Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- Available methods for rapidly increasing blood leukocytes
- Nail and skin fungus will not resist the coffee grounds
- Crocus furniture exhibition. Furniture exhibitions
- Owl tattoo on arm value
- The biggest members in the world
- Fractures of the phalanges of the foot photo
- What is “bad” and “good” cholesterol
- What to do if the skin around the nails dries
- The safest natural varnishes list
- Olive oil: is there any point in buying expensive varieties?
Advertising
| Proper dry skin care: the five most effective ingredients. Moisturizing the skin. Natural Moisturizing Factor |
|
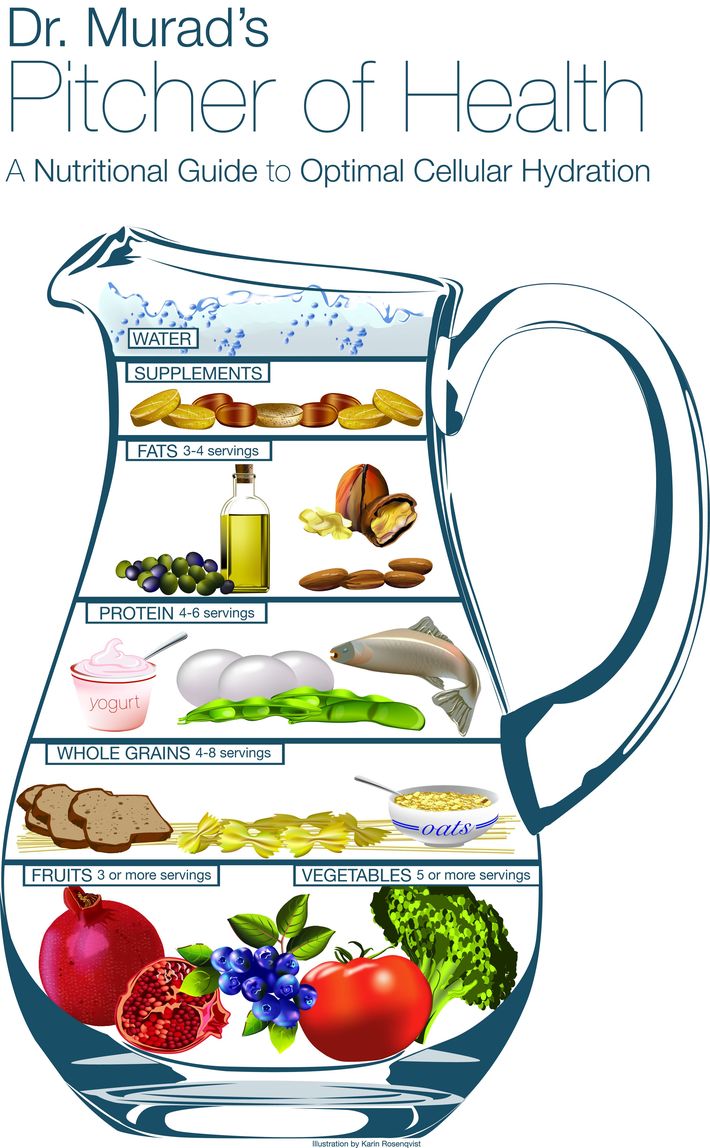
"We are what we eat, and this is not a myth at all." Spring still does not come, instead of the promised renewal, we have dry and dull skin, nerves are at the limit, and the desire to eat something harmful goes off-scale ... If this is about you, then advice from Dr. Murad is necessary for you, just like me. The doctor shared with me the secrets of beautiful and healthy skin. For reference: Dr. Gowar d Murad- a world-known dermatologist, creator of his own brand, author of several books on health and beauty. Dr. Murad came to the conclusion that the condition of the skin depends largely on the general condition of the body, so he started developing his own method of maintaining the health and youthfulness of skin cells: Inclusive Healthcare. Among Dr. Mark fans. Murad Renee Zellweger, Jennifer Enniston, Kim Katrol, etc. It is unfortunate that external care products moisturize the skin by only 20% on the surface of the skin in the epidermal layer. Rest 80% moisturecomes with food and drink, with those products, including dietary supplements that are able to retain moisture in the cells. Therefore Murad developed 3 componentsinclusive Health, which will improve skin condition and help to look much better.
