|

A new study of the University of Copenhagen (Denmark) demonstrates that the lack of folic acid can be much more dangerous in its consequences for the body than previously thought. Scientists have discovered that with a deficiency of folic acid, the process of DNA replication and cell division is disturbed, which is fraught with the development of cancer. According to Eurek Alert, scientists recommend regularly measure the content of folic acid in the body, [...]

A popular food additive, folic acid belonging to the discharge of vital substances, does not help the prevention of infarction, strokes, cancer and premature death, found out British scientists. Conducted by doctors from the University of Oxford (United Kingdom) - a respected publication of the American Medical Association. The authors of the work compared the many separate tests of folic acid together and summarized their results in the so-called metashext.

Anyone interested in their health people knows about important trace elements, vitamins and nutrients in which needs. Every day the body gets some of them through food, the rest is from food additives, leading to the thought that the body gets everything you need. Iron, calcium, vitamins, each of which is specific and indispensable; Amino acids, antioxidants, salts, trace elements ... This list is inexhaustible.

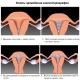
After you have finished protected, before the twelfth week of pregnancy, folic acid is simply necessary for the body. This vitamin refers to the group B. It must be taken to avoid hostile defects of the spinal cord. The known vice called the "Bift Spin" may appear due to the lack of folic acid. In fact, from the first days after fertilization, the process of forming a spinal cord, which [...]

Every woman dreams about the opportunity to make healthy child. In the process of navigating, vitamins taken by a pregnant woman occupy an important place. The most important vitamin for pregnancy planning, conception up to delivery is folic acid (it is vitamin B9). This vitamin is required to divide cells, the development of all organs of the fetus, the blood formation process. Its shortage in the body is fraught underdevelopment [...]

Canadian researchers found that additives with folic acid, taken by patients with breast cancer, can contribute to the growth of malignant cells. Folic acid (folate, or vitamin B9) is a water-soluble vitamin necessary for the growth and development of blood and immune systems. Its disadvantage can cause megaloblastic anemia in adults, and during pregnancy increases the risk of developing the nervous tube defects, [...]

People taking high doses of folic acid do not have an increased oncological risk, convince scientists. Some concern about possible side effects appeared partly from the concern that additional doses of folic acid can increase the risk of cancer cells. For analysis, the researchers analyzed the data of 13 separate observations in which participants were randomized by folic acid or preparations [...]

A new study has proven that the reception of folic acid and other B-vitamin additives cannot protect against the colon polyps. Some so-called observational studies assumed that people who get more vitamins in have less chances to get colon cancer. However, this assumption was refuted. In a new study, scientists suggested randomly selected women to take folic acid daily [...]
general information
Folic acid (Folate) is a water-soluble vitamin group B, contained in some products added to other and affordable in the form of food additives. Folate, previously known as folacine, is a common term for natural folate food and folic acid, a fully oxidized mono-coatable form of vitamin, which is used in food additives and to enrich food. Folic acid consists of a p-aminobenzoic molecule attached to a Ptemberce ring and one residue of glutamic acid. Flat foods that exist in a variety of forms contain additional remnants of glutamic acid and are thus polyglutamats.
Folate performs the role of coenzyme or space of single-carbon fragments in the synthesis reactions of nucleic acids (s) and amino acid metabolism. One of the most important folate dependent reactions is the gomocysteine \u200b\u200btransition to methionine in the synthesis of S-adenosyl methionine, an important donator of methyl groups. Another foal-dependent reaction, methylation of deoxyuridilate in thymidial during DNA production, is needed for proper cell division. Violation of this reaction leads to megaloblastic anemia - one of the most characteristic signs Folate deficiency.
After eating, food fouls are hydrolyzed in a mono-coat form in the intestine. Then they are absorbed by active transport in the intestinal mucosa. Passive diffusion is also possible when taking pharmacological doses of folic acid. Before entering the blood, the monoglutamate form is reduced to tetrahydrofolate (THF) or in methyl, or in formyl form. The main form of folate plasma plasma is 5-methyl-tgf. Folic acid is present in the blood and in a constant form (the so-called non-metabolized folic acid), but it is unknown whether such a form has biological activity and whether it can serve as a marker.
The total content of folate in the body is estimated at 10-30 mg; About half of this amount refers to the liver, the rest is in the blood and tissues. The concentration of pholta in serum is often used to assess its content in the body; The value reflecting the adequate folate content is more than 3 nanograms (NG) / ml. This indicator, however, fluctuates depending on the recent flow of folate with food, so it may not reflect the picture for a long time. To evaluate the folate status for a long period, such an indicator is responsible as the folate concentration in red blood cells. In people who have the consumption of Folate fluctuates from day to day - for example, patients, or recently taking the addition of folate, this figure reflects the folate reserves in tissues than the serum folate concentration. Additional folate reserves in the body corresponds to the level of the folate in red blood cells above 140 ng / ml, although some researchers suggest that the lower boundary should be higher to exclude defects in the development of the nervous tube.
The combination of serum and erythrocyte folate concentration and metabolic indicators can also help in the assessment of the foland status. The plasma concentration of homocysteine \u200b\u200bis often used as a functional indicator of the foland status, since the level of homocysteine \u200b\u200bincreases with the impossibility of converting homocysteine \u200b\u200bto methionine with a lack of 5-methyl-THF. The level of homocysteine, however, is an indicator of low specificity, as other factors affect it, including violation of the activities of the kidneys and disadvantage and other micronutrients. The most frequently used upper limit of the normal content of homocysteine \u200b\u200b- 16 micromol / l, sometimes lower values \u200b\u200bin 12 or 14 micromol / l are used.
The required amounts of folate are reflected in the recommended consumption standards (RNP),. RNP is a common term for several indicators used to plan and evaluate consumption in healthy people. These indicators depend on age and gender and include:
- Actually recommended consumption rate (RNP): Daily use of food vitamin, which is sufficient for everyone (97% - 98%) of healthy people in each age group
- Adequate consumption (AP): Secondary consumption at a given level or is more likely to be inadequate; This indicator is used to establish the PNP insufficient data.
- Expected average need (OSA): average daily consumption at this level adequately needs 50% of healthy people. Usually this indicator is used to assess the consumption of nutrients in the population, and not in individual individuals.
- Maximum portable consumption (MPP): Maximum regular daily consumption of a separate nutrient, not accompanied by undesirable effects
Table 1 shows the current RDP for the Folate in the MKG of the Food Folate Equivalent (PFE). This unit of measure was designed to reflect greater than that of food pholta, bioavailability of folic acid. According to scientific estimates, at least 85% of folic acid adopted with food is absorbed; For folate, this indicator is only 50%. Based on this, PFE is defined as:
- 1 μg PFE \u003d 1 μg of food folate
- 1 μg PFE \u003d 0.6 μg of folic acid from food additives taken with food, or enriched products
- 1 μg of PFE \u003d 0.5 μg of folic acid from food additives received by an empty stomach.
For children from the moment of birth and up to the year, the Folate is installed, equivalent to the average consumption of Folate with healthy babies on breastfeeding
|
|
|---|
|
Age groups
|
Men
|
Women
|
Pregnant
|
Nursing
|
|---|
|
From birth to 6 months *
|
65 μg PFE *
|
65 μg PFE *
|
|
|
|
|
80 μg PFE *
|
80 μg PFE *
|
|
|
|
|
150 μg PFE
|
150 μg PFE
|
|
|
|
|
200 μg PFE
|
200 μg PFE
|
|
|
|
|
300 μg of PFE
|
300 μg of PFE
|
|
|
|
|
400 μg of PFE
|
400 μg of PFE
|
600 μg of PFE
|
500 μg PFE
|
|
Older 19 years old
|
400 μg of PFE
|
400 μg of PFE
|
600 μg of PFE
|
500 μg PFE
|
* Adequate consumption (AP)
Folate sources
Food
Folate is contained in many products, including vegetables (especially dark green vegetables and leaves), fruits and fruit juices, nuts, beans, peas, dairy products, bird and meat, eggs, seafood, cereals. Most of the whole folate in spinach, liver, yeast, asparagus and Brussels cabbage.
In many countries, manufacturers need to add folic acid into bread, flakes, flour, pasta, rice and other grains. Since grain products are very popular among residents of many countries, they have become important sources of folic acid.
In a number of countries, folic acid includes in many grain products, such as wheat flour, pasta, flakes.
Nutritional supplements
Folic acid is available in the composition of multivitamins (usually at a dose of 400 μg), vitamins for pregnant women, in the preparations of group vitamins B and as a separate additive. Multivitamins for children typically contain from 200 to 400 μg of folic acid. The bioavailability of folic acid from the additives taken together with food is about 85%. When receiving an empty stomach, this indicator is approaching 100%.
In developed countries, one third of adults and children aged 1 to 13 years accept additives containing folic acid. Adults aged 51-70 take them more often.
Folate consumption level
Some people have increased risk of receiving too much folate. People have 50 years old and older has the highest level of folate consumption in the population, in 5% of them, it exceeds the MPP, equal to 1000 μg per day. Mainly this is a consequence of folate-containing additives.
Folate deficiency
The deficiency of alone folate occurs infrequently, a combined shortage of several nutrients is usually observed. This happens with defective nutrition, alcoholism and sometimes with suction disorders. Megaloblastic anemia, in which red blood cells are greatly increased and also have a nucleus - the main clinical sign Folate or Vitamin B12 deficit. Symptoms of megaloblastic anemia include weakness, fatigue, concentration disorder, irritability, headache, heartbeat and shortness of breath.
The deficiency of the folate may also lead to inflammation of the language and formation on it and the mucous membrane of the mouth of the shabby ulcers, a change in skin pigmentation, hair or nails and an elevated level of homocysteine \u200b\u200bin the blood.
In women with a lack of folate, the risk of children with violations of the nervous tube is increased, although the mechanism of this phenomenon is unclear. The insufficient level of the folate is also associated with a low birth weight, early genus and slowdown in the growth of the fetus.
Folate Risk Risk Groups
An explicit Folate deficiency is a rarity in developed countries, however, some individuals have a borderline level. Below are the categories of people whose risk of folate failure is increased.
Patients S. alcohol addiction
Nutrition of patients with alcohol addiction is often defective and does not contain an adequate amount of folate. In addition, alcohol affects the absorption of folate and its metabolism, speeding up its destruction. The nutrition of people suffering from chronic alcoholism in Portugal, where food is not enriched with folate, has shown that more than 60% of these people have a low level of folate. Even moderate alcohol consumption, for example, 240 ml of wine, or 80 ml of vodka per day, for two weeks can reduce the folate concentration in serum healthy men, although not lower than 3 ng / ml; At the values \u200b\u200bbelow it develops folate failure.
Women of childbearing age
All women who can become pregnant should receive enough folate to prevent the nervous tube defects and other malformations of future children. Unfortunately, the consumption of folate in many women is not high enough, even if they take additives. Women of childbearing age should take 400 μg of folic acid per day in additives and / or enriched products, not counting the natural folate content in food.
Pregnant women
Due to the participation of the Folate in the synthesis of nucleic acids, the need for it during pregnancy increases sharply. To satisfy her, pregnant women need one and a half times more folate than non-empty, namely 600 μg per day. So much folate is difficult to get only from food. Therefore, the reception of vitamins is recommended to ensure the need for essential nutrients, including folic acid.
People with suction disorders
Some diseases increase the risk of foul deficiency. In humans with suction disorders (), including tropical persons, inflammatory bowel disease, the absorption of folate can be observed compared to healthy people. Reduced secretion of gastric hydrochloric acid associated with atrophic
, Operations on the stomach and other states are also able to worsen the absorption of the folate.
