Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- Technology and step-by-step instructions for nail gel: steps, rules, process
- White spots on the nails, reasons for what to do, white spots on the nails and folk signs
- Available methods for rapidly increasing blood leukocytes
- Nail and skin fungus will not resist the coffee grounds
- Crocus furniture exhibition. Furniture exhibitions
- Owl tattoo on arm value
- The biggest members in the world
- Fractures of the phalanges of the foot photo
- What is “bad” and “good” cholesterol
- What to do if the skin around the nails dries
Advertising
| Aspirin is an induced respiratory disease. |
|
Aspirin asthma is one of the varieties of this disease, it occurs when using drugs based on acetylsalicylic acid and other anti-inflammatory painkillers. This form has its own diagnostic criteria, it is worth deciding in which cases the disease occurs, what symptoms it usually manifests itself, what are the methods of treatment. What it is?Aspirin asthma is not the most common type of this disease. It develops due to the effects of acetylsalicylic acid on the body, and it is rather difficult to predict the possible increased susceptibility to this substance. According to statistics, the majority of cases - women aged 30 to 50 years. There is no verified information on the hereditary transmission of the propensity for the disease. In general, cases of aspirin form make up more than 20 - 40 percent of all cases of asthma, different sources provide different information. In children, the disease usually occurs less frequently, but this possibility exists. In general, in most cases, the presence of this disease is determined only at the beginning of the treatment of any condition with the help of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. For aspirin asthma is characterized by a triad of symptoms, if it is not fully disclosed, they speak of an incomplete triad. This triad is one of the main diagnostic criteria for this disease; if it is absent, it is impossible to speak about aspirin asthma in most cases. The triad usually includes the following features:
The pathogenesis of this disease is a rather complicated process, there are several theories why some people become too sensitive to acetylsalicylic acid. The formation of aspirin asthma is associated with metabolic processes in the body. If the triad of aspirin asthma is absent, the cause of the symptoms may be different. In general, if you experience signs of bronchial asthma, you need to conduct a full examination, which will help to determine the exact cause. The main symptom of this disease is shortness of breath, coughingturning into suffocation, as with any type of asthma. The further, the harder the symptoms become, especially if their main cause, the presence of acetylsalicylic acid, does not disappear. The disease in most cases begins to develop with inflammatory process in the nasopharynx. It is usually rhinitis, very often with the formation of polyps on the nasal mucosa. Also, with this form of asthma, people who are sick may note the following:
If you experience these symptoms, be sure to consult a doctor. It is worth noting that other types of asthma may be accompanied by these signs, so before starting treatment a full diagnosis is required.
Who treatsIf you experience asthma attacks and signs of this disease, you can contact the otolaryngologist or directly to the pulmonologist. You may need to consult an allergist and other specialists. Most varieties of this pathology cannot be completely cured, since they depend on the internal processes of the body, which are extremely difficult to influence. However, avoiding irritants, taking anti-inflammatory drugs, choosing the right treatment to stop the seizures, can lead to stable remission.
Aspirin Asthma TreatmentTreatment of this disease is usually complex, it includes several different methods. They must be combined to achieve the most pronounced result:
If polyps form in the nose, surgical removal may be necessary. In general, the treatment plan may vary depending on the evidence. Therapy of asthma can take place exclusively under the supervision of a physician. Antibiotics for this disease are usually not prescribed, they can be used if due to rhinitis any infection of the respiratory tract and nasopharynx has developed. The use of such drugs is not prohibited in this type of asthma. How to bring down the temperature in aspirin asthma? During catarrhal diseases It is difficult to do without painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. If you need to bring down the temperature, you can do more simple means: for example, cold compresses, intake of fluids, plain water, in large quantities.
