Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- Hyperplasia of the cervix and endometrium: why treatment is necessary
- How much fracture is fused
- How do leaves change in autumn
- All you need to know about pumping honey
- Manifestations and recovery in case of marginal fracture of the first toe
- Wine fermentation at home
- Chicken with mushrooms - recipes with photos
- Treatment and rehabilitation for knee fracture
- Chicken fillet with porcini mushrooms in a pan
- What drugs lower cholesterol
Advertising
| What does the reactive change in the cylindrical epithelium mean. Hyperplasia of the cervix and endometrium: why treatment is necessary |
|
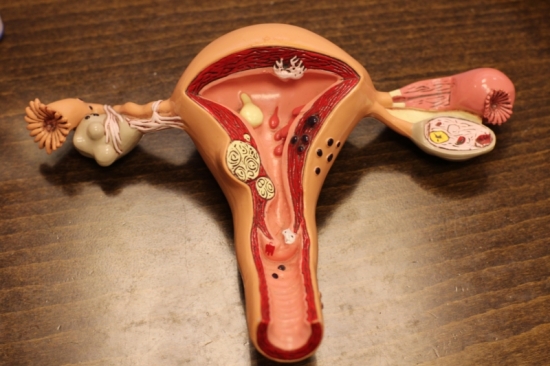
Almost all organs and systems affect the reproductive function. But nevertheless, it is genital organs that are especially important. Everyone knows that frequent inflammatory diseases in the absence of effective treatment can go into the chronic process. In this case, the symptoms are already not so pronounced, which makes the woman believe that she has no problems. But such processes are dangerous not only by chronicity. At the site of inflammation, hyperplasia of the glandular epithelium of the cervix often occurs. This pathology affects women of all ages when there are predisposing factors in the form of inflammation and other causes. But the most dangerous thing is that this disease has the property of degenerating into cancer. Moreover, the older the patient, the higher this risk. How to protect yourself from the disease and exclude the occurrence of cancer processes? To do this, it is enough to understand what constitutes hyperplasia and when to begin to sound the alarm. Why do extra cells appear?This disease is characterized by pathological growth of glandular cells, which ultimately leads to thickening of the walls and volume of the uterus. The mechanism of such a process as epithelial hyperplasia is explained by enhanced proliferation or division of endometrial cells. Naturally, any growth of cells above normal is pathological, but hyperplasia itself is a benign disease.
The photo shows the layout of the woman’s uterus But this does not mean that you can “close your eyes” to the pathology and not conduct treatment. The whole danger of the condition lies in a very high risk of degeneration of glandular cells into cancerous. That is, this disease is a provoking factor for cancer and, therefore, requires timely treatment and long-term follow-up after it. Thus, we can conclude that the timely diagnosis of such a pathology as endometrial cervical hyperplasia and the inner layer is cancer prevention. It should be noted that in young girls with this pathology malignancy is practically not observed, while during the menopause the risks are very high, which is explained by a large number of provoking factors, such as a decrease in immunity, a slowdown in metabolic processes, and a deterioration in the functioning of many organs and systems, and so on. Further. Knowing what it is, you can easily understand what is the impetus for the development of pathology. As a rule, this is a change in hormonal levels. This explains the fact that most often the first signs of the disease appear at the age of 14-20 and after 45. It was at this time that young girls underwent a sharp change in hormonal levels due to puberty, and menopause and related changes began in women. In addition, pathology is often diagnosed in women with a history of inflammatory processes of the genital organs, abortion, the use of intrauterine contraceptives, pelvic surgery, and even a sharp rejection of hormone-containing drugs. All this violates the natural processes in the body and, under a certain set of circumstances, leads to enhanced cell growth, that is, hyperplasia. Among the common causes that can affect the development of such a pathology as endocervix and endometrial hyperplasia are smoking, obesity, metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, uterine fibroids, cystic lesions, and so on. Forms of pathology and its signsDepending on what kind of changes occur in the endometrium, pathology can be divided into the following forms:
The first is characterized by the growth of glandular epithelium with the formation of a large number of cysts. With damage to the cervical canal, the appearance of brushes along its course and in the area of the pharynx is observed. It is important to note that most often cervical hyperplasia occurs simultaneously with endometrial damage, which requires more thorough diagnosis in order to conduct treatment aimed at all areas of the lesion. The second form proceeds with an increase in glandular cells, which can vary both in size and in localization on the endometrial mucosa. The atypical form is the most dangerous, since every tenth woman degenerates into cancer. As for the focal form, it is characterized by the complexity of the diagnosis, since changes in tissues are located only in some areas. The rest of the endometrium is not affected. That is, when conducting a biopsy, there is a chance of taking material from the unaffected part of the endometrium, which will give false negative results. At the same time, glandular hyperplasia of the cervix of the focal form is diagnosed quite easily due to visible polyps on the pharynx and in the cervical canal.
