Website sections
Editor's Choice:
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Signs, Diagnosis, Treatment - Online Diagnosis
- To whom and when is the treatment with thrombolytics prescribed Thrombolytic system of the body
- Guillain-Barré syndrome: symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment
- Diagnosing scarlet fever in a child using a blood test, throat swab, or rapid test
- Pulmonary hypertension in the new guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology (2015
- Examination of a patient with ox at the prehospital stage. Absolute contraindications for TLT
- Immunohistochemical tests How an IHC study is performed
- Myxomatous degeneration of the heart valves Treatment and prevention
- Modern standards of pharmacotherapy for stable angina pectoris Enteral routes of administration
- How does a pathological condition arise, and can it be cured?
Advertising
| Her2 positive breast cancer prognosis. Morphological testing of HER2-status in breast cancer. A unique diagnostic technique for patients with early stage breast cancer |
|
Summary: in order to select the optimal method of diagnosis and treatment (targeted therapy) of breast cancer (BC), the determination of the HER-2neu oncoprotein and comparison of the obtained data with clinical and morphological parameters makes it possible to identify the predictive value of HER-2neu. As a result of the study, the significance of oncoprotein expression in the clinical course of the disease was assessed, as well as in determining the likelihood of disease recurrence and sensitivity in relation to targeted therapy. Maintaining
Breast cancer (BC) occupies a leading place in the structure of cancer incidence among the female population. Despite the rather high level of early diagnosis, almost 700 thousand new cases of breast cancer are registered in the world every year, and in the CIS countries - more than 50 thousand. As for the Republic of Armenia, 700-800 primary breast cancer patients with a persistent tendency to increase are detected annually. The encouraging news in our millennium is that in some countries, including Armenia, the death rate from breast cancer is decreasing. In recent years, significant advances have been made in the diagnosis and treatment of various forms of breast cancer. In assessing tumor potential, in addition to traditional criteria, molecular genetic markers are used, most of which are not yet firmly established in routine practice, which is determined by the high cost of such studies and the complexity of interpreting the data of the simultaneous analysis of many prognostic factors. The results of the study of their predictive value differ significantly among different authors due to the use of different methods and the variability of the results obtained in different laboratories. Meanwhile, the use of traditional molecular markers (expressiononcoprotein HER-2neu) and their correlation with clinical and morphological indicators using modern methods of statistical analysis will allow developing models for individual prediction of the course of the disease. Purpose of the study To determine the expression of the HER-2neu oncoprotein and to reveal the relationship of the obtained data with the clinical and morphological characteristics of breast cancer in order to select the optimal diagnostic and treatment method, which will allow to determine the prognostic significance of the HER-2neu oncoprotein. To achieve the goal, the following tasks were set:
Material and methods For the study, material from 256 patients with breast cancer, aged 25 to 78, was used, most of whom (194) were aged 41 to 60 years. All patients underwent complex clinical and laboratory examinationand received treatment at the RA National Oncology Center(NCO) in the period 2007-2010. Pathohistological examination is an essential informative method that allows to obtain the most complete information about the histological form of cancer, the degree of malignancy, to assess the state of the regional lymphatic collector, and in some cases (during neoadjuvant therapy) to determine the degree of therapeutic pathomorphosis. The histological examination of the material was carried out on the basis of the Department of Clinical Pathomorphology. Tumor tissue, peritumorous areas and lymph nodes were examined. The material was fixed in 10%solution of neutral formalin, dehydrated, carried out through intermediate media (alcohols 1, 2, 3), followed by embedding in paraffin. Sections from paraffin blocks 5-6 μm thick were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Immunohistochemical studies were carried out on the basis of the Department of Clinical Pathomorphology of the National Center of Oncology in conjunction with the Center of Genetics according to the standard method (Hercept- test - DAKO ). The generally accepted and most adequate method for assessing tumor sensitivity to Herceptin is the use of immunohistochemical staining of tumor tissues for the HER2-neu protein. It should be emphasized that the evaluation of the results was carried out only in invasive cancer, since the structures of cancer in situ, despite the pronounced overexpression of the protein, cannot be taken into account ... When evaluating the results of the reaction, only the expression in the invasive component of the tumor was taken into account. The evaluation of the reaction results was carried out using a point scale of 0, 1+, 2+, 3+, developed by the test manufacturer and approved by the US FDA (Food and Drug Administration). Research results and discussion
The study included 256 patients with breast cancer aged 25 to 78 years. In the majority of patients - 153 (59.8%) - negative expression of the oncoprotein HER-2 neu (0/1 +) was detected, in 67 (26.2%) - positive (2+), and in 36 (14.1%) - positive (3+). In order to diagnose and select the optimal treatment, the data obtained were compared with clinical and morphological factors and a detailed statistical analysis was carried out. Clinical and morphological factors include: age, stage of the disease -p TNM, histological form of cancer, grade of malignancy, hormonal status - estrogen, progesterone, tumor localization, weight and growth factor, heredity, comorbidities, breastfeeding, abortion. 1. According to the age factor, the patients were divided into 3 groups:
Thus, according to the results of the statistical analysis, it became clear that in the group of patients aged 41 to 60 years, negative expression of the HER-2 oncoprotein neu (0/1 +) accounted for the largest percentage - 62%. At the same time, it was found that the positive expression of the HER-2neu oncoprotein predominates in the group of patients aged 25-40: 2+ in 26% and 3+ in 19%, and in the group 61 and older, respectively, 43% and 9%. 2 . Disease stage - pTNM
Among the examined patients, T2 occurred in 59%, T1 - 28.9%, and T3 and T4 accounted for 5.5% and 6.6% of the total number of patients, respectively.