If the disease is impossible to do without anti-inflammatory drugs of this series, it is advisable to turn to the method of dissensitization. In the presence of evidence, it is always trying to implement. What painkillers are possible?Since most painkillers are banned for this disease, it becomes difficult to find the right medicine. In most cases, if it is impossible to do without aspirin and similar drugs, dissensitization is required. Hormonal painkillers based on steroids are usually allowed. However, it should be borne in mind that these drugs can usually be used exclusively by prescription. In general, for aspirin asthma, you need to be careful when selecting drugs against heat and pain. In some cases, when taking painkillers prescribed antihistaminesto help smooth out the symptoms of aspirin asthma. Can I prick lidocaine?Studies show that lidocaine does not worsen the condition of patients with aspirin-type asthma. Therefore, it can be used as an anesthetic. However, it is worth noting that you need to strictly observe the dosage, you must always consult with your doctor before starting treatment. Aspirin Triad - what is it? The answer to this question is not known to many patients, but almost all doctors can easily define this term. basic informationAspirin Triad - what is it? Experts say that this term refers to the intolerance of aspirin, as well as the consequences that arose against the background of its administration. The classic aspirin triad includes not only intolerance to the substance, but also bronchial asthma and nasal polyps. Some statisticsSurely everyone took pills "Aspirin." It has long been known, as well as the usual analgesic and antipyretic agent. However, the properties can make significant changes in the structure of the blood. As a result, taking the harmless drug for pain can turn into a dangerous condition for the patient. The aspirin triad is a type of bronchial asthma. To date, 40% of cases of bronchial disease occur with intense. Almost all of them are associated with medicines. The nature of the disease and its causesUnlike allergic reactionsThe aspirin triad is completely different. This disease has nothing to do with the production of histamines. Its development is provoked by pathological transformations of platelets and leukocytes. By the way, similar reactions occur not only after taking acetylsalicylic acid, but also after eating foods that contain large amounts of salicylates. It should be noted that the aspirin triad may develop as a result of the use of the following drugs:
That is why, before prescribing such drugs, doctors are obliged to ask the patient if he has any allergic reactions to the drugs. Other reasonsThe aspirin triad, the treatment of which will be described below, is sometimes hereditary. In this regard, the relatives of those who have asprinous asthma, should be extremely careful when taking these drugs. By the way, more than all the representatives of the weaker sex at the age of 30-50 years are predisposed to the disease in question. Symptoms of the diseaseAs you know, due to the usual allergic reaction with an increased formation of histamines, it is much easier than the aspirin triad. Having studied a lot of cases and symptoms of this pathological condition, the experts designated it with the Fernand-Widal triad. The main symptoms of this disease are:
In the event that aspirin asthma manifests itself in two types or one (that is, there is no any sign), then it is called an asthmatic undisclosed triad. Signs at the initial stage and in the acute periodAt the very beginning of the development of this disease is quite reminiscent of a cold. At the same time, its duration can significantly exceed the periods of a common cold. As for the symptoms of aspirin asthma occurring in the acute period, the following symptoms are present here:
Aspirin triad: treatment, dietIn the treatment of the disease in question, as in the treatment of any other allergy, it is extremely important to eliminate contact with aggressive substances that provoke asthma attacks. In this regard, the patient with a tendency to aspirin triad is prohibited from taking any nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as hydrocortisone hemisuccinate. Many experts argue that the drug "Paracetamol" also causes unpleasant symptoms. Therefore, as an anesthetic for aspirin triad, it should be prescribed with extreme caution. One of important moments in the treatment of the disease under consideration is the adjustment of the patient's diet. The diet for the aspirin triad prohibits the use of the following products: nuts, vegetables and fruits, which include salicylates in high doses. These ingredients include all varieties of citrus fruits, grapes, apples, plums, raspberries, peaches, black currants, strawberries, blackberries, cucumbers, melons, tomatoes, artichokes, peppers, almonds, and more. It should be noted that in order to eliminate the already manifested aspirin triad (its symptoms), patients are often prescribed inhaled drugs. As they use glucocorticosteroids. By the way, such funds, but only in the form of drops, are used for the treatment of allergic rhinitis. If the aspirin triad is very difficult, then the same glucocorticosteroids are prescribed to the patient, but only for systemic treatment. Let's sum upNow you know what it is. The treatment of this disease has also been described above. It should be especially noted that when aspirin triad a person needs immediate medical assistance, otherwise asthma attacks can be fatal. Bronchial asthma refers to chronic diseases of the respiratory tract of an allergic nature and is characterized by paroxysmal course. Any substance can provoke an attack, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - acetylsalicylic acid, or aspirin. Aspirin asthma is manifested not only with the use of drugs, but also with the use of products, which include natural salicylates. According to