Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- Plaque formation and composition
- How do irons for hair
- Technological map of the lesson structure of seeds of dicotyledonous plants
- Overview of Old Testament Sexual Vocabulary
- After how much plaster is removed
- Handbook for kissing a woman's hand
- Summary of the lesson "first aid for bruises and fractures"
- Food Sources of Ascorbic Acid
- The most dangerous poison for humans
- We study a tree, playing: riddles about a birch
Advertising
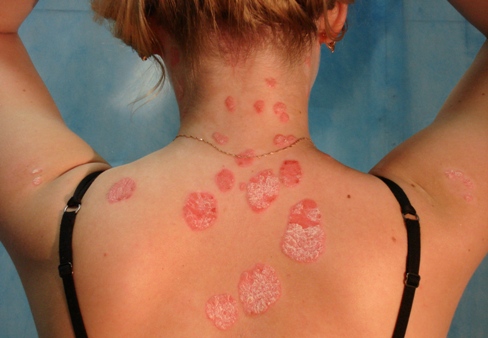
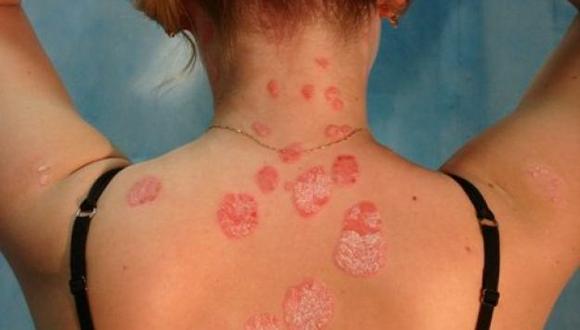
| Plaques appeared on the body. Formation of plaque and their composition. Popular treatment: the use of plants and other natural ingredients |
|
Cholesterol plaques - is a pathological accumulation of fat-like substance (cholesterol), calcium, connective tissue waste and fat on the walls of blood vessels. There is a definite relationship between increased cholesterol plaque, fat intake and the risk of developing diseases. Cholesterol, which is part of it, is formed in the liver of the human body. It is simply necessary for the construction of cell membranes and nerve fibers, it also participates in the production of hormones. In addition, cholesterol is simply needed to combine very important substances: corticosteroids, which are involved in improving immunity, contribute to stress resistance, help the body to resist inflammatory reactions. Cholesterol is necessary for vitamin D, which increases calcium absorption processes, and these are preventive measures; sex hormones that are responsible for fertility; for the production of bile acids. Thus, such a cholesterol body is simply necessary. It is formed in high-density lipoproteins (HDL), and returns to the liver, and the resulting cholesterol in low-density lipoproteins (LDL) supplies fat from the liver to various arteries. Almost 25% of cholesterol, thanks to food, enters our body, so if it contains a large amount of this substance, then cholesterol is not able to oxidize in the liver and in this form enters the blood, and this leads to the formation of cholesterol plaques. In nearly 99% of deaths, cholesterol plaques are found after fifty years, and after twenty years - in almost every sixth deceased. Sometimes the cholesterol plaque in the vessel is broken and the contents are poured out of it, after which a clot from the blood is formed - a blood clot. When content in the blood of more than 200 mg% of cholesterol, the characteristic pathological formations will necessarily be deposited on the walls of blood vessels. At first they will be a separate yellowish specks, and then already plaques. With the available cholesterol in the blood up to 240 mg%, the formation of atherosclerosis is almost doubled, and above 240 mg% - five times. Unfortunately, a very small number of people know what percentage of cholesterol is in their blood. Cholesterol plaques in the vesselsTheir appearance in the vessels indicates the development of such a disease as. Cholesterol plaques are formed on the rough walls of blood vessels in the form of layers of fat, which appears as a result of impaired metabolism. This disease can affect the medium and large sized arteries. Therefore, today the main task of medicine in the modern world is the prevention and treatment of cholesterol plaques that are in the lumen of blood vessels, and in severe cases contribute to their blockage. In vessels, cholesterol plaques consist of accumulations inside the cells and outside of their fats, growth of smooth and muscle cells, as well as connective tissue. In its zone, damage occurs to the protective endothelium, and this contributes to the formation of clots of the parietal nature, which to a greater extent disrupt the blood flow in the damaged vessel. Formed blood clots in the future partially destroyed, and their particles due to blood flow are transferred to the small vessels and cause thrombembolia, which is the cause of frequent death, stroke, cardiac muscle infarction in acute form. Since cholesterol plaques contribute to a sharp decrease in the elasticity of the vessel and its tensile properties, this causes an increased vascular resistance to blood flow and a rise in blood pressure in the affected vessel. If this pathological process affects the aorta or other large vessels, then there is an increase not only in local intravascular pressure, but also in general, systemic blood pressure. In addition, a vessel that is completely filled with cholesterol plaques cannot become wider in response to the increased oxygen requirements of the organs while their activity is increased. Thus, ischemia develops due to stress. Statistically, cholesterol plaques can affect vessels always, and not depend on the age category and type of human activity. Moreover, almost 10% of lesions occur at the age of up to fifteen years, 30% are found among the adult half of the population and 80% are elderly people. Cholesterol plaques causesThe pathological processes of cholesterol plaque directly affect: disturbed fat (lipid) metabolism, hereditary genetic predisposition and the state of the vessel wall. Cholesterol is fat and performs a significant number of functions in the body. It is necessary for him as a building material for cell walls, is in the composition of vitamins and hormones, which are necessary for the normal existence of the organism. Almost 75% of cholesterol is synthesized in the liver, and everything else is supplied by food. Cholesterol in the human body is in a complex combination of fats and proteins (lipoproteins), which are carried by the blood flow from the liver to various tissues, and when the cholesterol content is higher than that, the return process of lipoproteins and their utilization occurs. Just when this process is disturbed, cholesterol plaques form in the vessels and atherosclerosis develops. The main reason for the formation of