Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- Exhibition of autumn crafts "Amazing near" in kindergarten
- Technology and step-by-step instructions for nail gel: steps, rules, process
- White spots on the nails, reasons for what to do, white spots on the nails and folk signs
- Available methods for rapidly increasing blood leukocytes
- Nail and skin fungus will not resist the coffee grounds
- Crocus furniture exhibition. Furniture exhibitions
- Owl tattoo on arm value
- The biggest members in the world
- Fractures of the phalanges of the toes of the photo
- What is “bad” and “good” cholesterol
Advertising
| Prevention of norovirus infection in children. Norovirus infection is a dangerous disease! |
|
Both adults and children often suffer from intestinal infections, which are caused by various pathogens. These include norovirus, which provokes the development of the so-called intestinal flu. Symptoms and treatment of norovirus intestinal infection in children and adults differ little from the treatment of rotovirus infection, but there are some differences. General characteristics of the virus
Now known 25 strains of norovirus, each of which represents a danger to human health. Most often, the pathogen, penetrating into the body, provokes the development of acute gastroenteritis, or intestinal flu. This bacillus is very contagious and easily transmitted from person to person. Intestinal flu is most common during the cold season., although they can be infected in the summer. The incubation period after penetration into the body is from 12 to 48 hours. During this time period, the person does not feel sick, but can infect other people.
Methods of transmission
A person who has contracted norovirus is considered infectious during incubation periodduring the acute phase, as well as about three days after complete subsiding of all unpleasant symptoms.
Signs of diseaseNorovirus intestinal infection is characterized by the appearance of disorders of the digestive system. The main signs of the disease are:
Most often, all these conditions do not require treatment and disappear without a trace in a few days. In especially severe cases, especially in young children, dehydration develops without adequate medical care. At the same time, the water-electrolyte balance is disturbed in the body of a sick person, which can lead to a comatose state or even death. Young children, the elderly and pregnant women are most affected by this disease.. This disease in such groups of patients is very difficult, in some cases, urgent hospitalization is necessary.
First aid
The room in which the patient lies, it is necessary to air often. All surfaces are regularly wiped with disinfectant solutions. If the condition has worsened, despite the assistance provided, then an urgent need to call a doctor, especially if we are talking about a child or an old man. What else to help the patient
The broth is cooled and given to the patient in half a glass every 20-30 minutes. In such a healing drink many minerals and vitamins, in addition, a decoction of rice has enveloping properties and gently relieves irritation from the stomach. Principles of treatment of severe casesIf norovirus is severe, the doctor may prescribe a number of drugs to stabilize the patient's condition. In special cases, treatment is carried out in the hospital of the infectious disease ward.. The treatment protocol is as follows:
Medicines to eliminate diarrhea at first do not give. With diarrhea, pathogens and toxins are removed from the body, self-purification occurs. If the gap between the urging to the toilet does not increase and the state does not normalize, then the smect is prescribed. This medicine gently relieves inflammation from the intestinal walls and reduces motility. Disease preventionAny disease is always harder and more expensive to treat than to prevent, especially when it comes to severe cases. There are no vaccines for norovirus, but, despite the fact that these bacilli are resistant to many external factors and remain active for a long time, preventive measures are elementary. In order not to get an intestinal infection, you need to follow these rules:
Any intestinal infection is very unpleasant, but you shouldn't panic. First you need to objectively assess the severity of the patient, give him first aid and, if necessary, call a doctor. When started on time proper treatment the disease passes without a trace in just a few days. Since there have been reports that cases of the disease by these types of virus have recently become more frequent, the Mother's Club decided with the help of specialists to figure out how they differ and how you can protect yourself and your child from them. At first glance, the symptoms, the method of infection, and the course of rotavirus and norovirus are very similar. See for yourself by reading the data in the table.