statistics, among people suffering from bronchial asthma, every fifth person is hypersensitive to aspirin and other NSAIDs. This disease is not congenital, more often it affects women over the age of 30 years. Aspirin asthma has a pronounced clinical manifestationsaccompanied by the general serious condition of the patient. When aspirin is applied to the walls of the bronchi, the metabolism of archidonic acids changes, which leads to an imbalance between substances that stimulate bronchospasm and substances that expand the bronchi. As a result, the bronchi are narrowed, their walls begin to produce a large amount of thick viscous secretion, which complicates the process of respiration. Aspirin asthma is provoked not only by exposure to acetylsalicylic acid, but also by other drugs of the NSAID group, for example, Ibuprofen, Xefocam, Ketorolac, etc. SymptomsAspirin bronchial asthma is characterized by severe persistent attacks and manifests itself as a triad of Fernan-Widal, including the development of polypous rhinosinusitis, asthma attacks of varying severity and intolerance to drugs from the group of NSAIDs. In the early stages of development, the disease can cause hormonal imbalance, which can manifest as a violation of the menstrual cycle in women, early onset of menopause, miscarriage of pregnancy. Aspirin asthma is manifested in the form of disruptions in the thyroid gland. The main symptom of aspirin bronchial asthma is asthma attacks, which have certain characteristic features:
Often the disease begins with a long and abundant coryza, which practically does not respond to therapeutic measures. Often, rhinitis becomes polypous rhinosinusitis, combining the following signs:
Symptoms such as choking and intolerance to drugs may occur simultaneously, with a small time interval. For example, the response to the reception medicinal product may appear in 30 to 60 minutes, while asphyxiation develops much faster. Symptoms of hypersensitivity to a group of NSAID drugs can be:
With timely treatment to the doctor and conscientious follow his recommendations, patients can minimize such manifestations and live a full life. Required examinationsIn order to diagnose asthma, the doctor takes anamnesis (for accurate diagnosis, the patient should fully and clearly describe the manifestations of the disease) and the patient's complaints; radiography of the lungs to exclude other pathologies of the respiratory system and identify increased airiness of tissues (emphysema); measurements of external respiration. If necessary, conduct an allergy test for aspirin or other drugs. Treatment
With the abundant proliferation of polyps in the nasal cavity, their surgical removal is proposed, after which it becomes easier to breathe through the nose.
If you or your loved ones have breathing faster, and you are suspicious, read it, and you will understand the causes and treatment of this ailment. If you notice, the treatment will be different, keep this in mind. All about the syndrome of obstructive sleep apnea will tell you, for the authorship of our experienced pulmonologist. DietTreatment of bronchial aspirin asthma includes not only medication, but also compliance with a specific regimen and diet, which allows you to strengthen the body's defenses. A diet for bronchial asthma implies the following:
Thus, each person who is faced with this disease can live a full life and play sports. To do this, he must be extremely careful about his health, strictly follow the diet and daily regimen, and follow the instructions of a specialist. Allergic reactions are common today, which may be due to unfavorable environmental conditions, increased use of sensitizing products, and medication. Medicines are designed to alleviate the condition of the patient, but sometimes NSAIDs lead to the development of aspirin bronchial asthma. What it isAspirin asthma is one of the forms of an allergic reaction of the body in response to the ingestion of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), the most popular representative of which is acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin). This drug can only be taken by adults and children over 15 years old, so in childhood This pathology does not happen.
It is more common among women aged 30-50 years. The disease is transmitted about inheritance, that is, is family-friendly. Video: First AidEtiologyAllergen for aspirin asthma are drugs containing salicylates, for example: acetylsalicylic acid (ASA). The drug has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, antiplatelet effect, therefore, has wide application in various diseases. Aspirin is an irreversible inhibitor of the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), which is secreted by cells of the body during pathological reactions. COX converts arachidonic acid to mediators inflammatory responsewhich cause all the symptoms in various diseases. Other drugs of the NSAID group are reversible inhibitors and are safer to use, so they do not emit other types of asthma. Although the diagnosis and prevention of the disease must take into account the group of the drug that the patient is taking. In the body when taking an ASC, the COX is blocked and the following phenomena are noticeable:
What diseases take aspirin?Aspirin is an almost universal remedy, so it is used to treat wide spectrum diseases. Today, the list of diseases decreases due to side effectsexerted by this drug.
People suffering from allergic diseases need to take NSAIDs with these diseases with caution! Preparations containing acetylsalicylic acid:
Be careful when taking these drugs! PathogenesisPathogenesis - the course of the disease, due to the mechanism of action of ASA. Once in the body, ASA actively and irreversibly blocks cyclooxygenase in healthy people. In people with aspirin asthma, instead of COX, the synthesis of lipoxygenase begins, which contributes to the conversion of arachidonic acid to leukotrienes.
