|
Diabetes mellitus: causes, forms, symptoms and signs Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease of the human endocrine system, characterized by a prolonged increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood and concomitant changes in the metabolic process. The basis of the development of diabetes is the insufficiency of the pancreatic hormone insulin, which controls the processing of glucose at the level of cells and tissues of the body. The cause of diabetes can be the destruction of pancreatic cells that produce insulin or a change in the sensitivity of body tissues to insulin circulating in the blood. There are two main types of diabetes: Type 1 diabetes (insulin-dependent diabetes) and Type 2 diabetes (non-insulin-dependent diabetes). The main symptoms of diabetes without treatment are strong thirst, an increase in the amount of urine released, weight loss, etc. What diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus is a disease characterized by a chronic increase in blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia), which develops as a result of insufficient production (secretion) of insulin or a decrease in the sensitivity of the body's cells to insulin. Diabetes occurs in about 1-3% of the population. In children, the frequency of diabetes is lower: 0.1-0.3%. Every year the number of patients with diabetes mellitus increases by 6-10%. This leads to a doubling of the number of patients every 10-15 years. For the year 2000, there were more than 120 million patients with diabetes. Currently, the number of patients with diabetes exceeds 200 million. What are the risk factors for diabetes? There are certain conditions or diseases that predispose to the development of diabetes (risk factors). The risk factors for diabetes are as follows: The combination of several risk factors significantly (up to 30 times) increases the risk of developing diabetes.
What is insulin?
Insulin is a hormone (biologically active substance) of the pancreas that controls the concentration of glucose (sugar) in the blood. In humans, food is broken down in the intestine to various substances, including glucose, necessary for the body to work. From the intestine, glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. High blood sugar after a meal stimulates the secretion of insulin by the pancreas. Insulin helps glucose from the blood into the cells of our body, and, therefore, reduces the concentration of glucose in the blood. Without insulin, some cells in our bodies are completely unable to absorb glucose from the blood. In the cells of the human body, glucose is stored or immediately transferred to energy, which is used for the needs of the body. The level of glucose in the blood varies throughout the day and depending on the meal. After eating, the glucose level rises and gradually normalizes within 2 hours after eating under the influence of insulin. As a rule, when glucose normalizes, insulin secretion (excretion) decreases by the pancreas. If the body does not produce enough insulin, the body's cells lose their ability to absorb glucose, which accumulates in the blood. An increase in blood sugar concentration leads to diabetes symptoms and its complications.
Causes of diabetes There are the following causes of diabetes: Viral infections that destroy pancreatic cells that produce insulin. Among the viral infections that can cause the development of diabetes can be listed: rubella, viral parotitis (mumps), chicken pox, viral hepatitis, etc. Some viral infections have a high affinity for pancreatic cells and are often complicated by diabetes. For example, the incidence of diabetes in people who have had rubella is 20% or more. It must be emphasized that viral infection manifests its effect in individuals with a hereditary predisposition to diabetes. Especially often a viral infection causes diabetes in children and adolescents (See). Hereditary factor. As a rule, diabetes is several times more common in relatives of patients with diabetes. If both parents are sick with diabetes, the risk of having diabetes for their children is 100% throughout their lives, one parent ate 50%, and 25% in the case of diabetes with a brother or sister. Regarding the development of type 1 diabetes, one important fact should be mentioned, namely: even in the presence of a genetic predisposition, diabetes mellitus may not develop. The probability that a parent with type 1 diabetes mellitus will pass a defective gene to a child is very small (4%). There are cases when only one of the two twins fell ill with diabetes, and the other remained healthy. Even in the presence of factors predisposing to the development of type 1 diabetes, the disease may never occur if a person does not have a certain viral infection. Autoimmune diseases (an attack of the body’s immune system on the body’s own tissues) - glomerulonephritis, autoimmune thyroiditis, hepatitis, lupus, etc., can also be complicated by diabetes. In this case, diabetes develops due to the destruction of pancreatic cells that produce insulin, the cells of the immune system. Overeating (increased appetite) leading to obesity is one of the main factors in the development of type 2 diabetes. If among persons with normal body weight, the incidence of diabetes is 7.8%, then with an excess of body weight by 20%, the frequency of diabetes is 25%, and with an excess of body weight by 50%, the frequency is 60%. By reducing body weight by 10% through diet and exercise, it is possible to significantly reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
Classification of diabetes. How can diabetes be? The WHO (World Health Organization) identifies 2 types of diabetes mellitus: Type 2 diabetes, in turn, is divided into diabetes in people with normal body weight and diabetes in people with obesity. According to the research of some specialists, they distinguish such a state as prediabetes. Pre-diabetes is a condition in which human blood sugar levels are above normal, but not high enough to state the presence of diabetes (glucose levels between 101 mg / dl and 126 mg / dl (slightly above 5 mmol / l)). In most cases, without proper treatment prediabetes (latent diabetes) becomes diabetes. On the other hand, the timely detection of pre-diabetes and the adoption of measures for its correction significantly reduces the risk of developing diabetes. Also described is such a form of diabetes as gestational diabetes, that is, diabetes mellitus, which develops during pregnancy and may disappear after childbirth. What is type 1 diabetes? In type 1 diabetes mellitus (insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus), more than 90% of the pancreatic cells that secrete insulin are destroyed for one reason or another. The cause of the destruction of pancreatic cells can be viruses, autoimmune diseases, etc. (see the causes of diabetes mellitus). Thus, in patients with type 1 diabetes, the pancreas secretes less insulin or does not release insulin at all. Of the total number of people with diabetes, type 1 diabetes occurs in 10% of cases. In most people with type 1 diabetes, the onset of the disease most often comes to 30 years. Scientists believe that viral infection is of paramount importance for this type of diabetes. The important role of the infection is that it not only has a direct destructive effect on pancreatic cells, but also causes the human immune system to destroy its own pancreatic cells that produce insulin (antibodies against pancreatic b-cells are determined in the blood of patients with type 1 diabetes) producing insulin). Patients with diabetes mellitus type 1 in the literal sense of "depend" on insulin, which is necessary for them to ensure the normal digestion of glucose in the body. The name of the disease comes from this dependence: insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. What is type 2 diabetes?
