopedic surgeon, a rheumatologist (or other specialists, depending on the intended pathology) or to the in-patient department. The main examinations are as follows: 1. Blood test; Treatment of joint pain in children:Naturally, the principles of therapy completely depend on the diagnosis of the baby. Joint pain is a common problem faced by pediatricians. Babies with such complaints may be referred to such specialists: Rheumatologist; If pain is associated with inflammatory processesthen the treatment will be directed to its removal and removal painful sensations. The main groups of drugs that are prescribed to children: Antibacterial agents with established bacterial infectious process; As a rule, first-aid drugs for joint pain at home before a visit to the doctor is a group of NSAIDs. It is recommended to have in the first-aid kit at least two products with different active ingredients. Be attentive to your kids! At the moment, the child complains of pain in the legs every day - always in the evening. A child complains of pain in his hand, showing a brush. I started talking about it when I bought him gloves. The pain passes, the child begins to move his arm at the elbow joint. If you have registered before, then "log in" (login form in the upper right part of the site). If you register, you can continue to track the answers to your posts, continue the dialogue in interesting topics with other users and consultants.
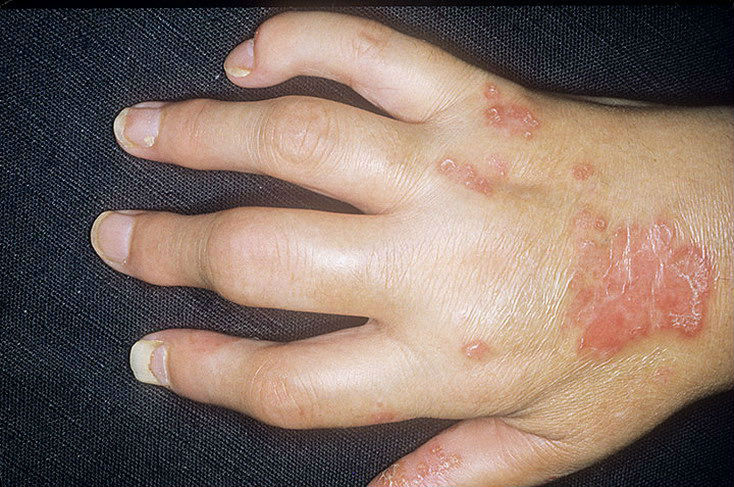
Causes of pain in the joints of the handsIn this article, you will learn what the joints of the upper limbs can hurt, what it can lead to, what to do in such cases. Hands consist of a large number of bones and joints. People of all ages and even children suffer. Women suffer 3 times more often than men. Muscle strength decreases, some people cannot even squeeze their hand into a fist, gradually the muscles of the hands atrophy. Over time, the pathological process causes destruction of the joints, which leads to severe and disabling hand deformities typical of rheumatoid arthritis. Therapy can be divided into basic (permanent, supportive) and treatment during exacerbations. Sick feet in a child of 6 yearsAt the beginning, patients complain of a aching character that occurs after work involving hands. After rest all discomfort pass. As the progression of osteoarthritis progresses, the pain does not disappear on its own, begins to disturb the person and at rest, the damaged joints crackle, stiffness develops in them and deformity. In about 10-15% of cases, this pathology occurs with damage to the joints. Most often inflamed joints of the hands and feet. In this case, it dramatically swells, turns red and becomes like a sausage. Arthritis in psoriasis has a chronic course with periods of exacerbations and remissions. Over time, such inflammation of the joints also leads to deformities, loss of function of the limb, and disability of the person. Gout is characterized by damage to the joints on the feet, but the atypical variant of this metabolic disease is also quite common. Help in the diagnosis of data history and additional techniques. In arthritis, the pain is aching, appears after the working day, accompanied by a crunch in the joint, the gradual development of its stiffness and deformation.