cholesterol plaques is the low density of lipoproteins, which carry out the transport functions of cholesterol from the main blood-forming organ (liver) to the vessels. Excessive levels of this LDL increase the risk of atherosclerosis. The anti-atherogenic form of lipoproteins, which performs the transport of cholesterol back to the liver from tissues, is called high-density lipoprotein (HDL). This form cleans cells from excess cholesterol. Elevated levels of LDL and lowered HDL promote cholesterol plaque formation. As a rule, the first changes in the walls of vessels of large and medium sizes appear in youth and go through the whole process of evolution before the formation of cholesterol plaques, which are characterized by education after forty years. Vascular disease is observed at the age of twenty years in seventeen percent of cases, up to forty years - in 70%, and after fifty years - in 90%. Cholesterol plaque is characterized by the penetration of fibrin, cholesterol and some other substances into the vessel wall. With an excess of cholesterol, it becomes large in size, and this impedes normal blood flow in places of vasoconstriction. Thus, a decrease in blood flow is observed, inflammation develops in the vessels, thrombi are formed, which can break off and clog vital vessels, which will result in the termination of blood delivery to organs. The development and formation of cholesterol plaques are influenced by factors that are amenable to elimination and adjustment, as well as those that can no longer be changed. The first group of factors can be attributed to the patient's lifestyle: physical inactivity, smoking, a stressful state of character, abuse of alcoholic beverages and fatty foods with a significant amount of cholesterol; hypertension; hypercholesterolemia; with glucose levels above 6 mmol / l on an empty stomach; abdominal nature. The second group of factors includes first of all the age of the patients - these are men after forty-five years and women after fifty, or with early menopause. Also in men, cholesterol plaques appear in vessels much earlier, unlike women. And the last predisposing factor is familial hypercholesterolemia at the genetic level. This, as a rule, refers to strokes, heart attacks, the sudden death of close relatives under 55 years old among men, and women under 65 years old. All these adverse factors violate the integrity of the inner layer of blood vessels due to the pathological formation in them and contribute to the development of serious pathologies of the SS.C. Cholesterol plaque symptomsFor a long time, the symptoms of the existing cholesterol plaques in the arteries clearly do not manifest themselves. But with the passage of a certain amount of time, they undergo a transformation under the influence of physical exertion, stress, as a result of emotions, cardiac arrhythmias and high blood pressure. All these factors cause cracks or tears of cholesterol plaques, and thrombi form on their unstable surface, contributing to the progressive process of vasoconstriction. After that, blood circulation in the tissues and organs is disturbed, which contributes to the appearance of clinical symptoms that are already visible to the patient. It is very important in which vessels the pathological process is localized. On this depends the development of certain diseases with their symptoms. Cholesterol plaques underlie many diseases, such as, sudden death,; cerebrovascular diseases; Atherosclerosis various arteries and aorta. The formation of cholesterol plaques causes the simultaneous destruction of several vessels. A stroke increases the likelihood of heart muscle infarction in such patients by almost three times, and in the case of arterial lesions on the periphery, myocardial infarction can develop four times more often, and stroke three times. Symptomatic picture of the defeat of cholesterol plaques of the coronary arteries consists of a variety of manifestations, which are characterized by attacks of angina, the occurrence of myocardial infarction and insufficient functioning of the heart. In addition, all forms occur as a result of a characteristic vascular lesion. Cardiac manifestations account for almost half of the cholesterol plaque lesions. For example, aortic pathologies are more common after sixty years. And during the pathological process in the thoracic aorta, patients complain of the appearance of an intense nature of pain that bakes behind the sternum and radiates to the neck, back and upper abdomen. Against the background of stressful situations and physical exertion, this pain becomes stronger. It can also last for days, periodically intensify and weaken, which distinguishes this pain from that which is characteristic of angina pectoris. Sometimes the patient is disturbed by the process of swallowing, the voice becomes hoarse, the head is whirling and the patient may lose consciousness. With the defeat of the aorta, in the abdominal region there is pain in the abdomen with some swelling as well. If cholesterol plaques form in the place where the aorta splits into branches (aortic bifurcation), signs of intermittent claudication develop, the lower limbs become cold, ulcers form on the toes, and impotence often occurs. One of the serious complications of aortic damage is considered to be an aortic aneurysm and its rupture. With the defeat of the vessels of mesenteric properties, there are pains of a sharp, burning, cutting nature in the abdomen during eating, which lasts for almost three hours, and then there is swelling and a violation of the stool. In those moments when cholesterol plaques affect the renal arteries, blood pressure persists and urine composition changes. And with the defeat of the arteries in the periphery, there are signs of weakness with increased fatigue of the muscles of the lower extremities, while the legs begin to freeze, and then there is pain while walking (). Treatment of cholesterol plaquesIn order to begin treatment, primary diagnosis is performed with pressure measurement, weight determination and identification of risk factors (obesity, diabetes, hypertension). If you suspect the presence of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels, consult a cardiologist, oculist, neurologist, nephrologist, and vascular surgeon. And to clarify the extent of the damage, an ECG is performed using stress tests; Ultrasound of the aorta and heart; angiography, ultrasound inside the vessels, coronagraphy. These methods make it possible to identify cholesterol plaques and, in general, assess the damage. But duplex scanning, as well as triplex, allows to investigate the blood flow and the presence of a pathological process in the carotid artery, in the aorta of the abdominal section, in the arteries of the extremities. MRI is used to visualize the walls of blood vessels and cholesterol plaques. Without typical clinical manifestations with total cholesterol higher than five mmol / l, treatment begins with lifestyle modification. To begin with, they reject nicotine and alcohol, adhere to the anti-cholesterol diet and increase physical activity. After the indicators of total cholesterol are reached to five, and LDL is lower than three, it is recommended to repeat the examination in five years. But patients at high risk and total cholesterol higher than five mmol / l are recommended to change their lifestyle for three months, followed by re-examination. With the achieved performance standards of cholesterol, annually monitor lipid levels. In case of high risk (more than 5%) resort to drug therapy. As a rule, all patients with signs of vascular lesions with cholesterol plaques of any location are prescribed a cardinal lifestyle change and therapy with the use of medications. The basis of this treatment is a varied, cholesterol-free diet. This applies to obesity, and diabetes, and arterial hypertension. In the daily ration, the calorie content of foods should maintain a normal weight of the patient. Recommend to limit animal fats, replacing them with vegetable. In addition, you need to consume 400 grams of fruits and vegetables daily; lean meat and poultry without a peel, sour-milk, blown cottage cheese, bran bread, sea fish and oceanic. Be sure to limit salt intake to one teaspoon per day. Thus, the diet can reduce cholesterol, and thereby remove cholesterol plaques to almost 10%. To normalize body weight, an appropriate diet is selected, which takes into account the patient's age and concomitant diseases. In addition, patients who do not have symptomatic manifestations of vascular lesions are prescribed physical stress for up to 40 minutes daily. And with the pathology of SS.C. recommend walking, dancing, swimming with moderate intensity 1 or 1.5 hours a week. Do not allow power loads. It is advisable to walk, and not to use in the movement of transport. An important point in the treatment of cholesterol plaques is the refusal of smoking, as it drastically reduces HDL, pathologically affects the vessels, violates the rheological properties of blood. And this all increases the risk of disease and death by 20% from cardiovascular complications. People who smoke, almost doubles the risk of stroke, in contrast to non-smokers. The same applies to alcohol. The use of different types of drugs also leads to a sharp fluctuation of pressure, causes inflammation in the vascular system and disrupts the composition of the blood. For the treatment of pathologies caused by lesions of blood vessels with cholesterol plaques, four groups of drugs of lipid-lowering properties are used, that is, those that reduce cholesterol levels. Among them, nicotinic acid, statins, fibrates and sequestrants of bile acids are distinguished. These drugs have a stabilizing effect against cholesterol plaques, help to improve the functioning of the endothelium, suspend the occurrence of atherosclerosis and thereby affect the processes of lipid metabolism. Quite often, in medical practice, statins are used that reduce mortality and prevent complications. The dosage of drugs is chosen strictly individually, and the drug is taken only at night. Also sometimes prescribed essential phospholipids, which are preparations of auxiliary value based on fish oil. They are always used in complex treatment, in combination with statins. In some cases, surgical methods of therapy are used to treat cholesterol plaques in the vessels. This is carried out in cases of various complications of the underlying disease. Treatment with surgery helps restore arterial vascular patency, that is, it allows revascularization. In IHD, in order to prevent the occurrence of a heart attack, a bypass or stenting of the coronary vessels is performed. With the defeat of cholesterol plaques of cerebral blood vessels, the carotid artery bypass is performed. And in order to exclude the occurrence of gangrene in the lower extremities, prosthetic vessels of the main property are prosthetic. The scope and need for a specific surgical procedure is established by a surgeon, cardiac surgeon, or vascular surgeon. As a rule, surgery to eliminate cholesterol plaques does not lead to an absolute cure. Basically, with the help of the operation, it is possible to avoid complications, and not to eliminate the very cause that caused the formation of these pathologies inside the vessels. Therefore, after the operation, the main methods of treatment remain upgrading to the positive side of their lifestyle with food, as well as the use of conservative therapy. In addition, an important primary prevention of cholesterol plaque formation in vessels is to control cholesterol indicators, exclude nicotine, alcohol and drugs from your lifestyle, adequate load distribution, weight reduction to normal, avoidance of emotional overloads, normalization of glucose and blood pressure, as well as compliance