In type 2 diabetes mellitus (insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus), the pancreas continues to secrete insulin, sometimes even more than is necessary. However, in the human body, for some reason, cell resistance (insulin sensitivity) develops. Thus, the right amount of glucose does not get into the cell, even with a large amount of insulin. The debut of the disease most often occurs after 30 years. Hereditary factors and obesity play an important role in the development of type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes can develop if some are misused. medicines (for example, corticosteroids in Cushing's syndrome), as well as in some other endocrine diseases (acromegaly, Cushing's disease, etc.).
|
Criterion
|
Type 1 diabetes
|
Type 2 diabetes
|
| Diabetes Debut |
|
|
| Obesity |
|
|
| The appearance of the first symptoms of the disease |
Within weeks or months after onset
|
For several years after the onset of the disease
|
| Insulin concentration in plasma. |
Very low
|
Varies; may be low, normal or high.
|
| The presence of antibodies to pancreatic b-cells |
|
|
| Complications (retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy). |
|
|
Symptoms and signs of diabetes. Both types of diabetes have similar symptoms. The first symptoms of diabetes, as a rule, appear due to the high level of glucose in the blood. When the concentration of glucose in the blood reaches 160-180 mg / dl (above 6 mmol / l), it begins to enter the urine. Over time, when the patient's condition deteriorates, the level of glucose in the urine becomes very high. As a result, the kidneys excrete more water in order to dilute the enormous amount of glucose excreted in the urine. Thus, polyuria is the initial symptom of diabetes mellitus (the release of more than 1.5-2 liters of urine per day). The next symptom, which is the result of frequent urination, is polydipsia (constant thirst) and drinking large amounts of fluid. Due to the fact that a large number of calories are lost in the urine, people lose weight. As a result, people experience a feeling of hunger (increased appetite). Thus, the classic triad of symptoms is characteristic for diabetes mellitus: Also, each type of diabetes has its own characteristics. For people with type 1 diabetes, as a rule, the first symptoms occur suddenly, in a very short period of time. And such a condition as diabetic ketoacidosis (see) can develop very quickly. In patients with type 2 diabetes, for a long time the disease is asymptomatic. Even if there are certain complaints, their intensity is negligible. Sometimes on early stages Development of type 2 diabetes mellitus blood glucose can be lowered. This condition is called hypoglycemia. Due to the fact that there is a certain amount of insulin in the human body, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, ketoacidosis usually does not occur in the early stages. Other, less specific signs of diabetes mellitus can be: Patients with type 2 diabetes often find out about their illness by chance, several years after its onset. In such cases, the diagnosis of diabetes is established either on the basis of determining an elevated blood glucose level, or on the basis of the presence of diabetes complications. Every year the number of people with a diagnosis of diabetes is growing steadily. Pathology is determined at the later stages, so it is completely impossible to get rid of it. Early disability, the development of chronic complications, high mortality - this is what is fraught with the disease.
Diabetes has several forms, can occur in the elderly, pregnant women and even children. All the symptoms and signs of pathological conditions are united by one thing - hyperglycemia (elevated numbers of glucose in the blood), which is confirmed by laboratory methods. In the article we will consider at what level of blood sugar the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus is made, what are the criteria for confirming the severity of the disease, with which pathologies a differential diagnosis of the disease is carried out.
What is the disease and why does it occur
Diabetes mellitus is considered a chronic pathology that occurs against the background of the lack of sufficient production of the hormone insulin or dysfunction of its functions in the human body. The first option is characteristic of type 1 disease - insulin-dependent. For a number of reasons, the pancreas insular apparatus is unable to synthesize the amount of hormonally active substance that is necessary for the distribution of sugar molecules from the bloodstream into the cells at the periphery.
Important! Insulin provides glucose transport and "opens" the door to it inside the cells. This is important for the receipt of a sufficient amount of energy resources.
In the second variant (non-insulin-dependent diabetes), the gland produces enough hormone, but its effect on cells and tissues does not justify itself. The periphery simply "does not see" insulin, which means that sugar with its help cannot enter the cells. The result is that the tissues experience energy hunger, and all the glucose remains in the blood in huge quantities.