All these components of healthy life support the body's cells healthy, prevent the destruction of cells, prolong their life and contribute to the achievement of the main goal - to live better every day. LOOK BETTER Look for the right mix of tools! "External moisturizing of the skin is a very important aspect. The skin must be well-hydrated in order to look good. Also, when the skin is well-hydrated, its protective functions are enhanced, the skin copes better with the external detrimental effects of the environment. It is very important that moisturizers contain ingredients that attract and retain moisture inside the cells and on the surface of the skin. The best moisturizers: lecithin, hyaluronka, plant extracts (cucumber, aloe), oil (shea and borage seeds). " Moisturizing begins with what we eat! “As I said, high-quality hydration is necessary for the health of the body’s cells. In opposition to the myth of having to consume at least 8 glasses of water a day, I suggest a healthy diet rich in vegetables that can maintain an optimal level of body hydration, while helping to reduce the amount of water you need to drink during the day. I call it that — eat your water (yes, that’s it!). Very often the body loses a significant amount of nutrients, with excessive fluid intake and too frequent visits to the toilet. If you consume the right foods that supply the body with the necessary moisture, you will not need to count the glasses you drink. Even if you replace one glass of water with one serving of fresh fruits or vegetables, the body will be moistened for a significantly longer period. The consumption of food rich in structured water, especially fresh fruits and vegetables, will not only increase moisture levels, but also increase the levels of antioxidants, fiber and nutrients in the body. "Very important during fasting. FEEL BETTER Do not let stress oppress you! "What happens when you are under stress? Wet palms, excessive sweating, pressure rises. All this leads to a decrease in the body's moisture level. Today, stress is an integral part of life in a civilized society. Prolonged stress further enhances the effects of stressful situations organism, reduces the body’s ability to resist stressful situations.It is important not to forget about yourself and sometimes give yourself the opportunity to take a deep breath and remember that the main person on earth is you are yourself! "
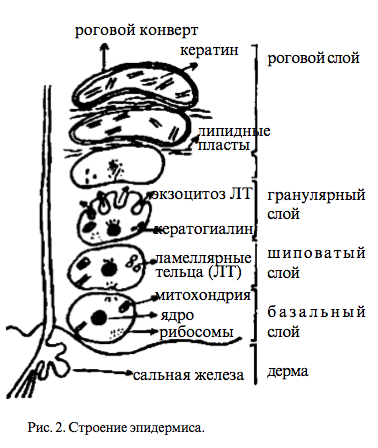
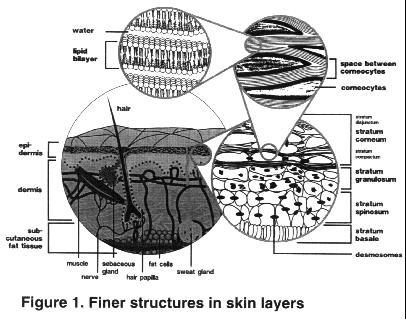
Add these seasonings to the text and try to follow the nutrition according to the "jug of health". The doctor advises everyone: " Do not be afraid of being children - this will prolong your youth. "Talking about this approach, he cites the example of himself. Recently, namely at 70, Dr. Howard Murad discovered a new passion for drawing. “I am not afraid to be myself, most likely not everyone will like my paintings, but this hobby gives me a lot of pleasure, which prolongs my youth. Do not be afraid to be who you really are. Do not be afraid to discover new talents. ” Physiology and skin functionThis article will allow you to get a deeper knowledge of the physiology of dry skin and better understand the principle of action of the creams you use. Leather - It is a physical barrier between the body and the environment. Violations in protective systems skin cover and its actual damage can cause dryness and dermatitis when exposed to water, soap, chemicals and harsh climatic conditions. The elimination of injuries with creams is possible due to the physical and chemical interaction between the ingredients and the protective systems of the skin. These are difficult to understand mechanisms, and therefore it is necessary to have extensive knowledge of the structure and functions of the skin in order to understand whether the cream can improve its condition. Skin Physiology: Basics of Structure and FunctioningEpidermis is an outer layer that serves as a physical and chemical barrier between internal environment organism and environment. Dermis - This is a deep layer that provides structural support for the skin. Epidermis and the stratum corneum: structure and regeneration of skin cellsThe epidermis consists of several layers of constantly renewed cells. Cells are connected using protein bridges - desmosomes. The lower layer adjacent to the dermis consists of regenerative basal cells. With the help of semi-desmosmos, they are associated with the dermis epidermal membrane.