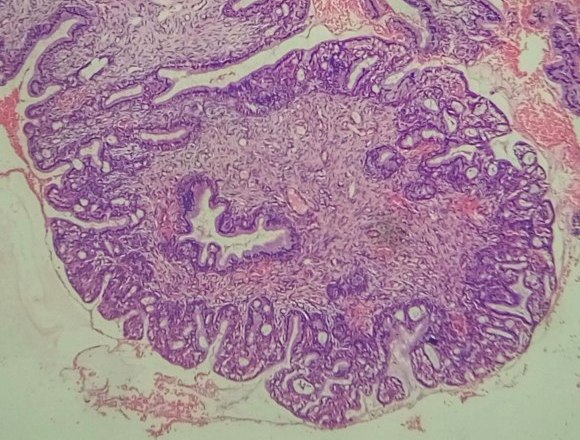
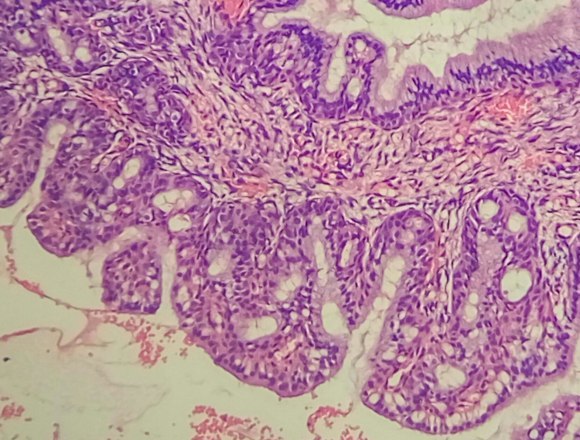
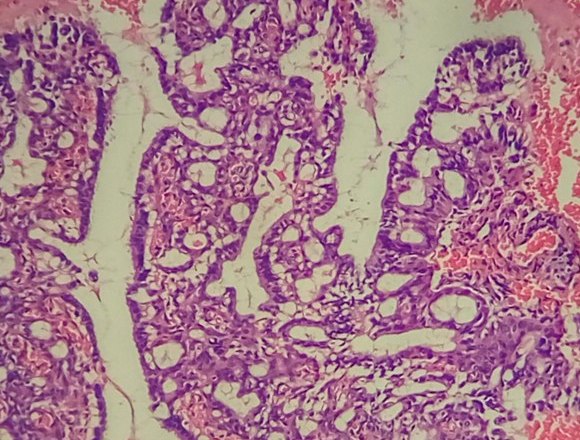
More details about the causes of cervical pathologies are described in the video: Diagnosis and treatment of the diseaseIf during the examination the gynecologist suspects that there is hyperplasia of the cervical endometrium or the inner layer of the uterus, ultrasound is first prescribed. Thanks to him, the thickness of the organ is determined, which normally should be no more than 9 millimeters. In addition, it is possible to determine the nature of the lesion, since in the photo the glandular and glandular-cystic form have a uniform tissue change, and the focal, in contrast to them, is represented by normal endometrium with areas of hyperplasia. Almost always, treatment begins with curettage of the uterine cavity and cervical canal under the control of hysteroscopy, which eliminates focal hyperplasia, which is often localized in the corners of the uterus. After this, a course of hormonal therapy is selected, aimed at restoring the endometrium, normalizing the menstrual cycle and reproductive functions. In women over 45, the goal is to achieve persistent menopause. After completing the course, patients should be kept at the dispensary for a long time and undergo ultrasound examination twice a year to exclude recurrence of the pathology. Only with all the recommendations can the risk of developing cancer of the uterus and cervix be completely eliminated. Glandular hyperplasia is characterized The task of the cytological study is not so much to ascertain the presence of glandular epithelium on the vaginal portion of the cervix, as to carefully examine the smears in order not to miss the pathological changes (atypia) in the glandular, metaplasized or squamous epithelium. It is not always possible to conduct a differential cytological diagnosis between superficial endocervicosis (physiological ectopy, ectopy associated with inflammation, hormonal imbalance) and proliferating (progressive) endocervicosis. Ectopia is more characterized by "calm" cells of a cylindrical epithelium of normal size and shape, located in the form of "honeycombs" or single, double-row "strips". With proliferating endocervicosis, the cells are arranged in groups or glandular structures, sometimes bilayer. The nuclei are enlarged, nucleoli are found in individual cells. Chromatin is distributed evenly, slight hyperchromia of the nuclei is noted. The nuclei are located mainly eccentrically. The cytoplasm is plentiful, basophilic or light foamy. Cells in the structures are somewhat layered on each other, differ in size within the structures and smear (Fig. 85, 86, a). With healing endocervicosis, a large number of metaplastic cells are also found in smears. In many medical institutions of the country it is customary to “cauterize" (carry out cryo-, Fig. 85. Hyperplasia of the glandular epithelium: a - glandular-like structure of cells of a cylindrical epithelium with a lumen in the center (indicated by an arrow). The nuclei are located eccentrically, the cytoplasm is plentiful (goblet cells). Papanicolaou staining. x500; b - a papillary-like structure of cells of a cylindrical epithelium (indicated by an arrow) and scattered lying glandular cells with enlarged nuclei. A smear with a vaginal portion of the cervix. Pappenheim staining. x500 electro- or laser coagulation of all “erosion”. This leads to the fact that many women with ectopia undergo unjustified surgical intervention. In addition, such interventions are fraught with the danger of development under the coagulated areas deep in the remaining glands and areas of the immature epithelium of dysplasia. Such dysplasia can develop for a sufficiently long time without cytological manifestations, since its surface is covered with normal epithelium. Fig. 86. Glandular hyperplasia: a - scraping from the vaginal portion of the cervix (histologically - proliferating endocervicosis). The cells are piled on top of