Nevertheless, these viruses differ somewhat from each other, because the name of them is also different. would be the same. With the help of interviewed experts, we managed to find out the main differences. 1. Rotavirus - diarrhea and heat, norovirus - vomiting The symptoms of these viruses, as we have already seen, are similar, but, if there is a difference, this is symptom number one. “In case of a disease with norovirus, this is vomiting, there may be no high fever at all. With rotavirus, diarrhea almost always appears first, which is accompanied by an elevated body temperature,” says rita Korotinsk, epidemiologist of the Latvian Center of Infectiology. Yes, instead of diarrhea, there may be vomiting, if it is not there immediately, then it may appear a little later. 2. Rotavirus appears bright, norovirus is hidden "Rotavirus usually starts very badly: diarrhea, temperature, vomiting. Norovirus is more cunning. Everything starts with vomiting, but there is no temperature and most immediately write it off not as a virus, but as an ordinary food poisoning. You regulate for a while their diet seems to be better, but there is some weakness. It takes several days or even a week and again vomiting. The temperature usually rises by 3-4 or even on the 7th day of the virus ", - explains family doctor, pediatrician Larisa Zakharova. That is, if the rotavirus manifests itself in all its glory at once, then the norovirus is wavy, incrementally, disguised as a violation of the gastrointestinal tract. "Therefore, the rotavirus can be ascertained more quickly, whereas the norovirus gives up to two or three exacerbations, everything seems to be fine, 4 days have passed and again vomited 2-3 times," adds L. Zakharova. 3. Norovirus is relevant in winter, rotavirus is always The people conceived norovirus called "winter vomiting disease" and it is - not just. He really is especially relevant in the winter. Rotavirus is relevant at any time of the year. Yes, there are certain seasonal outbreaks, but there is always a risk of getting sick. 4. Rotavirus more sick kids, norovirus older children This is confirmed by the statistics of the Latvian Center of Infectology. Rotavirus more sick young children up to two years, especially from 6 to 23 months. Whereas older children, including adolescents, suffer from norovirus. This also indicated infectologist of the Children's Hospital Ilze Grope. Last year, 1,774 diseases of norovirus were recorded, of which children from 0 to 17 years inclusive included 626 people, including 271 children aged 0 to 1 year. Sick children aged 1 to 6 years out of a total of 698. "But this does not mean that a small child cannot get sick with norovirus. In my practice, there were cases when norovirus was diagnosed in a six-month-old baby, and a two-year-old, and a ten-year-old child," he shares his experience. family doctor, pediatrician Lolita Sorge. Ilze Grope also noted that "representatives of all age groups can get sick in case of contact with a patient." According to the epidemiologist, last year the norovirus in Latvia was in the top. Now, compared with the data of 2011, the disease is not so relevant, but what it is now is typical, because it's winter, and this is her time. As my mother's club was told at the Children's Hospital, there is no evidence that the number of patients with norovirus has significantly increased, thereby providing the leeway of information from the Latvian Infectology Center. 5. When rotavirus comes rapid dehydration, norovirus itself releases substances that poison the body This opinion was shared by Larisa Zakharova. And in fact, and in another case, the body is subject to dehydration, but the reasons are different. In the case of rotavirus, the body loses fluid through diarrhea and vomiting and it is very important to restore it. In the case of norovirus, dehydration can occur not only as a result of vomiting, but also from if the virus has remained an unidentified object in the body for too long, hiding under various other diseases, the same poisoning. 6. Rotavirus is harder than norovirus Not always, but, as practice shows, children with rotavirus are often admitted to hospital than with norovirus. “Norovirus is a little softer, it is more long-lasting than rotavirus. In the case of rotavirus, the hospitalization rate is higher than in the case of norovirus,” says Lolita Sorge. The probability of hospitalization uniquely determines the patient's age, emphasizes the infectiologist: "Most often, treatment in a hospital is required in the first year of life. It is known that rotavirus causes such severe gastroenteritis, that in 75% of cases treatment in a hospital is necessary. In turn, the norovirus is easier and according world statistics only 5-10% require hospital treatment. " 7. There is a vaccine against rotavirus, norovirus - no Rotavirus vaccination is planned to be included in the national vaccination calendar in 2014, so for now it can only be done for money. A total of two doses are provided. They are introduced through the mouth. No shots! Vaccination is recommended up to 6 months. There is no separate vaccine for norovirus. Perhaps because it affects the child in a more conscious age, when the immunity is no longer so weak and able to fight. In addition, it is not as dangerous as rotavirus, as a result of which dehydration occurs very quickly. However, it is imperative to observe preventive measures that are the same for almost all infectious diseases that are transmitted by airborne droplets or by dirty hands. Mother's Club summarized the advice of interviewed specialists, here's what they recommend: Wash your hands often, especially after going to the toilet, before and after cooking, when changing a diaper, after any contact with a sick infection; If the child is sick: Do not take the child to the kindergarten, if the first signs of the disease appear, go to the family doctor - otherwise the child may infect other children in the group and staff. PERSONAL EXPERIENCEKsenia, Sofia's mom (2.8 years), daughter suffered from both rotavirus and norovirus We first learned what an intestinal infection is when Sophia was 7 months old. I confess that we have "enjoyed" these diseases in full. For less than three years, she has already suffered from diarrhea and vomiting four times, she was in the hospital with a temperature of 41 times three times ... And all this was due to roto and norovirus, and during our first hospital stay, both of these viruses were diagnosed in a child. How do they differ, how to treat