Folate and Health
Folate is effective at:
- Treatment and prevention of folic acid deficiency.
Folate is most likely effective for:
- Reducing the level of homocysteine \u200b\u200bin people with kidney disease. About 85% of people with serious kidney disease have an elevated homocysteine \u200b\u200blevel. High level of homocysteine \u200b\u200bis associated with the risk of heart disease and. The reception of folic acid reduces the level of homocysteine \u200b\u200bin people suffering from kidney disease.
- Reducing the level of homocysteine \u200b\u200b("Homocysteinemia") in people with an increased level. High level of homocysteine \u200b\u200bis associated with the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Reducing the toxicity of the drug called Methotrexate, which is sometimes used for rheumatoid arthritis therapy and. The reception of folic acid seems to reduce nausea and vomiting - possible side effects of methotrexate.
- Reducing the risk of certain defects of the development (nervous tube defects) when taking pregnant women.
Folate may be effective for:
- Reducing the risk of developing cancer in thick and rectum. The reception of folic acid, both in the composition of food, and from the additives, probably reduces the risk of breaking the colon cancer. Folate is unlikely to help people who already have cancer.
- Risk reduction. The effect is more pronounced when an in addition to folic acid women get vitamins B6 and B12.
- Treatment skin diseaseknown as vitiligo.
- Reducing the risk of pancreatic cancer.
- When depressed, together with conventional antidepressants. According to one of the studies, however, the folate does not help when depressed.
- In case of problems with the gums observed when taking phenytin, subject to applying to gums.
- When problems with gums during pregnancy, when adding to the rinsel.
- With macular degeneration. According to some studies, the joint reception of folic acid and other vitamins, including B6 and B12, may help in the prevention of age macular degeneration (NMD).
Folate is hardly effective for:
- Reducing the risk of heart attack, stroke, etc. People with the disease of the coronary vessels.
- Reducing the risk of re-stroke.
- Reducing the severity of the side effects of the medication called Lometrecocol.
- At.
Folate is most likely ineffective with:
There are data, but not enough evidence of folate efficiency with:
- Prevent repeated closure of the vessel after angioplasty. The reception of the folate in combination with and, may, however, affect the healing of the vessel at the site of the introduction of the stent.
- . A few certificates indicate that the elderly people taking folic acid in a dose, greater than the recommended consumption rate (RNP), less than the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
- To improve memory and thinking of older people. There are conflicting evidence of the effectiveness of folate taking for these purposes.
- In the prevention of cervical cancer. There are some certificates in favor of obtaining a large amount of Folate from food and additives in combination with, and can help in preventing cervical cancer.
- Male infertility. Some studies suggest that the reception of folic acid together with the zinc can increase the amount of spermatozoa in men with a number reduced.
- Lung cancer. The links between the low level of folate and the lung cancer did not detected.
- Restless leg syndrome. Folate intake can facilitate symptoms. Studies are underway for whether Folate deficiency can lead to restless legs.
- In the prevention of colon cancer on the background of ulcerative colitis. The reception of folic acid can help patients with ulcerative colitis reduce the risk of cancer.
- Liver diseases.
- Alcoholism.
- Other states
Possible risks in excess consumption of folate
A large amount of folic acid can cure megaloblastic, but not damage to the nervous tissue caused by the disadvantage. Therefore, some researchers were concerned about the possibility of large doses of Folate "mask" lack of vitamin B12 until neurological consequences become irreversible. But anemia is currently not the basis for the diagnosis of vitamin B12, so it is now much more important is the possibility that high doses of folate accelerate or exacerbate anemia and cognitive disorders associated with vitamin B12, possibly by increasing the level of homocysteine \u200b\u200bor Methylmalonic acid. However, the high concentrations of homocysteine \u200b\u200band methylmalone acid in people with low levels of vitamin B12 and high-folic acid may be observed rather due to serious or pernicious anemia than a high level of folic acid. The high concentration of folate in the blood of young healthy adults does not aggravate the symptoms of the lack of vitamin B12. The question of the possible progression of precancerous changes under the influence of high doses of folate is also raised. This may increase the risk of developing colon and rectum cancer and some other types of cancer in predisposed people.
Based on the metabolic relations between pholom and vitamin B12, the Food and Power Supply Department established the MPP for the synthetic form of the folate (that is, folic acid) contained in the nutritional additives and enriched products (Table 2). The MPP for the form of the Folate, originally present in food, is not established, since there is not a single confirmed case of the occurrence of unwanted effects from the Folate from food. The MPP does not apply to individuals taking high doses of folic acid for its intended purpose and under the control of the doctor.
* Allowable sources of folate for babies should be: breast milk, artificial formulas and food
Interaction with medicine
Folic acid can interact with some drugs. Several examples are shown below. People who regularly host these medicines should be advised to the doctor before taking Folate.
Methotrexat
Methotrexate (Trexal®), the drug used in the treatment of cancer and is a folate antagonist. Patients taking methotrexate from cancer should consult with an oncologist before taking folate-containing additives, since folic acid can affect the antitumor effect of methotrexate. However, patients hosting methotrexate at low doses in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis or, folate-containing additives can help facilitate the side effects of methotrexate associated with the gastrointestinal tract.
Preparations against epilepsy
Anticonvulsant medications, such as phenytoin (Dilantin®), carbamazepine (Epitol®, Tehretol®) and Valproat (Depacon®) are used not only in epilepsy, but also in psychiatric and other diseases. These drugs are able to reduce the serum concentration of the folate. Moreover, additives containing folate can reduce the serum level of these drugs, so that people accepting these drugs before taking folate-containing food additives should be consulted with a doctor.
Sulfasalazine
Sulfasalazine (Azulfidin®) is mainly used in treatment. Sulfasalazine inhibits the suction of the folate in the intestine and can lead to its deficit. Patients hosting sulfasalazine should be consulted with a doctor about increasing the content of Folate in a diet, or on the reception of folate-containing food additives.
Folate and healthy eating
Recommendations for proper nutrition Indicate that "nutrients must come mainly from food. Food in the almost unchanged form contains not only the necessary vitamins and minerals, often included in the composition of food additives, but also fiber and other natural substances, which are beneficial on health ... Food additives ... may be appropriate in certain situations to increase the admission to the body of a particular vitamin or Mineral »
- Contains a lot of fruits, vegetables, wholegrain products, low-fat dairy products or low fatty dairy products. Many fruits and vegetables are reliable sources of folate. In developed countries, bread, flakes, flour, pasta, rice and other grain products are enriched with folic acid.
- Includes low-fat meat, bird, seafood, legumes, eggs, nuts and seeds. Many folate is in the beef liver. Peas, beans, eggs and nuts also contain folate.
- Contains a limited amount of solid fats (saturated and trans-fats), cholesterol, salt (sodium), sugar and refined carbohydrates.
- Contains the amount of calories not exceeding daily needs.
Citation:Gromova O.A., Rebrov V.G. Vitamins and oncopathology: a modern look from the standpoint of evidence-based medicine // RMZH. 2007. №16. P. 1199.
Vitamins, as part of the natural environment, stood at the origin of the birth of life. All system of homeostasis, adaptation mechanisms and age-related person are focused on this environment. Vitamins in a chemical sense are organic, low molecular weight compounds, absolutely necessary for human activity. They have enzyme and / or hormonal functions, but are not a source of energy, plastic material. They are necessary for all aspects of the vital activity of the body, including for antitumor immunity. Vitamins play an important role in the exchange of xenobiotics, the formation of antioxidant protection of the body, and at the same time, in some cases, vitamins are either not synthesized, or their synthesis, the formation of active forms is largely suppressed (especially in oncological patients, during dysbiosis, after myocardial infarction, with liver diseases, etc.). Finally, they can simply enter the body with food in insufficient quantities. The content of vitamins in food products, as a rule, does not ensure the daily need of the body. A number of patients with vitamins may not be absorbed (gastric cancer, reduction of suction area when removing a portion of the small intestine, dysbacteriosis, the aging of epithelocytes, vomiting, etc.). In this regard, there is a need for additional provision of the body with vitamins.
Vitamins come with food, which in itself can contain many potential carcinogens and mutagens (mycotoxins, nitro-compounds, pyrolysisidinic alkaloids, heterocyclic amines, fourocumarines, quinoline and chinoxaline derivatives, separate aromatic hydrocarbons), not balanced in the composition of fats, proteins, carbohydrates, Vitamins, trace elements (ME). Mutagenes and carcinogens under certain conditions can be food additives: potassium bromate, tin chloride, sorbic acid, thiobendazole, formaldehyde, sodium nitrite, sodium bisulfite, butylhydroxytoluluole (E321), butylhydroxyanisol (E320), food green, methanyl yellow, orange II, Floxin , Punchy SX, chromium picolinate et al.; inorganic compounds: bivalent metal cations (Mo, Hg, Cu, Mn, Cr, Ni, Co, etc.), inorganic compounds CO, CD, HG, AS, CR3 +, CR6 +, various Ni compounds, bivalent PB salts; acetate, oxide, sulfide and zinc chloride; Tourwaste vanadium, some compounds SE, MO, BE, AL, PL, SB, CU, MN, SN, etc.; Antiparasitic, antimicrobial, antivirus, etc. Medicinal preparations. Common property Most carcinogens are their ability to metabolic transformation into strong electrophilic reagents, actively interacting with nucleophilic centers of the cell of the cell. This is decisive in the process of damage to the cell and its transformation, including oncological.
Interest in the theme "Vitamins and carcinogenesis" appeared in the focus of their potential anticarcinogenicity. In the late 80s of the 20th century, data were obtained on an anticarceregenic effect of all vitamins in physiological doses, as well as data on the benefits of a green-board diet (the effect of folates, fiber, epihalocatekhins, selenial elements, calcium, magnesium, etc.) for Prevention of colon cancer. The expression "folic anticraft diet" received wide use.
In developed countries, an increase in the duration of life is noted and, as a result, the growth of tumors in the elderly and old age. At the same time, the elderly people with the maximum percentage of episodes of the occurrence of oncopathology, the reception of vitamins, Selena, other biodeadows rose tenp to times. The use of micronutrients is a period of systematization and evidence analysis. Most researchers note weak anticarcogeneity or neutrality against tumor growth, characteristic of vitamins in physiological doses. In some studies, safety is shown in oncological patients and higher, rather than physiological, doses of vitamin C, vitamin B1, its fat-soluble derivative (benfothyamine), vitamin B12, Nicotinomide, and others Linus Polinging on the anti-cancer action of pharmacological doses - hypeDosis (above physiological doses of 3-10 times) and megadosis (above physiological more than 10-100 times) vitamin C. Experiment-Men-Talnic and clinical studies in vitamins have been activated. A dose-dependent An-Ti-oncological threshold, natural or natural isoforms of vitamins and synthetic derivatives began to be studied. It turned out that the onco protection effect of physiological doses of vitamins begins to act still inside-morning: a placebo-controlled study showed that the use of pregnant vitamin complexes for two trimesters (6 months) reduces the risk of brain tumors in newborns (probability ratio (OR) \u003d 0, 7; 95% confidence interval (Ci) \u003d 0.5, 0.9) with a trend of risk reduction with long-term use of vitamins (tendency p \u003d 0.0007). The greatest reduction in the risk of developing brain tumors under the age of 5 was observed in the group of children born from mothers who took vitamins throughout all three trimesters (i.e. 9 months) (or \u003d 0.5; ci \u003d 0.3, 0, eight). This effect did not change depending on the histology of the tumor. Experimental proofs of the safety of the use of vitamins complexes, including vitamins of group B, C, E, D with cancer, the absence of metastasis, improving the overall state, is very important.