Keratinocytes - the main type of epidermis cells formed in the basal layer, just above the dermis. These are metabolically active cells with normal constituents, such as the nucleus and cytoplasm. Keratinocytes perform many important functions, including the production of keratin structural proteins. As keratinocytes move upward through the epidermis, they become impractical corneocytes in the granular layer. Corneocytes do not have a nucleus and cellular structure. The shape of corneocytes and their keratin structure make the stratum corneum more durable. There are a total of 10-30 adjacent layers of corneocytes. Thick skin of the palms and soles has the largest number of layers of interconnected corneocytes. The connection between them is provided by protein bridges called desmosomes. A double layer of lipids surrounds cells in the extracellular space. The resulting structure is a natural physical barrier capable of retaining moisture. Filagrin: disintegration of epidermal cellsIn the process of maturation, living cells moving towards the stratum corneum begin to group protein granules. These granules can be found in the granular layer of the skin, and they consist of a protein called filagrin. The synthesis of filagrin and keratin begins in the cells of the granular layer: the resulting compound is resistant to proteolytic degradation. As the degenerating cells move to the outer layer of the skin, the enzymes break down the keratin fillagin compound. Filagrin is outside the corneocyte, and hydrophilic keratin remains inside the cells of the stratum corneum. When the skin becomes less moist, special proteolytic enzymes begin further cleavage of filagrin into free amino acids. Natural moisturizing factor: the skin’s natural ability to retain moistureFree amino acids, along with such biochemical substances as lactic acid, salts and urea, are present in the stratum corneum of the epidermis. Taken together, these substances represent the “natural moisturizing factor” (NMF) and are hydroscopic, that is, they are responsible for maintaining the skin’s moisture and elasticity by attracting and retaining fluid. Filagrin splitting into amino acids occurs only in dry skin, which serves to regulate osmotic pressure and the amount of retained fluid. The need for splitting filagrin in wet weather conditions is lower than in dry. The formation of a natural moisturizing factor of the skin: 1. Maturation and differentiation of epidermal cells in the middle layer of skin 2. Filagrin protein is grouped into granules in the granular layer of the skin. 3. Filagrin combines with keratin to form a proteolytic breakdown-resistant compound. 4. Cells lose their usual structure and become corneocytes, saturated with keratin / filagrin proteins. 5. Corneocytes move into the outer layer of the skin. 6. Enzymes cleave keratin / filagrin compound into original elements. 7. Filagrin splits into free amino acids. 8. Along with other substances, amino acids are related to natural moisture factors. 9. They retain fluid to restore normal moisture levels. Desquamation (peeling of the skin)Desquamation also plays an important role in keeping skin soft. Desquamation - It is an enzymatic process of destruction by desmosomes, protein compounds between corneocytes, and their further exfoliation. Proteolytic enzymes not only participate in the formation of amino acids during the cleavage of filagrin, but are also responsible for desquamation in a well-moistened stratum corneum. These enzymes are located inside the cells. With a lack of water, the process of exfoliation of cells does not occur properly, as a result of which the skin becomes thick, dry, rough and rough. There is a natural balance between the formation of corneocytes and their exfoliation. An increase in the number of cells produced (in a disorder such as psoriasis) or inadequate desquamation (for example, in ichthyosis) leads to an accumulation of cells on the surface of the skin, due to which it becomes rough and dry. Cell desquamation 1. Healthy Corneocytes in a Moisturized Horny Layer 2. Proteolytic enzymes cleave protein compounds between cells. 3. Corneocytes peel off 4. The skin remains in good condition without forming dry scales. Intercellular LipidsTo understand what processes are involved in keeping moist and elastic skin, it is necessary to take into account the last factor, namely the functioning of intercellular lipids. Lipids form a multi-layered structure - adjacent lipid bilayers surrounding the corneocytes and holding the fluid inside this structure. Lipids are produced in the process of cell degradation in the granular layer of the skin (similar to protein granules). Special lipoid compounds, called lamellar granules, are released by degrading cells into the extracellular space. Lipid release also comes from former cell membranes. The composition of secreted lipids includes cholesterol, fatty acids and sphingolipids. Ceramide, a type of sphingolipid derived from lamellar granules, is one of the most important components responsible for the formation of multi-layer lipid structures. Lipids hold water molecules in their hydrophilic (water-absorbing) layer. The lipid layer formed around the corneocytes serves as an impermeable barrier to the release of water from the stratum corneum, and also prevents the erosion of natural moisture factors from the surface layers of the skin. After 40 years, there is a sharp decrease in the number of intercellular lipids, which makes the skin more susceptible to lack of moisture.