and when to urgently run to the hospital? Hmmm ... I can talk about this for a long time and not worse than what is written in medical textbooks. What is the difference between roto and norovirus? Norovirus is called “winter vomiting syndrome” or the disease of winter vomiting, and all because it appears most often at this time of year. The most interesting thing is that being in a hospital in Belarus they don’t even know about such a disease. Apparently, since the Soviet times, all intestinal infections were equated with dysentery. Having stayed with the child in the hospital, I was very surprised by the fact that doctors consider Novorovirus more dangerous than roto infection. If roto symptoms usually appear within 2-3 days: a person can be tormented by terrible bouts of vomiting, diarrhea, the temperature may rise, then the same symptoms of norovirus can last up to two weeks. Prevention: Visit public places less Wash your hands often Buy a hand sanitizer How I treat a child: 1. Babies up to 2 years old with diarrhea can be given one packet of Smecta, diluted with a floor with a glass of water. This liquid is drunk throughout the day. In the case when the child’s condition worsens and I don’t really want to go to the hospital, I give Nifuroxazide-Richter - an antibiotic suspension, which is taken within five days. If vomiting does not stop, like diarrhea ... always go to the hospital. There, the doctor prescribes treatment depending on the condition of the child. 3 droppers per day are provided for everyone! How I treat myself: 1. With diarrhea, Lopiramid was an amazing discovery for me. After two pills, even in the worst case, diarrhea stops. Depending on the manufacturer, this medicine can be used by children from 5 years old, from 12 years old (Grindeks). Be sure to see the instructions. From the mouth of the nurses: Immunity to roto and norovirus is valid for six months after suffering the disease. After this time, a person can become infected again. These diseases are carried not only by contact, but also by airborne droplets. So, especially in the winter months, we are practically defenseless. In case of diarrhea and vomiting of 10 kilograms of weight, a person should drink 1 liter of water, preferably saline. The rotovirus vaccine only protects the child from this disease, while the other dozens of intestinal infections can still catch the child ... So the point of vaccination in this case is very doubtful. Immediately after vomiting, do not let the child drink. Wait five minutes, give a spoonful of water to drink, if after 5-10 minutes vomiting does not recur, continue to give water. It is advisable to do this every 15-20 minutes so that the body is replenished with fluid reserves. - Be sure to consult your doctor if: In fact, all of the above indicates that the child is in an extremely serious condition. Be careful, it is very important to see the edge when you should not skip to the hospital or, conversely, when it is just necessary. Given the above, I want to emphasize that this is only my experience and in each case I recommend to consult a doctor without delay. Only a doctor can recommend treatment and medications that are right for you. It also helps the round-the-clock telephone 66016001, by calling which doctors always give advice. Especially if you do not want to go to the hospital. Every person at least once in his life faced with intestinal diseases. The main cause of the development of pathologies is an infection, the pathogens of which are bacteria, toxins and microbes. Often, intestinal infection provokes the development of dangerous diseases, and detrimental effect on the entire digestive system of a person. The condition of the patient depends on the severity of its course. It is worth remembering that the intestinal infection has symptoms, treatment in adults should be carried out immediately, as soon as they appear. Acute intestinal infection, symptoms in adultsConcept acute infection in the human digestive system is of a general nature, which depends on several factors. These include the main causative agents of the disease (viruses and bacteria) and toxic poisoning of the body with food. An infection that has entered the body begins to develop rapidly, affecting some departments. digestive tract. Basically, the inflammatory process begins in the stomach, duodenum, small and large intestines. This condition leads to disturbances in the system of assimilation of food, and also provokes inflammation of the mucous membranes of the corresponding organs. To know how to determine whether this disease is infectious or not, you need to know its signs.
Symptoms of acute intestinal infections:
Often there is a temperature during intestinal infection. She may be called inflammatory processesthat are triggered by the spread of viruses. Sometimes the heat reaches 39 degrees, which is dangerous for the human condition. In order to avoid negative consequences, when the disease first appears, it is necessary to consult a doctor. Rapid fluid loss in the form of vomiting and diarrhea can lead to dehydration, which is very dangerous for the body.
Types of intestinal infectionIntestinal infection is a dangerous disease that lurks both adults and children. It is insidious in its complications, and it is a great threat to the entire human body, as it can affect all organs and affect their functioning. A similar disease is often caused by viruses that have several varieties. Clinically, they are similar, the symptoms of leakage also sometimes coincide, but there are nuances that make them classify. Types of intestinal viral infection:
Norovirus infectionIn a short time, it can cause an epidemic. Ways of transmission of norovirus:
You must understand that such an infection is very dangerous, has easy ways of entering the human body. Eating unwashed foods, drinking water from contaminated sources, and contacting a sick person can all lead to rapid infection. You need to be extremely careful, and know how this disease manifests itself. Signs of norovirus infection:
The disease manifests itself for 2–4 days and can be accompanied by all the symptoms as well as solely vomiting and diarrhea. It is worth noting that after a few days the disease recedes.
If norovirus occurs mainly in the warm period, then rotavirus infection affects the body during the cold season (from November to April). It is also called intestinal flu. In adults, the disease is mild and does not cause much discomfort. This pathology is transferable, and quickly transmitted by contact.