There is a platelet theory explaining the pathogenesis of the disease through the effect of ASA on platelets. They degranulate (destroy), resulting in cytotoxic (destructive cells) and proinflammatory (inflammatory) mediators. It turns out the opposite effect of aspirin: should have helped, and it only got worse! In healthy people, no pathological effect of aspirin on platelets was found, and in those suffering only platelets change their properties under the action of ASA, other cells are not involved in the process. Symptoms of Aspirin AsthmaSymptoms of the disease depends on the effect produced by the pills and on the dose of the drug. Signs of asthma:
The patient does not necessarily show all the symptoms, only one or two non-specific signs may appear, which complicates the diagnosis of the disease. The long course of the disease leads to the development of bronchial asthma, so when making a diagnosis of aspirin asthma, consult an allergist!
DiagnosticsA large role in the diagnosis given to the collection of data about the patient, you need to find out:
A patient suffering from bronchial and aspirin asthma, notes that the effect of the drugs is first there, the spasm disappears, but after a couple of minutes it appears again. This effect is explained by the fact that the composition of theofedrin includes a drug with the content of ASA. Initially, teofedrin inhibits histamine synthesis and spasm disappears, but leukotrienes ensure the development of later bronchospasm and their edema, therefore, taking teofedrin does not relieve an attack. To prove the presence of aspirin asthma, provocative tesa with salicylic acid is performed in specialized clinics. The patient is given a small dose of the drug, and the doctor observes with the help of special equipment for changes in the respiratory system. Changes in the respiratory system are fixed on the sensors, and make a diagnosis.
Patients with aspirin asthma have a high content of leukotrienes in the urine, contents of the bronchi and nasal cavity, therefore, studies of urine, nasal cavity and bronchial mucus are conducted. The diagnostic criterion can be the improvement of the patient's condition after taking antileukotriene preparations, preservation of symptoms while taking antihistamines. TreatmentTreatment can be emergency and systemic. Emergency needs to be carried out if the patient has a sharp attack, before the arrival of the ambulance.
Emergency treatment:
Systemic treatment:
The treatment is difficult and must be chosen correctly, as it is unfavorable for the patient to use any drugs of the NSAID group! Prevention
Products containing salicylates, which are best avoided:
ForecastWith the development of a sharp and bright attack, the prognosis of the patient is unfavorable in the absence of outside assistance.
For a positive outlook it is important:
The diagnosis of aspirin asthma is not fatal, so do not panic, but treat the disease! DietDiet - one of the main conditions for recovery and treatment of diseases. It is difficult to keep it, because salicylates are contained in a large amount of food. When not following the diet, the patient is expected to:
Prohibited products for aspirin asthma:
Aspirin asthma is a rare condition that can lead to a person’s disability.
Knowledge emergency aid when an attack can save someone's life, so remember the information and be healthy! Definition Aspirin is an induced (aspirin-dependent) respiratory disease (andspirin orasthmatic triad) characterized by three main clinical manifestations - polypous rhinosinusitis and intolerance to aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)in which symptoms such as rhinitis and asthma exacerbation develop when taking drugs of this group and products containing substances of natural or artificial origin that are chemically similar to them. The mechanism of this intolerance is not, therefore, the probability and severity of exacerbations of the disease depends on the dose of the drug or the amount of the product (1, 2, 3, 4). The urgency of the problem The description of the aspirin triad was first mentioned in 1922. Cases of an asthmatic attack when taking aspirin have been described since the beginning of the twentieth century with the introduction of this medication into clinical practice. The name "aspirin triad" was first given to this syndrome in 1968, but today the name is more common in foreign literature aspirin - induced (aspirin-dependent) respiratory disease (aspirin - exacerbated respiratory disease AERD). This disease is more common in women in the third or fourth decade of life, as well as in 13–40% of patients with nasal polyps. The frequency of intolerance to these drugs among healthy people is 1%, in patients with bronchial asthma - up to 12%. In patients with intolerance to aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, bronchial asthma develops only 10 to 20%. The urgency of the aspirin-induced respiratory disease problem is associated not only with the high prevalence