each other, the nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio is shifted towards the nucleus. x200; b - polyp of the cervical canal (smear from the polyp) - elongated cells, the nucleus is oval, the chromatin structure is uniformly granular, single, small nucleoli. The cytoplasm is elongated, vacuolated in some cells. Pappenheim staining. x1000 The term " cervical hyperplasia"Primarily refers to epithelium and refers to proliferation and excessive cell growth. This process is diagnosed only with histological examination and does not have clear clinical manifestations. Since the cervix is lined with two types of epithelium - stratified squamous and glandular, hyperplasia can be of two types. Cervical hyperplasia is a compensatory-adaptive reaction related to background precancerous processes. The risk of tumor transformation in women of reproductive age is extremely low. In women in pre- and menopause, any stimulation of cell growth is dangerous, which requires greater caution. If morphological signs of atypia are detected, the process should be attributed to the tumor. Glandular cervical hyperplasiaThe most common cause of the development of glandular hyperplasia is dishormonal disorders, in particular, an increase in the level of estrogen in the body of a woman. Estrogens stimulate synthetic processes and directly control cell proliferation. Hyperplasia of the glandular epithelium is most often found in young girls, this is due to the formation of hormonal levels. In reproductive age, an increase in estrogen levels is usually observed with cysts and hormone-producing ovarian tumors, as well as obesity and hormone replacement therapy. Hyperplastic mucosa forms a different size of the papilla, and sometimes. The progression of the process can lead to a displacement of the glandular epithelium to the outer part of the cervix with the formation of the so-called papillary. Active proliferation of the epithelium can lead to the development of microglandular hyperplasia - a condition in which the glandular epithelium begins to form multiple small glands. Sometimes the glands can be stretched by secretion and form cysts, in this case the term “cystic hyperplasia” is used. Often microglandular cervical hyperplasia develops simultaneously with cancer of the uterus, especially in women in peri- and menopause. This is due to the fact that estrogens affect all target organs, including the endometrium. If glandular hyperplasia of the cervix is detected, a full examination of the female genital area is necessary.
Glandular hyperplasia is diagnosed only with histological examination of the material, i.e. if a cervical biopsy or curettage of the cervical canal was performed. Treatment should be based on the exclusion of the main process, since proliferation of the cervical epithelium is only a consequence. After removal of excess mucosa, duphaston is usually prescribed to neutralize the estrogen effect. Duphaston belongs to gestagenic drugs and is an antagonist of estrogen. Hyperplasia of the squamous cervixThis type of hyperplasia refers to reactive changes in the squamous epithelium, which covers the outer part of the cervix. Proliferation of squamous cells is characterized by thickening of the epithelial layer and the expansion of the basal germ layer - basal cell hyperplasia. Among the causes can be identified chronic inflammation and viral damage to the epithelium, especially the defeat of the human papillomavirus. The epithelium can also thicken in response to any irritation, be it physical, mechanical or chemical effects. With the exception of all provoking factors, hyperplasia of squamous epithelium passes without a trace. In morphological diagnosis, it is important to differentiate basal cell hyperplasia with impaired maturation of squamous epithelium, as this may be a consequence of dysplasia. Sometimes these processes are combined, since at the 1st degree, the growth of the germ zone also occurs with active proliferation and atypia of cells.