Analysis of the data presented showed that with an increase in the T symbol, the number of patients with HER-2-neu positive tumors increases. The distribution of HER-2 neu expression depending on tumor size in each group is:
According to the criterion of metastases in lymph nodes, the largest percentage was made up of patients with pN1 - 42.6%, (pN0-41.4 %), рN2 - 9.8% b, and рN3 1.6% and (рNx 4.7%), were insignificant. The distribution of HER-2neu expression depending on metastases in the lymph nodes in each group showed that with an increase in factor N +, the positive expression of HER-2 neu also increases, which in total (2+ 25%, 3+ 50%) was 75 %.
Since no distant metastases (Mx) were clinically detected in 96.1% of patients, it was not possible to draw any conclusion based on the available data. 3. Histological type of breast cancer
Invasive ductal carcinoma (IPR) was the most frequent - 60.2%. In this group of 154 patients, negative expression of HER-2 neu was recorded in 55.8%, and positive: 2+ in 27.3% and 3+ in 16.9%. Then mixed type of cancer: invasive ductal carcinoma(IPR) and invasive lobular carcinoma (IDR) - 21.9%. In this group of 56 people, negative expression of HER-2 neu was recorded in 66.1%, and positive: 2+ in 21.4% and 3+ in 12.5%. In the third place is IDR 10.9% - 28 patients, of which negative expression of HER-2 neu was observed in 60.7%, 2+ in 32.1% and 3+ in 7.1%. In patients with other types of cancer - medular (0.8%), tubular adenocarcinoma (1.2%), Paget's cancer (1.2%), mucous cancer (0.8%), IPR with an intraductal component (1.6%) - negative expression of HER-2 prevailed neu, which averages 70%. Thus, the positive expression of HER-2neu prevailed in invasive ductal and mixed breast cancer. 4. Degree of malignancy
The degree of malignancy was observed in a small number of patients - 3.1%, in whom HER-2neu expression was negative.
Among the examined patients, 58.6% had grade II tumor malignancy, in which the positive expression of HER-2 neu was 2+ in 27% and 3+ in 13%. However, positive expression of HER-2 neu reached a peak at grade III, which was 2+ in 28% and 3+ in 25%. Consequently, there is a direct relationship between the tumor grade and the expression of the HER-2neu oncoprotein. 5 ... Hormonal status - estrogen, progesterone
The research results showed that 30.5% were patients with estrogen-progesterone negative status, 60.2% had a positive status. 6.3% had estrogen positive and progesterone negative status. Finally, estrogen negative and progesterone positive were recorded in 3% of patients.
Analysis of the data showed that negative expression of HER-2neu prevailed in estrogen-progesterone-positive status, and positive expression of HER-2neu in estrogen-progesterone negative status. It should be noted that statistically significant patterns were not observed with estrogen positive-progesterone negative and inverse statuses. 6 ... Localization of the tumor
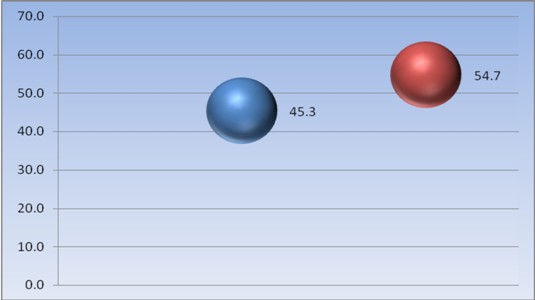
The figure shows the percentage of tumor localization. Thus, 54.7% of cases were left breast cancer, and 45.3% - right breast.