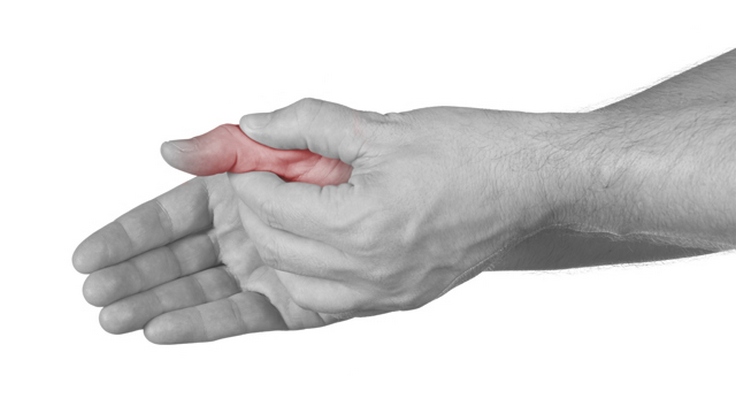
The elbow joint is complicated and superficial. Pain in the elbow bothers not only athletes, but also other people. Consider the main diseases that are accompanied by this symptom. Arthritis (inflammation) of the elbow joint can be caused by several factors. Arthritis can be acute and chronic. In the case of inflammation of the bursitis occurs. Therefore, bursitis refers to diseases that need quick help. In the treatment regimens must include antibacterial drugs. Otherwise, surgery may be necessary. Why the wrist joint hurtsIf you are worried about pain in your hands for a long time, and it is accompanied by other warning signs, then it is imperative that you seek medical help. He dresses them at home, and immediately says it hurts. I looked, not swollen, my fingers wiggling well, running, jumping. I do not understand, whether he is manipulating me already, seeing that my experiences and waiting for me to kiss my hand, or really run to the surgeon? We go down the street, she falls and says, the leg hurts, carry me. I thought it was being transformed, and after a week or two I was looking at a toed foot and became one foot. Hello. Child (boy) 4 years 1 month. Since April last year, went to kindergarten, since then endlessly sick, a week go, two sick. The pediatrician said it was growing pains, stay away from the child. Were examined during this time in the neurology department of the regional clinical children's hospital. There, the child was given simple nervous tics and polyneuropathy. Treatment did not work. Pain in the hands became more common. An investigation was carried out in the cardio-rheumatology department of the same hospital. There is considerable pain when turning the forearm to the sides, flexion and extension of the arm are not broken. Emergency Aid The arm is gently bent at the elbow joint and traction over the forearm. After some time, the forearm is transferred to the supination position. At this time, you can hear the characteristic "click". Cook for 15 minutes, filter and pour into the bath at a temperature of 36-38 degrees. A cold is no more than two times a year. The daughter is active, inquisitive, developed. His daughter has a twin, he has no problems with this, thank God. The birth took place in a natural way, at 38 weeks of gestation, the children were born almost three kilograms each. Sometimes both legs hurt at once, sometimes some kind of one. There is no redness, changes in shape, temperature, pain that is aching. Complaints about pain in the legs and joints should not be ignored: it can be a symptom dangerous disease, including juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Causes of disease Brachial syndromes are characterized by an extraordinary variety of etiological factors. I. Among the most frequent causes are vertebral pathology and traumatic injuries. Ii. Another group, which should be attributed to the frequent pathology, is myofascial pain syndrome. Iii. Despite the existing independence of the relationship of brachialgia with each of these factors, in practice there are very frequent cases of various combinations of them, when it is difficult for one patient to establish a cause-effect relationship between them. Mechanisms of occurrence and development of the disease (pathogenesis). The clinical picture of the disease (symptoms and syndromes)The main feature of the brachial syndrome in general is that it is in most cases clinically inseparable from algic syndromes in the neck and shoulder. This may be due to several reasons. First of all, these painful phenomena can be manifestations of a single disease. In other cases, the pathological process (in particular, in the neck) often leads to the formation of pain and other manifestations in the shoulder and upper limb. Brachialgia as a whole can cause a process localized at any point - from spinal cord to the distal extremities. The head, neck, shoulder joints and upper limbs are very mobile and are the constituent elements of a complexly coordinated system that provides various forms of motor activity. Pathological processes associated with each of its components, cause participation and clinical sound, respectively, of others. Probably, this circumstance is connected with the fact that among all forms of regional muscle pain, neck-brachial localization is the most common in the population (30.3%). Another feature of pain syndromes in the upper limb is the frequent maintenance of pain with a variety of vegetative, vascular and trophic disorders. This is due to some anatomical and physiological features of the upper shoulder girdle region: soft tissue (nerves, blood vessels, muscles, ligaments and articular capsules) are often compressed in narrow spaces of this zone. At the same time, pathological processes causing pain may be associated with local factors or due to distant