diet that eliminates the use of harmful products. But the secondary prevention of cholesterol plaques caused by the use of previous measures with the use of antiplatelet agents and statins. Mar 12 Cholesterol plaques on the body. What is the problem?Reduced working capacity, memory impairment, high blood pressure are just a few of the consequences that people inevitably expect if they have cholesterol plaque formation. And all because these plaques, settling on the inner walls of blood vessels, interfere with the normal flow of blood, which means that the body as a whole and each of its organs in particular receive an insufficient amount of oxygen and other elements, which carries blood with it. Interestingly, the cholesterol plaques on the body almost do not appear, they are visible only on the face in the eye area. Thus, the body signals that the metabolism is seriously disturbed. Bad and good cholesterolTo the credit of cholesterol, it should be noted that not all of it is harmful to the body. On the contrary, there is, let's say, "good" cholesterol, which plays a very important role in the process of human life, being a building material in the course of cell formation, because it is perfectly absorbed by the body, ensuring its full functioning. The other cholesterol is the “bad” one, which is ingested with animal food, especially fatty. It is not absorbed into the blood, but, like no one else needs, dangles through the vessels until it sticks to one of the walls. This is where it all begins ... Cholesterol plaque formationBy itself, cholesterol is a viscous mass, similar to wax. And here some mass of this substance settles on the vessel wall. It is not only new pieces of “bad” cholesterol that immediately join it — calcium molecules are right there. The latter serve as a fixer. And now ready, durable cholesterol plaque stands in the way of blood flow. If the number of plaques was insignificant, then the risks of strokes and heart attacks would be minimized. But, unfortunately, a person is so arranged that he loves to eat more tasty and fatter, and as a result he gets blood vessels clogged with cholesterol plaques and, as a result, serious diseases. Cholesterol controlThe body beats the alarm when there is no longer any strength to endure - it shows the person cholesterol plaques on the body so that they are immediately visible - right on the face, in the eye area. This means that an urgent need to check the entire cardiovascular system and cholesterol levels in the blood. Everyone must know the rate of "bad" cholesterol in the blood. It ranges from 4 to 5.2 mmol / l. Anything higher than this is already dangerous. Treatment and PreventionRestore the normal activity of the body is quite possible. To do this:
Let's talk about nutrition in particular, since it is the consumption of fatty animal food, including:
causes the appearance in the blood of the very "bad" cholesterol. In other words - all the troubles come from the irrepressible appetite. And it is worth replacing the above products with:
and the result in 2-3 weeks will be noticeable. Cholesterol levels will go back to normal. It is only necessary to eat reasonably not in the period of exacerbation, when life is already hanging in the balance, but constantly. Just when this process is disturbed, cholesterol plaques form in the vessels and atherosclerosis develops. In nearly 99% of deaths, cholesterol plaques are found after fifty years, and after twenty years - in almost every sixth deceased. Cholesterol plaquesAt first they will be a separate yellowish specks, and then already plaques. Cholesterol plaques are formed on the rough walls of blood vessels in the form of layers of fat, which appears as a result of impaired metabolism. Statistically, cholesterol plaques can affect vessels always, and not depend on the age category and type of human activity.
The main reason for the formation of cholesterol plaques is the low density of lipoproteins, which carry out the transport functions of cholesterol from the main blood-forming organ (liver) to the vessels. Elevated levels of LDL and lowered HDL promote cholesterol plaque formation. With an excess of cholesterol, it becomes large in size, and this impedes normal blood flow in places of vasoconstriction. The development and formation of cholesterol plaques are influenced by factors that are amenable to elimination and adjustment, as well as those that can no longer be changed.
Red spots on the body itch: causes and concomitant diseases.Also in men, cholesterol plaques appear in vessels much earlier, unlike women. For a long time, the symptoms of the existing cholesterol plaques in the arteries clearly do not manifest themselves. On this depends the development of certain diseases with their symptoms. Cardiac manifestations account for almost half of the cholesterol plaque lesions.
If you suspect the presence of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels, consult a cardiologist, oculist, neurologist, nephrologist, and vascular surgeon.
MRI is used to visualize the walls of blood vessels and cholesterol plaques. As a rule, all patients with signs of vascular lesions with cholesterol plaques of any location are prescribed a cardinal lifestyle change and therapy with the use of medications. Where did these plaques come from?The same applies to alcohol. For the treatment of pathologies caused by lesions of blood vessels with cholesterol plaques, four groups of drugs of lipid-lowering properties are used, that is, those that reduce cholesterol levels. In some cases, surgical methods of therapy are used to treat cholesterol plaques in the vessels. This is carried out in cases of various complications of the underlying disease. With the defeat of cholesterol plaques of cerebral blood vessels, the carotid artery bypass is performed. As a rule, surgery to eliminate cholesterol plaques does not lead to an absolute cure.