Rotovirus infectionStages of rotavirus infection:
Rotovirus infection in adults can occur without obvious manifestations. A person may not feel much deterioration, but at this time infect other people. It also happens that the disease is gaining high speed, and reaches moderate - vomiting, frequent diarrhea, fever - and severe (pressure reduction, intense diarrhea up to 20 or more times a day, dehydration) forms. If the condition worsens, urgent hospitalization is required. Causes of intestinal infection in adultsThere are many factors that lead to the development of the disease. It should be understood that the reason is not only in bacteria. This is a specific disease that depends on many pathogens. The main causes of intestinal infection:
With a bacterial infection, people are the source of the disease. They may simply be carriers of viruses, or suffer from obvious / hidden signs of pathology. Microbes leave the body with feces, vomiting, saliva, urine. How long the period in which you can get such a disease lasts is difficult to say. With each infection it is different. On average, it begins with the first symptoms, and ends a few weeks after the patient has recovered.
It is possible to get infected from a sick person by a handshake, as well as using common objects with him in everyday life (door handles, toilet seats, dishes, etc.), if you do not wash your hands after contact. Therefore, personal hygiene should be paramount. Bathing on the sea or open water also carries the risk of infection with intestinal infections. Since there is no certainty that there was no infected person. Accidental swallowing of infected water is the shortest path to the disease. When poisoning with sea water, you should try to drink more liquid, and at least eat (only easily digestible products).
Before the arrival of the doctor, you need to know what to do and how to help the patient, when nausea, chills and diarrhea appear. First aid measures:
Such measures will not aggravate the condition before the arrival of the doctor, and help alleviate the symptoms of the disease. Traditional treatment of intestinal infectionsIn the acute course of the disease, hospitalization is extremely necessary. To learn how to treat, the doctor must conduct a comprehensive examination, a survey (to determine the cause of the poisoning of the body), to prescribe certain tests. For an accurate diagnosis, feces, urine, vomit, water that is collected after washing the intestines are examined. Only after identifying the cause of the disease treatment is prescribed. Therapy is usually aimed at neutralizing harmful bacteria, restoring water balance in the body and removing toxins. A gastric lavage is required, and vomiting is provoked. This helps cleanse the body of harmful substances. During treatment, sorbents are prescribed (Attapulgite, Smekta, Polyphepan). These drugs are aimed at neutralizing toxins, their excretion.
DietDuring diet therapy is very important. The patient should explain what you can eat, and he must follow the instructions of the doctor exactly. Rice and wheat cereals, cooked without salt, have a calming effect on irritated intestines. Rules of nutrition during treatment:
In complex therapy, rehydron solution is used. With it, you can restore electrolyte balance. The solution must be taken in several sips 1 time in 15–20 minutes. It is worth noting that quite often weakness after an intestinal infection is manifested in humans. This is due to the fact that the body was weakened by the disease, medical preparations and bed rest. To recover from an infection you need to know what to eat. Since the main factor here is the diet after the illness.
Eating in the first few weeks after the disease is little different from the diet during the illness. The only thing is that you can increase the dose of food intake. It is also necessary to give preference to homemade food, to abandon convenience foods and snacks on the go. Water should be boiled before drinking, and fruits and vegetables should be heat treated. Hygiene is an important factor. After each trip to the street, you should wash your hands with soap and water several times, and always before meals.
AntibioticsAntibiotics in treatment are prescribed in the case when the disease is in acute form, and the symptoms are pronounced. It is not recommended to take antibacterial drugs in the initial stages of infection, as they negatively affect the normal functioning of the intestine, and can harm its microflora. Self-medication with antibiotics is highly undesirable. They can appoint only a specialist. The most common and safest antibacterial drugs are Linex and Lactobacterin.