It should be noted that there were no statistically significant regularities in the dependence of the positive expression of HER-2neu on tumor localization. The distribution by quadrants was also considered.
The most common primary tumor was in the upper-outer quadrant.(56,6% ) In 7.7% of patients, the tumor was located in the central zone. The defeat of the lower-internal quadrant and the multicentric location of the tumor were observed, respectively, in 6 , 4% and 5.9% of patients. 7 ... Weight and height factor
In order to find outthe relationship of weight, height of patients and expression of HER-2 neu, a coefficient equal to the ratio of weight and height was introduced. For example, with a weight of 75kg and a height of 150cm, the coefficient is 0.5. From the diagram below it becomes clear that in the group of patients with a pronounced obesity factor (33.2%), the expression of HER-2neu was observedless often than in those women whose weight-to-height ratio is within the relative norm (66.8%). 8. Factor of heredity - accounted for only 16.4% of the total number of patients. The positive expression of the HER-2neu oncoprotein prevailed in the group of patients with the presence of the heredity factor (42 patients): 2+ in 29% and 3+ in 19%: There was no natural relationship between heredity and the expression of the HER-2 neu oncoprotein.
9. Concomitant diseases
There is no information about concomitant diseases in 46.9% of patients.When forming the group, the following factors were taken into account:hyperplastic and inflammatory diseases of the ovaries and uterus, endocrine-metabolic factors - obesity, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, liver diseases, pathology of the thyroid gland.Among concomitant diseases, the largest percentage - 21.9% werehyperplastic and inflammatory diseases of the ovaries, uterus and mammary glandsfollowed by diabetes mellitus - 5.1%,thyroid pathology - 3.9% and other diseases - 22.3% (pituitary adenoma, arachnoiditis, kidney angiomyolipoma, nephropathy, hepatitis, liver hemangioma, cholelithiasis, gastritis, varicose veins).
Data analysis showed that positive expression of the HER-2 neu oncoprotein predominates in the presence of - 2+ y28%, 3+ y20%, then with pathologythyroid gland and other diseases, which is respectively - 2+ in 30% and 27%, 3+ in 10% and 12%. In diabetes mellitus, no statistically significant results of positive expression of HER-2 neu were revealed, which is only 2+ in 8% and 3+ in 15%. 10. Breastfeeding
Of the total number of patients, 54.3% were patients who were breastfeeding, 41.8% were not breastfeeding and 3.9% with complications.
The factor of breastfeeding did not have a significant effect on the expression of HER-2 neu; however, it should be noted that in the group of patients with complications there was a tendency for the expression of HER-2neu to increase.: 2 + at 20% and 3+ at 30%. 11. Abortion
In the majority of patients - 62.5% - abortions were recorded, in which there was an increase in the expression of HER-2neu 2+ in 24% and 3+ y9%. Conclusion Positive expression of HER-2neu predominates in invasive ductal and mixed forms of breast cancer (solid tumors). There is rightproportional relationship between the degree of malignancy (G ) tumors and the expression of the HER-2neu oncoprotein. When estrogen-progesterone is negative, HER-2neu is expressed positively. With an increase in the T criterion, the number of patients with HER-2neu-positive tumors increases; with an increase in factor N +, the positive expression of HER-2neu also increases. Since no distant metastases were clinically detected in 96.1% of patients, it becomes impossible to come to any conclusion based on the available data.P in multicentric breast cancer, positive expression of HER-2neu dominates. In other cases, no statistically significant patterns were revealed. Positive expression of the HER-2neu oncoprotein predominates in groups of patients aged 25-40 years and over 61 years. There is no dependence of HER-2neu expression on weight, height, heredity and breastfeeding factors. expression of the oncoprotein HER-2neu prevails in the presence ofhyperplastic and inflammatory diseases of the ovaries, uterus and mammary glands. Analysis of the data shows that the biological activity of the tumor is in direct proportion to the overexpression of the oncoprotein HER-2neu. Bibliography
Breast cancer is not just one disease. This is actually a group of diseases. When diagnosing breast cancer, one of the first steps is determining which type you have. how cancer can behave.When you have a breast biopsy, the tissue is tested for hormone receptors (HR). It is also tested for what is called human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). Each of them may be involved in the development of breast cancer. In some pathology reports, HER2 is referred to as HER2 / neu or ERBB2 (Erb-B2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2). rs are identified as estrogen (ER) and progesterone (PR). HER2 is a gene that makes HER2 proteins or receptors. These receptors help control the growth and repair of breast cells. Overexpression of the HER2 protein causes uncontrolled multiplication of milk cells. HER2-positive breast cancers tend to be more aggressive than HER2-negative breast cancers. Along with the stage of cancer and cancer, HR and HER2 status helps determine your treatment options. Continue reading to learn more about HER2-positive breast cancer and what you can expect. Survival. What are the survival rates? There are currently no specific survival studies for HER2-positive breast cancer alone. Current research on breast cancer survival applies to all types.According to the American Cancer Society, this is the five-year relative survival rate for women with all types of breast cancer: Stage 0 or Stage 1 (also known as localized or non-metastatic): nearly 100 percent