But the secondary prevention of cholesterol plaques caused by the use of previous measures with the use of antiplatelet agents and statins. A few years ago I had brown plaques on my body.
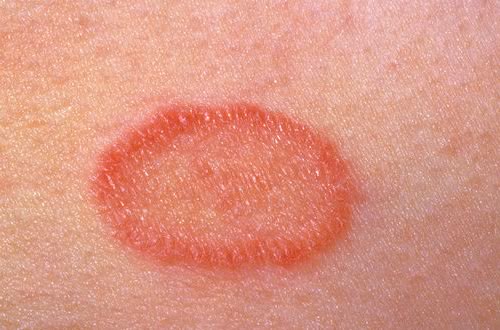
What ointment can be used for the treatment of pink lichen?HLS ”: So, does any yellow spot on the body become keratoma over time? I.SH .: Each one is different: one spot will remain a spot, someone will grow into a plaque, and the third will have both.
No one has commented on this entry yet. I had brown plaques under my breasts and on my back, and in some places on my hands. Please tell us about this disease. Recipes tinctures and decoctions to eliminate cholesterol plaquesThis is a different type of keratosis. They need to eliminate work with these substances. And this is not by chance. In this regard, it is important to carry out the treatment of plaques in the vessels in a timely manner in order to prevent the development of diseases and their complications. Diet - a method for the prevention and treatment of plaquesCholesterol is necessary for vitamin D, which increases the processes of calcium absorption, and these are preventive measures of osteoporosis; sex hormones that are responsible for fertility; for the production of bile acids. When content in the blood of more than 200 mg% of cholesterol, the characteristic pathological formations will necessarily be deposited on the walls of blood vessels.
Symptoms of pink lichenTheir appearance in the vessels indicates the development of such diseases as atherosclerosis. This disease can affect the medium and large sized arteries. The pathological processes of cholesterol plaque directly affect: disturbed fat (lipid) metabolism, hereditary genetic predisposition and the state of the vessel wall. Cholesterol plaque is characterized by the penetration of fibrin, cholesterol and some other substances into the vessel wall. The second group of factors includes first of all the age of the patients - these are men after forty-five years and women after fifty, or with early menopause. The formation of cholesterol plaques causes the simultaneous destruction of several vessels. Cholesterol plaques are a pathological accumulation of a fat-like substance (cholesterol), calcium, connective tissue waste and fat on the walls of blood vessels. Atherosclerotic plaques
With atherosclerosis - a chronic lesion of the arteries - sooner or later, atherosclerotic plaques inevitably form, narrowing the arterial lumen and provoking the occurrence of a gradually increasing circulatory deficit in a particular area. Why do they appear? How to prevent their development? What if the vessels are already affected? These and other questions will help you find the answer in this material. ICD code 10:
The appearance of plaques in atherosclerosis: causesPlaques are cholesterol deposits on the vascular arterial wall. In appearance they resemble small tubercles, or growths. At the moment, a large number of different assumptions regarding the causes of the formation of these growths are being considered, but the most reliable of them is considered to be an elevated amount of cholesterol in the bloodstream. It should be noted that, in addition to cholesterol, its components (fractional components) also play a big role. Many of them behave quite negatively and provoke the development of atherosclerotic changes in all vascular walls. But there are also such factions that try to prevent the negative effects of the first components on the vessels. For a more accurate and visible assessment of the degree of damage to blood vessels, specialists use the so-called “atherogenic index (coefficient), the normal indicator of which should not exceed 3. It is determined by laboratory method, donating blood to the lipid spectrum. It is important to note that growths are formed not only in the arteries related to the heart, but also in any other vessels. The nature of the developing disease and its clinical picture depend on which organ has the most vascular lesion. Each patient has its own peculiarities in the development of atherosclerosis. The factors that can directly affect the rate of plaque formation are identified:
If you do not make an effort and do not eliminate the above factors, then sooner or later atherosclerosis will certainly be felt. How do plaques appear: pathogenesisFor the successful deposition of fats on the walls of the arteries, it is necessary that some favorable conditions be present in the vessel - for example, a minor defect in the vascular wall, or slowed down blood flow in a certain area. Most often, this problem occurs in the area of artery branching. At the same time the vessel wall becomes edematous and friable. The duration of this stage can be different, because in a healthy body, near-wall enzymes prevent the deposition of fat, dissolving them - this process can be observed even in one-year-old children. If the protective mechanisms fail, then the formation of complex compounds, which consist of proteins, lipids, cholesterol, begins, and in the complex of this interaction the build-up of growths on the vascular wall begins. Subsequently, where there was a fatty deposit, there is an increase in fresh connective tissue, the development of liposclerosis is observed. Over time, the growth becomes more and more formed. The structure of an atherosclerotic plaque is the core and the outer layer (lid), which consist of fats and connective tissue