or reflected, radiating causes. Local changes may be limited to the joint, its capsule or the nearest tendons, muscles and nerves. In remote processes, pain may radiate along the neurovascular bundles. Reflected pain is the result of pathological impulses from other musculo-articular areas, organs of the thoracic and upper abdominal cavities. The phenomenology of pain in the limbs is characterized by diversity. There are several types of pain: 1. Radiculoalgia- dagger-sharp (lantsiniruyuschaya) pain, paroxysmal, shooting, spreads throughout the dermatome from proximal to distal. At the same time, the main signs of a radicular lesion are observed: paresthesias and sensitivity disorders in the root innervation zone, a decrease in muscle strength and hyporeflexia. 2. Neuralgia- pain with lesion of the trunk of the nerve is nagging, rarely cutting, relatively long, reduced at rest, aggravated by movement, tension and palpation of the nerve. 3. Mialgia- deep pain (truncal), aggravated by pressure and muscle tension, often localized in separate zones, constant. 4. Dysesthesia - pain in the form of a burning sensation, tingling, superficial, of various duration, localized on the skin more distally, aggravated by active movements. Vertebral and posttraumatic brachialgia a) Brachialgia is a common symptom of various neurological complications of cervical osteochondrosis. They can be observed in the picture of compression syndromes in the form of radiculopathy. The main causes of cervical radiculopathy may be a hernia. intervertebral disc and osteophytes. In this case, clinically, as a rule, a lesion of one root is found. b) Radiculopathies in the hand may be a manifestation of a spinal (usually extramedullary) tumor. However, more often, symptoms of lesions of several spinal roots are detected. c) Pain in the arm due to a radicular lesion can be observed with a so-called whiplash injury. At the same time, along with the radicular there is damage to the muscles and ligaments, intervertebral joints and discs. This injury is characterized by headaches, pains in the neck and shoulders, dizziness, restriction of head movements. These symptoms appear in the first few hours or days after the injury and are often disturbed in the form of residual effects for many years. d) Pain in the upper limb may also be associated with lesions of the brachial plexus. The most common causes of plexopathy are trauma, tumor mass, or the effects of radiation therapy. The clinical picture depends on the involvement of the upper or lower portion of the brachial plexus. In the first case, the picture of Duchenne-Erb syndrome develops: weakness, atrophy and sensitivity disorders in the proximal shoulder. In the second, the Dejerin-Klumpke syndrome clinic: paresis of the hand and fingers, hypesthesia on the inner surface of the forearm. In any case brachial motor plexopathy and sensory disorders often accompany hand pain. e) In the case of the traumatic origin of brachialgia, the pain phenomenon itself is often associated with the detachment of the spinal root. In these cases, there is a sharp, acute, intractable pain, which has a cutting burning character and, as a rule, spreads along the corresponding root. Reflex neurodystrophic and neurovascular syndromes One of the most common causes of pain in the upper extremity is brachialgia in the picture of cervical reflex neurodystrophic and neurovascular syndromes. In all these embodiments, the source of pain impulses are receptors of the fibrous ring of the vertebral disc, posterior longitudinal ligament, joint capsules, etc. At the same time, the actual pain sensations have several regularities: Whining character Irradiation to the back of the head, shoulder, forearm and hand Increased pain during movements in the neck or prolonged posture. The above forms of brachialgia can be observed in the picture of several syndromes. With the existing diversity of neurovascular, neuroreflex and neurodystrophic syndromes, accompanied by pain in the upper limb, in clinical practice, only some of them are most common. 1) The shoulder and periarthrosis ("frozen shoulder"). The main manifestations of this syndrome are associated with primary changes in the spine with osteochondrosis, which lead to neurodystrophic disorders in the tissues of the shoulder joint. However, in some cases, an adhesive capsulitis can give a similar picture when a “frozen shoulder” is formed against the background of chronic fibrous inflammation of the capsule of the shoulder joint. Clinical manifestations consist mainly in pain and limitation of movement in shoulder joint. Pain sensations are mainly located in the shoulder joint, but may radiate to the neck, shoulder and scapula. Restriction of movements in the shoulder joint is associated with the development of the adductor contracture of the soft tissues of the shoulder, resulting from prolonged overstrain of various muscles, ligaments and fascia. In the initial stages of the disease, the restriction of movement is caused by pain, which in turn causes an increase in the tone of the adductor muscles. At the next stages dystrophic changes in the periarticular tissues are included in the pathological process. At the same time, active movements are sharply limited, while the volume of passive movements, especially in the frontal plane, is somewhat larger. The course of humeroscapular periarthrosis often ends with a cure for several months. Therapeutic measures include the use of analgesics, various variants of novocainic blockades, acupuncture, as well as active physiotherapy. 