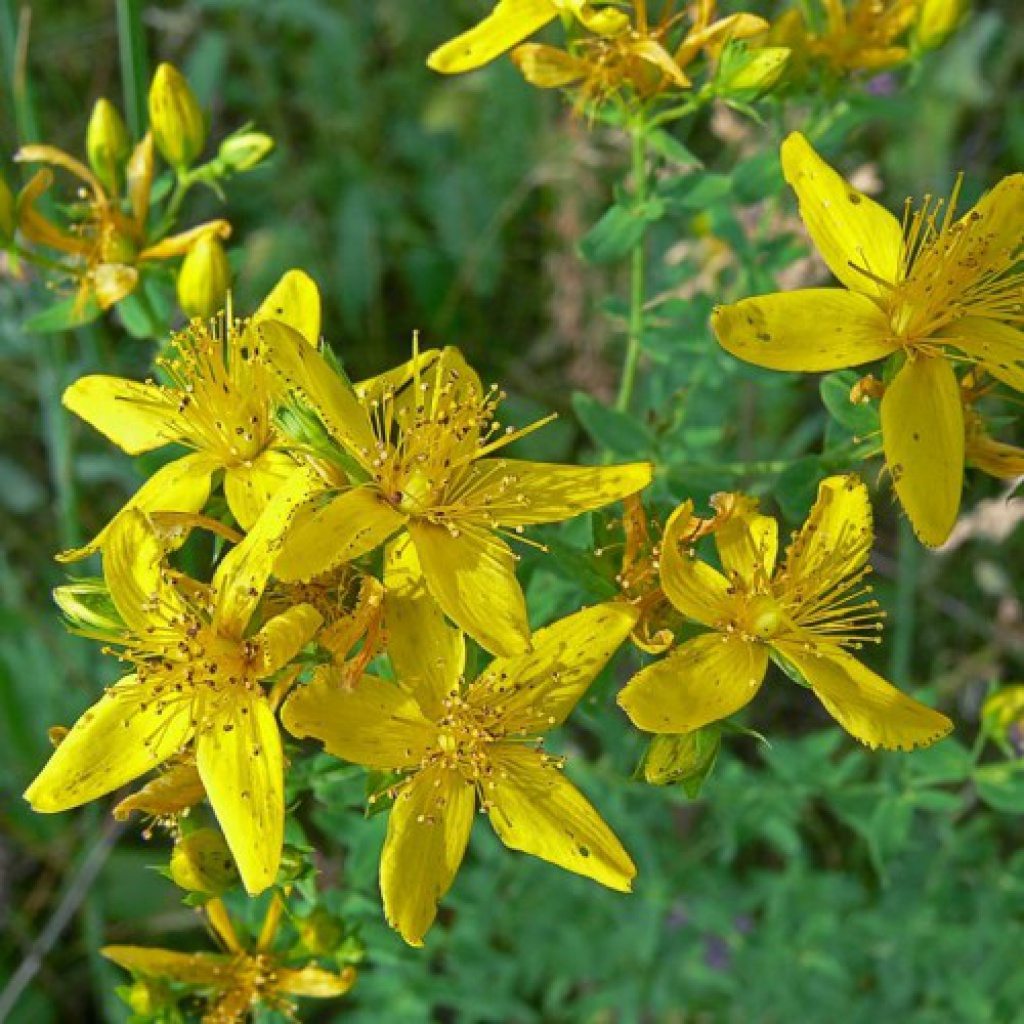
Treatment of folk remediesComprehensive treatment of the disease includes not only conservative therapy, but also the use of folk remedies. They complement each other, and increase the effectiveness of treatment. Hypericum at intestinal infection2 tbsp. l chopped herbs brew in two cups of boiling water and insist on the steam bath for about 30 minutes. Strain the broth, add water to the initial amount, and take a third of a glass for half an hour before meals.
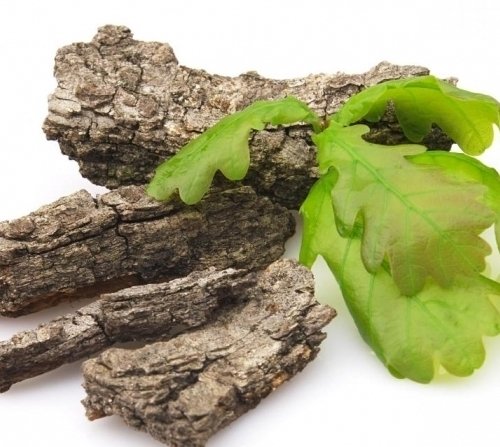
Oak bark decoctionIt is necessary to boil 1 l of water, add 50 g of chopped oak bark to it, and boil everything on a quiet fire for about 30 minutes. It is recommended to drink such broth at least 5–6 times a day.
Herbal collection against intestinal infectionIt is necessary to combine the potentilla root and nettle, add chopped alder cones (green). All components must be in equal quantities (2 tablespoons). Mix well and cook in 0.5 l of water in a water bath for about 10 minutes. The finished liquid must be filtered and cooled. Take a decoction of 0.5 st. before meals, and in the same proportion after meals.
The use of these recipes will not only alleviate the symptoms of the disease, but also help get rid of diarrhea, abdominal bloating, vomiting. Herbs have an anti-inflammatory and binding effect. Intestinal infection is a very insidious and dangerous disease. It can trap a person on the street, at sea, in everyday life. Pathology affects children, adults and the elderly. Where to expect it, you can not guess, but there are ways to warn yourself.