fibers. The composition of the nucleus - some of the free cholesterol with esters. Around the nucleus are "foamy" cellular structures - macrophages containing fats. Over time, the fats pass into the nucleus, destroying macrophages. The outer layer is part of the growth that projects into the lumen of the vessel. It is a fibrous casing with collagen fibers and elastin, the percentage of which directly affects the tendency of the tire to break. Initially growths have a semi-fluid consistency and are still soluble. However, this does not make them less dangerous. Due to their weak density and looseness, growth of the growth elements can occur, which can lead to blockage of the arterial lumen. What it threatens: loss of vascular elasticity, damage to blood vessels, the formation of blood clots - blood clots. All this only exacerbates the already problematic situation. Over time, the tire of an atherosclerotic plaque is compacted, and calcium salts are deposited in it. The final stage of its formation begins - atherocalcinosis. Calcified atherosclerotic plaque is already distinguished by its stability and slow growth, which gradually leads to a deterioration in blood flow and supply in this area. There is also such a thing as a heterogeneous atherosclerotic plaque. This plaque can be attributed to the complicated course of the disease, as it is characterized by the presence of ulcerations and hemorrhages, uneven contours and loose grooves. Atherosclerosis plaques are stable and unstable, which depends on their structure, volume and structure. Stable atherosclerotic plaque is characterized by constancy and slow progression over the years. It contains a large amount of collagen, which makes its walls elastic and resist rupture. Unstable atherosclerotic plaque is rich in lipids. It tends to rupture and expose the endothelium, which leads to the formation of a blood clot overlying the affected vessel. Atherosclerotic plaque rupture can occur without any special symptoms. The further clinical picture and the patient's condition will depend on the rate of formation and localization of the subsequent thrombus. "Old" calcified growths do not represent such a danger as semi-fluid, since they are not prone to ulceration, but they are practically not amenable to involution. In most cases, atherosclerotic changes are irreversible and lead to prolonged tissue ischemia, development of heart failure, coronary heart disease, heart attack or arrhythmias. The most significant stages in the development of atherosclerotic plaque can be characterized as follows:
What signs may indicate the appearance of plaques?Symptoms of the formation of atherosclerotic changes in the vessels may not appear for a long time, because the reduction of the lumen due to growth is a rather slow and long process. Signs of damage can be different, depending on the location of problem areas, the size of sediments and other factors. Galls can not be destroyed for a long time and remain in one place, gradually increasing only to a certain size. In this case, signs of vascular damage may not be. If the plaque grows tirelessly, reducing the degree of blood flow in the organs and tissues, then there may be such a sign of the disease as pain (especially after physical exertion, with accelerated blood circulation). Another symptom variant is observed when the growth is decomposed, and its elements migrate along the vascular grid. A thrombus forms at the site of the destroyed plaque, which increases the likelihood of blockage of the vascular lumen. Such a condition can provoke a heart attack or stroke (in case of blockage of the coronary and cerebral vessels). Absolutely all the symptoms of atherosclerosis are comprised of signs of circulatory disorders and nutrition of certain organs and body systems. Atherosclerotic carotid plaque often asymptomatic, which, of course, can cause a number of complications. But, more attentively listening to your body, you can notice some signs of atherosclerosis. For example, ischemic attacks can occur periodically, which manifest themselves:
These signs are already considered a serious reason for going to the doctor. Atherosclerotic plaques in the aorta may give different symptoms depending on which of the aortic parts they are located in — in the thoracic or abdominal. With thoracic localization severe painful sensations that last several hours or days may occur. The pain appears behind the sternum, or in the region of the heart, sometimes gives to one of the limbs, shoulder region, neck, shoulder blade. Such pain, in contrast to the heart, can not be eliminated by taking nitroglycerin. Over time, dyspnea, heart failure, and elevated upper blood pressure may occur. Signs of cerebral ischemia develop:
With defeat of the abdominal aorta disorders of the abdominal organs appear:
Atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels of the lower extremities The first time also does not give pronounced symptoms. Only with circulatory disorders can there be pain while walking, lameness, which is explained by a lack of oxygen and nutrients in the muscles. Subsequently, trophic disorders develop:
In the later stages, an additional sign of lesion of the leg vessels is the disappearance of the pulsation at the points of proximity of the arteries (on the thighs, under the knee, behind the inside of the ankle). Atherosclerotic plaques in the head (lesion of cerebral vessels) are manifested, first of all, by mental disorders.
At the same time, there are three stages in the development of pathology:
Atherosclerotic changes in the vascular wall: effectsAtherosclerotic growths on the vascular walls is a slow and continuous process that affects large areas of the artery network. The effects of plaque are almost unpredictable. For example, for a sufficiently long period of time, the growth may be hidden, and then suddenly manifest itself with a coronary attack. In addition, the complications and their nature depend on the location of the atherosclerotic process. For example, in lesions of cerebral vessels, transient ischemic attack and stroke are considered the most frequent complications. Less common, but a serious consequence of the neglected process of atherosclerosis may also be dementia - the development of post-atherosclerotic dementia. With the defeat of the abdominal and thoracic aorta, such adverse conditions can occur:
However, the most common complication of atherosclerosis is stroke. It can happen as a result of a blockage of a vessel with a blood clot, due to a lack of blood circulation and a violation of the trophic tissue of the brain. In order to avoid troubles, it is necessary not only to provide timely treatment, but also not to forget about preventive measures. Diagnosis: Disease Recognition TechniquesTo establish the diagnosis of atherosclerosis, in principle, is not difficult. However, to more accurately characterize the disease, it is necessary to undergo a series of studies that will help to assess the complexity of the pathology, the location of the lesion site, and the likely consequences. The general diagnostic scheme is based on the following stages:
Analyzes in the laboratory are conducted to establish the initial cause of the disease. Examine the body for the presence of infection, as it has long suggested that infectious diseases may be involved in the development of atherosclerosis. Also conduct the following laboratory tests:
Instrumental diagnostics involves the use of high-precision survey techniques. The first thing to do is an ultrasound of the vessels, which helps to detect the presence of atherosclerotic changes. In order to determine the degree of damage to the arteries, prescribe such studies:
Differential diagnosis of atherosclerotic plaques carried out depending on the localization process:
TreatmentHealing activities usually begin with the appointment of a diet. Medications are prescribed if after 1-2 months the atherogenic index does not decrease, or when the doctor knows in advance that the patient suffers from coronary heart disease. It is wrong to assume that there is no need to adhere to the diet in the course of drug therapy. Successful treatment results can only be obtained by applying an integrated approach. Currently, the number one drugs to reduce the amount of cholesterol and its fractions are statins. The effect of statins on atherosclerotic plaques is effective and harmless, in addition, these drugs have a specific pleotropic effect. What does this mean? This means that, thanks to the statins, the general condition of the patient improves, since the metabolism is activated in most organs, which is in no way connected with the percentage of cholesterol in the bloodstream. Statins include drugs based on the following active ingredients:
These drugs can inhibit cholesterol synthesis in the liver. It has been proven that almost half of all cholesterol is ingested with food, and another half is produced by the body itself. From this it can be concluded that the simultaneous observance of certain rules of nutrition can significantly limit the amount of "external" cholesterol, and the use of statins reduces the production of "internal" cholesterol. In addition to statins, fibrates can also be prescribed - these are drugs that also lower cholesterol, but are prescribed only in combination with statins, and only when the treatment with the first group of drugs fails to cope with elevated triglyceride levels. Such drugs as Fenofibrate, Cyprofibrate, Clofibrate can be considered drugs-fibrates. In some cases, doctors also prescribe nicotinic acid, but this drug has a large number of side effects, which does not allow to use it for a long time. Also in the treatment can be used anion exchange resins and sorbents that reduce the absorption of cholesterol in the intestinal cavity. Such drugs include Cholestyramine, Colestipol, Neomycin, Enterosgel, Polyphepanum, etc. Of the vitamin remedies, Askorutin, Aevit, Aneurin, Biovital vitamin C are the most popular. Popular treatment: the use of plants and other natural ingredientsIn order to reduce cholesterol absorbability and reduce its penetration into the endothelial tissue of the vascular wall, these drugs are often prescribed:
From this collection, you should prepare an infusion (for 4 tablespoons of collection - 500 ml of boiling water) and drink it in 100 ml three times a day after meals.
Infusions are prepared and taken according to the principle of the first recipe.
Prepare the infusion (2 tablespoons. Collection per 400 ml of boiling water) and use in small sips throughout the day. It is recommended to carry out such treatment courses, for one and a half to two months, with intervals on rest in 1 month. To adjust the level of cholesterol, you can prepare this mixture of herbs:
A mixture of herbs poured boiling water (400 ml of water - 2-4 tablespoons of the mixture) and consumed throughout the day in small sips. To stabilize the permeability of blood vessels, you can prepare this collection:
Four tablespoons of the mixture is poured 500 ml of boiling water, infused, filtered and consumed in 2 cups per day, regardless of the meal. A good effect is also expected from the addition of medicinal plants such as strawberries, field horsetail, St. John's wort grass, coltsfoot leaves, fennel, dried marsh, motherwort to beverages and dishes. It is successfully used in the treatment of plaques garlic tincture, 20 drops up to 3 times a day, as well as alcohol tincture on the bulb onions, 25 drops three times a day. The duration of treatment is about one month. Herbal treatment must be supplemented with proper nutrition, which provides for a reduced intake of cholesterol and animal fats. Dietary nutrition with atherosclerotic plaquesTreatment of atherosclerotic changes in the vessels will not be so successful if you do not pay due attention to the principles of nutrition. The medical diet provides for the restriction of the use of products that contain cholesterol - animal fats, meat and by-products, eggs, canned food (both meat and fish), as well as chocolate, cocoa, and fatty dairy products. Preference is given to foods rich in iodine, ascorbic acid and B vitamins. For example, sea cabbage, legumes, zucchini and eggplants, broccoli and cauliflower, berries, nuts, dried fruits, citrus fruits are considered to be useful foods. Extremely useful when the growths on the walls of blood vessels to eat watermelon, which, in addition to the diuretic action, actively removes excess cholesterol from the bloodstream. Instead of butter and margarine, you should eat vegetable oils that contain large amounts of unsaturated fatty acids. As for drinks, it is preferable to drink green tea - it is rich in antioxidants, perfectly tones the blood vessels and strengthens their walls. Important: at the first signs of the formation of atherosclerosis, it is necessary to sharply limit the consumption of sugar and sweets, as well as salt. Homeopathy and its use in atherosclerosisHomeopathic remedies are often used to treat vascular diseases, in particular, atherosclerosis. Such drugs can be purchased at the pharmacy, as a prescription from the doctor, and in the free market. There are also specialized homeopathic pharmacies where you can get expert help in selecting the most appropriate drug. What homeopathic remedies are most often recommended for atherosclerotic growths in the vessels?
Homeopathic treatment is not recommended on their own, without consulting a doctor. These drugs do not cause harm and have virtually no side effects, but the decision on the appropriateness of their admission should be made by a specialist. Atherosclerotic plaque resorptionUnfortunately, it is almost impossible to completely clean the vessels from growths. Any methods involving the removal of an atherosclerotic plaque can lead to such complications as the formation of blood clots and blockage of the vascular lumen. As for the calcified growths, these plaques cannot be either dissolved or destroyed. Therefore, the treatment of vascular deposits is reduced, as a rule, to alleviate the patient's condition and prevent further appearance of plaques. But what to do in severe and neglected cases, for example, when the narrowing of the lumen of the arteries threatens the life of the patient? For such cases, there are special procedures.
Of course, scientists around the world continue to work on the problem of the formation of deposits in vessels. Maybe soon there will be new effective ways to combat this disease. PreventionAccording to statistics, every fifth person on the planet has atherosclerotic changes in the vessels. Indeed, atherosclerosis is a very common disease. Therefore, great importance is given to the prevention of this pathology. What are the preventive measures?
Take care to avoid stressful situations, do not be nervous, be benevolent and cheerful. If you still get nervous - drink a soothing tea based on valerian, mint, or use pharmacy drugs (novopassit, phytosed, valerian extract, etc.).
Try to get enough sleep, rest, and not once a week, but every day. It is best to go and wake up every day at the same time so that the body has time to recover.
If possible, periodically check blood pressure indicators. Remember: increasing these indicators at the same time increases the risk of atherosclerosis.
Such seemingly banal tips like giving up bad habits, an active lifestyle, physical exertion will help preserve your health for many, many years.
Avoid junk food, alcohol. Prefer plant foods, dairy foods, nuts - such healthy foods help lower blood cholesterol levels. In addition, try to periodically visit the doctor, as well as to conduct a blood test for glucose and cholesterol. Only in this way you will be able to suspect the disease in time and prevent its further development. ForecastPrognostic findings are determined by the stage of the process and its localization. For example, aortic atherosclerosis proceeds most favorably, and a more negative course is observed when coronary vessels are affected, especially if the patient already has angina pectoris attacks. Sluggish coronary sclerosis of small vessels can lead to severe circulatory failure. The possibility of employment is determined by the degree of vascular lesion and the nature of the process, as well as the specific characteristics of the patient’s profession. Damage to the cerebral vessels in most cases requires the termination of professional activity, if such work is associated with mental and physical exertion, frequent stress and nervous tension. General working capacity is disturbed, as a rule, at later stages of the disease, as well as with the development of complications. Atherosclerotic plaques are dangerous for the development of stroke and heart attack. At the first suspicion of a disease, it is necessary to immediately contact a cardiologist or a vascular surgeon. Medical expert editorPortnov Alexey Alexandrovich Education: Kiev National Medical University. A.A. Bogomolets, specialty - "Medicine" ReferencesChronic heart failure - Kalyuzhin V.V., Kalyuzhin O.V., Teplyakov A.T., Karaulov A.V. 2005 The main classifications and scales of risk in cardiology - Yu.A. Balanova, A.O. Konradi, A.V. End, O.P. Rotar, S.A. Shalnova. 2015 Heart arrhythmias - Belyalov F.I. 2014 Alphabet ECG and Pain in the heart - Zudbinov Yu.I. 2008 Cardiology - Yu.N. Belenkov, R.G. Oganov - Quick Guide. 2012 |
| Read: |
|---|
Popular:
Injured with pelvic injuries
|
New
- How an optometrist checks eyesight
- How to take grape oil
- Getting a driver's license: restrictions on vision
- Skin care at home
- Inexpensive personal care products
- How to get margarine and how to choose it correctly?
- How to speed up cervical dilatation before childbirth
- Peonies do it yourself: do it together
- Panting in a dream: causes of lack of air at night during sleep
- Mushroom poisoning: symptoms and signs, treatment and prevention