2) Often, the picture of the humeroscapular periarthrosis occurs in combination with edema and vegetative-trophic changes in the hand and wrist. These disorders are much less common, but they are much more severe. The described symptom complex is called shoulder-hand syndrome (Paget-Schrötter). Pain syndrome occurs at the onset of the disease, and vegetative and trophic changes are formed rather quickly: the brush becomes swollen, painful on palpation, bluish, hot. Pain syndrome can regress against the background of developing dystrophic changes in the ligamentous and bone apparatus. 3) Pain in the upper limb may be one of the manifestations of the anterior scalene muscle syndrome (scarlenus syndrome, Nuffziger syndrome) or the pectoralis minor muscle syndrome (pectalgic syndrome). In both cases, the clinical picture is due to reflex musculo-tonic disorders in the scalene or pectoral muscles and the associated compression of the brachial plexus and subclavian artery. The main manifestations are pain and swelling in the arm, later hypalgesia and weakness join in the ulnarly located formations of the hand and forearm. Characterized by a variety of sensitive disorders (numbness and paresthesia), weakness in the elbow of the hand, vegetative-trophic disorders (pallor, acrocyanosis, sweating of the hands, trophic changes in the skin, nails). At the same time, palpation of the small pectoral and anterior scalene muscles often reveals active trigger points with a characteristic irradiation of pain in the chest, shoulder, hand, shoulder blade. 4) Intense shoulder pain is characteristic symptom neuralgic amyotrophy (Personage-Turner syndrome). The disease often develops acutely after an infection, after vaccination or serum. The first symptom is usually acute pain, and a few days later, flaccid paresis of the muscles of the shoulder girdle develops. One of the characteristic phenomena of neuralgic amyotrophy is the frequency of bilateral lesion of the muscles of the shoulder, less often of the forearm, and the high rate of development of amyotrophy. In general, the prognosis of the disease is favorable - complete regression is possible within a few months. Myofascial pain syndromes It should be noted that myofascial pain phenomena are very often involved in the origin of brachialgia. In this case, one or another localization of pain has a clear pattern of formation of the zone of reflected pain with the presence of active triggers in certain muscles. Most often with brachialgia active trigger points are located in the following muscles: Ladder Supraspheric Subacute Coraocevicular Double headed Shoulder Three headed Wrist extensors Finger fingers extensors Instep Long palmar muscle In the origin of myofascial pain in the shoulder girdle, the same factors are relevant as for myofascial pain in general: Pose overvoltage Long immobilization Muscle compression Hypothermia Traumatic injury Crick Tunnel Syndromes Compression-ischemic neuropathies (tunnel syndromes) are one of the most common causes of pain in the upper limb. Nerve compression with the development of ischemic disorders often occurs in places of natural morphological formations in the form of holes, channels or tunnels, in places of bends of nerve trunks. A variety of factors can be involved in the origin of tunnel neuropathies. The main reasons for some of them are: 1) professional features or habitual poses 2) in some cases, long-term immobilization may be important (for example, in case of fractures or fixation of the hands during surgery) 3) common cause tunnel neuropathies are endocrine disorders (hypothyroidism, acromegaly, menopause) 4) oral contraceptive use 5) metabolic disorders with diabetes, alcoholism Clinical manifestations of compression-ischemic neuropathies consist of sensory, motor, vegetative and trophic disorders and depend not only on mechanical traumatization of the nerve by surrounding tissues. In many ways, these disorders are caused by ischemia and venous stagnation, developing tissue edema. Therefore, both the actual pain, and vegetative and trophic phenomena have a complex genesis and are associated with a number of pathogenetic mechanisms. In the