Today, the oncological incidence is considered as a variant of pathological phenopothesis. The prospect of a healthy longevity and cancer prevention is shown by the scientific program of the "human genome". The proportion of the significance of "Oncological polymorphisms of genome: oncogens of the external environment" is 6-8%: 92-94%, i.e. The genes responsible for the development of oncology are the targets whose state is changed by micronutrients. Despite the fact that many years have passed since the opening of the first vitamin, scientific passions are boiling around the vitamins. On the one hand, vitamins are just indispensable, essential micronutrients, and on the other - powerful medicinal products (Vitamin C - Treatment of Qingi, Vitamin B1 - Treatment of Polyneropathy). Normally, cyankobalamin and folates activate normal division and differentiation of cells. Tumor cells are undifferentiated or differentiated, divided by unguarded and superactively. How to be with vitamins, especially with an additional appointment of vitamins oncological patients? What to be with the provision of vitamins of the aging population that falls into the risk band for malignant diseases by age?
Vitamin C. Tumor cells synthesize a significant amount of collagenase and strromeview, as well as plasminogen activator, which helps to break the intercellular matrix, violation of cytoarchitectonic cells and release them for metastasis. The unique role of vitamin C is that Vitamin C takes part in the synthesis of collagen and together with the amino acid, lysine - in the formation of collagen bridges in the connective tissue. It gives it a purpose to purposefully use vitamin C in the rehabilitation period after operational interventions on tumors, in the methods of slowing down metastasis, stimulation of wound pressure and overcoming asthenization. For no less interesting studies on the prevention of tumors using vitamin C. In the life of the cells and the body, oxidation processes prevail in the process of the occurrence and development of malignant tumor. Maintaining a pH of the resource of gastric juice, blood is another vector of anticarcinogenic action of vitamin C, bioflavonoids and food products concentrating. In this regard, anticarcinogenic dietology is actively developing, ensuring the maintenance of the pH of the gastric juice, blood, urine in the range of the norm. The profilating possibilities of vegetables and fruits with a high content of vitamins C, E, β-carotene with respect to malignant transformation of the gastric mucosa was studied by Plummer M. with co-auto. (2007) in 1980 people, under the control of histological research of mucous membranes. Patients 3 years received one of the vitamins or placebo. Vitami-us antioxidants did not affect the malignation of the gastric mucosa. Another study studied the value of the provision of various vitamins for cancer damage kidney (767 patients, 1534 - control). It has no reliable communication with retinol, A-carotene, β-carotene, β-cryptoxanthine, lutein-zeaxanthin, vitamin D, vitamin B6, folate, nicotinic acid. Bosetti C. et al. (2007) a "profitable" effect for patients with kidney cancer sufficient security with vitamins C and E is noted. The composition of ascorbic acid and arsenic three-blocks with dexamethasone is effective in patients with multiple myeloma.
Low security vitamin C, insufficient consumption of fruits and vegetables rich in ascorbic acid and ascorbates, contributes to the infection of Helicobacter pylori; Both also provokes stomach cancer. The sick with atrophic gastritis was carried out by an eradication therapy of amoxicillin and omeprazole for 2 weeks about the presence in the stomach of Helicobacter pylori. In the future, for 7.3 years, they prepared preparations of vitamin C, E, selenium, garlic extract, distilled garlic oil. Repeated endoscopy with biopsy showed that Helicobacter Pylori eradication contributed to a significant improvement in the state of the stomach mucosa, but the subsequent long-term vitamin therapy and drugs of garlic did not affect the frequency of development in patients with gastric cancer. If, when broken down by type of cancer and the use of any single vitamin, it is possible to detect a reliable difference in terms of protection against tumors, then when considering all tumors and receiving all vitamins in reliable links is not detected. On the contrary, when analyzing Bjalakovic G. et al. (2007) 385 publishing, according to 68 studies, in 232606 participants in the category of elderly patients mortality from cancer turned out to be slightly higher among those who have used antioxidants for a long time (vitamin E, β-carotene, retinol), and in 47 tests in 180938 antioxidant participants showed slightly higher accuracy to increase mortality. In this case, the long-term preventive reception of selenium and vitamin C has a weak correlation with a decrease in mortality and risk of tumors. The researchers are not at all inclined to consider these data as "the sentence of antioxidants." The analyzed patients are a special part of the human population. They had severe chronic diseases and low health status. It is known that it is older people with chronic diseases In the US, Europe, China is much more likely to use biologically active additives with antioxidants than healthy. At the same time, the harder condition of the patient, the more often it resorts to the use of vitamins. Thus, the "comparison" group in this analysis is more healthy people. That is why the authors are in no way tend to consider the reception of vitamins and trace elements as the cause of increased mortality. It is very important for a doctor to be able to get acquainted with such important final studies in the form of full-text articles, and not by summary or only by the title of the article. The doctor cannot rely in his estimates of vitamins and trace elements on the information of popular publications, some sites on the Internet, which in pursuit of catchy headlines represent the most important material in a somewhat modified form. Evidence-evidence is still a cohort analysis and compare the level of health, mortality and reception of vitamins in adequate comparison groups. The entire experience of vitial and bio-elementology speaks in favor of a balanced secure prophylactic approach.
Different combinations of vitamins and minerals were investigated in order to reduce mortality from lung cancer among 29584 healthy Chinese (Retinol + Zinc; Riboflavin + Nicotinic acid; ascorbic acid + molybdenum; β-carotene + A-tocopherol + SE). During the test period (1986-1991) and after 10 years (2001), 147 mortal events from lung cancer were noted. The absence of differences in mortality rates from lung cancer for any of the four types of vitamin and mineral additives is shown. A five-year-old study on the effect of ascorbic acid (50 mg and 500 mg) on \u200b\u200brisk risk is carried out in Japan. Vitamin C, regardless of dose, significantly reduced the frequency of rhinitis and its appearances, but did not have any impact on the duration of the disease.
The question of oncological safety of highly seated dosage forms Vitamins was raised by research on β-carotine. At the end of the last century, the so-called "β-carotine paradox" was installed: the physiological doses of β-carotene had a protective effect when cancer of the bronchi and lungs in smokers, high doses of carotene led to an increase in the occurrence of the disease. Such is accurately convincingly established that the physiological consumption of β-carotene significantly reduces the percentage of primary tumors of the head, neck, light and esophagus, leuko- and erythrosquet, dysplastic and me-plastic changes of the cells. A significant reduction in the level of retinol, B-carotene, and, especially, the lycopene is found in children, AIDS patients associated with the threat of malignant rebirth. Numerous multicenter placebo-controlled studies show the role of carotene in suppressing the expression of receptors to the epidermal growth factor (EFR), which leads to the induction of apoptosis in the cells transformed under the influence of carcinogenesis. β-carotene protects DNA from damage and, moreover, reduces the expression of the anomalous Isoform of the P53 - Cancer cytomarker. The experiment found that β-carotene increases the expression of the key protein of intercellular contacts of Connexin 43 (C43) mouse fibroblasts and prevents the contact braking and the milignization of the epithelium. β-carotene suppresses proliferation only at the bases of intestinal crypt and does not act on the top of enterocytes, which are more often exposed to various external carcinogens.
Early Placebo-Controlled Research Hennekens C.H. et al. (1996) duration of 12 years (22,000 people) indicate that the long-term B-carotene physiological dose does not have a favorable or harmful effect on the frequency of occurrence malignant neoplasms and cardiovascular diseases in men. However, excessive consumption of B-carotene is considered as a likely risk of lung cancer in smokers (especially in malicious smokers). The four-dimensional placebo-controlled double blind study (Caret, 2004) in 18,000 people demonstrated that the long-term use of B-carotene in high doses (30 mg / day) in combination with vitamin A megatic (retinol; 25000 IU) not only Provides a favorable effect in people with elevated risk of lung cancer (smokers with cigarette consumption from 1 packs per day for up to 20 years), but even somewhat increases the risk of death from lung cancer and on other reasons associated with impaired metabolic disorders, especially in women . Sound proved long use B-carotene hypers, vitamin E, retinol in individuals with a polymorphism of a genome associated with an increased risk of lung cancer, while smoking and working with asbestos. In this case, the causal carcinogen is considered not b-carotene, as such, and the resulting complex compounds of free (excessive) B-carotene fraction with products combustion products of tobacco smoke, asbestos. Increased consumption of vegetables and fruits, including containing all the isoforms of carotenoids, including B-carotene, on the contrary, reduces mortality from lung cancer. Obviously, to resolve these contradictions, research should be supplemented with the assessment of the Balance ME (SE, Zn, Mn, etc.). Analysis of the established anticarcinogenic effects of physiological doses of B-Karotno implies the existence of immunopharmacological mechanisms for cumulation and microsomal biotransformation of B-carotene, which make it possible to ensure the elimination of carcinogens through identical microsomal disposal paths. Probably there is a synergism of B-carotene and ME in elimination of a significantly larger spectrum of carcinogens. Individual Du-although differences in biochemism, the immunotropic effect of B-carotene varies quite. The role of other carotenoids extracted from human blood plasma (Licopene, Lutein, Zeaxanthin, Pre-B-cryptoxanthine, B-cryptoxanthine, A- and G-carotene, polyenov connections) is studied.
Retinoides are a collective term for compounds included in the polyisoprene lipid family; They include vitamin A (Retinol) and its various natural and synthetic analogues. According to the mechanism of action, these are hormones that activate specific receptors (RAR-α, β, G). Reta-Noi-Di act at different levels: they control growth, differentiation, embryonic development, apoptosis of the cell. Each retinoid has its pharmacological profile, which determines the prospects for its application in oncology or dermatology. The most important and studied endogenous retinooid is retinoic acid. Natural retinoids (retinic acid, retinol, some vitamin A metabolites, etc.) and their synthetic analogs can actively influence differentiation, rapid growth and apoptosis of malignant cells, which determines their role in oncology (treatment of patients with promoelocytic leukemia) and dermatology. Research V.C. NJAR et al. (2006) showed that the therapeutic effect of retinic acid is limited to its multifactorial inhibitors, for example, cytochrome P450-dependent-Mi-4-PO-las enzymes (especially CYP26S responsible for the metabolism of retinic acid). In 2007, two research groups (Jing Y. et al. And Fenaux P.) stated that in the treatment of acute proposal blood leukemia with retinoic acid with arsenic preparations, remission can be achieved. The next Analogues of Retinol - Tamiberotin (AM80) (High Effective at Psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis ), Fenriti-Dean - Activator apoptosis of cancer cells. Near-static-com all synthetic retinoids is their toxicity and teratogenicity. Megadoses of vitamin A and its analogues and elevated doses of pyridoxine are studied for the treatment of bladder cancer. Recall that vitamin A is involved in the regulation of vehicles of iron and copper from the liver to the target organs, and the excessive flow of Fe and Cu promotes free radical oxidation and tumor, especially in the elderly.
XU W.H. et al. (2007) It was found that the Endometrial Cancer Prevention is the value of food retinol, β-carotene, vitamin C, E, food fibers (inulines).
Micronutrients and their concentrated forms: retinoids, polyphenol antioxidants (epigalocatechins, silimarine, isoflavon - genes, curcumin, liqueur, beta-carotene, vitamin E and selenium) are very promising and are already used in the treatment of skin cancer, along with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, diphluoromethylornitin, T4 Endonuclease v. Retinoides and vitamin A are used in prostate cancer therapy; They act antiproliferative, reinforcing cell differentiation, reducing the division index and the potentiation apoptosis.
Actual research on individual types of vitamins and groups of vitamins (vitamins of group B) were performed. To improve the quality of life of oncological patients, Vitamin B1 is very important. Mitochondria is the main intracellular organelles producing ATP molecules. Tiamine and other vitamins of group B are primarily a coherelfments of the most important enzymes that ensure the functioning of the cell, especially mitochondria, enzymes that restore energy resources in the central nervous system, liver, kidneys, heart muscle.