The causes of the insulin-dependent pathology are:
- heredity - if there is a sick relative, the chances of “getting” the same disease increase several times;
- diseases of viral origin - we are talking about parotiditis, Coxsackie virus, rubella, enterovirus;
- the presence of antibodies to pancreatic cells that are involved in the production of the hormone insulin.
Type 1 "sweet disease" is inherited by the recessive type, type 2 - by the dominant
Type 2 diabetes has a larger list possible reasons. These include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- high body weight - a factor especially scary when combined with atherosclerosis, elevated blood pressure numbers;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- violation of the rules of healthy eating;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system in the past;
- the constant impact of stress;
- long-term treatment with certain medications.
Gestational form
The diagnosis of gestational diabetes form is made to pregnant women in whom the disease arose against the background of their “interesting” position. Expectant mothers face pathology after the 20th week of carrying a baby. The mechanism of development is similar to the disease of the second type, that is, the pancreas of a woman produces a sufficient amount of a hormonally active substance, but the cells lose their sensitivity to it.
Important! After the baby is born, diabetes disappears on its own, the mother’s body is restored. Only in extreme cases, the transition of the gestational form to type 2 disease is possible.
Diagnostic criteria for disease in non-pregnant patients
There are a number of indicators on the basis of which confirm the diagnosis of diabetes:
- The level of sugar in the bloodstream, which is determined by taking a biomaterial from a vein after 8 hours of fasting (i.e. fasting), is higher than 7 mmol / l. If we talk about capillary blood (from a finger), this figure is equal to 6.1 mmol / l.
- The presence of clinical signs and complaints of the patient in combination with glycemic numbers above 11 mmol / l in the collection of material at any time, regardless of food intake.
- The presence of glycemia more than 11 mmol / l on the background of the test with sugar load (GTT), namely 2 hours after drinking a sweet solution.

GTT is performed by taking venous blood before and 1–2 hours after consuming the solution with glucose powder.
What is HbA1c and for what purpose is it defined?
HbA1c is one of the criteria that allows you to establish the presence of diabetes. This is glycated (glycosylated) hemoglobin, showing the average number of glycemia over the last quarter. HbA1c is considered to be an accurate and reliable criterion confirming the presence of chronic hyperglycemia. With it, you can also calculate the risk of developing complications of a “sweet disease” in a patient.
For the diagnosis of diabetes:
- The diagnosis is established if the numbers are above 6.5%. In the absence of symptoms of the disease, it is necessary to repeat the analysis in order to make sure that the previous result was not false positive.
- The analysis is carried out in children with suspected endocrine pathology, which is not confirmed by a vivid clinical picture and high glucose level according to the results of laboratory diagnostics.
To determine the group of patients who are at high risk of developing the disease:
- Patients who have signs of impaired glucose tolerance should be tested, because a simple blood test for sugar is not able to display the continuity of the disease.
- The analysis is prescribed to patients in whom the previous evaluation result of glycosylated hemoglobin was in the range of 6.0-6.4%.
Patients who do not suffer from the specific symptoms of diabetes should be tested in the following situations (as recommended by international experts):
- high body weight in combination with a sedentary lifestyle;
- the presence of close relatives of the insulin-dependent form of the disease;
- women who gave birth to a baby weighing more than 4, 5 kg or had established gestational diabetes during pregnancy;
- high blood pressure;
- polycystic ovary.

Such a patient should go to an endocrinologist for diagnosis.
Important! All patients older than 45 years old without the presence of the above conditions must undergo an analysis to assess the level of glycated hemoglobin.
How to diagnose pregnant?
There are two options for the development of events. In the first case, the woman bears a child and has a pregestational form of the disease, that is, she developed a pathology even before the onset of conception (although she can learn about the presence of diabetes during pregnancy). This form is more dangerous both for the mother's body and for her baby, since it threatens with the development of congenital anomalies on the part of the fetus, independent termination of pregnancy, stillbirth.
The gestational form occurs under the action of placental hormones, which reduce the amount of insulin produced and reduce the sensitivity of cells and tissues to it. All pregnant women for 22–24 weeks are tested for glucose tolerance.
It is conducted as follows. A woman takes blood from a finger or vein, provided that she has not eaten anything in the past 10-12 hours. Then she drinks a glucose-based solution (powder is purchased at pharmacies or obtained in laboratories). For an hour, the expectant mother should be at rest, not walk much, do not eat anything. After the time, blood is taken according to the same rules as the first time.
Further for another hour, the subject does not eat, avoids stress, elevation of steps and other loads, and again the biomaterial is collected. The result of the analysis can be found out the next day from the attending physician.
The gestational type of the disease is established on the basis of two phases of the diagnostic search. Phase I is carried out at the first visit of a woman to the gynecologist for registration. The doctor prescribes the following tests:
- assessment of sugar in venous blood on an empty stomach;
- random determination of glycemia;
- glycated hemoglobin level.
Diagnose gestational diabetes mellitus with the following results:
- blood sugar from a vein - 5.1-7.0 mmol / l;
- glycated hemoglobin - more than 6.5%
- random glycemia - above 11 mmol / l.