There are many factors that your doctor must consider when considering your gaze. Among them: stage of diagnosis
Prevalence What is the prevalence of HER2-positive breast cancer? Approximately 12 percent of women in the United States will develop invasive breast cancer at some point. Anyone, even men, can develop HER2-positive breast cancer. But this is more likely to affect young women. HER2-positive represents about 20 percent of all breast cancers.RecurrenceCan HER2-positive breast cancer recurring? HER2-positive breast cancer is more aggressive and more likely to recur than HER2-negative breast cancer. Repetition can happen at any time. But this usually happens within five years of treatment.The good news is that relapse is less likely today than ever before. This is largely due to the latest targeted treatments. In fact, most people treated with early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer do not recur. If your breast cancer is HR-positive, hormone therapy may help reduce your risk of recurrence. HR status and HER2 status may change. If breast cancer recurs, it is necessary to check for the new tumor so that treatment can be reassessed. Treatment What treatment is available? Your treatment plan is likely to include a combination of treatments, such as:surgery
Radiation therapy can target any cancer cells that may remain after surgery. It can also be used to shrink tumors. Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment. Powerful drugs can search for and destroy cancer cells anywhere in the body. HER2-positive breast cancer usually responds well to chemotherapy. HER2 positive breast cancer can also be HR positive. If so, hormonal treatments may be an option. Targeted treatments for HER2-positive breast cancer include: Trastuzumab
Once treatment for non-metastatic breast cancer is over, you will still need periodic testing for signs of recurrence. Most of the side effects of treatment will improve over time, but some of them may be permanent.Metastatic breast cancer is not considered curable. Treatment can continue as long as it works. If any treatment stops working, you can switch to another. It is estimated that over 3.1 million women in the United States have a history of breast cancer. The outlook for HER2-positive breast cancer varies from person to person. Progress in targeted therapy continues to improve the outlook for both early stage and metastatic disease. Editor's Choice Health line Overview Avascular necrosis (AVN) is a disease of the bone. Necrosis is a general term that means that a cell has died. AVN is also called: osteonecrosis aseptic necrosis ischemic bone necrosis AVN bone infarction can lead to joint pain, especially in the hip joint. Bone damage occurs due to a lack of blood flow to the bone cells. Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer death among women worldwide. It accounts for almost 11% of all cancers and ranks first in the world in terms of prevalence. Fortunately, in many developed countries, mortality from breast cancer has declined significantly over the past 20 years, driven by both the emergence of new drugs (chemotherapy and biological agents) and improved screening and early detection of tumors. Human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 (HER2)HER2 is a transmembrane protein that plays a key role in growth factor signaling. HER2 is a member of the HER protein family that includes four types of growth factor receptors: HER1 (also known as the epidermal growth factor receptor EGFR), HER2, HER3, HER4. In healthy tissue, HER2 transmits signals that regulate cell proliferation and survival, but overexpression of HER2 can lead to malignant transformation of cells. The relationship between HER2 overexpression and carcinogenesis has been better studied in a breast cancer model, but HER2 is also an important marker of gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancers (16% of gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancers are HER2-positive, that is, protein overexpression is recorded in them (IHC 2 + / FISH-positive or IHC 3+)). Determining the HER2 status is extremely important, since based on the result, a decision is made about. If the tumor is HER2 positive, the patient is indicated for targeted anti-HER2 therapy. This therapy is not indicated for HER2-negative tumors due to its low efficacy. Current approaches to treating breast cancer today include a combination of chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, biologics, and surgery and / or radiotherapy. For patients with early stage HER2-positive tumors or metastatic breast cancer, targeted anti-HER2 