You can protect yourself from such a disease by adhering to the rules of hygiene, being careful in the use of certain products. If the infection got into the body, do not delay with self-treatment, you need to see a doctor. Timely pathology can cause much less damage to the body than a disease in the advanced stage. Adults and children suffer from intestinal infections. There are viruses that cause diarrhea: norovirus, astrovirus, rotavirus, coronavirus. Rotavirus and norovirus infections are common. Recently, rotavirus and norovirus were not separated, they were diagnosed with rotavirus infection. Kinds intestinal diseases similar, but different symptoms, the course of the disease. Norovirus infection was detected in the early 70s of the twentieth century in the United States. Infection occurs in public places (kindergartens, educational, entertainment), by contact, in the presence of a virus in the air. All people suffer with norovirus, children, people with reduced immunity suffer more heavily. 50% of infectious diseases in adults and 30% in schoolchildren are caused by noroviruses. Children up to seven years more often suffer from rotavirus. Norovirus infection is transmitted by the oral-fecal, respiratory routes. The virus is obtained through unwashed vegetables, fruits, boiled water, door handles, and a rim of a toilet bowl. Norovirus intestinal infection is contagious. The virus is resilient, not afraid of cold, hot temperatures; Killed with detergent disinfectants with chlorine. The person who has been ill has immunity to infection for up to 7-8 weeks. Rotavirus infection, intestinal flu - infectioncaused by rotavirus. Infections are sick adults, children. The patient is contagious during the entire period of the disease, about a week. The person who has recovered has immunity to rotavirus. The cause of infection - the use of unwashed vegetables, fruits, absorption of food with dirty hands. You can catch the infection through respiratory, coughing, runny nose. Rotaviruses tolerate cold, do not die in chlorinated water. Determination of the type of virusPatients do not immediately pay attention to the ailments in the gastrointestinal tract. The faster the diagnosis is made, the faster the recovery. To determine the difference between norovirus and rotavirus, the manifestations of ailments are described. Common signs of infectionSigns of rotavirus and norovirus infection:
Characteristic signs of infectionsIntestinal infections are confused. There are differences in determining the type of virus, prescription drugs. For intestinal flu or rotavirus is characterized by an acute manifestation of the disease - emetic urge, diarrhea, increased body temperature (more than 38-39 degrees). Infected people develop cold symptoms - sore throat, nasal congestion. Patients complain of weakness, aching joints, loss of appetite.
For norovirus is characterized by sluggish beginning. Appears to feel unwell during the first days after the defeat of the virus. Vomiting, frequent diarrhea, low temperature (37-37.5 degrees), chills, headache begin. Vomiting is observed, the infected writes off on the usual food poisoning. The infection passes on its own within 1-3 days, in severe cases - up to 7 days. Necessary measures when infected with virusesRotavirus and norovirus infections require a different treatment approach. With a mild course of norovirus infection, no medication is required. The virus passes by itself, without serious consequences. For patients - abundant use of water at room temperature, to prevent dehydration, rest. It is advisable to drink the liquid after each attack of diarrhea, follow a diet (chicken broth, fresh compote of dried apples). If the condition has improved, a diet is maintained for a couple of days. At home - to make a special solution for the normalization of water-salt balance. Take two tablespoons of sugar, one teaspoon of soda, one teaspoon of salt, pour a liter of warm boiled water. When norovirus infection antidiarrheal medications prohibited: cause serious consequences. With frequent vomiting, the doctor prescribes "Promethazin", "Ondansetron", "Prochlorperazin". In case of severe course of the patient, they are hospitalized, they are prescribed droppers with electrolytes: “Trisol”, “Disol”.
It is forbidden to include in the diet of lactic and lactic products: milk is the optimal medium for the reproduction of bacteria. With severe vomiting, diarrhea, intoxication is dangerous. Infected people are given a warm liquid, a special solution (a teaspoon of salt is poured with a liter of water). Food and water are often taken in small portions, so as not to provoke another attack of vomiting. Droppers with electrolytes prescribed for severe cases of dehydration. The doctor prescribes sorbents for removing toxins from the body: Enterosgel, Smekta, Activated carbon. With rotavirus infection It is recommended to take medication for diarrhea - Enterofuril is prescribed. To improve digestion, patients are prescribed "Pancreatin", "Mezim". Intestinal flu is accompanied by increased body temperature. Use of antipyretic drugs - if the patient does not tolerate temperatures up to 38 degrees: high temperature kills the virus. Use physical methods to reduce body temperature: washing with warm water, airing the room in the absence of the patient. With improved well-being, the patient is prescribed probiotics that restore the flora of the intestinal mucosa: Atsipol, Probifor, Linex. If norovirus with severe rotavirus, sign up for an infectious disease specialist. In the absence of complications, contact your local GP, a gastroenterologist.
In the post-infectious period, consult a nutritionist. The doctor will prescribe nutrition to normalize digestion. With treatment, follow the diet. Disease preventionIn case of infections, it is important to prevent the disease. Vaccination against intestinal infections of norovirus and rotavirus is not derived. It is recommended to comply preventive measures virus prevention: resilient. After buying products in the store, on the market, rinse under running water, pour over boiling water. Pay attention to the shelf life of lactic, lactic acid products: spoiled products may contain pathogenic microbes. Use boiled water for food. When you visit the pool, lake, river, do not swallow the water. If an infected person lives in the apartment, carefully observe hygiene. It is more correct to allocate to the patient a separate room. Wash the floor and surfaces touched by the patient with chlorine disinfectants daily. Wash clothes and bedding in a typewriter at a temperature of more than 60 degrees. It is important to seek treatment in medical institutions. Features of intestinal infections in a childParents are experiencing symptoms of intestinal infection in children every day. Kids more often suffer from rotavirus, older children - norovirus. Infection with infections occurs in public places (kindergarten, school, group of additional education) attended by the child.