Important! If the numbers are higher, this indicates the presence of newly detected pregestational diabetes mellitus in a pregnant woman that existed even before the conception of the baby.
Phase II is carried out after 22 weeks of gestation, is to assign a test with sugar load (GTT). When what indicators confirm the diagnosis of gestational form:
- glycemia on an empty stomach - above 5.1 mmol / l;
- at the second blood sampling (in an hour) - above 10 mmol / l;
- at the third intake (after another hour) - above 8.4 mmol / l.
If the doctor has determined the presence of a pathological condition, an individual treatment regimen is selected. As a rule, insulin therapy is prescribed for pregnant women.
Diagnosis of type 2 diabetes in children
- the presence of an insulin-independent form of pathology in one or several close relatives;
- race to high risk of developing the disease;
- the presence of high blood pressure, high numbers of cholesterol in the blood;
- maternal gestational diabetes in the past.
The large weight of the child at birth is another reason to diagnose the disease during puberty
Diagnosis must begin with the age of 10 and repeat every 3 years. Endocrinologists recommend researching fasting glucose numbers.
Criteria for determining the severity of the disease
If diabetic pathology is diagnosed, the doctor should clarify its severity. This is important for monitoring the patient’s condition over time and for selecting the right treatment regimen. Mild diabetes is confirmed when the sugar figures do not cross the threshold of 8 mmol / l, and in the urine it is completely absent. Compensation of the state is achieved by adjusting the individual diet and active lifestyle. Complications of the disease are absent or the initial stage of vascular lesion is observed.
Medium severity is characterized by glucose numbers up to 14 mmol / l, a small amount of sugar is observed in the urine. Already, ketoacidosis can occur. One diet to keep the level of glycemia will not work. Doctors prescribe insulin therapy or receive tablets with antihyperglycemic drugs.
Against the background of severe hyperglycemia is diagnosed with numbers above 14 mmol / l, a significant amount of glucose is detected in urine. Patients complain that their sugar levels often jump, and ketoacidosis appears, both up and down.
Important! Experts diagnose pathological changes of the retina, renal apparatus, cardiac muscle, peripheral arteries, nervous system.
Differential diagnostics
Based on laboratory and instrumental studies, it is important to conduct a differential. diagnostics not only between diabetes and other diseases, but also forms of the “sweetest disease” itself. A differential diagnosis is made after comparison with other pathologies based on the main syndromes.
By the presence of clinical signs (pathological thirst and heavy discharge urine) need to distinguish the disease:
- from diabetes insipidus;
- chronic pyelonephritis or kidney failure;
- primary hyper aldosteronism;
- parathyroid hyperfunctions;
- neurogenic polydipsia and polyuria.
For high levels of sugar in the bloodstream:
- from steroid diabetes;
- itsenko-Cushing syndrome;
- acromegaly;
- adrenal tumors;
- neurogenic and food hyperglycemia.
Pheochromocytoma is one of the states with which differential diagnosis is needed.
By the presence of glucose in urine:
- from intoxication;
- pathologies of the kidneys;
- glycosuria of pregnant women;
- food glucosuria;
- other diseases in which hyperglycemia is present.
There is not only medical, but also nursing diagnosis. It differs from those put by specialists in that it includes not the name of the disease, but the main problems of the patient. On the basis of a nursing diagnosis, nursing staff performs proper care for the patient.
A timely diagnosis allows one to select an adequate treatment regimen, which will make it possible to quickly reach a compensatory state and prevent the development of complications of the disease.
One of the most common diseases of the endocrine system is diabetes, the symptoms and manifestations of which are associated with an increase in blood glucose and urine levels, impaired carbohydrate metabolism, and other metabolic dysfunctions in the body. The disease is caused by absolute or relative lack of insulin - a hormone produced by the pancreas. Causes of Diabetes
The main cause of diabetes mellitus type I is an autoimmune process that arises due to disruption in the immune system. In the event of a malfunction in the body, antibodies are synthesized that negatively affect (inhibit and destroy) the pancreatic cells. To provoke the development of the disease against the background of a hereditary factor can be diseases caused by viruses, in particular: hepatitis, rubella, epidemic parotitis, measles, etc. Most often, diabetes mellitus type II develops against a background of genetic predisposition and. It turns out that in people with these factors the risk of getting diabetes is 5-6 times higher than in others. When the insulin-independent form of manifestation is not so pronounced, the disease develops slowly, and the symptoms are aggravated with increasing insulin deficiency. The main risk factors for the development of diabetes mellitus:
- genetics (heredity);
- obesity;
- carbohydrate food abuse;
- infectious diseases;
- pancreatitis and other diseases of the pancreas;
- all diseases of the endocrine organs;
- liver diseases, including hepatitis;
- gout, etc.
There are 2 types of diabetes:
In type I diabetes, the metabolic imbalance is compensated by regular insulin injections. In type II diabetes, the patient is prescribed oral hypoglycemic agents. Be sure to follow a diet, because without therapeutic menu therapy gives minimal results. In the mild stage of type II, the need for insulin and glucose-lowering drugs can be minimized with a carefully thought-out diet and moderate exercise, but this should be done only under medical supervision.  Diet for diabetes Diet for diabetes
1.