therapy in combination with chemotherapy is the current standard of care. Although HER2-positive status is indicative of a more aggressive tumor progression, the addition of anti-HER2 drugs to chemotherapy improves the course of the disease in many patients. Methods for determining HER2 statusThe gold standard for HER2 studies is that it is possible to use two methods - IHC and in situ hybridization. This combination of methods provides the most complete picture of the pathological process, allowing one to assess both the morphological characteristics of the research object and quantitatively interpret the expression of HER2. Is a dark field microscopy technique that uses DNA probes coupled to a fluorescent label to quantify the amplification level of the HER2 gene. In this case, the HER2 probe binds to the HER2 gene locus on chromosome 17, and the CEP17 probe binds to the centromeric region of chromosome 17. The result is estimated as the ratio of the number of copies of the HER2 gene to the number of copies of 17 chromosomes. A FISH positive sample is one in which the HER2: CEP17 ratio is greater than or equal to 2.0. In situ hybridization is often used to confirm ambiguous IHC results, but can also be used as an initial method for determining HER2 breast tumor status. Patients whose samples are assessed positive by in situ hybridization on initial ISH testing are referred for anti-HER2 therapy. When IHC is used as the initial testing methodology, in situ hybridization should be performed on all IHC 2+ results to confirm HER2 status and to quantify HER2 gene amplification. Less sensitive to preprocessing variations in the preanalytical and collection phases; its interpretation is more objective and quantitative than with IHC. The FISH method identifies HER2-positive cases within an undefined category (IHC 2+). However, sometimes the phenomenon of polysomy causes the appearance of false-negative results of in situ hybridization with IHC 3+. Targeted therapy is most effective in patients with HER2 overexpression (IHC 3+ or IHC 2 + / ISH-positive). It is believed that patients whose samples were assessed as IHC 3 + have a positive HER2 status, and IHC 0/1 + are negative. IHC 2+ samples are considered undetermined and should be retested by in situ hybridization. Samples of IHC 2+ / ISH-positive, classified as HER2-positive. If there is any doubt about the result, assessed as IHC 3+, re-determine the HER2 status using a different method. Below is information about tests for HER2 and breast cancer. HER2 is a protein that can interfere with the growth of cancer cells. This information should be read with knowledge of breast cancer and trastuzumab (Herceptin®). We hope you will find answers to your questions about HER2 and breast cancer testing here.
Receptors are certain proteins that are found on or inside the membrane of cells. Other proteins or chemical compounds that are in the body can attach to these receptors to bring about changes inside the cell (for example, to provoke its repair or reproduction). Growth factors are chemical compounds that attach to receptors and stimulate cell growth. HER2 is a protein found on the membrane of some cancer cells. It is created by a special gene called the HER2 / neu gene. HER2 is a receptor for a specific growth factor called human epidermal growth factor, which naturally exists in humans. When human epidermal growth factor attaches to the HER2 receptors on breast cancer cells, it can stimulate the growth and division of these cells. Some breast cancer cells may have many more HER2 receptors than others. In this case, the tumor is defined as HER2-positive. It is believed that one in five women with breast cancer has a HER2-positive tumor. HER2-positive breast cancer Herceptin attaches to the HER2 protein and prevents human epidermal growth factor from reaching breast cancer cells and stimulating their growth. Herceptin is only effective if the person has high levels of the HER2 protein. Herceptin and early breast cancer Herceptin was licensed for early breast cancer in 2006 in the UK. The National Institute of Clinical Excellence, which runs courses on prevention and treatment, published guidelines for the use of Herceptin in women with HER2-positive early breast cancer in July 2006. According to the guidelines, Herceptin should be considered a possible treatment after surgery and additional chemical and radiotherapy. The guidelines recommend using Herceptin every three weeks throughout the year. HER2 and hormone therapy Hormone therapy is effective when a woman's cancer cells have receptors for estrogen and / or progesterone. They are defined as estrogen- or progesterone-positive. There are many different types of hormone therapy and they function only slightly differently from each other. It has been suggested that a woman's HER2 status may affect the effectiveness of a particular type of hormone therapy. However, additional research is required to summarize the final results. HER2 test The two main methods that are used for testing for HER2 are immunohistochemistry and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH): Immunohistochemistry
Fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH) There is no numeric scale to measure the result of the FISH test. Possible outcome:
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with breast cancer, you may be wondering what HER2 is. You may also be wondering what it means to have HER2-positive or HER2-negative breast cancer. This acronym, which stands for Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2, is one indicator. The hormones estrogen and progesterone can also determine the pathology of your particular breast cancer. Your HER2 status can also help determine how aggressive the cancer is. Your doctor will use this information to evaluate your treatment options. In recent years, there have been significant changes in the treatment of those with HER2-positive breast cancer, resulting in a better prognosis for those with the condition. What is HER2?HER2 is a protein made by HER2 ge northeast HER2 proteins are receptors on breast cells. They are involved in normal cell growth. HER2 appears on some cancer cells, especially for breast and ovarian cancers. Sometimes the HER2 protein doesn't work properly. This can cause the cells to multiply too quickly. Excessive reproduction can cause fast-growing breast cancer. If a cancerous tumor forms, then more often than HER2-negative cancer, it recurs. What does HER2 positive mean?If HER2 is present in your breast cancer cells, it is known as HER2 positive breast cancer. HER2-positive breast cancer occurs in about 25 percent of breast cancers. HER2 testing: what your test result means HER2 was discovered in the 1980s. During this time, the researchers realized that the presence of the HER2 protein could lead to the rapid spread of cancer to other parts of the body. This discovery led to research into how to slow down or alter the growth process of these cancer cells. Over the past 20 years, significant treatment options have been developed to treat HER2-positive breast cancer. What does HER2 negative mean?If breast cancer cells do not contain HER2, the condition is called HER2 negative breast cancer. If you have HER2 negative breast cancer, your doctor will consider breast cancer groups 1 and 4 when determining your treatment plan. Group 1 or lumen A, breast cancer is likely to benefit from hormone therapy and chemotherapy. Group 4 or basal-like, breast cancers are likely to benefit from chemotherapy. Testing on HER2There are several tests that can determine your HER2 status, including:
It is important to know that the HER2 test is used because it will determine if you will respond to certain medications for HER2-positive breast cancer. Usually, doctors use the IHC test first. FISH tests are considered more accurate, but they are more expensive and the results may take longer. Treatment for HER2-positive breast cancerResearchers have been studying HER2 and treatments for over 30 years. Successful targeted treatments have now changed the prognosis of cancer from 1 to 3 from poor to good. Genetics Assessment: Is HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Hereditary? The humanized monoclonal antibody trastuzumab, also known as Herceptin, has improved the outlook for HER2-positive breast cancer patients when used in tandem with chemotherapy. A 1998 study found this treatment combination slowed the growth of HER2-positive breast cancers when compared to chemotherapy alone. For some, the use of trastuzumab with chemotherapy has resulted in long-term remissions. Other treatments for HER2-positive breast cancer include lapatinib (Tykerb). This drug can be used in combination with capecitabine (Xeloda), a type of chemotherapy, or letrozole (Femara), a type of hormone therapy. A new drug, ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla), debuted in 2013. This drug shows that it can be an effective initial treatment with fewer side effects than trastuzumab. The Cleveland Clinic is currently conducting trials to determine the effectiveness of two powerful targeted drugs. The aim of the study is to "develop an optimal long-term treatment protocol" with minimal side effects that also do not require chemotherapy. Talking to your doctorIf you have been diagnosed with invasive breast cancer, be sure your doctor has tested you for your HER2 status. The test results will determine the best treatment options for your cancer. New developments in the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer have improved the outlook for people with the disease. Treatment can slow the growth of HER2 proteins in cancer cells. Editor's Choice |
| Read: |
|---|
Popular:
New
- Cholera. Epidemiology. Cholera Vibrio Vibrio cholerae - the causative agent of cholera Cholera - anthroponous especially dangerous toxic infection, characterized by profuse watery diarrhea, - the presentation of Cholera as an especially dangerous infection is capable of
- Presentation "The structure of the cell of animals and plants. Tips on how to make a good report of a presentation or project
- How does a closed aquarium ecosystem work?
- Lymphatic system presentation
- Presentation on cancer The main direction of improving the oncological situation in Saratov
- Anatomy and physiology of the heart
- A presentation on appendicitis was done by a student of group f
- Presentation - the eye as an optical system
- Anatomy and physiology of the digestive system
- Spinal Cord Presentation