Control is needed for children of preschool age - they take everything in their mouths. The task of parents is to instil in children the rules of personal hygiene from an early age to reduce the risk of infection. Parenting at the first sign of infectionAt the first signs of intestinal infections contact a pediatrician. Assign the appropriate treatment. In case of severe illness, immediately call an ambulance. It is forbidden to give painkillers to the child without a doctor’s appointment: the diagnosis will be erroneous. In children, the body is intoxicated faster. In case of illness of the child, be near, control well-being. When signs of illness occur, fluid is supplied to avoid dehydration. Liquid is offered in small portions (per teaspoon) with an interval of 15-20 minutes. Suitable drugs "Regidron", "Hydrovit", "Hydrovit Forte." Syfeps "Cefekon", "Nurofen" will help to bring down the increased temperature. Candles are ineffective in the presence of diarrhea. If rotavirus is detected, the pediatrician prescribes the course “Enterofuril” in the form of a suspension. Sparing dietObserve the diet: porridge on the water, compotes of dried fruit, crackers. If baby on breastfeedingdo not limit it. Thanks to breast milk, lactic acid bacteria enter the intestines of the child, helping to recover. Originally, the norovirus was called Norork, Ohio, where in November 1968 an outbreak of acute gastroenteritis was registered among schoolchildren in a primary school. In 1972, as a result of immuno-electronic microscopy of canned feces samples, a virus was discovered, which was called Norwalk virus. The cloning and sequencing of the Norwalk virus genome has shown that these viruses have the same genomic organization as the Caliciviridae viruses. The name Norovirus (genus Norovirus) was approved by the International Committee on Virus Taxonomy in 2002. EtiologyThe genome of norovirus is a single-stranded RNA. The virus contains 5 active proteins, the main structural protein (VP1) within 58 ~ 60 kDa and the minor capsid protein (VP2). When viewed through an electron microscope, viral particles exhibit an amorphous surface structure, the size of viral particles is between 27-38 nm. Noroviruses have 5 genogroups (GI, GII, GIII, GIV and GV). Genogroups I, II, and IV cause disease in humans, and genogroup III in cattle. Genogroup V has recently been found in mice. EpidemiologyNoroviruses are transmitted by direct contact with the patient or indirectly through infected food, water, household items. A person can release a virus up to 1 month after recovery. Clinical pictureThe incubation period for norovirus infection is from several hours to 2 days. The disease manifests itself in the form of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea up to 8-10 times a day, pain in the abdomen, sometimes - loss of taste sensitivity, increase in body temperature to 37.5-38 ° C, symptoms of general intoxication, manifested by weakness and pallor skin integument. Vomiting is the leading symptom of norovirus infection. The state of health is normalized within 2-5 days. Treatment of acute intestinal infections in childrenDiet therapy In recent years, approaches to diet therapy have changed. Nutritional therapy is a constant and important component of diarrhea therapy at all stages of the disease. Fundamentally an important point in the organization of nutrition of sick children is the refusal to conduct water-tea pauses, because even with severe forms of diarrhea, the digestive function of most of the intestines is proved, and starvation diets help slow down the repair processes, reduce the intestinal tolerance to food, contribute to malnutrition and significantly weaken body defenses. The volume and composition of food depends on the age, body weight of the child, the severity of diarrheal syndrome, the nature of previous diseases. Good nutrition is important for the rapid restoration of bowel function. In the acute period of gastroenteritis, it is recommended to reduce the daily amount of food by 1 / 2-1 / 3, in the acute period of colitis - by 1 / 2-1 / 4. It is possible to increase the multiplicity of feedings up to 8-10 times per day for infants and up to 5-6 times for older children, especially with the urge to vomit. At this time, the most physiological is considered an early, gradual resumption of nutrition. Renewal of the qualitative and quantitative composition of the food characteristic of the child’s age is carried out as soon as possible after the rehydration and the disappearance of the signs of dehydration. It is believed that early resumption of the normal diet together with oral rehydration helps to reduce diarrhea and more rapid bowel repair. Rehydration therapy The content of sodium and potassium in solutions for oral rehydration should correspond to their average loss in acute intestinal infections. The concentration of glucose in them should contribute to the resorption of water not only in the intestine, but also in the tubules of the kidneys. Optimal absorption of water from the intestinal cavity is carried out from isotonic and light hypotonic solutions with an osmolarity of 245-250 mosmol / l. Method of oral rehydration Determination of fluid deficiency during dehydration There is a simpler and more affordable way to determine the severity of dehydration recommended by WHO. The amount of fluid required for dehydration is calculated, depending on the degree of exsiccium. As a rule, oral rehydration without the use of