Cancer cells have high energy metabolism and level of glycolysis. For its growth, they need huge amounts of glucose, and it is well known that an excess of simple carbohydrates in Pi-Tania is a favorable environment for tumor growth. Currently, the global expansion of glucose-oleraidity of the Population of the Planet (Russia is located in the zone of the special risk of glucose-olarship distribution!), Especially in adulthood and old age, is considered as an additional factor in the decline in antitumor immunity. Excess sugar increases the need for patient in thiamine and thiamine-dependent enzymes, primarily in transcetolase. The production of ATP decreases as cancer grows and leads to cancer cachexia, energy deficiency, zyabacity. Many experimentally caused cancers (for example, breast cancer in rats) with a positive result are treated with thiamine, as well as riboflavin, nicotine acid, the Q10 coenfer in combination therapy. At the same time, thiamine with its deficiency is precisely the somatic state of cancer and does not promote the development of the tumor and its metastasis. The therapeutic importance of using a combination of vitamins modulating energy (B1, B2, PR), coenzyme Q10 has a greater perspective with breast cancer.
Peripheral neuropathy is a fairly frequent disease in old age; It is especially often developing in patients with diabetes, alcoholism. Polyinshairopathy polyethological staff; Without metabolic vitaminotherapy, its flow is preventable and may be unfavorable according to the forecast of disease and life. In the medical tactics used to use large doses of thiamine. In recent decades, a more efficient fat-soluble and penetrating vitamin B sembrane vitamin B semibra - benfothyamine is used. Under polyneuropathy, the use of other nutrients are justified: pyridoxine, vitamin E, B12, folates, biotin, as well as α-lipoic acid, glutathione, omega-3 fatty acids, Zn, Mg preparations. With the preventive purpose, the prevention of hypovitaminosis B1 is still carried out by enriching the physiological doses of thiamine (1.2-2.5 mg / day, depending on the energy industry). The participation of thiamine and benfothyamine in the metabolism of the glucose of the endothelial cell, preventing the transformation of glucose to sorbitol in the final result limits the possibility of the development of characteristic complications in diabetes patients, reduces glucosotolation (mandatory tumor satellite).
Thiamine has an anti-slip effect in gerontological patients with painful syndrome different etiology, including oncological; It is dose-dependent (increasing from physiological to pharmacological doses). However, even the high doses of water-soluble thiamine (250 mg / day) were not effective and did not affect the oxidative blood voltage in patients with age-related hyperglycemia, located on controlled hemodialysis. What is the reason? Quality of cell membranes and their permeability for micronutrients are a new page of clinical pharmacology. When studying age pharmacodynamics and kinetics of vitamins, a very important role is played by the factor of age-related change of plasticity Mem-Bran (reducing fluidity, impregnation into the membrane of cells of pathological transgenic fats, depletion or trasformation of the receptor signaling machine, etc.). The fat-soluble analogues of vitamin B1 are allium (from lat. Allium - garlic) - Fujiwara M. discovered in 1954, in the plants known for its immunomodulatory properties - garlic, bows and onions. It turned out that the resulting fat-soluble TIAMIN Derivates are repeatedly penetrated through the bilayer lipids of cell membranes. The reception of fat-soluble forms increases the levels of vitamin B1 in the blood and tissues is much greater than water-soluble salts of thiamine (thiamine bromide, thiamine chloride). The bioavailability of benfothiamine is 600, Fursultiamine is about 300, and thiamine-disulfide is less than 40 mg / h / ml. Benphotymin can counteract due to diabetes exaitotoxic processes in the brain through a mechanism that is not associated with tissue factors, and without reducing the activity of developing the necrosis of TNF-A tumors (Tumor Necrosis Factor-A).
Vitamins B6, B12 and folic acid obtained the status of gene-protective vitamins. Vitamin B12 contains cobalt and cyano group forming a coordination complex. Sources of vitamin is an intestinal microflora, as well as animal products (yeast, milk, red meat, liver, kidneys, fish and egg yolk). Folate and choline, as is known, are the central donors of methyl necessary for the synthesis of mitochondrial protein. It is these vitamins that actively contribute to the protection of the mitochondrial genome. There is now a serious study of the role of vitamins of the group in the neutralization of the cell toxic effect of a number of xenobiotics, poisons, as well as molecular, cellular and clinical consequences of the deficit of these vitamins. The distribution of vitamin B12 deficiency increases in old age due to the development of atrophy of the stomach mucosa, stomach tumors and disorders of the corresponding enzymatic treatment of food required to convert vitamin B12 into the absorbable form. With a combined shortage of vitamin B12 and folic acid due to the presence of folate metabolism (congenital Malabsorption of the Folate, the instability of methylene-cohabitrahydroofolateredides, deficiency of forminotransferase) The likelihood of atherosclerosis, venous thrombosis and malignant pathology will increase significantly, and higher doses of vitamin B12 are sometimes required to correct these hereditary violations, Folic acid, vitamin B6. At the same time, the vitamin B12 subsidies in the elderly is particularly relevant. In 2007, the Morris M.S. Research Group et al. Interesting observation was made: in senior patients, there is often a reduced level of vitamin B12 in the blood in combination with a level of folic acid on the upper boundary of the norm of the norm. Effective and safe dose of vitamin B12, leading to full compensation for the signs of the deficit, for older and old people ranges from 500 μg / day. up to 1000 μg per os. If the diagnosis of vitamin B12 deficiency is confirmed by laboratory, it is necessary every 2-3 months to conduct vitaminated therapy courses vitamin B12 daily at a dose of up to 1000 μg. Head K.A. (2006) and Martin S. (2007) urge to consider the high level of homocysteine \u200b\u200bin the blood as the actual indicator of vitamin B12 deficiency and folic acid in the body and the new oncological marker. Therefore, vitamin B12 deficiency should be suspected not only in all those with intestinal diseases (especially with colorectal adenoma), inexplicable anemia, polyneuropathy, in persons with senile dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, but also at hypergomocysthenemia.
The level of cyanobalamin in the blood is normal 180-900 pg / ml; When metastasizing tumors in the liver, it can be enhanced. In case of liver diseases (acute and chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, hepatic coma), the level of vitamin B12 may exceed the rate of 30-40 times, which is associated with the yield of depositated cyanocobalamina from destroyed hepatocytes. This level increases by increasing the concentration in the blood of transport protein - transkobalamin, while the true reserves of vitamin B12 in the liver are depleted.
It is known that the metabolism of vitamin B12 occurs very slowly and the mutagenic products are not formed. According to the meta-analysis conducted by Bleys J. et al. (2006), the long-term integrated use of biologically active additives to food in the form of groups of vitamins in (B12, B6 and folic acid) is safe and does not increase the risk of atherosclerosis even in the elderly group with long-term use.
Also by itself, in the composition of additives or in the form of drugs, vitamin B12 is neutral with respect to prostate cancer. Studies in 27111 Finns aged 50-69 years, of which in 1270 cases, prostate cancer was diagnosed, showed that higher food intake of vitamin B12 does not protect against prostate cancer.
At the same time, perennial epidemiological studies that assess the role of nutrition and the risk of prostate cancer are published. Red meat and liver, solid fats, hypodynamics significantly increase the risk of disease. Red meat concentrates iron, on-low fats, including vitamin B12. The details of the significance of a number of components of these products found "guilty" in the promotion of tumors. These are solid saturated fats, with aggressive heat treatment (frying on vegetable oils, grieving) - transgira, alcohol and iron as part of red meat. At the same time, in itself, the use of vitamin B12 and groups of group vitamins B (B6, folic acid and B12) in patients with cancer prostate turned out to be neutral. Purpose of Patients with prostate cancer and having a established Cyancobalamin's deficiency in vitamin B blood plasma improves the somatic state of patients with prostate cancer and does not affect its growth and metastasis, therefore the relationship between vitamin B12 and prostate cancer requires further research and currently research continues. In addition, for the occurrence of prostate cancer, the factor of low motor activity is significantly established, the effects of high temperature, alcohol and smoking. Fresh vegetables, as well as selenium (including as part of garlic, algae, black pepper, onions, fresh nuts, seeds, but not as part of fried nuts, fried seeds, swine bass, shrimp and sour cream) - Important protection factors for prostate cancer . Exception from the power of red meat and solid fats, alcohol, biologically active additives containing iron without laboratory confirmed iron deficiency anemia - An important preventive and therapeutic recommendation for men suffering from prostate adenoma and having a high risk of disease (age, heredity, prostatitis).
The low level of folates (insufficient use of fresh green-oxide plants) is associated with a high risk of fat intestinal cancer and breast. With a high level of alcohol consumption, this risk is summed up. Analysis of 195 cases of sporadic colon cancer and 195 volunteers-peers showed that the level of the folate is lower in patients with colon cancer; Vitamin B12 values \u200b\u200bdid not differ in the main and control groups, i.e. In colorectal carcingenesis, the reduced folic acid metabolism plays a major role. Adequate folic acid consumption protects from breast cancer. A particularly bright protective effect is manifested in a population with polymorphisms of the genome associated with violations of the sharing of folate. Detection of these polymorphisms in childhood and lifelong correction of folates (green-shaft diet, fresh cheese, vitamin complexes) level the genetic component. This is confirmed by nine-year observation in 62739 women during menopause; Of these, in 1812 cases, breast cancer developed.
Immunological and biochemical studies of SchroeCKSnadel K. Currently conducted to the current time. (2007) showed that folic acid deficiency not only contributes to the homocysteine \u200b\u200bremotely - a previously proven risk factor for the development of a malignant tumor (the lower the concentration in the blood of three water soluble vitamins - folic acid, vitamin B6 and vitamin B12, the higher the level of homocysteine \u200b\u200bin the blood), but also indicates a decrease in the total T-cell immune anti-coroncological protection. Increased consumption of folic acid, Vitamins B6 and B12 reduces the risk of breast cancer. In 475 Mexican women with breast cancer revealed low consumption of these vitamins, while 1391 women aged 18-82 years of the control group consumption was adequate. The results of the study are recognized as evidence; They once again confirmed the fact that the normal consumption of folic acid and vitamin B12 reduces the risk of developing breast cancer.
Bolander F. (2006) In the analytical review "Vitamins: not only for enzymes" showed the evolution of scientific views from traditional and initial (interpretative vitamins as coenses that accelerate chemical reactions) to new, based on the study of the biochemical route of vitamins using new molecular biology technologies and physico-chemical medicine. Not only vitamins a and d possess additional hormone-like properties. This is known for more than 30 years. Four more vitamin: vitamin K2, biotin, nicotinic acid and pyridoxal phosphate - perform hormonal functions. Vitamin K2 is involved not only in carboxylation of coagulation factors, but also is a factor in trans-criticism of proteins bone tissue. Biotin is necessary for the differentiation of the epidermis. Pyridoxal phosphate (coenses of vitamin B6), except for decarboxylation and transministration, can inhibit polymerase DNA and several types of steroid receptors. These qualities of vitamin B6 are used to potentiate cancer chemotherapy. Nicotinic acid not only converts NAD + in NADP +, which are used as hydrogen / electronic conveyors in oxidative reaction reactions, but also has vasodilatory and anti-bean effect. For decades, nicotinic acid is used in the treatment of patients with dislipidemia, but the molecular mechanisms were not deciphered. The tide of the blood (the vascular effect of nicotine acid, considered in terms of the situation and as therapeutic, and as a side effect of therapy) is associated with excessive emissions of vasodinating prostaglandins. Increasing the susceptibility of the tumor of the thyroid gland to radiation therapy J131 under the action of nicotinamide is due to the ability of vitamin to increase blood flow in the thyroid gland.