of this pathology, but also with the severity of bronchial asthma, if present, compared with other patients with bronchial asthma. On the other hand, the prevalence of drugs and food ingredients that can cause exacerbation in such patients is very high (3, 4). Substances that are intolerable in the aspirin triad The cause of exacerbation of aspirin - induced respiratory disease is the intake of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs used to reduce very high temperature when fever, stopping headache or toothache, as well as when eating products containing substances like aspirin - natural salicylates: raspberry, strawberry, apple, apricot, orange, grapefruit, lemon, grape, peach, melon, plum, blackberry, cherry, black currant, prune, raisin, almond, artichoke, tomato, cucumber, pepper. Also, with this disease, aggravation is caused by products containing: dyes - tartrazin E 102, yellow - orange SE 110, azorubin E 122, amaranth E 123, red cochineal E 124, erythrosin E 127, diamond black BN E 151, preservatives - benzoic acid derivatives E 210 - 219, sulfites and their derivatives E 220 - 227, nitrites E 249 - 252, antioxidants E 321, flavors - glutamates B 550-553. The use of, first of all, red wine and beer, but also any others, also exacerbates the course of the disease (3, 7). Aspirin Triad Mechanism The mechanism of the disease is associated with metabolic disorders arachidonic acid, splitting off from phospholipid molecules of cell membranes under the action of enzymes phospholipase A 2, phospholipase C, diacylglycerol - lipase. Enzymes cyclooxygenaseturn it into a group of biologically active substances of prostaglandins. Cyclo-oxygenase 1 enzyme (COX-1) is constantly present in physiological conditions in the body cells (constitutional enzyme) and forms prostaglandins responsible for the stability of gastric mucosa cells, regulating renal blood flow, and the formation of thromboxane A 2 - a mediator of platelet aggregation (aspirin preparations in special small cardiac dosages prescribed to reduce platelet aggregation in patients with coronary heart disease). Cyclo-oxygenase-2 enzyme (COX-2) - pathological or induced - is formed only in the foci of inflammation and is responsible for the synthesis of proinflammatory prostaglandins, under the influence of which, during inflammation, pain, an increase in local temperature, swelling and redness of the inflammatory focus, and during circulation in the systemic circulation - the occurrence of fever. Cyclo-oxygenase - 3 (COX - 3) is found in the cerebral cortex, drugs that block it selectively are also effective against fever with inflammation and headache. Another metabolic pathway for arachidonic acid is the formation of cysteinyl leukotrienes under the influence of the enzyme 5 - lipoxygenase. These biologically active substances are important mediators of allergic inflammation, primarily in the wall of the bronchi. They, as well as prostaglandin D 2, cause a spasm of the bronchi, increase the secretion of mucus, edema of the mucous membrane, the migration of eosinophils into the airways. Also in the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract and the skin, leukotrienes can cause the classic symptoms of allergic inflammation: rhinitis, urticaria. The increased sensitivity of the enzyme cyclooxygenase - 1 to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs leads to the development of recurrent attacks of bronchial asthma, symptoms of urticaria and rhinitis when taking non-selective NSAIDs, the use of food additives similar in chemical structure; fruits and berries with natural salicylates, as well as the development of nasal polyps, which recur during their removal. The theories of the pathogenesis of the aspirin triad exist independently and do not explain the peculiarities of the course and development of the complete asthmatic triad in separate clinical and immunological groups. Thus, to date, the causes of the excessive formation of leukotrienes, the rapid progression of the disease and the formation of glucocorticosteroid dependence in patients who have excluded NSAIDs and aspirin (2, 4, 9) have not been elucidated. Clinic The clinical picture of the disease consists of a combination of nasal polyposis, intolerance to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. This characteristic combination of the three symptoms caused the name of the disease "aspirinoy triad." As a rule, the disease begins with polypous rhinosinusitis. After another removal of polyps or taking NSAIDs, the first attack of bronchial asthma develops. Sometimes her repeated seizures are not associated with taking these medications. The use of NSAIDs as an analgesic for dental and headache, renal colic, migraine, for minor surgical interventions, etc. can lead to rapid (5 - 10 minutes) development of bronchospasm and asphyxia. Less commonly, the reaction develops 1 to 2 hours after administration. Aspirin bronchial asthma differs, as a rule, in severe course, slow