diagnosis of tunnel neuropathies, analysis of the nature and location, the spread of pain, the distribution of sensory and motor disorders are of fundamental importance. Important special diagnostic techniques. For example, the Tinel test is the occurrence of painful paresthesias in the innervation zone of the nerve under investigation during percussion of the place of its possible damage. The second important technique is the Phalena test - passive flexion or extension of the wrist joint reinforces paresthesias and pain in carpal tunnel syndrome. The application of novocaine hydrocortisone injection to the nerve compression zone may also have a diagnostic value. With tunnel neuropathies, these measures, as a rule, bring significant relief of pain. There are some types of tunnel neuropathies for which the pain in the hand is characteristic. This primarily applies to the following types of pathology: Carpal tunnel syndrome - the most common variant of tunnel syndromes on the upper limb. Patient complaints about night pains in the hands and numbness of the fingers of the hands (usually 1, 2 and 3), which are of a periodic nature, are typical. With an unfavorable course, these phenomena become permanent. In the most severe cases, tenar hypotrophy develops; thumb muscle The cause of intense pain in the hand is often a chronic, household or sports injury. An example of this is the pronator syndrome that occurs in individuals of certain professions (when using a screwdriver, squeezing underwear), with prolonged posture of overstrain or pressure on the palmar surface of the upper third of the shoulder ("honeymoon paralysis"). Compression median nerve in the area of the round pronator, there is a sharp pain in the forearm radiating to the fingers, as well as sensory disorders. Pain is the main manifestation and ulnar neuropathy. Compression of the ulnar nerve can be carried out at several levels: at the level of the elbow joint in the cubital canal and at the exit from it, as well as in the Guyon bed. The earliest signs of neuropathy are paresthesias, pain and itching along the ulnar edge of the hand and fingers. As the disease progresses, weakness and amyotrophy of the muscles of the hypotenar and interosseous muscles occur with the formation of a "clawed hand." A common phenomenon of brachialgia is the neuropathy of the radial nerve. The most characteristic is its defeat in the area of the elbow joint. The injury of the radial nerve in this zone with the formation of epicondylitis ("tennis elbow") usually occurs as a result of the overstressing of the extensor muscles of the hand and the upper support of the forearm. The first symptom is pain in the lateral epicondyle, which is acute. With repeated trauma pain becomes constant. In cases of damage to the superficial branch of the radial nerve in the elbow joint pain occurs in the elbow region and forearm, characterized by aching pains rest. At the same time, paresthesias and sensory disorders are absent. This is the so-called algic form of radial nerve tunnel syndrome. Complex regional pain syndrome The brightest pain in the upper extremity is found in the picture of the complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS). CRPS is a symptom complex, polyetiologic in nature. The main clinical phenomena of CRPS are: The pain is burning, aching or breaking, combined with a variety of sensitive disorders (hypesthesia, hyperpathy, allodynia); Vegetative-trophic disorders - swelling, discoloration skin integument, local hyperthermia, impaired sweating, changes in hair and nail growth, osteoporosis; Movement disorders. There is an extraordinary variety of etiological factors that are believed to be the cause of CRPS: injuries of the central and peripheral nervous system, fractures and sprains, inflammatory diseases joints, tunnel neuropathies, degenerative and autoimmune diseases of the nervous system, strokes, myocardial infarction. Despite the variety of causes causing this symptom complex, in all cases the formation of algic and vegetative-trophic disorders with it has its own regularities: 1) First, the delay of its development in relation to the action of the damaging effect - the CRPS always develops after a few days or weeks and, as a rule, within one limb. 2) Secondly, for the clinic of this disease, the presence of bright vegetative and trophic disorders is necessary. In the course of CRPS, it is often possible to determine some staging. 1) Acute stage characterized by the appearance of pains of a burning, breaking nature with various sensitive phenomena. 2) There is a dystrophic stage with the development of pronounced vegetative and trophic disorders: the skin acquires a bluish tint, it becomes hot to the touch, hyperhidrosis is observed, muscle tone is increased, the tendon reflexes are revitalized, joint damage develops. 