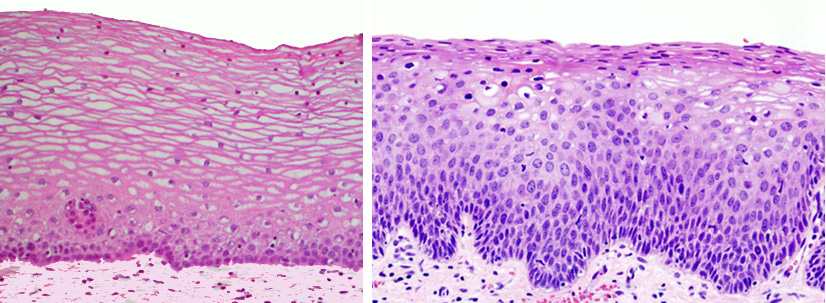
The left photo shows normal squamous epithelium, right - hyperplasia, characterized by the expansion of the basal germ layer, an increase in cell size and density. Findings:1. Cervical hyperplasia is a benign reactive process, but with a prolonged course it can be a source of tumor growth. Site - a medical portal for online consultation of pediatric and adult doctors of all specialties. You can ask a question about "glandular epithelium hyperplasia" and get a free online doctor's consultation. Ask your questionPopular articles on the topic: glandular epithelium hyperplasiaMastopathy is a breast disease characterized by a wide range of proliferative and regressive tissue changes with a violation of the ratio of epithelial and connective tissue components. Diseases of the breast outside pregnancy, united by the general term ... modern concept of pathogenesis, approaches to therapy "\u003e Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a preventable and treatable disease characterized by airflow restriction through the airways that is not completely reversible. Airway obstruction ,. Malignant neoplasms of the cervix Despite the existence of a clear concept of background and precancerous processes at present, as well as a fairly reliable test control (cytological, colposcopic), cervical cancer remains one of the urgent problems to date ... Endometrial hyperplastic processes Endometrial hyperplastic processes are a benign pathology of the uterine mucosa, which develops against the background of absolute or relative hyperestrogenism. Great scientific and clinical interest in this problem is caused by how high ... Adequate curation of patients with colonic polyps - effective prevention of colorectal cancer The identification, study and timely treatment of obligate precancerous neoplasms - colon adenomatous polyps (PTCs) - are the main and most effective measures to reduce morbidity and mortality from colorectal cancer (CRC). Currently... Ask your questionQuestions and answers on: glandular epithelium hyperplasia2015-04-29 06:16:06 Tatyana asks: Hello! I am 37 years old, 1 childbirth 11.5 years ago and 1 abortion in December 2014. In April I passed a smear and cytology, the result Colposcopy Answers Bosyak Julia Vasilievna: Hello Tatiana! It is impossible to draw conclusions virtually; you need to see the situation with your own eyes. In any case, before performing any manipulation on the cervix, the doctor must first take a biopsy of the cervix, and only after a histological conclusion can a cone or other procedure be planned. 2015-03-29 20:50:16 Asks Kira: Good afternoon. Tell me please, is it possible to make a cone with moderate dysplasia (note: sharply expressed viral. Ism (alt. Epit. More viral. Character than T3B + hormone. Meas. Preclimax-?). proliferation of glandular epithelium. -infection.-cells of glandular epithelium.-Hyperplasia of glandular epithelium is questionable. Microscopy: leukocytes 5-10 to 30. mucus - in large quantities. flora - see very different images (cocci, diplococci + leptotrix). chlamydia ? Marked HSV, HPV, CMV.Miko-, ureoplasmic infection? 2014-05-14 14:53:42 Elena asks: Good day! Biopsy revealed 1-2 grade dysplasia, HPV analysis - the presence of HPV type 52, PAP test based on liquid cytology: flat epithelium unchanged, glandular epithelium hyperplasia, cytogram without atypia, specific infectious agents absent, inflammatory reactive changes are mild . The doctor prescribed Laferon 3 million. 10 injections in sh / m, treatment with liniment cycloferon. I am very worried about injections, because I did not give birth, and I plan a pregnancy this year. Will such a number of injections (a doctor injects in several places in the neck) affect pregnancy? Perhaps there is a more gentle treatment in my case? Thank. 2013-07-24 21:48:50 Ksenia asks: Hello! 2012-06-02 17:17:56 Anastasia asks: Hello! My gynecologist diagnosed me with colpitis, cervicitis, cervical dysplasia, but when I passed the tests in another laboratory, the diagnosis is as follows: glandular epithelial hyperplasia, the degree of purity of my vagina is III. Tell me, are hyperplasia and dysplasia the same diseases? Answers Vengarenko Victoria Anatolyevna: Anastasia, no, of course, put colposeptin or terzhenan for 10-12 days, then genferon for 1 million 20 days in the vagina and after a month retake the smear. 