infusion therapy is sufficient for rehydration of patients with exsiccosis of grade 1–2. After 4-6 hours after the start of treatment, it is necessary to evaluate the effect of therapy and choose one of the following options: Parenteral rehydration A parenteral rehydration therapy program should take into account The principle of calculating the volume of infusion therapy for rehydration Physiological needs of the child for fluid An example of the calculation of the physiological fluid demand by the Holiday-Segar method: in a child weighing 28 kg, the daily physiological fluid demand is: (100 ml X 10 kg) + (50 ml X 10 kg) + (20 ml X 8 kg) = 1660 ml / day. Current pathological losses are determined by weighing dry and used diapers, diapers, determining the amount of vomit, or by means of the following calculations: Calculation of the need for salts in exsicosis Electrolyte deficiency recovery Next, it is necessary to determine and take into account the amount of sodium and potassium in solutions that overflow, the volume and ratio of which have already been calculated. After emergency intravenous rehydration, it is necessary to check the level of sodium and potassium in the blood plasma. Considering the importance of magnesium ions for the child’s body, as well as the loss of magnesium in parallel with the loss of potassium, the first stage of rehydration therapy shows the introduction of a 25% solution of magnesium chloride at a dose of 0.5-0.75 mmol / kg body weight (1 ml solution contains 1 mmol of magnesium). Isotonic type. It develops with the uniform elimination of water and electrolytes from the body of the patient. This kind of exsicosis, most often, occurs in children with acute intestinal infections. Hypertensive type.Sodium content in blood plasma - more than 150 mmol / l. It develops as a result of the predominance of fluid loss over the loss of salts with stools, vomiting, with an excessively rapid introduction of salts against the background of an insufficiently introduced amount of liquid. Clinically, it is manifested by thirst, aphonia, crying without tears. Fabric turgor saved. The skin is dry, warm, in young children a large fontanel does not sink as a result of an increase in the volume of cerebrospinal fluid. In severe cases, an increase in osmotic concentration of cerebrospinal fluid can lead to seizures. Hypotonic type. Sodium content in blood plasma is less than 130 mmol / l. The reason for this is the predominance of salt loss over the liquid, or the excessive introduction of water without an adequate amount of salt. It occurs at intestinal infectionswhich are accompanied by frequent vomiting or during oral rehydration with solutions that contain insufficient amounts of salts. Observation of the child during rehydration therapy, if necessary, to conduct rapid rehydration, is as follows: After the entire volume of fluid is injected, the condition is again evaluated: Antibacterial therapy Indications for the appointment of antibiotics for OCI Indications for parenteral administration of antibiotics Adjuvant therapy |
| Read: |
|---|
New
- Which leaves blush first in autumn
- Sequence of procedures
- The program of intensive moisturizing of the skin on cosmetics bark
- What you need for acrylic powder
- What does owl mascot mean
- Analyzes for pancreatitis: what research should be done and what indicators show
- Owl - a talisman to attract money and good luck
- What bird screams at night with a kitten's voice?
- Cholesterol and stress
- Manicure at home

 Noroviruses, like rotoviruses, are considered the main causative agents of all intestinal infections. Rotavirus and norovirus were not initially distinguished, so patients in all cases were diagnosed with “rotavirus infection”. In 1972, thanks to a series of genetic studies, norovirus was isolated as a separate group. It was found that this pathogen belongs to the family Caliciviridae.
Noroviruses, like rotoviruses, are considered the main causative agents of all intestinal infections. Rotavirus and norovirus were not initially distinguished, so patients in all cases were diagnosed with “rotavirus infection”. In 1972, thanks to a series of genetic studies, norovirus was isolated as a separate group. It was found that this pathogen belongs to the family Caliciviridae. Infectious disease begins after the penetration of norovirus into the organism. There are three mechanisms of transmission of this infection:
Infectious disease begins after the penetration of norovirus into the organism. There are three mechanisms of transmission of this infection:
 When the first symptoms of norovirus infection appear, a number of actions can be taken that will slightly alleviate the patient's condition:
When the first symptoms of norovirus infection appear, a number of actions can be taken that will slightly alleviate the patient's condition: With norovirus, it is important to maintain the electrolyte balance in the body and recuperate the patient.. For this, a strong decoction of rice with raisins is suitable. Two tablespoons of pure rice is poured with a liter of water and brought to a boil. Add a tablespoon of washed raisins and simmer for half an hour.
With norovirus, it is important to maintain the electrolyte balance in the body and recuperate the patient.. For this, a strong decoction of rice with raisins is suitable. Two tablespoons of pure rice is poured with a liter of water and brought to a boil. Add a tablespoon of washed raisins and simmer for half an hour.