3) At the late atrophic stage, as a rule, pain subsides, skin color is set to pale, hypotrophy develops, skin temperature decreases, hair and nail growth changes, depigmentation, marked osteoporosis. Each stage can last several months. If untreated, the disease often leads to disability. Treatment of CRPS is carried out taking into account the analysis of possible etiological factors, central and peripheral mechanisms involved in its formation. Along with the use of various analgesic agents and local blockages, anticonvulsants, antidepressants, calcium channel blockers, beta-blockers can be successfully used. In some cases, diuretics, venotonic and other symptomatic agents are indicated. This requires the mobilization of the affected limb and the use of various non-pharmacological treatment methods: acupuncture, various methods of physiotherapy, hyperbaric oxygenation. Arthrogenic Brachialgia One of the causes of persistent pain in the upper limb may be damage to the joints. Pain in the hand and arm often accompanies rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthrosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis. Characterized by pain in the distal upper limb and psoriatic arthritis, chronic gout, Reiter's syndrome. In all cases, to exclude damage to the joints, both a clinical study of the joints (swelling, change in configuration, painful palpation, local temperature change, clicks during movement), and additional laboratory and X-ray examination are necessary. Arm pain can also be a symptom of neurogenic arthropathy (Charcot's joint). The development of neurogenic arthropathy is associated with a violation of deep pain sensitivity or propriception, leading to the loss of normal protective reflexes that protect the joints from injury (especially recurrent) and periarticular fractures. There are many pathological conditions conducive to the development of neurogenic arthropathy: Degenerative diseases of the spine with compression of the nerve roots, Tumors and damage to the peripheral nerves and spinal cord, Anomaly Arnold-Chiari, Hereditary family neuropathy (Charcot-Marie-Tut disease, hereditary sensory neuropathy, Dejerine-Sott disease, Riley-Day syndrome), Violations of pain sensitivity caused by the use of indomethacin, Intra-articular administration of corticosteroids, Alcohol abuse Similar causes of pain in the hand can be observed in the picture of arthropathy in diabetes mellitus, dorsal tabes and syringomyelia. When syringomyelia neuroosteoarthropathy occurs in 20% of patients, there are also painless forms. In general, syringomyelia is characterized by pain, including in the arm, which occurs already on early stages diseases are spontaneous and are one-sided. In this case, pain syndrome is accompanied by sensitive disorders, which, when syringomyelia, are segmented-dissociated. It is sensitive disorders (analgesia) that cause the frequency of injuries, especially burns, and contribute to the development of neurodystrophic changes, so characteristic of syringomyelia. Brachialgia with polyneuropathy Hand pain can also occur in various forms of polyneuropathy. Pain in this case generally depends on the severity and severity of the underlying disease. The most characteristic pain syndrome in such a rare disease as hereditary sensory-vegetative polyneuropathy. Algic manifestations are fulminant and spontaneous, accompanied by sensitive disorders and often painless, progressive, nonhealing, deep ulcers of the feet. All the symptoms on the hands are less pronounced. In diabetic neuropathy, pain is more common in the pattern of distal symmetric polyneuropathy. However, this is more characteristic of the lower limbs. In diabetes, damage to the nervous system can be observed in the form of isolated multiple neuropathies. In these cases, with the defeat of the peripheral nerves in the upper limb, the development of pain in the arm is possible. At the same time, the nature and distribution of pain have patterns of the ulna or median neuropathy. Viscerogenic brachialgia Do not forget about such possible reason pain in the shoulder, as viscero-radical syndrome (zone Zakharyin - Ged). Shoulder pain may be accompanied by: 1. Acute coronary pathology (angina pectoris, acute myocardial infarction) 2. Pathology of the gastroduodenal zone and gallbladder 3. Broncho-pulmonary pathology, etc. Therefore, when complaining of pain in the shoulder, the patient should undergo a comprehensive, in-depth, detailed examination. |
| Read: |
|---|
New
- Sequence of procedures
- The program of intensive moisturizing of the skin on cosmetics bark
- What you need for acrylic powder
- What does owl mascot mean
- Analyzes for pancreatitis: what research should be done and what indicators show
- Owl - a talisman to attract money and good luck
- What bird screams at night with a kitten's voice?
- Cholesterol and stress
- Manicure at home
- Effective facial