1. Lipids form granules in the granular layer of the skin 2. Lipids enter the extracellular space during cell degeneration in the granular layer. 3. Lipid granules and lipids released during cell degeneration join together to form an intercellular lipid structure. 4. The lipid layer surrounding the corneocytes is an impermeable barrier and retains moisture. Thanks to the joint work of intercellular lipids and corneocytes containing proteins and natural moisturizing factors, an effective barrier is formed that can retain moisture and prevent its leakage, while the tissues retain their elasticity. Protective forces protect the skin from drying out and the negative effects of the environment. Irritants and damage to the skin barrierThe main factor responsible for dryness, skin roughness and dermatitis may be associated with leakage of fluid from the stratum corneum. This process is called transepidermal moisture loss (TEPV) (dehydration of the skin). The cells of the stratum corneum receive water from the dermis and the environment. Water softens the skin, making it smooth and supple. The cause of dehydration of the skin can be a large number of external factors. Other external factors can damage the stratum corneum barrier through denaturation of keratin, elimination of natural moisturizing factors and impaired lipid bilayers. These factors include the use of solvents, detergents and other substances that irritate the skin, as well as abuse of soap and water. The severity of the damage depends on the type and strength of the irritants. An irritant is any agent capable of causing damage with sufficient concentration and duration of contact. Sometimes repeated or more prolonged exposure is necessary in order for the damage to become noticeable. People exposed to constant contact with cleaning products and water — medical professionals, hairdressers, catering staff, bartenders, and dishwashers — can observe significant changes in their skin condition. Water at the same time is a weak irritant. Paradoxically, frequent contact with water leads to TAPV, causing the loss of soluble moisturizing factors and some protective lipids. As a result of constant hydration under the influence of water: Foreign substances penetrate the skin; These factors are useful surfactants that remove external contaminants, bacteria, skin oils, sweat and dead skin cells. Frequent and prolonged contact with this kind of cleansers causes denaturation of skin proteins, destruction of lipid bilayers, elimination of natural moisturizing factors and deterioration of cell adhesion. Warm water can increase the irritant effect of skin cleansers, increasing their absorption with more high temperatures. In this case, the adverse effect on protective lipids is also enhanced. The end result of prolonged contact with water and cleansing agents is changes in the water-holding capacity of the epidermis and aggravation of TAPV. Dry and rough skin less plastic and more susceptible to physical damage. There are also endogenous factors that make human skin more susceptible to external influences. These factors include existing skin diseases like psoriasis and This is a problem for many girls not only due to the fact that peeling appears on it. leads to the formation of early wrinkles, redness and acne. That is why the skin of this type requires very careful care with the selection of special moisturizers. Moisturizers can improve complexion and slow down skin aging, and significantly. The elasticity of the skin, its elasticity is directly related to how skin is moisturized. An impermeable barrier to the penetration of moisture into the skin is the stratum corneum, which contains only 15% moisture. Slow down the excretion of moistureThe moisture content in a layer like the epidermis can be increased because there is a continuous rise of water from the deep layers of the skin and evaporation on the surface. So, how to increase the moisture in the skin? You just need to cover it with something wet, though not in the truest sense of the word. Used cream-coating should not be like a plastic film, because otherwise dry skin spoil even more. Rapid wetting of the upper layer of the skin will not do it good. The evaporation of moisture should be only slightly slow ingredients of the cream, but not stopped. Moisture catchersThe component that is able to slow the evaporation of moisture is occlusion. This ingredient can act as a main or aids in cream. If the role is auxiliary, then the main ones are substances that retain moisture. Moisture catchers have the ability to bind water molecules. It is best to apply such a cream immediately after washing without wiping with a towel, because such components are most effective in a moist environment. Hunters do not penetrate the skin. Moisturized by fixing the moisture catchers on the surface of the skin, where they work on the principle of a sponge. MineralsMolecules of mineral