relief of symptoms, low efficacy of traditional treatment, and the need to take systemic corticosteroids. It is often combined with (the frequency of atopy among patients with the asthmatic triad has increased lately), infectious-allergic and mixed bronchial asthma. Intolerance to NSAIDs can manifest itself as in the form of bronchospasm, and rhinitis phenomena,. After taking NSAIDs, urticaria and angioedema without bronchospasm may occur. Such a syndrome is called aspirinindutsirovannoy urticaria and angioedema (2,3). Diagnostics The diagnosis of aspirin asthma can often be assumed on the basis of complaints typical of asthma, the onset of symptoms after taking NSAIDs, and long-term rhinitis, especially in women older than 30 years. Reliable laboratory tests of intolerance to NSAIDs do not currently exist. In some clinics conducted. The essence of the method is to rinse oral cavity saline, then a solution of a small concentration of the test drug, then again with saline without the drug. Count the number of leukocytes who emigrated to the saline from the patient's saliva before rinsing with the drug and after. A decrease in leukocyte count by more than 30% indicates a positive test for intolerance, regardless of its nature (allergic or pseudo-allergic). The method is currently not recommended in international documents; it is impossible to make a diagnosis on the basis of this test alone. The “gold standard” of diagnostics is the sublingual test with aspirin or other NSAIDs. In some countries, inhalation, nasal and. All of the above tests should be conducted in a specialized hospital. If side reactions when taking aspirin occur repeatedly and repeat time after time, then provocative tests are not necessary. Patients undergo a full, necessary for patients with bronchial asthma (external respiration function + test with a bronchodilator drug, allergological examination) (1, 2, 3, 4). Treatment Treatment includes all groups used in bronchial asthma. Due to the severe course, the patient is often prescribed systemic glucocorticosteroids for exacerbations (2, 3). Some drugs from the group of methylxanthines (theophyllines), due to their chemical structure, can themselves cause exacerbation of the disease. Great hopes were pinned on the compounds of a new biological class — the antagonists of leukotriene receptors. However, the lack of clinical efficacy in monotherapy and the high cost of treating these medicines limits their use. In addition, it has been shown that the effectiveness of anti-leukotriene therapy is comparable in patients with aspirin intolerance and lack thereof (1). For many years, various domestic and foreign centers have been developing methods for desensitizing aspirin by administering, in hospital conditions, increasing doses of the drug (similarly). To date, some authors consider this method to be the most effective in treating a disease (11). However, the need for long-term inpatient observation of the patient, the possibility of the development of adverse pharmacological reactions to aspirin, as well as the unstable clinical effect of treatment with drug withdrawal limited the use of this method (one). Nasal polyps in the aspirin triad are not surgically removed, due to the fact that this can provoke the debut of bronchial asthma or make it heavier. At present, a method of influencing polyps with a combined preparation of an enzyme that breaks down collagen in the composition of a polyp and an immunomodulator is being introduced (5). Prevention of polyp recurrence is carried out by regular administration of intranasal glucocorticosteroids (10). Prevention Secondary prevention of the disease consists in caution in deciding on the removal of polyps in the nose, maximally limiting the consumption of vegetables, fruits and berries containing natural salicylates and nutritional supplements for aspirin intolerance detected in all patients with bronchial asthma for pain relief and reducing the temperature of only selective NSAIDs, cyclooxygenase blocking - 2 and 3 (6, 8). All painkillers and antipyretics, as well as means to reduce platelet aggregation in cardiac diseases, asthmatics should be taken only by prescription of a physician, who should be warned about the presence of bronchial asthma. The same applies to patients not suffering from bronchial asthma, but having polyps in the nose. Literature:
|
| Read: |
|---|
New
- Sequence of procedures
- The program of intensive moisturizing of the skin on cosmetics bark
- What you need for acrylic powder
- What does owl mascot mean
- Analyzes for pancreatitis: what research should be done and what indicators show
- Owl - a talisman to attract money and good luck
- What bird screams at night with a kitten's voice?
- Cholesterol and stress
- Manicure at home
- Effective facial






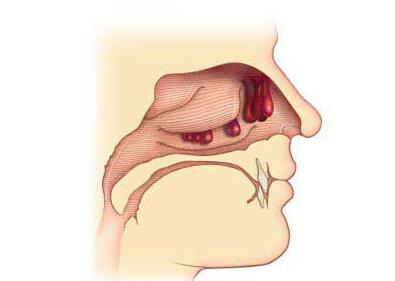
 Attention! Asthmatics in no case be done. And indeed this medicine to take.
Attention! Asthmatics in no case be done. And indeed this medicine to take.