Nicotinamide, a coenzyme form of amide nicotinic acid, is the precursor of the adenine nicotinine adenine dinucleotide and plays a significant role in increasing the cell survival. Li F. et al. (2006) studied the possibilities of nicotinamide as a new agent capable of modulating cellular metabolism, plasticity, inflammatory cell function and influence the duration of its life cycle. It is assumed that Nicotinamide can be successfully used in senior patients not only with brain ischemia, Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer, but also during cancer. It has been established that Nicotinamide increases the life expectancy of normal human fibroblasts. The nicotinomide cells supported a high level of mitochondrial membrane potential, but a reduced respiratory level, a superoxide anion, active radicals of oxygen was marked.
Sundravel S. et al. (2006) In the experiment with the grafted cancer of the endometrial carcinoma, it was shown that the combination of tamoxifen with nicotine acid, riboflavin, ascorbic acid reduced the increased activity of glycolithic enzymes in the blood plasma and increased - glukenets, leading indicators to normal. It was suggested that nicotine acid, riboflavin and ascorbic acid can be used in therapy during endometrial carcinoma. And indeed, a year later (2007) Premkumar v.g. et al. showed that treatment with tamoxifen patients lung cancer With metastases, supplemented by nicotine acid, riboflavin, the Q10 coenbeid, contributed to a decrease in the activity of the tumor metastasis in terms of carcinosembrium antigen and oncomarkers (C15-3). The addition of nicotinamide contributed to a more pronounced 5-fluorouracyl accumulation in colorectal cancer metastases.
Immunotropic (and anti-tumor) effects of vitamin D with hormonal effects are clearly traced in the experiment, and in the clinic. As for retinoids, for vitamin D, an active part in the regulation of immunogenesis and cell proliferation is proved. Monocytes and lymphocytes produce a receptor protein with a molecular weight of 50 kDa for vitamin D3 with an identical amino acid sequence, as in the intestinal receptor protein. Lymphocytes are also additionally synthesized cytosol receptor protein with MM 80 kDa. The signal from these receptor proteins reaches an NF-κB transcriptic factor that regulates differentiation and cell growth from bone marginal stem predecessors to mature monocytes of lymphocytes. Vitamin D3 potentiates the effect of cytostatics into the tumor, the therapeutic effect is prolonged and allowed to minimize the load with a basic chemotherapy.
Active metabolite vitamin D3 - calcitriol (1-α, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3) - also has a pronounced antitumor effect in vitro and in vivo. Calcitrol inhibits the growth and development of cancers using various mechanisms. Thus, the inhibition of the growth of prostate cancer vitamin D3 is carried out by exposure to protein 3 (IGFBP-3), on the fermented cyclogenase and dehydrogenase and 15 prostaglandins and a number of other factors. S. Swami In 2007, on the basis of clinical experience, proposed to supplement the use of prostaglandin drugs in the treatment of prostate cancer patients with a combination of calcitriol and genisteine. Both drugs act antiproliferatively. Calcitrol inhibits PGE2 prostaglandin path (carcinogenesis potentiator) to cancer cell in three ways: reducing the expression of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2); stimulating the activity of 15-s-dro-xiprostaglandnegegerenase (15-PGDH); Reducing the sensitivity of PGE2 and PGF-2α receptors. This leads to a decrease in the level of biologically active prostaglandin PGE2 and, ultimately, to inhibit the growth of prostate tumor cancer cells. Genisteine, one of the main components of the soybean, is a powerful inhibitor of cytochrome CYP24, an enzyme that regulates the calcitriol metabolism, increasing its half-life. As a result, the synergistic effect with ginstiny expands the spectrum of calcitriol.
There is an antitumor activity in a synthesized H. Maehr with et al. (2007) Calcitrol derivative - Epiming with two side chains in the C-20-III position, on the model of colon cancer. Calcitrician-free antiproliferative indifference protects from other types of cancer, for example, under its influence, the growth of the culture of human choriocarcinoma cells is suppressed. It is believed that in conditions of low protein content during cancer, calcitriol products are reduced due to the disturbed activity of the cytochrome system CYP27B1.
With vitamin D research, the discovery of the seasonality of the lung cancer in the residents of Norway is connected. Friendly seasonal fluctuations in the content of calcitriol in the blood were identified, reducing the level of vitamin D3 during the period of insaled insolation and the occurrence of lung cancer. The maximum level of vitamin D3 in serum is celebrated from July to September. In the corresponding winter period, the level of vitamin D3 is reduced by 20-120%. It is supposed to predict the winter growth of morbidity not only with lung cancer, but also colon cancer, prostate, breast, Hodgkin's lymphoma. The results of chemotherapy, surgical interventions and forecast of life in patients with lung cancer, colon, prostate is better if the treatment is carried out in summer. It becomes obvious the need for preventive anti-nitamination programs in the winter period of preventive vitaminization programs in residents living in the northern regions and experiencing a shortage of natural light. To restore the functions of macrophages and lymphocytes in immunodeficiency due to D-insufficiency, it is enough to receive 400-450 MM vitamin D3 per day for 2-3 months.
Vitamin D3 metabolism is closely related to the exchange of elements. In particular, the CA-binding proteins induced by D3 are associated with Cu, Zn, Co, Sr, Ba, Ni, Mn, CD, PB, BE. Chronic insufficient CA consumption and vitamin D is a risk risk factor of a large intestine cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, breast, hodge-cine lymphoma.
The tumor and its owner receive nutrients from one source; This is an axiom. However, the host's body, without receiving an adequate norm of vitamins, has already initially has a low resource of antitumor immunity. Adequate prophylactic provision of vitamin, microelement, pectin ba-lane in food - a rehabilitation rehabilitation reserves of human immunity in general and antitumor immunity in particular. Information on individual polymorphisms of the genome discloses the possibility of targeted use of highly dose nutritiology. Tactics of "aggressive" vitaminotherapy and intensive therapy perform a new one, just even revealing their capabilities with a backup tool for salvation of lives and long-term patients. This requires a genetic certification of a person, preferably at birth or at a young age. In this case, there is a large resource of time and biological health for conducting individually selected vitamin therapy that meets the principles of clinical pharmacology: high efficiency and safety.
One of the important tasks in the development of diagnostic and cancer therapy methods is to obtain agents capable of selectively accumulating in tumor cells and tissues. In particular, in nuclear medicine, the isotopic tumor of radiopharmaceuticals is used to diagnose tumors by methods of positron-emission tomography and single-photon emission computed tomography. Recently, approaches based on application have begun intensivelyD. -amin acids, folic acid and its derivatives (folates) to detect tumors and delivering drugs in them.
In malignant neoplasms, transport in amino acid cells across the membrane associated with the intensification of protein synthesis in them increase dramatically.D. - amino acids unlikeL. -amin acids from which our proteins are constructed, falling inside the cells, do not metabolize, do not participate in the synthesis of proteins, and accumulate in them, and in the cancer, they accumulate much more eager than in normal cells. In this regard, it was proposed to useD. - amino acids as specific agents to determine malignant neoplasms, and followers on mice confirmed that using 2-iodineD. -Phenylalanine, labeled isotopeI 123. , It is possible to achieve preferential accumulation of the drug in tumor tissue up to 350%. However, later data appeared that the real situation is not so simple and may depend on the species affiliation of cells and on the type of tumor.
Another agent that has election affinity for malignant cells is folic acid. Cells transport folates through two types of proteins associated with membrane - the carrier of the recovered folate and the folate receptor. The first is present almost on all cells and is the main way of physiological inclusion of folates. The second is responsible for binding to the cell oxidized forms of folates. Although the low level of concentrations of reducive folate carriers is sufficient to supply most normal cells, the folate receptor is excessively expressed on malignant cells, giving them advantages in competition with limited access to this vitamin. There are numerous instructions on the fact that the folic acid receptor is often hyper express on the surface of cancer cells. Folic acid has a very high affinity for its receptors, while the receptor is effectively absorbed by the cell when the agent containing folic acid is bonded. It is these features of folate transport in cells are widely used to develop ways to deliver various agents, including drugs in tumor cells. Today, many folic acid-based preparations are synthesized for these purposes.
A few years ago, the departure of molecular and radiation biophysics Piyaf was proposed a strategy for finding the election labeling of malignant formations: by synthesizing derivatives of amino acids, nucleic acid precursors and folic acid, labeled iodine radioisotopes, studies of the features of their binding to cancer cells. Further, according to the results of these studies, it is planned to develop diagnosticum and therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals for the treatment of malignant formations. The branch has highly qualified chemists with long-term experience in the synthesis of radioactive-labeled compounds, as well as specialists in cell biology operating over the years over the problems of the rebirth of normal cells into cancer.
Preliminary studies have established boundary conditions for the synthesis of iodofolic acidI. 125
Based on the interaction of folic acid with a soft oxidizing agent - an idiotic chlorine (Icl), it is extremely difficult to introduce into the molecules of aromatic compounds of iodine atoms with extremely low yields of the target compound (about 1%) and requires a duration of 18 hours of synthesis in harsh environments. We have developed conditions for rapid synthesis in soft conditions of iodofolic acidI. 125
with high product yields (30-40%), which is very important for the successful synthesis of drugs labeled by short-lived isotopesI. 121
andI. 123
. Preparations further studied in biological experimentsiN.
vitro.
on the binding of iodofolic acid with various cell lines of malignant formations compared with normal cells. The first experiments in which the conditions were not optimized for the maximum binding of the drug with cells, showed that iodopholic acid is much preferable to be associated with cells of some tumors. In particular, cancer cellsHe.LA A hundred times more preferably connected iodofolic acidI. 125
compared to the fibroblasts of human lung embryos. Already from these results it follows that the preparations of iodofolic acid labeled with radioisotopes are promising for the purposes of diagnosis of malignant formationsiN.
vivo
. The experiments on the study of comparative sorption of folates with cancer and normal cells were deployed in order to establish the conditions for the maximum level of iodfoliic acid binding with various cell lines, which will determine the real prospects for using it for diagnosing and tumor therapy and the spectrum of applications of this technique to various malignant formations. For examples are held And at present, for which it is necessary to develop original methods for the synthesis of iodine-containing reduced forms of folic acid, methylated and formed derivatives of these folates. In the experiments on sorption of restored folate cellsHe.LA The presence of two sorption mechanisms - slow and fast components of the sampling process. Further, for the first time we were synthesized by diodh phthicic acid, which, by assumptions, should show a stronger affinity for cancer cells than monoiodfoliic acid. Experiments have shown that diodeidthic acid is 4 times more firmly associated with a protein inside the cell than monoiodfoliic acid.
Upon completion of this stage, it is planned to proceed with the study of the use of brompholy acid (Br. 82
) For the aforementioned diagnostic and therapy purposes. The fact is that some characteristics of the isotopeI. 125
are far imperfect for preparations introduced into the patient's body. These include a large period of the half-life of this gamma emitter - 60 days, as well as the risk of accumulating in the thyroid gland of radioactive iodine, released in the process of iodofolic acid metabolism in the patient's body, which can lead to high levels Local transmission. These flaws are devoid of isotopeBr. 82
: The half-life of it is 35 hours, and, in addition, different forms of inorganic bromine do not have the property of preferential accumulation in any organs of animals. Therefore, in further research it is planned to develop the synthesis of brompholy acid (Br. 82
) and conduct a detailed study of possible use of it for the diagnosis and therapy of cancer tumors.