Meals should be 5-6-time, fractional, i.e. in small portions. 2.
The amount of carbohydrates, especially easily digestible, is limited. 3.
Calorie intake is reduced. 4.
Food should contain high doses of vitamins. 5.
Avoid overeating. 6.
Nutritionists prescribe a therapeutic menu depending on body weight, blood glucose level indicators and individual patient characteristics. 7.
In no case can not take diuretics (diuretics). 8.
The following types of products are excluded: smoked foods, alcoholic beverages, canned and pickled foods, spices, spices and hot peppers. Home events required by the patient:
- control of blood sugar with a glucometer;
- control of cholesterol in the blood (testing);
- following a diet prescribed by a doctor;
- intake of prescribed drugs without gaps.
Products that reduce the level of glucose:
1. Baked onions.
To normalize sugar, especially in the initial phase of the disease, you can use daily consumption of baked onions in the morning on an empty stomach. The result can be traced after 1-1.5 months. 2. Mustard seeds.
½ a coffee spoon of seeds eaten daily not only reduces the level of sugar, but also normalizes the processes of digestion, relieves constipation and flatulence, activates bile secretion. 3. Flax seeds.
Have all the listed properties of mustard seeds. They are a natural source of essential fatty acids. Eat in the form of a hammer on 1-3 tbsp. spoons daily. To prevent oxidation, grind immediately before use. 4. Bay leaf.
10 medium leaves are steamed in a thermos with a glass of boiling water, insisting 24 hours. Take in the form of heat 50 ml 4 times a day, filtering directly from the thermos. The course of treatment is from 3 to 6 days. 5. Sophora Japanese.
Alcohol tincture Plants helps with diabetes: 2 tbsp. place the spoons of seeds in a glass bottle, pour ½ liter of high-quality vodka (it can be replaced with distilled water diluted in half with medical alcohol), seal tightly, insist in a dark place for about 30 days, occasionally stirring the medication. Strained tincture take 5 ml (1 teaspoon) 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 1 month. 6. Blueberries. Use fresh and dried berries as well as leaves. medicinal plant. Infusion is prepared as follows: 1 tbsp. a spoonful of fresh (1 teaspoon dried) pour 250 ml of hot water, put on the fire, bring to a boil, remove, wrap and insist about 2 hours. Take the composition hot, a glass, 3 times a day instead of tea. The course of treatment in compliance with the diet is six months. During this time, sugar completely returns to normal. 7. Oak acorns.
The dried oak fruit is ground into a powder grinder. Take 1 teaspoon three times a day, before meals, with half a glass of green tea or boiled water. 8. Lime-rowan tea.
½ cup dried rowan fruits and the same amount lime blossom boil 1 liter of boiling water, boil in an enamel saucepan on low heat for 3 minutes, let stand for about 50 minutes. Take 1/2 cup 3 times a day. The course of treatment is unlimited. 9. Lilac buds.
The infusion of lilac buds helps normalize blood glucose levels. At the end of April, the kidneys are harvested in the swelling stage, dried, stored in a glass jar or paper bag and used year round. Daily rate infusion: 2 tbsp. spoons of dry raw materials pour 0.4 liters of boiling water, insist 5-6 hours, filter, divide the resulting liquid 4 times and drink before meals. Applying folk remedies, be careful. Be sure to consult with a specialist watching you, do not self-medicate. Remember that timely diagnosis and adherence to prescribed therapy is the key to your well-being. Be healthy!
Diabetes mellitus is a disease of the endocrine system, which is characterized by impaired metabolism, especially carbohydrate metabolism. In people with diabetes, because of a lack of insulin, the blood contains an elevated glucose concentration. ClassificationWhy does diabetes develop and what is it? The disease is divided into 2 types: 1) (type I) develops due to insulin deficiency. The cells of the pancreas as a result of damage lose their ability to produce insulin or produce it in insignificant concentrations. Thin people younger than 30 years are ill more often. 2) (type II) is characterized by loss of insulin sensitivity, although the pancreas produces a sufficient and even excess amount of insulin. Mostly obese people over 30 are ill. Diabetes is:
- 1) Mild (no complications observed);
- 2) moderate degree (affects the eyes, kidneys and nerves);
- 3) Severe (there are a huge number of highly developed complications).
Causes of DiabetesInsulin-dependent diabetes is most often formed as a result of viral infections, autoimmune diseases, stressful situations. The development of insulin-dependent diabetes is mainly promoted by obesity, a sedentary lifestyle and unhealthy diet. The main cause of diabetes is a genetic predisposition. Also call it help: - overweight;
- pancreatic diseases;
- autoimmune disorders;
- diseases of the vascular system;
- nervous stress;
- injuries;
- viral infections;
- elderly age;
- hormonal disorders.
Symptoms of diabetes: the first signs As a rule, diabetes mellitus develops unnoticed and gradually in women and men, so it is very difficult to detect symptoms in the initial stage. As a rule, diabetes mellitus develops unnoticed and gradually in women and men, so it is very difficult to detect symptoms in the initial stage. For accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to pass the appropriate tests, the rate of glucose in the blood is 3.5-6.5 mmol per liter. If you find yourself in the first few signs that are presented below: consult your doctor, or check your blood sugar level yourself. Symptoms common for diabetes Type 1: - polyuria - excessive urination;
- polydipsia - a feeling of constant thirst;
- dramatic weight loss, accompanied by excessive appetite.