substances are able to penetrate into the stratum corneum, into its thickness, due to its small size. The moisture that the skin needs is maintained until the skin is renewed. Creams with minerals do not give such a quick result as a moist compress. In order to dry skin become really moisturized and healthy, you will need to use the cream for a long time. However, the advantage of this type of moisture is a longer effect. Minerals penetrate the horny layer of the skin and restore its function, which boils down to preserving water. Such components stimulate the entry of moisture from the lower layers of the skin. Cause of dry skinDry skin can be a consequence of heredity or be the result of using the wrong tools, which leads to a change in its structure. Dryness can occur not only on dry skin from nature. Creams with a rich texture will suit owners of dry skin type. The composition of such funds must necessarily include not only moisturizing ingredients, but also various nutrients. Some moisturizing agents can cause skin irritation. Such cases are not uncommon. The reason for this is the fact that the stratum corneum is simply supersaturated with water, as a result of which it becomes more permeable. In other words, this layer is able to pass through the harmful substances that lead to irritation. Almond and sesame oils are not suitable for sensitive skin. For the appearance of the skin, first of all, those functions of the skin are important, which simultaneously serve as a protective mechanism against the influence of the external environment, i.e., keratinization processes that determine the character and appearance of the skin surface, the functions of the sebaceous and sweat glands that participate as in skin formation. films, and in hydration of the epidermis. In turn, the hydration of the epidermis plays a large role in maintaining it in a normal state, which ensures adequate performance of the barrier function. Keratinization is a complex enzymatic process of converting the protoplasm of living epidermal cells into keratin protein polypeptide chains. Transformation of keratinocytes is carried out under hormonal control and is regulated by the vegetative nervous system. This zone has a high metabolic activity and is an essential part of the epidermal barrier that regulates trans-epidermal resorption and homeostasis of body fluids. Hydration of the stratum corneum is determined by the content of hydrophilic substances capable of binding water: amino acids, ribose, pyrrolidonecarboxylic acid, etc. The skin color of the face, its overall appearance is influenced by the tissues of the skin itself and the underlying tissues, as well as the skin pigment and color of the blood, which appears through the epidermis. A good complexion depends on the amount of fluid in the skin tissue. For the normal functioning of the skin the most important is the water-salt metabolism. The water content in the skin is up to 70%, with a lower content of the skin loses its elasticity and elasticity. Almost all the physiological processes of the cell associated with metabolism, as well as the delivery of food to the cells and the excretion of decay products, occur with the participation of water. The water balance in the cells of the skin and in the extracellular substance is regulated by osmotic pressure. Cells tend to take in potassium, while sodium accumulates in the extracellular fluid. The osmotic pressure balance between the blood and the extracellular fluid surrounding the capillaries determines the water content in the tissues. This fluid tension (turgor or tone) provides the skin with fibers. connective tissue resilience or elasticity. The water content of the skin depends on the internal regulation. 100 to 200 ml of water evaporates from the skin per day (6 mg per 1 sq. Cm), including sweating. Outside, the water almost does not penetrate the skin. With aging of the skin, its ability to retain moisture decreases sharply, which is accompanied by a loss of elasticity and elasticity, drying of the skin, the appearance of wrinkles. Sodium and potassium ions are involved in the maintenance of acid-base balance, protein, carbohydrate and vitamin exchanges, stimulate the activity of enzyme systems. Violation of the salt metabolism in the skin leads to its morphological and functional changes. Keratin (the substance of the stratum corneum) is completely insoluble in water, but it can temporarily take in water. Keratin softens and swells. Neither fat nor oil softens keratin. Pyrrolidonecarboxylic acid, urea, lactic acid and various sugars bind water to the stratum corneum (widely used in cosmetic productsoh). The ability of these substances to maintain moisture is directly dependent on the humidity of the surrounding air. Sooner or later, every woman experiences a difficult and painful moment of spiritual drama, having looked at herself in the mirror once for a long time and