At the same time, the general disadvantages of isotopesI 125 and BR 82 It is that they are gamma-emitters that give with radiation therapy due to a large run in the tissues diffuse and rather large stains, affecting not only tumors, but also healthy fabrics. It is tempting to use radiopharmaceutions based on alpha emitters that have a mileage in the tissues of the order of several microns, which is commensurate with the size of the cells. Astana ASTAT 211 is a possible applicant for the role of the most effective therapeutic agent, which, however, cannot be produced in the country in the country of low-power cyclothedrons, since cyclotron installations in IEE them. Kurchatova and in Tver are designed to achieve maximum particle energies to 30 MeV, which is not enough to obtain such isotopes. Halogen Astat 211 is an analogue of iodine, for which it seems natural in the form of astatfolic acid to stab to one or another tumor and most effectively and selectively destroy cells of malignant education. Taking into account the plans of the building in the Piyaf in the near future of the cyclotron mainly for medical purposes on energy in 80 and 200 MeV, the prospects for creating these drugs do not seem so fantastic.
In the future, a search engine is also planned for the synthesis of fluorinated aromatic amino acids, sugars with an eye on the development of biological compounds labeled with short-lived isotope for use in positron emission tomography. For the same purposes, it seems tempting to implement isotopesI 121, I 123, as well as Br 76 which are short-lived positron-spackers, then it will be necessary to carry out foliaic acid synthesis, labeled with these isotopes, and use them in PET to identify tumor formations. An important advantage-minded folic acid synthesis methodology, labeled halogen isotopes, is the lowest time required to obtain finite products - the synthesis time is calculated in minutes, in contrast to the many hours of the procedures in existing synthesis methods less effective drugs Folic acid derivatives.
The above works were carried out and are planned in the future to implement in close cooperation with the divisions of the Radium Institute. Chlopin and Tsnirry, which are located on the territory of the Piyaf. These joint efforts of large sectoral institutions under the Program "Nuclear Medicine" can lead to a PIC reactor in the operation of the specified cyclotron installation to establish the issue of creating a regional oncological center in Gatchina, which has a wide arsenal of the most modern diagnostic and therapeutic agents for successful combating malignant formations. .
Ved.Nauch.Sotr. Piyaf
G.A. Bagyan.
Folic (peeroilglutamine) acid is another name for a water-soluble, vital compound B9 (Sun), which scientists are referred to as "Vitamin of Good Mood." This is due to the fact that the folacine is needed to produce happiness hormones, providing excellent psycho-emotional state.
Given the fact that the substance in a significant amount is contained in the leaves of plants, it has acquired its name from the word "Folium", which translated from Latin means "Sheet".
The structural formula of vitamin B9 (M) is C19H19N7O6.
Folic acid participates in the synthesis of DNA, hemoglobin, exchange processes, blood formation, maintaining immunity affects conception.
An important role is played for pregnant women, having an impact on the formation of the nervous tube of the fetus and the placenta, preventing the development of its defects.
The lack of a substance may lead to the emergence of serious deviations in the neural system of the kid, from the second week of the "interesting" position. Often, in this period, women still do not realize the conception of the child, while the BB9 deficiency in the mother's body is negatively displayed on the development of the fetus.
Scientists have proven that pealglutamine acid participates in DNA replication. Its lack of a growing organism increases the risk of oncology, the emergence of congenital deviations of mental activity. Therefore, when planning a pregnancy, a woman should regularly, for half a year before conception, take 200 milligrams of substances of natural (with food) or synthetic (in tablets) daily or synthetic (in pills).
The systematic flow of folic acid for 9 months to the mother's body, reduces the likelihood of premature birth by 35%.
The healthy intestinal microflora is capable of synthesize some amount of vitamin B5 alone.
Historical information
The discovery of folic acid is associated with the search for the method of treating megaloblastic anemia.
In 1931, scientists found that the addition of hepatic extracts, in the diet of the patient contributes to the elimination of the symptoms of the illness. In the following years, research was recorded that a state similar to macrocytic anemia progresses in chimpanzees, chickens when feeding their refined food. At the same time, the pathological manifestations of the disease managed to eradicate by adding alfalfa leaf, yeast to the food, liver extracts. It was clear that these products contain an unknown factor, whose deficit in the body of experimental animals leads to a violation of blood formation.
As a result of three-year-old attempts to gain an active principle in its pure form, in 1941, scientists were identified from spinach leaves, yeast extract, liver of substances of the same nature, which were called: folic acid, vitamin BC, factor U. Over time it turned out that the compounds were identical Friend.
The period, from the discovery of a folacine before washing it in its pure form, is characterized by intensive studies of the compound, starting with the study of its structure, synthesis, ending with the definition of coenchant functions, exchange processes in which the substance takes part.
Chemical and physical properties
 The composition of the vitamin connection molecule B9: The composition of the vitamin connection molecule B9:
- P-aminobenzoic acid;
- derivative of pterydine;
- L-glutamic acid.
Due to the fact that the concept of "pealglutamic acid" denotes an extensive group of compounds, during the studies it caused some inconveniences, since not all categories of substances represented biological activity for living organisms, in particular for a person. Therefore, scientists decided to concretize concepts. Thus, the combination of compounds that contain the core of the pteroic acid, the Committee of the International Society assigned the name "pholate", and substances with the biological activity of tetrahydropteroylglutamic acid - the term "folacine".
Thus, the concepts of "folic" and "pteroilglutamine" Group are synonyms. At the same time, folates are the chemical name of "related" connections vitamin B9.
Folic acid is a yellow small crystalline powder, there is no taste, smell. When heated, the compound leaflet is slowly dark, but not melted, the further increase in temperature to 250 degrees leads to their charring.
Vitamin B9 quickly decomposes into the light. At a temperature of 100 degrees in 100 milliliters of water, 50 milligrams of substances dissolve, at zero - one unit. Flacin is easily cleaved in caustic alkalis, poorly in dilute hydrochloric, acetic acids, air, chloroform, alcohol, acetone, benzene, organic solvents. Silver, zinc, lead salts vitamin B9 insoluble in water.
Flacin is well adsorbed by fullere earth and activated carbon.
The role of vitamin B9 in the human body
Consider than useful folic acid:
- Participates in the production of red blood cells, namely, in carbon exports for protein synthesis in hemoglobin.
- Stimulates the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
- Provides proper functioning nervous system (regulates the transmission of pulses, braking / excitation processes), head, spinal cord. It is part of the liquor.
- Takes part in synthesis, DNA and RNA, nucleic acids, as well as in the formation of Purines, in particular, cell cores.
- Stabilizes emotional background. Folic acid affects the level of production of norepinephrine and serotonin, reduces the negative impact of stress, improves the mood, helps to get rid of postpartum depression.
- Smoothes menopacteric disorders.
- Reduces the risk of premature births.
- Beneficially affects digestive system, liver health, leukocyte functionality.
- Reduces chromosomal sperm defects, enhances the activity of male genital cells.
- It is necessary for women and men to improve fertility. Systematic reception of high vitamin connection products helps to avoid deterioration of the reproductive function.
- Reduces the risk of developing heart diseases, vessels, metabolic syndrome in a child. However, in the presence of heart pathologies, non-controlled intake of vitamin B9 may lead to the onset of myocardial infarction, angina.
- Adjusts the concentration of homocysteine, due to this decreases the risk of stroke. Daily reception 5 milligrams of folacine, as a dietary supplement, has a prophylactic effect on the body.
- Reduces the likelihood of colorectal cancer. However, as a result of a large-scale screening of the disease, scientists found that it is impossible to apply the compound for the prevention of breast oncology, since folates have a negative impact on the development of breast modified cells. Vitamin B9 plays an important role for men, regular consumption of a useful connection reduces 4 times the risk Prostate cancer development.
- Reduces the "bad" cholesterol in blood serum.
- Normalizes blood pressure.
- Supports immune system, increases the number of leukocytes.
- Improves memory, mastering vitamins of group V.
- Increases performance.
- Pulls the onset of menopause, which is especially important for women.
- Accelerates mental activity.
In addition, you should not forget about the value of folic acid for conception and tooling a healthy child. Regular admission of nutrient at the planning stages (200 micrograms per day) and during pregnancy (300-400 micrograms per day) by 70% reduces the risk of developing congenital pathologies in the embryo.
Vitamin B9 is a real panacea in cosmetology. It helps from acne, hair loss, serves as a universal means to level the skin tone, eliminate pigmentation, red spots.
 In the event of a lack of vitamin B9, the human body loses the ability to transfer a useful nutrient to the brain, which leads to problems with vision, movement, coordination, seizures begin. At the same time, adults increase the risk of anemia, glossite, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, gingivitis, osteoporosis, neuritis, atherosclerosis, osteoporosis (in women), stroke, infarction, and even cancer. In the event of a lack of vitamin B9, the human body loses the ability to transfer a useful nutrient to the brain, which leads to problems with vision, movement, coordination, seizures begin. At the same time, adults increase the risk of anemia, glossite, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, gingivitis, osteoporosis, neuritis, atherosclerosis, osteoporosis (in women), stroke, infarction, and even cancer.
The connection deficit in pregnant women can harm the baby. In particular, there is a risk of having a premature child with a small weight with violations of the development of the nervous system.
Chronic lack of a compound in the body of children leads to a slowdown in general development, in adolescents - to the delay in puberty.
Characteristic symptoms Vitamin B9 deficiency in the body:
- forgetfulness;
- irritability due to insufficient generation of serotonin and norepinephrine;
- headaches;
- confusion of consciousness;
- diarrhea;
- depression;
- loss of appetite;
- apathy;
- high blood pressure;
- fatigue;
- insomnia;
- labored breathing;
- red tongue;
- hOW;
- reduction of cognitive functions;
- anxiety;
- inability to focus;
- memory problems;
- disorders of digestion due to insufficient production of hydrochloric acid;
- hair loss;
- lamination of the nail plate;
- pallor, due to the reduction of hemoglobin, which "falls" as a result of insufficient transportation of oxygen to peripheral tissues, organs;
- weakness;
- the lack of muscle mass occurs because of the poor absorption of proteins, due to the low acidity of the stomach.
The hypovitaminosis of folic acid is often observed in people with intestinal diseases, which have a suction process of useful substances. In addition, during pregnancy, breastfeeding, the need for substance increases 1.5 - 2 times.
 The lack of vitamin B9 aggravates alcohol, which interferes with the folate metabolism, preventing the connection to the connection to the destination (to fabrics). The lack of vitamin B9 aggravates alcohol, which interferes with the folate metabolism, preventing the connection to the connection to the destination (to fabrics).
The level of folic acid in the human body is diagnosed by analyzing. 3 Folate micrograms in the serum liter of serum testifies to the lack of vitamin and the need to replenish the reserves of the useful connection.
Often signs of vitamins of B9 and in the body are identical. To distinguish a lack of one compound from the other, the level of methylmalone acid (MMK) should be measured. Increased value indicates a lack of B12 in the body, normal (within the normal range) indicates a lack of folic acid.
How much to drink vitamin B9 to fill the shortcomings of the connection?
Therapeutic daily dose of folic acid depends on the severity of the manifestation of symptoms and the presence of side diseases caused by a substance deficiency. To correctly establish the norm, you should pass the survey and seek help for your doctor.
As a rule, the reception of vitamin B9 in medicinal purposes varies in the range of 400 - 1000 micrograms per day.
With megaloblastic anemia, treatment should also begin to check the level B9, B12 in the body. This is due to the fact that with the deficiency of cyanocobalamin, the addition of folic acid can not only facilitate the symptoms of the disease, but also worsen existing neurological problems.
In 80% of cases, people with an active lifestyle, lovers to sunbathe, patients with celiac and obesity, with a body mass index for 50. In addition, the B12 deficiency can lead to a lack of folates, which increases the level of homocysteine, creating a favorable soil for Development of cardiac, vascular diseases.
The lack of folate contributes to changes in the bone marrow, peripheral blood.
Consider the process of developing pathologies in detail.