Also the following signs can be added to: - feeling weak;
- impotence;
- numbness of the limbs;
- heaviness in the legs;
- slow cure of infectious diseases;
- slow wound healing;
- rapid fatigue;
- sleep disturbance;
- irritability and nervousness;
- the appearance in the mouth of iron taste;
- furunculosis;
- heartache.
Diabetes Type II mostly asymptomatic, but you may experience the above symptoms. Read also - how to measure the level of sugar at home.

Complications of diabetesDiabetes mellitus is especially dangerous with complications that always accompany the course of the disease. No wonder diabetes is called a disease of complications. Complications arise from the fact that all the organs along with the blood constantly receive a lot of sugar, causing changes in the cells and tissues. Therefore, diabetics should constantly monitor blood glucose levels. Frequent and sharp fluctuations in glucose concentration increase the risk of complications. It is difficult to prevent complications by the fact that they develop gradually (over 10-15 years) and do not manifest themselves for a long time. Most of all changes concern vessels, especially those. that are found in the fundus, kidneys, legs, heart and brain. In order to identify complications in time, all patients with diabetes need to be examined annually by an ophthalmologist, have a urine test for protein (to detect kidney disease), monitor blood pressure and fat metabolism. All occurring complications can be divided into 2 groups:
- 1) Acute, which quickly appear and lead to a comatose state;
- 2) Chronic, appearing after quite a long time.
TO acute complications Carry a diabetic coma: - ketoacidosis or diabetic ketoacidosis;
- hyperosmolar;
- hyperglycemic;
- lactic acidosis.
Diabetic coma is the most dangerous complication of diabetes caused by poisoning the body with products of incomplete fat breakdown.
It is characterized by the fact that acetone is excreted through urine and through the lungs, appetite disappears, weakness, nausea, vomiting and drowsiness appear. If the patient does not receive the necessary help in time, then he loses consciousness and falls into a coma. TO chronic complications belongs to a very large number of diseases that can be divided into groups, depending on the location: Eye diseases: - diabetic retinopathy - lesions of the fundus vessels;
- retinal detachment;
Diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract;- diabetic nephropathy - kidney vascular lesions;
- cm. ;
Diseases of the cardiovascular system:- diabetic angiopathy - lesions of the vessels of the legs;
- heart failure;
Diseases of the respiratory system:Nervous diseases: - diabetic neuropathy - nerve damage that is characterized by loss of sensitivity;
- diabetic - brain damage;
Diseases affecting limbs:- diabetic brush;
- gangrene of the lower extremities;
Skin diseases:- ulcers;
- dark spots;
- rash;
- purulent-septic complications;
- nail deformity;
Vascular complications are divided into:
- 1) Microvascular (kidney disease, nerve damage, diabetic retinopathy);
- 2) Macrovascular (diseases of the cardiovascular system).
Diagnosis of diabetes To establish an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to analyze (repeated) the sugar content in the blood and urine. In some cases, you will need to analyze the content of acetone in urine. You can purchase a portable blood glucose meter that allows you to identify the level of glucose in the blood at home. Normally, an empty stomach allows for 6.1 miles per mole of blood glucose per 1 liter of blood, and no more than 7.8 miles per liter at 2 hours after eating. Excess concentration indicates the possible development of diabetes. In urine, normal glucose should not be perfect. Diabetes TreatmentDiabetes mellitus cannot be completely cured. Treatment aims to prevent and reduce complications. Although diabetes is not cured, you can live with this disease without feeling any discomfort. But for this you need:
- 1) Follow the recommendations of the endocrinologist;
- 2) Monitor the concentration of glucose in the blood,
- 3) follow a diet (see);
- 4) Do physical exercises - they have an effect on the body similar to the action of insulin.
Used to fight diabetes complex treatmentconsisting of diet therapy, taking medication and physical therapy. Methods of treating diabetes of different types are somewhat different. Treatment of insulin-dependent diabetes For the treatment of this type of diabetes mellitus, the following measures are mainly needed: For the treatment of this type of diabetes mellitus, the following measures are mainly needed: - insulin injections daily;
- take civil (to restore the pancreas), medvin (to stabilize the hormonal background and normalize the immune system), livicin (for the expansion of blood vessels) and palm oil with beta-carotene (to reduce the concentration of glucose in the blood);
- doing physical exercise;
- control the concentration of glucose in the blood several times a day;
- monitor the concentration of glucose and cholesterol in the urine.
Preparations containing insulin, divided into 4 categories:
- 1) Possessing ultrashort action: insulin LizPro, insulin aspart (they begin to act after 15 minutes and their action lasts for 3-4 hours);
- 2) Having a quick action (start to act after 30 minutes and act for 6-8 hours);
- 3) Owners of medium-long-term action (they begin to act 1-2.5 hours later after administration and they act on a continuation of 14-20 hours);
- 4) Characterized by a long-term action (they begin to act only after 4 hours, but their action lasts up to 28 hours).