intently. Therefore, every woman should take care of her face in her youth. We must not forget that the skin condition depends on the general condition of the body and the disruption of normal activity. internal organs and the nervous system will sooner or later affect the condition of the skin, as well as the condition of the skin affects the state of the whole organism. In order for cosmetic care to be purposeful and successful, it is necessary to analyze the individual changes and manifestations that were previously considered solely, like, aging, from the point of view of their genesis, which will allow us to correctly navigate in solving this difficult task. It should be noted the inevitable signs of biological aging from the effects of external influences that contribute to premature regressive changes. Answering the question why the skin looks old, unwittingly imagine wrinkles. But wrinkles cannot serve as an unambiguous indicator of biological age, since their occurrence is caused by a number of reasons. They often appear at a young age as a result of repeated excessive contraction of facial muscles, squinting of the eyes, wrinkling of the forehead, grimacing - these are the so-called facial wrinkles. If a best remedy to prevent age-related wrinkles is proper care for skin and healthy living, then to fight mimic wrinkles only self-discipline, will, self-control are needed. As a result of self-control, the folds are not completely eliminated, but they, undoubtedly, are somewhat smoothed, do not deepen and do not increase. External signs of aging face and neck include: Initially, wrinkles are visible in the eyelids, temples, then at the corners of the mouth, nasolabial folds deepen, the line of the oval of the lower half of the face changes. The skin becomes thinner and drier, reduced elasticity, elasticity, sebaceous excretions. All layers of the skin become thinner, the protective function of the skin decreases, and the horny layer of the epidermis thickens. Due to this, the skin acquires a yellowish-gray tint. The cells of the epidermis lose water. The formation of new skin cells is slowed down to 5 - 7 weeks or more. In order to actively resist the biological aging process, the skin must fully support its main functions: nutrition, hydration, self-renewal, breathing and protection. Age-related skin changes begin after 30 years and are primarily a consequence of the aggressive action of external factors. The epidermis is recessed into the dermis, where the intensely dividing cells of the basal layer are located. With age, the dermis-epidermis border is smoothed and thinned. In the epidermis, due to a decrease in cell proliferative activity, apaptosis is slowed down (the process of transformation into horny scales). The mechanism of violation of keratinocyte differentiation can be attributed to genetically programmed aging. The decrease in the activity of fibroblasts causes a slowdown in the synthesis of collagen and elastin, and an increase in the work of proteolytic enzymes (proteases - hydrolyzing proteins molecules). Slowing down the synthesis and updating of glycosaminoglycans leads to a decrease in skin elasticity, a decrease in its turgor, and also causes disruptions in intercellular communication. The introduction of hyaluronic acid (HA) is not very effective, as it is constantly destroyed in the dermis. Exposure of cells that are responsible for the synthesis of HA is a more reliable way to increase its concentration. It is synthesized in keratinocytes and in fibroblasts. With age, the epidermis loses its ability to retain moisture - the keratinization process is disturbed (the appearance of peeling, blue keratosis, pigmentation disorder). The epidermis becomes thinner, the dermoepithelial junction line flattens - a network of fine surface wrinkles forms. The elasticity and elasticity of the skin depends largely on the state of collagen and elastin (old fibers are destroyed by collagenase, and new ones are synthesized in fibroblasts). With age, the active center of the enzyme is blocked, which leads to the cross-linking of collagen fibers, they accumulate in the tissue and inhibit the synthesis of new fibers, the skin loses its elasticity, skin folds are formed. Subcutaneous fatty tissue atrophies, deep wrinkles appear, facial contours are disturbed (grief mask). The reason for the stitching of collagen filaments can be lipid peroxidation (lipid peroxidation) and glycation. Under the control of macrophages are cells immune system, fibroblasts and keratinocytes. Activation of macrophages in fading skin stimulates collagen renewal, due to the release of proteolytic enzymes collagenase and elastase. Macrophages also secrete a growth factor that stimulates the division of epidermal cells, and an angiogenesis factor that is responsible for the formation of blood capillaries. The formation of free radicals accompanies all immune reactions, since immune cells actively