Changes in peripheral blood and in the bone marrow
A characteristic sign of the emergence of megaloblastic anemia on early stage is the formation of hyperseganized multi-core leukocytes in the blood: basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils.
As a result of the experiment, after the translating of a person on a scarce diet with folan deficiency, after 7 weeks of the subject, Pelgian-Ra Hueta anomaly appeared. Namely, an increase in the amount of heavy (threads) connecting the segments of the nucleus. Normally, this indicator is equal to one, in megaloblastic neutrophils - two or three.
In addition, pernicious anemia is accompanied by a sharp decrease in blood erythrocytes, and macrocytosis appears in the later stages of the disease.
There are cases when the insufficiency of iron is combined with the lack of folate in the body, in this situation an abnormally large red blood cells in peripheral blood may not be. The only characteristic indicators of combined anemia (iron-deficient and folic) are increased metamielocytosis in the bone marrow, hypersegmentation. Heavy stages of folate failure can lead to thrombocytopenia and leukopenia.
The typical forms of megaloblastic changes in the bone marrow are manifested in 3 sprouts: megacariocyte, myeloid, erythrocyte. Often in patients deviations affect all the degrees of maturation. At the same time, the main change in the nucleus forms of the erythrocyte series is a clearer detection of chromatin.
A typical sign of manifestation of megaloblastic anemia is considered a relatively low number of megaloblasts. With a combination of foliage failure and impaired hemoglobin synthesis, bone marrow cells may not have a change characteristic of megaloblasts.
Overdose of folic acid
Vitamin B9 has a low toxicity risk, excess compound is output with urine. However, the systematic reception of high doses of a substance (1000 and more micrograms per day) masks the effects of anemia, which, like any disease, is better to detect at the first stages of education.
Consider what side effects causes hypervitaminosis in adults:
- Hyperplasia epithelial cells kidneys, hypertrophy.
- Increased excitability of the CNS.
- Reducing the concentration of cyanocobalamin in blood (in the case of long-term reception of large doses of pteroidglutamic acid).
- Dispersion.
- Sleep disorder.
- Anorexia.
- Disorders of the digestive organs (intestinal disorder).
The overdose of vitamin B9 in pregnant women can lead to asthma in a newborn.
The long-term use of folic acid Over 500 micrograms per day reduces the concentration of B12 in the blood, thus, the oversupplication of one connection causes the lack of another.
Indications for appointment and contraindications
 Consider why drink Vitamin B9: Consider why drink Vitamin B9:
- For prevention of anemia.
- In the case of taking bactericidal, contraceptive, diuretic, anticonvulsants, analgesics, erythropoietin, sulfasalazine, estrogen.
- For weight loss.
- In order to stimulate the growth of red blood cells.
- When poisoning with methyl alcohol, alcohol.
- During lactation.
- With depressive states, crown disease, mental disorders.
- During pregnancy. Often, the question arises among women: to what period of drinking folic acid. Doctors recommend to use the connection throughout the entire period of pregnancy, in order to prevent the development of infant nervous tube defects.
- With psoriasis.
- Newborn with low weight (up to two kilograms).
- In the case of the development of hypo- and avitaminosis B9, hemodialysis, gastrectomy, intermittent fever of gastrointestinal diseases (hepatic insufficiency, persistent diarrhea, gluten enteropathy, alcoholic cirrhosis, malabsorption syndrome, tropical SPRU).
- During intensive training (especially in bodybuilding).
- With unbalanced nutrition.
- To strengthen hair.
Contraindications for the use of pealglutamic acid:
- malignant neoplasms;
- cobalamin deficiency;
- hemosiderosis, hemochromatosis;
- increased sensitivity (allergy) to the drug;
- pernicious anemia.
How much do you need to use vitamin B9 per day?
If it is necessary to include folic acid into the diet for children up to 3 years, enter the connection should be neatly small doses. According to the FAO / WHO expert group, the daily rate for a child from birth to 6 months is 40 micrograms, 7-12 months - 50 units, from 1 to 3 years - 70, from 4 to 12 years - 100. From 13 years old dose for Teenage and adult equals 200 micrograms per day.
However, it is worth considering that the daily rate of folic acid is purely individual. The minimum dose for an adult is 200 milligrams, the maximum - 500. During pregnancy, this indicator increases to 400 units, during breastfeeding period - up to 300.
 Folic acid can be included in a complex of multivitamine preparations or separately. Synthetic forms of vitamin B9 are 2 times more active than natural. Folic acid can be included in a complex of multivitamine preparations or separately. Synthetic forms of vitamin B9 are 2 times more active than natural.
What is the difference between "medicinal" and "natural" folates from products?
Interestingly, higher plants and most microorganisms are able to synthesize the folates, while, in the tissues of birds, mammals, these connections are not formed. A minor part of the pteroid monoglutamic acid was found in plant, animal cells. The main amount of folates in them is part of conjugates (di-, tri-, polyglutamates), which have additional glutamic acid molecules. They, in turn, are combined with a solid amide bond, according to peptide.
In bacteria, the predominant form of folate - pteroiditriglutamine acid containing 3 glutamate molecules in yeast - a complex with 6 particles, wearing the name of the gep taglutamate.
Often, "related" folacine included in food products, represented by polyglutamats, while the "free" group (CASEI mono-, di- and triggetamates) is no more than 30%.
Which products contain folic acid | Product name |
The content of vitamin B9 in the micrograms (per 100 grams) |
|---|
| Mung beans |
625
|
| Cranberry beans |
604
|
| Agar dried |
580
|
| Nut. |
557
|
| Yeast |
550
|
| Mint curly dried |
530
|
|
|
479
|
| Pink beans |
463
|
| Soy-dried |
375
|
| Basil dried |
310
|
| Wheat embryos |
281
|
| Peas |
274
|
| Coriander (kinza) dried |
274
|
| Mayran dried |
274
|
| Thyme (chamber) dried |
274
|
| Sage hammer |
274
|
| Estragon (Tarkhun) dried |
274
|
| Green Asparagus |
262
|
| Beef liver |
253
|
| Peanut |
240
|
| Chicken liver |
240
|
| Oregano (Orego) dried |
237
|
| Sunflower seeds |
227
|
| Pork liver |
225
|
| Soy protein |
200
|
| Spinach |
194
|
| Dips leaves |
194
|
| Mustard leaves |
187
|
| Bay leaf |
180
|
| Parsley dried |
180
|
| Laminaria (sea cabbage) |
180
|
| Wheat bread with bran |
161
|
| Rye toasts |
148
|
| Yolk chicken |
146
|
| Artichoke ice cream |
126
|
| Bran oatmeal |
120
|
| Parsley (Fresh) |
117
|
| Forest / Hazel |
113
|
| Cod liver |
110
|
| Beet (raw) |
109
|
| Sesame |
105
|
| Walnut |
98
|
| Wild Rice (Cycia) |
95
|
| Spirulina dried |
94
|
| Flax seeds |
87
|
| Kidney cow |
83
|
| Avocado |
81
|
| Beet (boiled) |
80
|
| Rice bran |
63
|
| Cocoa powder |
45
|
| Journey chicken egg |
44
|
| Oystered Oyshemka |
38
|
| Garnet |
38
|
| Brynza |
35
|
| Watermelon |
35
|
| Chees Feta |
32
|
| Milk dry |
30
|
| Orange |
30
|
| Buckwheat |
28
|
| Salmon |
27
|
| Champignon |
25
|
| Blackberry |
25
|
| Pomegranate juice |
25
|
| Kiwi |
25
|
| Strawberry |
25
|
| Pearl cereals |
24
|
| Corn |
24
|
| Cauliflower |
23
|
| Raspberries |
21
|
| Banana |
20
|
| Topinambur |
18,5
|
| Eggplant |
18,5
|
| A pineapple |
18
|
| Honey |
15
|
| Tomatoes |
11
|
| Lemon |
9
|
| Bulb onions |
9
|
| Potatoes |
8
|
| Milk |
5
|
The list of products containing vitamin B9 is useful for the preparation of a balanced daily diet that provides the organism with the necessary amount of beneficial substances.
In the process of laying the menu, important nuances should be taken into account:
- when cooking vegetables, meat is destroyed by 80 - 90% of folates;
- when grilled grains - 60 - 80%;
- when roasting offal, meat - 95%;
- when freezing fruits, vegetables - 20 - 70%;
- when cooking eggs - 50%;
- when preserving vegetables - 60 - 85%;
- when pasteurization, boiling paired milk – 100 %.
Thus, the culinary processing of products with a high content of folic acid leads to a partial or complete loss of a useful connection. To enrich the diet with vitamin B9, greens, vegetables, fruits should be in the raw form .. In addition, in winter, it is recommended to feed the body with food additives, vitamin complexes, which includes a daily dose of folates.
In order for the intestinal flora to better synthesize B9, it is recommended to eat yogurt daily, biocofer, preparations with bifidobacteriums.
 Consider detail the description of the absorption of Folatav. Consider detail the description of the absorption of Folatav.
In observations of people and experiments over the animals, it was found that Vitamin B9 adopted by Per OS (orally) is almost completely absorbed in the body as quickly as possible. With the introduction of 40 micrograms with a labeled pteroid glutamic acid per kilogram of body weight, the level of absorption of the substance in 5 hours reaches 98.5% of the administered dose. 50% of the total amount is excreted in the morning after the preparation.
The absorption of folic acid is carried out in the proximal part of the small intestine and the duodenum.
Of particular interest is the process of suction of food fouls, which are mainly contained in the form of polyglutamates, their produced (methyl, formyl).
Monoglutamates in the body are absorbed easily. At the same time, the polyglutamates are absorbed, produced in the intestines (conjugase, gamma-glutamylcarboxypeptidase) solely after the elimination of the excess glutamic acid.
In the intestine B9, it is first reduced to tetrahydrofoliic acid (THFC) under the influence of dihydrofolatide, then methylated. In some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (Malabsorption syndrome, children's non-infectious diarrhea, the SPRU, idiopathic steatheree) is disturbed by the absorption of folates. This leads to an absorption of a substance, the development of foliage failure, which may result in a decrease in enzyme-formative, hoc dispositive functions, destruction of the intestinal epithelium.
In the process of studying the absorption of tetrahydrofolic acid derivatives (formyl and methyl), the following is established: N-methyl-THFC is absorbed by simply diffusion without changing in the process of absorption. Upon admission to N-formyl-THFK (folin) acid into the human body, during the assimilation, it almost completely turns into methylterahydrofolate in the intestine.
After suction, the folates enter the gland of the external secretion - the liver, where they gradually accumulate, are transformed into active forms. There are about 7 - 12 milligram of this compound in the human body. At the same time, of which 5 - 7 units are concentrated directly in the liver. Some part of the folates occupy polyglutamates, of which more than 50% of folic acid derivatives are represented as methyltetrahydrofoliic acid. Scientists referred to it as a spare form of B9 liver.
Studies have shown that with the addition of pteroid glutamic acid into the diet of animals, the amount of folates in the gland increases significantly. Pholacine liver, unlike derivatives of other fabrics, very labile. The accumulated reserves of folate in the gland are capable of replenishing the useful compound in the body for 4 months, preventing the development of anemia. In addition, in the human body (intestinal mucosa, kidney mucosa) contains a certain reserve of vitamin B9.
The amount of folates in the liver is 4 times larger than in the urica organs. However, its ability to accumulate, to spend a useful connection directly depends on providing the organism with vitamins, amino acids, proteins. For example, as a result of an experiment conducted on rats, scientists found that the deficiency of cyanocobalamin (B12), methionine, biotin in the diet leads to a decrease in folates, especially polyglutamates, as well as the ability to turn them into THFC.
Do not cost to underestimate the important properties of the liver in the exchange of derivatives of folic acid. The functional state of the organ affects the level of absorption of folates, the flow of reactions with the participation of Vitamin B9 coenses. Fatty infiltration, liver cirrhosis violate its ability to accumulate, spend the connection. Often as a result of such lesions, severe disease is developing - megaloblastic anemia.
From the human body, the recycled residues of folic acid are removed with urinet, feces. At the same time, the amount of folates in the urine, in most cases, does not correspond to their flow with food. Namely, it is displayed more than coming.
 The best means of preventing folic failure - meals with inclusion in the daily menu of fresh vegetables, fruits. With a shortage of folates in food, it is recommended to additionally use 150 - 200 vitamin micrograms daily. The best means of preventing folic failure - meals with inclusion in the daily menu of fresh vegetables, fruits. With a shortage of folates in food, it is recommended to additionally use 150 - 200 vitamin micrograms daily.
If the lack of pteroidglutamic acid is caused by a violation of the absorption of vitamin, due to the disease gastrointestinal disease, the number of compound should be increased to 500-1000 units per day. Often, this dose guarantees the assimilation of the required level of the drug. An example of this kind of shortage is a severe disease of the SPRU (Netropic, Tropical), in which the absorption of beneficial substances is sharply deteriorating, atrophy of the mucous membrane of the small intestine. The introduction into the diet of patient folic acid has a positive therapeutic effect, which contributes to the improvement of the clinical picture, facilitating the state of the person.
With complete gastrectomy and atrophy of the gastric mucosa, megaloblastic anemia is observed, due to the deficit rather than the cyanocobalamin than folates. Daily reception 200 - 500 micrograms B9, in combination with a disposable intramuscular administration of 300 - 500 micrograms B12, have a favorable therapeutic effect. To eliminate megaloblastic anemia, arising against the background of alcohol intoxication, pregnancy, infection, the patient is prescribed an increased dose of folic acid - from 500 to 1000 micrograms per day.
During the treatment of leukemia antagonists of vitamin B9, there is a violation of the absorption of folates. These substances block the conversion of a useful connection to active tetrahydroform. As a result, long use of drugs cause severe complications, represents a potential threat to human life. For the treatment of patients, the active forms of folates are used: injections of N5-formyl-THFC (300 micrograms per day). In case of violation of the formation of the enzyme dihydropholatetase, it is recommended to use folinic acid.
Consider how to drink folic acid with specific diseases (testimony for use):
- Aphtose stomatitis. The deficiency in the organism of micronutrients, vitamins (iron, B9, B12) participating in hemopoiesze leads to the formation of cracks on lips and ulcers on the mucous membrane of the mouth (AFTU). To eliminate the disease, it is recommended to take 3 times a day 500 micrograms of folic acid and 1000 units of iron glycinet. The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the ailment and varies from 120 to 180 days. Throughout this period, once a month, the patient should make injections of 100 micrograms of cyanocobalamin. In the process of treatment, it is important to monitor the level of vitamin B12 in the blood.
- Atherosclerosis. The daily reception of 500 folic acid micrograms for 14 days (with a further transition to 100 units) binds the "bad" cholesterol in the intestines, strengthens the walls of the vessels, turns into the homocysteine, in methionine, preventing the body sealing. Compliance with diet, refusal to take alcoholic beverages, conducting a healthy lifestyle, regular use of folate, as part of a group of vitamin complex B, leads to an improvement in the health of the patient and complete recovery.
- Gingivitis and periodontitis. To remove the gum inflammation, the folic acid should be used orally at 100 micrograms per day. At the same time, it is necessary to add treatment with a daily rinse of the oral cavity with a 1% vitamin solution in the morning and in the evening. The course of therapy is 2 months.
- Viral hepatitis. Vitamin M (B9), in the treatment of inflammation of the liver tissue, is used as an auxiliary drug. The recommended supporting dose for the first 10 days of therapy is 1500 micrograms per day (500 units in the morning, at lunch, in the evening), then it decreases to one-time reception of 500 units during the day.
- Osteochondrosis. Folates take part in the formation of a frame of collagen, on which, in turn, calcium salts accumulate. Without a "bonding" substance, the bone does not gain the required strength. The use of vitamin B9 enhances the effectiveness of the main operating components (muscle relaxants of the central exposure, anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics). Folates affect generative processes occurring in joints, creating favorable conditions for accelerated tissue regeneration. Thanks to this, educated inflammatory process Between the vertebrae is suppressed. How to take: before or after meals? The recommended dosage of folic acid in the treatment of osteochondrosis is 500 micrograms per day, pyridoxine - 50, vitamins in a complex (for example, neurulivitis, ping) - 50. Tablets B9 take immediately after the meal, Paving small quantity Waters (100 milliliters).
- Spasm colon. The characteristic symptoms of the disease - the bloating, colic, alternation of confusion and diarrhea. For suppression of spasms, the patient introduces 1000 micrograms of folic acid per day. If after 2-3 weeks, progress is not observed, for therapeutic purposes, the dose increases to 2000 - 6000, until the patient's condition improves. After the occurrence of the positive effect (remission of the disease), the consumption of vitamin is gradually reduced to 500 micrograms. Simultaneously with Taking B9, vitamins of the B-complex of 10,000 micrograms per day should be used. Throughout the therapy, it is necessary to systematically check the level of cyanocobalamin.
- Epilepsy. After the appearance of a convulsive attack, the amount of folates in the brain drops to a critical value. In addition, its concentration in the blood plasma reduces anti-kvulsants. As a result, the deficiency of B9 causes side effects - The participation of the attacks. To reduce the risk of frequent seizures, specialists are prescribed to use 500 folate micrograms per day.
Remember, regardless of the type of disease, the therapeutic dose of vitamin B9 depends on the state of the patient and is chosen individually to the attending physician.
 In the course of studies useful properties Vitamin B9 revealed that the connection warns the development of oncology. However, if the disease has already begun, it is prohibited to take the drug. Otherwise, folates spur the process of dividing cancer cells. In the course of studies useful properties Vitamin B9 revealed that the connection warns the development of oncology. However, if the disease has already begun, it is prohibited to take the drug. Otherwise, folates spur the process of dividing cancer cells.
Instructions for the use of the drug in the treatment of malignant tumor
First of all, medicines that inhibit folic acid activity, in particular, methotrexate are used. The benefits of this drug lies in the fact that it slows down the process of increasing the tumor.
To eliminate and prevent disorders of metabolism, patients prescribe folinic acid - an analogue of vitamin B9.
Where is it contained?
Drug leukovorin is successfully used by specialists in chemotherapy oncological diseases. The drug eliminates the severity of intoxication (damage to bone marrow fabric, vomiting, diarrhea, hyperthermia), which manifests itself after taking cytostatic drugs.
Given the fact that the risk of developing cancer in the elderly 2 - 3 times higher than that of young people, to use the pholta pensioners without recommendation of the doctor is not recommended.
At the end of the 20th century, scientists in the United States conducted a number of studies for the identification of the dependence between the progression of the tumor of the large intestine and the intake of vitamin B9. As a result of the information collected, the specialists concluded that in 75% of cases of digestive organ cancer, if the prophylactic doses of folic acid systematically use (200-400 micrograms per day).
Moreover, the tumor met in people who regularly took vitamin complexes for 10 years.
Vitamin B9 and male health
Folic acid is needed not only for children up to a year, women to get pregnant and endure a child, but also to men. Chronic nutritional deficiency in the body of a strong gender increases the risk of developing megaloblastic anemia, as well as pathologies from the sexual system, up to infertility. The daily intake of vitamin B9 in the therapeutic dose completely eliminates these complications.
The main indicator of male health is the state of spermatozoa. So, nucleic acids and protein are needed for the synthesis of germ cells. The lack of folates leads to a violation of the production, deterioration of the state, a decrease in the concentration and mobility of spermatozoa. In addition, the deficiency of the vitamin compound may cause the formation of an improper amount of chromosomes in the seed fluid, which can lead to the emergence of hereditary diseases in a child (for example, Down syndrome).
Why do you need folic acid in a male organism?
Hormone Testosterone, Vitamin B9 causes the correct development of sperm. A particularly important role of folates play in the pubertal period, when the intensive process of the development of sexual signs begins (the appearance of hair on the face, body, cutting of the voice, intense growth).
The interaction of folic acid and medical drugs
Consider compatibility of vitamin B9 with other nutrients, drugs:
- Corticosteroid hormones wash folates from the body. At the same time take these drugs is not recommended.
- , B12 enhance the effect of folic acid.
- Nitrofuran drugs violate the exchange of a peerilglutamine compound.
- High doses of aspirin reduce the level of folates in the body.
- Antimetabolites, sulfonamides, alcohol-containing drugs, anti-hyperlipidemic drugs worsen the absorption of vitamin B9.
- Estrogenance therapy, taking anti-tuberculosis, anti-epileptic means (Derivatives of Gidantoin, Barbiturates) causes a strong shortage of folates.
Thus, folic acid is a vital nutrient, which is a starter, the controller of the synthesis of amino acids DNA, RNA and proteins, is involved in the construction of cells. The human body does not produce vitamin B9 in sufficient quantities. Therefore, to meet the need for the connection, it mines it from food.
Given the fact that folates have rapid metabolism, they practically do not accumulate in the body, and quickly output from then, urine.
Normally, the concentration of pteroid glutamic acid in the blood plasma is 7.0 - 39.7 nano liter. For the normal intrauterine development of the fetus, the minimum level of substance in the mother's body should not be lower than 10 nano liter.
To satisfy the daily need of the body in vitamin, you need to saturate the diet with products rich in B9 or additionally use folic acid preparations with a prophylactic dose of the compound. These include: Folazin, Folio, Vitrum Prenatal, Mantna, Elevit, Prognavit, Multi-Tab Pirinal. In the absence of folate deficit in the body, no additional adoption is required.
|








 The composition of the vitamin connection molecule B9:
The composition of the vitamin connection molecule B9: In the event of a lack of vitamin B9, the human body loses the ability to transfer a useful nutrient to the brain, which leads to problems with vision, movement, coordination, seizures begin. At the same time, adults increase the risk of anemia, glossite, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, gingivitis, osteoporosis, neuritis, atherosclerosis, osteoporosis (in women), stroke, infarction, and even cancer.
In the event of a lack of vitamin B9, the human body loses the ability to transfer a useful nutrient to the brain, which leads to problems with vision, movement, coordination, seizures begin. At the same time, adults increase the risk of anemia, glossite, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, gingivitis, osteoporosis, neuritis, atherosclerosis, osteoporosis (in women), stroke, infarction, and even cancer. The lack of vitamin B9 aggravates alcohol, which interferes with the folate metabolism, preventing the connection to the connection to the destination (to fabrics).
The lack of vitamin B9 aggravates alcohol, which interferes with the folate metabolism, preventing the connection to the connection to the destination (to fabrics). Consider why drink Vitamin B9:
Consider why drink Vitamin B9: Folic acid can be included in a complex of multivitamine preparations or separately. Synthetic forms of vitamin B9 are 2 times more active than natural.
Folic acid can be included in a complex of multivitamine preparations or separately. Synthetic forms of vitamin B9 are 2 times more active than natural. Consider detail the description of the absorption of Folatav.
Consider detail the description of the absorption of Folatav. The best means of preventing folic failure - meals with inclusion in the daily menu of fresh vegetables, fruits. With a shortage of folates in food, it is recommended to additionally use 150 - 200 vitamin micrograms daily.
The best means of preventing folic failure - meals with inclusion in the daily menu of fresh vegetables, fruits. With a shortage of folates in food, it is recommended to additionally use 150 - 200 vitamin micrograms daily. In the course of studies
In the course of studies