The endocrinologist prescribes the mode and dose of insulin for each patient individually. Treatment of non-insulin dependent diabetes People who have been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes should adhere to the following guidelines: People who have been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes should adhere to the following guidelines: - exclude foods containing sugar, fats and cholesterol;
- doing physical exercise;
- take daily insulin medications;
- measure blood sugar several times a week;
- do not allow an increase in blood pressure.
Patients with both types of diabetes need to abandon sugar and foods containing sugar and starch: bread, rice, cereals, leguminous fruits, raisins. Sugar can be replaced by saccharin, sprats, spolarin. You should increase the consumption of meat, fruits (except bananas, cherries, plums and grapes), dairy products and spices (they facilitate the digestion of food). Coffee is recommended to replace the drink made from chicory roots. Diabetes preventionPrevention is especially necessary for people at risk: those with burdened heredity and overweight. To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary: - eat right;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- fight extra pounds;
- limit the consumption of foods containing easily digestible carbohydrates (primarily refined sugar);
- refuse food rich in animal fats.
Which doctor to contact for treatment? If, after reading the article, you assume that you have symptoms characteristic of this disease, then you should We rarely think about diabetes. However, the danger of this disease should not be ignored. The prerequisite for the occurrence of the disease - low levels of insulin in the blood. Produced by the endocrine islets of the pancreas, it is an integral part of the metabolism. Low level insulin hormone affects the work of many internal organs. Modern medicine does not have absolute knowledge about what causes diabetes, but how the disease occurs and what serves as a trigger, has been studied in detail. Read about this in more detail later in the article. Types of diabetes and their causes Glucose is a source of energy, fuel for the body. Insulin helps to absorb it, but in the presence of diabetes, the hormone may not be produced in the right quantity, not produced at all or the cells may not respond to it. This leads to an increase in blood glucose levels, the decomposition of fats, dehydration. The lack of immediate measures to reduce the level of sugar can lead to terrible consequences, such as kidney failure, amputation of limbs, stroke, blindness, coma. So, consider the causes of diabetes: - Destruction of viral infections of pancreatic cells that produce insulin. Dangerous are rubella, mumps, chicken pox, viral hepatitis. Rubella causes diabetes in every fifth person who has had it, which can be complicated if there is a genetic predisposition. It poses the greatest danger to children and minors.
- Genetic moments. If someone in the family has diabetes, then the likelihood of the disease in other members increases many times over. If both parents are diabetics, the child will have a disease with one hundred percent guarantee, if one parent has diabetes, the odds are one to two, and if the illness is manifested with a brother or sister, then the other child will develop in a quarter of cases.
- Autoimmune problems such as hepatitis, thyroiditis, lupus, in which the immune system considers the body's cells hostile, can lead to the death of "pancreatic" cells, making it difficult to produce insulin.
- Obesity. The likelihood of diabetes increases many times. Thus, people who do not have excess weight, the chance of occurrence of the disease is 7.8%, but if the weight exceeds the normal twenty percent, the risk increases to 25%, and with an excess weight of 50 percent, diabetes occurs in two thirds of all people. In this case we are talking about diabetes of the second type.
Type I Type I diabetes (insulin-dependent) leads to the death of insulin-producing pancreatic cells. Because of this, it begins to produce much less hormone, or ceases to produce it at all. The disease manifests itself to thirty years, and its main cause is a viral infection, leading to autoimmune problems. The blood of people with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus has antibodies against insulin-producing cells. They need regular insulin flow from outside. Type II Insulin-independent diabetes is characterized by the fact that the pancreas can produce even more hormone than is required, but the body is not able to perceive it. As a result, the cell cannot skip the glucose it needs. The cause of type II are genetic conditions and obesity. It happens that the disease occurs as a reaction of the body to treatment with corticosteroids.
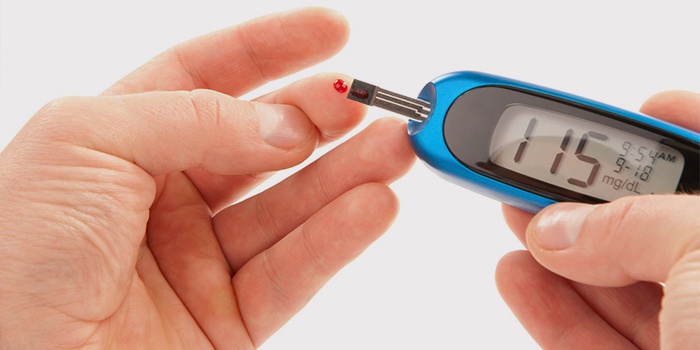
Risk factors Scientists find it difficult to reliably name the reasons for which appears dangerous diabetes. There is a whole set of conditions that affect the occurrence of the disease. An idea of all this allows us to predict how diabetes will progress and progress, and often prevent or delay its manifestation. Each type of diabetes has its own conditions that increase the risk of the disease: - Genetic predisposition. The risk factor for the occurrence of the first type. From parents, the child acquires a predisposition to the appearance of the disease. But the trigger is the external influence: the consequences of surgery, infection. The latter can cause the body to produce antibodies that will destroy insulin secreting cells. But even the presence of diabetics in the genus does not mean that you will certainly fall ill with this disease.