use the toxic properties of oxygen in the fight against bacteria. Lipid peroxidation (POL) leads to the destruction of the epidermal barrier and to the appearance in the epidermis of a large number of free radicals. Ultraviolet radiation damages not only the cells of the basement membrane, but also dermal fibroblasts and macrophages, activating the formation of hydroperoxides. To combat free radicals in the skin, there is an antioxidant system in which vitamin E and two enzyme antioxidants, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, play the main role. SOD manifests its antioxidant effect only when paired with catalase (as a result of SOD action, peroxide is formed, which is destroyed by catalase) - with an excess of hydrogen peroxide, SOD becomes a prooxidant. UV and negative radicals (-R) stimulate collagenase synthesis, but the synthesis of anti-collagenase remains the same. As a result of imbalance, the structure of the intercellular collagen fibers changes. UV radiation stimulates the release of iron and copper ions from cellular depots, which are catalysts for the formation of hydroxyl radicals, which provoke the formation of collagen dimers. Collagen crosslinks are formed as a result of the damaging effects of monosaccharides. The biological age of the cell is determined by the function of mitochondria. During oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria (ATP synthesis), toxic free radicals can form. Free radicals damage mitochondrial DNA, which is not protected by proteins and is very vulnerable. Mitochondrial DNA encodes proteins necessary for oxidative phosphorylation. If the DNA is damaged, the synthesis of proteins is disturbed, and thus the process of energy production in the cell is disturbed. Failure in the process of oxidative phosphorylation increases the production of free radicals. The intramitochondrial antioxidant system is Coenzyme Q. With age, the content of Coenzyme Q decreases and the cells become more sensitive to oxidation. As antioxidant additives in cosmetics traditionally used vitamins E, A, C and plant polyphenols. Polyphenols (flavonoids, flavones, tannins, etc.) are rich in red grapes, pine, rosemary, green tea, soybean, alfalfa, red clover, dwarf palm, gingo biloba and some other plants. Antioxidants act on various stages of the process of lipid peroxidation, from the neutralization of reactive oxygen species to interaction with molecular products of free radical oxidation. The combined presence of hydrophilic and hydrophobic antioxidants in tissues can provide more effective protection against a free radical attack. Pay attention to this fact. We will remember him, assessing the merits of "POWER OF COSMETICS". So we introduced you to your skin and hope that you penetrated to it with a sense of admiration and wonder, as one of the wonders of the body. The thickness of the epidermis is 0.1–0.2 mm, the dermis is 2 mm, and those complex morphological, biochemical, biophysical and physiological processes that you now know about occur in this thinnest organ, but very significant for life. The skin protects us from the environment, which, as an aggressor, tirelessly tests its strength. Dust, dirt, harmful chemical compounds, UV radiation, wind, temperature changes (frost, heat), bacteria are not a complete list of aggressive factors. Don't you think that not taking care of your skin, not helping it with cosmetics, is it something akin to betrayal of such a great friend as your skin? A person expects from the use of cosmetics not only the external effect, but also a beneficial effect on the body as a whole - action against aging, premature skin aging, baldness, breaking nails, hair, etc. Therefore, in the composition of modern cosmetics add biologically active substances (BAS), normalizing the vital activity of the body at the cellular level, i.e. contributing to faster growth of new cells instead of old, dying off. Cell cosmetology is the current level of scientific research in this area. The number of ingredients listed on the label of a lotion or cream seems huge and sometimes confusing. However, in order to understand the compositions and formulas of cosmetics, it is not at all necessary to be a professional: you just need to know how the main ingredients act, which play a key role in moisturizing the skin. How skin cells retain moisture The skin cell membrane retains moisture in the cell, which is necessary for skin regeneration processes. Young cells in the lower layers of the skin - for example, in the dermis - are round, elastic and easily retain moisture. However, aging and moving closer to the surface layer of the skin - the epidermis, the cells gradually die, losing moisture and structural lipids that were previously held inside the cell. Aging, the cells are no longer able to retain moisture, as before. As a result, moisture evaporates from the cells into the air - this process is called transepidermal loss of moisture. In addition, as skin cells age, the protective barrier no longer possesses the same strength, making water retention more difficult. With the weakening of the barrier dry skin becomes much more vulnerable to the harmful effects of the environment, free radicals, various infections and other problems. Using effectively moisturizing cosmetics is the key to solving many skin problems. 1. Alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) How do they act: alpha hydroxy acids allow you to get rid of dead, dry, flaking skin that accumulates on the face, and expose fresh, softened skin. Alpha hydroxy acids stimulate the exfoliation process, making the skin feel silky to the touch. Exfoliation is the key not only to the health and freshness of the skin, but also to the effective action of cosmetics: moisturizing ingredients can penetrate into the lower layers of the skin, restoring the necessary balance of moisture. However, alpha-hydroxy acids have an important drawback: removing the upper layer of the skin, these substances increase the skin's vulnerability to the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation, so you should not forget about sunscreen lotions or creams. Examples. Glycolic, lactic, malic, citric and tartaric acids. Where to find:
2. Antioxidants How do they act. Antioxidants - special molecules that protect the skin from the harmful effects of free radicals, which, in turn, appear under the influence of the sun, pollution and other consequences of the unfavorable external environment. Free radicals can cause dryness and skin damage, the occurrence of age spots and other signs of aging. Some antioxidants are part of moisturizing cosmetics due to its moisturizing effect. Antioxidants are transported through oils and fluids, often forming the basis of moisturizers. In addition, antioxidants play an important role in protecting the skin cell membrane. Since dry skin is much more vulnerable to the harmful effects of the external environment, antioxidants are one of the key ingredients in moisturizing products. Examples. Soy extracts, grape seed, vitamins A, C, E, coenzyme Q10, polyphenols and flavinoids. Where to find:  3. Softeners How do they act. Special substances strengthen the protective barrier of the lower layers of the skin, allowing skin cells to better retain moisture. In addition, these substances serve as a kind of “lubricant” - filling the space between coarse, dead skin cells, they make the skin softer and smoother. Examples. Lactic acid, shea butter, petroleum jelly Where to find:
4. Humidifiers How do they act. Special moisturizing agents direct moisture from the air to the skin. A prerequisite for the action of these substances is humidity at the level of at least 70%; if the air does not contain enough moisture, moisturizers will not be able to provide it to the skin. In addition, moisturizers promote the transfer of moisture from the lower layers of the skin to the epidermis, help protect the skin from dryness and sun, soften thick and rough skin on the feet, knees, elbows. Examples. Hyaluronic acid, glycerin, butylene glycol, propylene glycerol, sorbitol, sodium pentachlorophenate, panthenol, lactic acid. The most effective moisturizer is hyaluronic acid, capable of holding a volume of moisture up to a thousand times greater than its volume. In addition, hyaluronic acid does not allow moisture to evaporate. Occupying the space between the skin cells, hyaluronic acid makes the skin smoother, smoother, reduces the most noticeable wrinkles. Thanks high level hyaluronic acid in children is so soft and tender skin. With age, the level of hyaluronic acid decreases. Where to find:  5. Occlusal How do they act. These substances “lock” the cells, slowing down the process of evaporation of moisture from the skin surface. Occlusives form a dense protective film that covers the top layer of the skin and prevents evaporation of moisture. The most effective occlusive substances act when applied to moist skin. Unfortunately, the occlusal has one undoubted drawback - they leave a feeling of oily, sticky skin and, in addition, can clog pores, leading to the formation of acne. Most often, occlusives are part of body care products, not of the skin of the face - or of cosmetics intended for very dry skin of the face. Examples. Beeswax, cyclomethicone, mineral oil, lanolin, silicone, dimethicone, vegetable oils (avocado oil, olive oil), hydrogenated castor oil, caprylic triglycerides. Where to find:
|
| Read: |
|---|
New
- What you need for acrylic powder
- What does owl mascot mean
- Analyzes for pancreatitis: what research should be done and what indicators show
- Owl - a talisman to attract money and good luck
- What bird screams at night with a kitten's voice?
- Cholesterol and stress
- Manicure at home
- Effective facial
- What is a man after a broken leg?
- The trees and shrubs of the park survived the winter well