2012-06-01 08:01:42 Asks Lyudmila: Hello, please explain: in the cytogram, hyperplasia of the glandular epithelium, in the gynecological smear, leukocytes 10-12-14, sticks. Examination by a gynecologist: small endometriosis of the uterine wall. I am examined every year: always a cytogram without features. Whether the diagnosis of hyperplasia is dangerous, what to worry about, what tests to conduct yet, or whether an annual examination is enough, this is not a sentence. I really look forward to hearing, because I am very worried. Thank you. I’m 36 years old, some birth, abortions and pregnancies were gone. Answers Dikaya Nadezhda Ivanovna: Upon examination, the gynecologist can see only the cervix, the walls of the uterus can be seen with another procedure. A cytogram is a smear from the cervical canal and cervix. Hyperplasia of this kind may indicate an inflammatory process on the cervix or in the vagina or smear taken on the eve of menstruation. This is not a “sentence,” it is an excess of well-readness on the forum with a twist of medical terms. I recommend: make an ultrasound with a vaginal probe, come for an examination in the cervical pathology cabinet for colposcopy of the s / m and re-smear. 2011-12-21 09:59:01 Julia asks: Good day! Answer: Good afternoon, Julia. Firstly, given the history of sepsis and adnexitis, primarily a question for your immune system, endocrine changes are possible. Secondly, given such a strong inflammatory process as yours (white blood cells 100-120 !!!), it is unlikely that some ureaplasmas can cause it. Perhaps there is a mixed infection - ureaplasmas are combined with other microorganisms, and this is a bacterial infection (coccal flora, trichomonads, etc.). Other infections should be examined. Your analyzes are quite contradictory, because 10 * 5 lactobacilli (!!!) were detected in the bacteriological sowing and nothing more, and in the smears of these same lactobacilli (Dederlein's bacillus) they are generally absent, which is not surprising with such inflammation. Look for the cause of inflammation and fix it, make high-quality bacterium sowing, at least. Ureaplasmas themselves are conditionally pathogenic microorganisms and require treatment only in the presence of ureaplasmosis (inflammation caused by ureaplasmas). But you still cannot do without antibiotic therapy, as there is a strong inflammatory process. Be healthy! 2011-11-10 12:22:10 Julia asks: Good day! Answers Consultant of the medical laboratory "Sinevo Ukraine": Good afternoon, Julia. You are talking about the inflammatory process - colpitis. Given that you have a history of sepsis, it may be a question of your immunity. Alfarekin is a synthetic interferon that has, among other things, immunomodulating properties, however, I think that this may not be enough to raise your immunity. But inflammation must be treated necessarily. I don’t know what you have found (ureaplasmas in PCR, IgG or M to them), but ureaplasmas are microorganisms from the group of transient microorganisms. In other words, they can be temporarily in the genital tract of a healthy woman, without causing any problems. In this case, no treatment is required. If they cause inflammation - ureaplasmosis, treatment of this inflammatory process is necessary. From the provided data there is no way to say what exactly causes the inflammatory process, accordingly I can not answer whether you need to treat it. Be healthy! |
| Read: |
|---|
Popular:
After how much plaster is removed
|
New
- Plaster cast care
- How to moisturize dry skin in the winter
- Fish oil Biafishenol: instructions for use
- How to clean the apartment yourself from damage
- Amanita mushroom - healing properties, how to take tinctures and prepare ointment
- Pelvic injuries
- Nail extension devices: a list of everything you need
- Owl tattoo and its meaning for girls and guys
- Honey and Mustard Chicken
- Is pregnancy with one kidney possible?