- Reception drugs. Some drugs tend to cause diabetes. These include: glucocorticoid hormones, diuretic drugs, antihypertensive drugs, drugs to fight tumors. Diabetes can manifest itself as a result of prolonged use of nutritional supplements containing selenium, anti-asthma, rheumatism, and dermatological problems.
- Wrong way of life. Active lifestyle triples the risk of diabetes. For those who do not have physical activity, tissue glucose consumption is significantly reduced. By itself, a sedentary lifestyle leads to a set of extra pounds, and addiction to junk food, which does not provide enough protein and fiber, but more than you need - sugar, becomes an additional risk factor.
- Diseases of the pancreas. They lead to the destruction of insulin-producing beta cells and the development of diabetes.
- Infections. Mumps, Coxsackie B viruses and rubella are especially dangerous. At the same time, a direct connection was revealed between the latter and diabetes mellitus of the first type. Vaccination against these diseases, like any other vaccinations, cannot provoke the occurrence of the disease.
- Nervous stress. Officially recognized as one of the common causes of type 2 diabetes, which affects 83 percent of all people with the disease.
- Obesity. It is one of the most common causes of type 2 diabetes. When the body becomes too much fat, it fits the liver and pancreas, the sensitivity of cells to insulin decreases.
- Pregnancy. Being pregnant is a significant stress for a woman and can cause gestational diabetes. The hormones produced by the placenta raise the blood sugar level, the pancreas is forced to work with great tension, and it is not possible to create all the necessary insulin. After giving birth, gestational diabetes disappears.
Find out what the types and treatment of the disease.

First signs and symptoms There are cases when diabetes is manifested so weakly that it may remain imperceptible. Sometimes its symptoms are obvious, but at the same time the person does not pay attention to them. And only the deterioration of vision or trouble with the cardiovascular system compels him to turn to specialists. Early diagnosis of the disease will help in time to stop the destructive processes that occur in her body due to her fault, and not to turn into the chronic form. So, these are the symptoms that indicate the presence of the disease: - Increased appetite.
- Sensation of dry mouth.
- Unusually strong thirst.
- Frequent urination.
- Excessive sugar levels in the urine.
- The level of glucose in the blood exceeds the limit.
- Fatigue, weakness, general feeling unwell.
- A sharp increase or decrease in weight for no apparent reason.
- "Iron" taste in the mouth.
- Blurred vision, feeling of mist before eyes.
- The deterioration of the healing process of wounds, the appearance of ulcers on the skin.
- Perineal skin irritation, persistent skin problems.
- Frequent vaginal and fungal infections.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Numbness of the limbs and cramps.
- Rough, dehydrated skin.
In men Symptoms of the disease in men: - Repeated urination repeated at short intervals along with increased thirst can be a sign that the kidneys require more fluid to get rid of the increased volume of fluid.
- Weight loss without diets and more than before, fatigue can be signs of type 1 diabetes.
- Stitching in the arms and legs, numbness of the extremities can be a sign of nephropathy caused by high sugar levels and a symptom of type 2 diabetes.
- In men, the disease impairs the function of the reproductive organs and the genitourinary system.

Among women Symptoms of the disease in women: - Feeling of weakness and lethargy, fatigue after eating, deterioration of performance, dry mouth, increased urination, constant thirst, hypertension.
- Excess weight, provided that fat is concentrated in the waist.
- Repetitive headaches.
- Increased appetite, feeling of hunger and desire to consume sweets.
- Vaginal infections.
- Sores on the skin, often festering.
- Skin irritation, concentrating in the perineum. We should not forget that thrush, skin and venereal diseases, and allergies can also cause such an itch.
In children and adolescents Symptoms of the disease in children: - Great thirst.
- Weight reduction with a very good appetite.
- Polyuria, often mistaken for bed-wetting.
- Excretion of large amounts of light urine. A blood test for diabetes shows high levels acetone and sugar.
- Dry skin and insufficient moisture of the mucous membranes, crimson color of the tongue and loss of skin elasticity.
Disease prevention Direct prevention of diabetes is not invented, but efforts can be made to reduce the likelihood of its occurrence. You can’t do anything with hereditary risk factors, but you can fight obesity. This will help exercise and the absence of harmful food on the menu. Additional favorable measures will be attention to blood pressure and lack of stress. Video: why does diabetes appear? In the videos below, you will learn from what appears dangerous diabetes. Doctors have identified six causes of the disease and brought to the public. Clearly, informatively, as in the reference book, the information is conveyed to an adult viewer. The causes of diabetes mellitus are forced to think about the actions performed thoughtlessly, and the wrong lifestyle, which leads to obesity and other consequences.
|





 As a rule, diabetes mellitus develops unnoticed and gradually in women and men, so it is very difficult to detect symptoms in the initial stage.
As a rule, diabetes mellitus develops unnoticed and gradually in women and men, so it is very difficult to detect symptoms in the initial stage. 
 For the treatment of this type of diabetes mellitus, the following measures are mainly needed:
For the treatment of this type of diabetes mellitus, the following measures are mainly needed:  People who have been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes should adhere to the following guidelines:
People who have been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes should adhere to the following guidelines: