Sections of the site
Editor's Choice:
- "Amnesty" extended country amnesty dates for
- How to pass the closerization of an adult
- How to open coconut at home?
- How we opened a coconut
- How to open coconut at home: effective ways and advice
- Duphaston - Instructions for use when planning a pregnancy Dupaston changed the package
- Business called the most unprofessional supervisory authority Briefing Mikhail Abyzov at the end of the meeting
- Duphaston instructions for use, contraindications, side effects, reviews Duphaston Netherlands What a fake looks like
- Convolution or Varetle Stop Cava Vius
- Convolution or Varetle Stop Cava Vius
Advertising
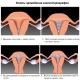
| Ovarian apoplexy forms. Apoplex ovarian - what it is, reasons, symptoms in women, treatment and prevention. Medical stimulation ovulation |
|
The apoplexy of the right ovary is a sharp hemorrhage with the subsequent rupture of the body tissue. It occurs spontaneously and is observed more often in the second half of the cycle during or after ovulation. This pathology is subject to women of reproductive age, usually up to 40 years. At the older age, the apoplexy happens much less frequently. Violation of the integrity of one of the ovary (apoplexy) In the middle of the cycle, when the egg ripens, then comes out of the dominant follicle, ovulation occurs. At the site of the burst follicle appears, generating progesterone. In the presence of various pathologies, hemorrhage can occur in the prioritial follicle, or a yellow body cyst, this is a right-sided apochia. The appearance of apoplexy during or after ovulation is explained by the fact that during this period, the vessels become fragile under the influence of hormones and are easily damaged. At the scene of hemorrhage in the ovary appears hematoma, which is quickly filled with blood. The shell of this hematoma under pressure is rapidly destroyed, the blood is poured into the abdominal cavity, internal bleeding appears. This condition is a greater danger not only for health, but even for the life of a woman, therefore requires emergency care. Apoplex in the right ovary is observed much more often than in the left. This is due to the fact that it is from the right side of large artery, and in general the vascular network is more extensive, as it is associated with the aorta. The ovarian is associated with the renal artery, which is less in size. Doctors distinguish many reasons why the right ovary can occur. It is not always possible to determine accuracy that it was played by the role in the development of a pathological condition. Next, consider the most basic reasons for the applement of the right ovary:  Sometimes right-sided apoplexy can occur at a healthy woman in the absence of any pathologies. Such cases make it difficult to diagnose. SymptomaticsIn the apoplexy of the right ovarian, the symptoms are characterized by two main signs: pain and bleeding (both external and internal). The painful form is moderate or intense, localized to the right at the bottom of the abdomen. Bleeding can resemble menstruation, with internal bleeding, the following features are observed:
With right-sided apoplexy, pain appears suddenly, it usually happens in the second half of the cycle during or after the onset of ovulation. Often painfulness is felt not only in the ovarian area, but also in the ivoid region (right under the diaphragm), can irradiate to the buttocks, lower back, sometimes in foot. With intensive pains may be nausea or vomiting. In the presence of strong internal bleeding, the danger of the occurrence of hemorrhagic shock.
DiagnosticsWhen one or more specified symptoms of this pathology are found, as well as with a sharp deterioration of well-being, urgent hospitalization is necessary. Diagnostic errors arise due to the fact that the right-sided apoplexy (ovarian break) has similar symptoms with many other diseases. These include:
To avoid negative consequences of erroneous diagnostics, it should be carried out carefully and comprehensively and include the following activities:
TreatmentEmergency assistance in the right-sided apoplexy of the ovary can be provided by the Ambulance of ambulance before arriving at the medical institution. An independent reception of any drugs is strictly prohibited, since it is fraught with a false improvement and erroneous diagnosis. In the case of conventional apoplexy, or if the ovary rupture occurred, the hospitalization is carried out at mandatory. Depending on the severity of the pathological process, treatment can be conservative, operational or combine both methods. Conservative treatment includes bed regime, taking antispasmodics and muscle relaxants, as well as hemostatic drugs and means against anemia (with a high content of iron). Sometimes it uses a cold heater on the right side of the abdomen. The drug treatment method is applied in the event of a light form of the disease, but is rather risky. Without surgical intervention, the risk of recurrence of the disease, the development of an extensive adhesion process (spikes are formed from blood clots, which were not removed) and as a result - infertility. Therefore, in order to avoid these complications, it is recommended to restore the external shells of the damaged ovary and remove the blood from the abdominal cavity. Fabrics, on the site of which the ovarian break occurred, stroke (at a cyst, its contents are removed), and then cavities (coagulation method). Usually after the operation, the patient is in the hospital under the supervision of doctors for 5-7 days, then it is released home. Further restoration at home includes physical peace, the reception of painkillers and other drugs that appoint the attending physician.
Consequences and preventionOperational treatment of right-handed apoplexy is carried out by gentle methods, which maximize the system to preserve the integrity of the ovary and its reproductive functions. Even with a break, persistent infertility does not always occur. Reproductive functions are lost only in particularly severe cases when pathology is observed on both sides, or is combined with other diseases that are incompatible with pregnancy. About a month later, a woman can return to normal life and even to moderate physical exertion. However, a regular visit to the doctor is necessary to monitor possible complications of the operation. The consequences of right-side apoplexy are mainly reduced to the development of adhesions, as well as chronic pelvic pains that are felt during ovulation. Doctors also do not exclude recurrence. To avoid this consequence, it is necessary to comply with all the recommendations of the doctor, in time to treat other gynecological diseases, eliminate intensive sports, as well as undergo regular diagnostics. The consequence of inflammatory diseases of the uterus's appendages, as well as hormonal disorders in the body, may become irreversible changes in the ovaries tissues. The spikes and cysts formed during inflammation impede normal blood circulation, the permeability of the vessels increases. This can provoke a sudden tissue and vessels, the appearance of bleeding. There is a so-called apoplexy of the ovary, in which the woman feels acute pain. This condition is dangerous for life. A woman needs urgent medical care. Content: Types of apoplexyThe apoplexy of the ovary is called a sudden violation of its integrity. At the same time, a woman has a sharp strong pain in the lower abdomen. If a large vessel is damaged, then hemorrhage in the peritoneum. In a different way, this disease is called an ovarian infarction. Depending on the specific manifestations, such pathology is divided into the following types:
With anemic apoplexy ovarian bleeding can be weak and strong. Depending on the volume of lost blood, 3 forms of such pathology are distinguished. Easy - The loss of blood is not more than 150 ml (the first degree of hemorrhage). Average - Volume of lost blood from 150 ml to 0.5 liters (second degree). Heavy - more than 0.5 liters of blood (third degree) is lost. Bleeding during the apoplexy of the ovary is caused by damage to the follicle vessels (grapham bubble) - the shell in which the egg generation develops. The reason is the gap of the follicular cyst (it can form inside the follicle, if for some reason the egg did not come out of it, that is, no ovulation occurred). Such anomaly is caused by hormonal violations. At the same time, the connective tissue is rupture, as well as the cysts of a yellow body. Such a cyst is formed from the burst follicle after the exit of the egg. It is filled with blood. Video: types of apoplections of ovary
Symptoms of apoplexyThe pain is a symptom of apoplexy of the ovary of any variety. It occurs suddenly, localizes in the lower abdomen. The pain can be permanent or appear in the form of attacks that continue from half an hour to 2-3 hours. Attacks after a small break can be returned. At the same time, colic or spasms like contractions. If painful apoplexy arises, then the causes of pain are irritation of nervous endings in the tissues during the breaking of the fibers, as well as the spasms of the ovarian artery. With such a kind of apoplexy of the ovarian, the pain is sometimes felt in the field of rectum, navel, loin. The appearance of nausea and vomiting. With anemic form, besides the bouts of pain, there are signs of bleeding: general weakness, dizziness, severe thirst, nausea, vomiting, headache, decrease in blood pressure, frequent pulse, fainting, pallor skin, cold sweat. It is possible to increase body temperature. The pain spreads to the leg, the crushes, the crotch area and the rear pass. The stronger the blood loss, the more pronounced symptoms. With the mixed apoplexy of the ovary, all the symptoms are combined, besides, the appearance of blood secretions from the genital tract. Strong pain is felt during the feeling of the ileal abdomen. At the place of the break is formed by hematoma. For the light stage of the apoplexy of the ovary, the periodic repetition of pain attacks is characterized, but they are short. With moderate severity, the bouts of pain cause loss of consciousness. If the disease occurs in severe form, the pain is permanently permanently, the abdomen (the so-called "sharp belly") occurs), heart failure appears, death can come. The blood supply to the right ovary is carried out through the ovarily artery, which is directly connected to a large vessel - aorta. The left is supplied with blood through the ovarian artery extending from the renal artery. Due to the best blood supply, the right ovary has a larger size, mass, he has a more developed vascular network. Therefore, the apoplexy of the ovary is 2-4 times more likely arises from the right side. According to symptoms, the apoplexy can be confused with ectopic pregnancy, acute appendicitis, renal colic, inflammation of the pancreas, cure ovary or its twist. Therefore, it is important to accurately determine the cause of pain in order to provide a woman in a timely manner. Video: Ovarian apoplexy symptoms
Causes of ruptureThe apoplexy of the ovary can occur at any woman of the childbearing age (about 12 to 50 years). Risk (40-60%) is quite large that the disease will repeat. The following factors can provoke a break:
However, sometimes it happens that the apoplexy of the ovary arises in the absence of such factors in a woman who does not have any deviations in a state of health. The gap can occur even during sleep. It is believed that the main reason is the imbalance of hormones, namely the increased production of the lactotropic hormone of prolactin and gonadotropic hormones - FSH (follicularity) and LH (luteinizing). FSH and LH regulate the work of the ovaries, the formation of eggs in follicles. Prolactin affects the ratio of sex hormones responsible for all the processes of the menstrual cycle. The cause of the apoplexy of the ovary can also be strong experiences, nervous breakdowns, neuropsychiatric diseases. The state of the nervous system has a direct connection with hormonal processes in the body. The greatest probability of the break is created at the time of ovulation (the middle of the menstrual cycle), as well as during the formation of a yellow body and its vascular system (the second phase of the cycle).
Possible complicationsA large loss of blood caused by a rupture of large vessels can lead to hemorrhagic shock - a sharp drop in blood pressure. If the help is not rendered on time, death can come. After the treatment of apoplexy of the ovarian, the formation of adhesions in the ovary becomes complications, the repetition of breaking subsequently, as well as infertility. Especially likely to appear such complications after conservative treatment. With laparoscopic timely treatment, the patient's reproductive health is possible. A warning: When acute pain in the lower abdomen occurs, especially in the middle or in the second half of the menstrual cycle, the woman must necessarily take a stay. It is necessary to immediately call "ambulance". With intra-abdominal bleeding in women, about 2-3% of cases, the cause of the ovarian apoplexy is. DiagnosticsSuch a sign like a "acute belly" is also characteristic of other serious pathologies in the bodies of the small pelvis. The purpose of the diagnosis is to confirm that the ovarian rupture (apoplexy) has occurred, and not damage to the phallopyheological pipe due to ectopic pregnancy. It is also necessary to exclude suspicion of appendicitis. The prehistory of the disease is studied to understand whether it has a connection with the phases of the menstrual cycle. Methods are used that allow you to quickly understand the nature of the pathology, to detect an increase in the size of the ovary.
General blood analysis Shows the content of hemoglobin and the speed of its coagulation. This suggests the presence of anemic or mixed apoplexy of the ovary. Increased concentration of leukocytes indicates the appearance of the inflammatory process. Puncture of the rear vessel of the vagina. In the peritoneum between the uterus and the rectum there is a deepening in which the liquid accumulates. The study of its composition makes it possible to establish the presence of intra-abdominal bleeding. To take the trial of this fluid, it is necessary to pierce the rear wall of the vagina using a special needle. The presence in fluid of blood and pus is determined. Ultrasound - To study the structure of the yellow body, the formation of hemorrhage in it. Laparoscopy. An optical instrument (endoscope) is introduced into the abdominal cavity through the puncture. The method allows you to accurately determine the cause of the bleeding and the nature of the apoplexy of the ovary. If necessary, this method can be immediately eliminated by pathology. Video: Treatment of apoplexy ovarian
TreatmentThere are two methods of treatment: conservative and surgical. Conservative treatment of apoplexy of ovaries includes the reception of antispasmodic drugs, weakening pain, and hemostatic (preparations that strengthen vessels). At the same time, the woman prescribes full rest, ice is laid on the bottom of the belly. Appointments of vitamins B1, B6, B12, as well as subsequent physiotherapy are prescribed. There is a round-the-clock observation of the state of a woman. When repetition of a painful attack and deterioration of well-being operations. This method of treatment can be used only with a light form of pain apoplexy of the ovary in the absence of bleeding into the abdominal cavity. About 50% of cases in women there is a repetition of such a disease. In the ovary and cavity of the peritoneum remains blood clot, spikes. The likelihood of infertility is great. Therefore, this method is not applied to the treatment of born women or planning other children subsequently. Surgical treatment is the main way to eliminate such pathology. Most often, even with a light form of apoplections of the ovary, endovidoscopic treatment (laparoscopy) is used. At the same time, the worshicle of the cyst is removed, coagulation (soldering) of vessels and ovarian sewing is made. After stopping bleeding, it is washing the cavity of the peritoneum by a disinfectant solution, removal of blood clots. Thanks to such a gentle operation, a woman maintains the opportunity to conceive a child subsequently, since the lack of adhesions on the ovaries guarantees their normal functioning. With severe forms of apoplexy of the ovary with strong bleeding and a large area of \u200b\u200brupture, laparotomy is carried out. In this case, an incision on the pureth wall is made. The ovary is usually trying to save. If the gap is very large, it is removed. Video: How laparoscopy is performed. Condition after surgery
Ovarian break during pregnancyThe emergence of apoplexy of the ovary is possible during pregnancy. In this case, only the surgical method of suturing of the ovary is used. Maximum efforts are applied to preserve pregnancy. At the same time, accuracy and speed of diagnosis becomes even more important. Different profile doctors are attracted: urologist, gynecologist, surgeon. Rehabilitation after treatmentAfter surgery, rehabilitation treatment is carried out to prevent the inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity, as a result of which spikes may form. Scars and spikes provoke the occurrence of repeated apoplexy of the ovary. The methods of physiotherapy are used:
In this case, it is necessary to use hormonal contraception to complete restoration of the ovarian functioning (at least 6 months after the operation to eliminate the apoplexy of the ovary). Planning a pregnancy after rehabilitation is recommended only after the diagnostic examination by the method of laparoscopy and confirm the full healing and the absence of the inflammatory process. Prevention of repeated apoplexyIf the patient has an apoplexy of the ovary in a light form and arose against the background of hormonal disorder, then special preventive measures are not required, since after restoring the functioning of the ovary, the hormonal background comes back to normal. If the disease occurs as a result of vascular disorders and vegetative disorders (increased tone of muscles, neurosis and others), accompanied by hemorrhagic bleeding, treatment is carried out. It is prophylactic, continues for 3 months. Preparations are prescribed to improve the blood supply of the brain, income into it oxygen (Cavinton, Tanakan), psychotropic drugs. In addition, diuretic drugs are used to eliminate internal edema.
To restore the hormonal background after the treatment of the ovarian apoplexy for 3-6 months, it is necessary to take microdosted contraceptive pills with estrogen and progesterone (Marvelon, Zhanin, Femoden). The gap of the ovary or the medical terminology "Apoplexia" (Apoplexia Ovarii) is defined as suddenly occurring hemorrhage into the body when the vessels of the vessels of the grapple bubble, the stroma of the ovary, follicular cyst or the cyst of the yellow body, accompanied by a disorder of the integrity of the ovarian tissue and bleeding in the abdominal cavity. More often the ovarian breaks are between the ages of 14 and 40, usually in 20-35 years. However, there are cases of hemorrhage among young girls and adolescents. Its frequency among gynecological pathology is 1-3%, recurrence with the disappearance of adequate rehabilitation reaches 40-70%. How does the ovarian apoplexy arises In the ovaries of a hawk woman there are growing follicles, ripening eggs in them, that is, preparation for the upcoming pregnancy. From the beginning of the menstrual cycle, the dominant follicle begins to grow, which by the middle of the menstrual cycle reaches its maximum size - about 20 mm. Then the follicle shell is broken, producing ripened eggs, - ovulation occurs. A temporary formation is formed on the site of the follicle, a yellow body, which produces certain hormones, prepare the body of a woman to pregnancy. This is the normal course of the ovarian cycle. In the dystrophic and sclerotic changes in the ovarian tissue, occurring during acute and chronic inflammatory processes in the apparatus of the uterus, with polycystic ovary syndrome, adhesive process and some other diseases, as well as during the drug stimulation of ovulation, there are certain disorders in the process of ovulation and the formation of a yellow body. As a result, blood vessels at the site of the ovarian break point are poorly reduced, international bleeding continues and enhanced, and in the yellow body, hematoma hematoma is formed due to the fragility of the vessels. All this is accompanied by pain syndrome, weakness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, pallor of skin, fainted condition. Without the appropriate treatment, internal bleeding when the ovarian break can increase, creating a real threat to the health and life of a woman. Causes of ovarian breakingMost doctors allocate "critical moments" for damage to the ovary. So, in 90-95% of patients the apoplexy of the ovary occurs in the middle and in the second phase of the menstrual cycle. This is due to the features of the ovarian tissue, in particular with the increased permeability of the vessels and the increase in their blood flow during the period of ovulation and before menstruation. The apoplexy of the right ovary is found at 2 - 4 times more often than the left, which is explained by its more abundant blood circulation, since the right ovarian artery is directly from the aorta, and the left - from the renal artery. In women, the inflammatory processes of the small pelvis are predisted in women, leading to adhesive processes and, as a result of this, sclerotic changes both in the ovarian tissue (sclerosis of stroma, fibrosis of epithelial elements, periophores) and in its vessels (sclerosis, hyaline ), as well as stagnant hyperemia and varicose veins of a small pelvic organs. Apoplexes of ovary can contribute blood disease and long-term intake of anticoagulants, leading to a violation of the coagulation system of blood. Among other reasons, abdominal injury, physical stress, stormy or interrupted sexual intercourse, horse riding, dying, vaginal research, etc. They may be the wrong position of the uterus, mechanical compression of vessels, adhesions in a small pelvis, etc. Sometimes occurs without visible reasons at rest or during sleep. The leading role in the development of this state is currently allocated disorders of hormonal status. One of the main reasons for the ovarian break is considered an excessive increase in the number and changes in the ratio of gonadotropic hormones of pituitary glands (FSH, LH, Prolactin), which contributes to ovarian tissue hyperemia. The main forms of apoplexy in the ovary Eliminate pain, anemic and mixed form of apoplexy of the ovary. Currently, the classification is most often used (Savelyeva G.M.), taking into account the severity of intraperous blood loss: 1. painful form. 2. Hemorrhagic form: I degree - light (intra-abdominal blood loss does not exceed 150 ml); Symptoms of ovarian breakThe main complaint with the ovarian breaking in women is a sudden pain in the lower departments of the abdomen. The pain is associated with irritation of the receptor field of the ovarian fabric and the impact on the abutant blood, as well as with a spasm in the ovarian artery pool. Such signs as weakness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, a fainting condition are associated with intra-abdominal blood loss. The painful form of apoplexy is observed with hemorrhage into the ovary or yellow body fabric without bleeding into the abdominal cavity. The disease is manifested by the attack of pain at the bottom of the abdomen without irradiation, sometimes with nausea and vomiting. There are no signs of intra-abdominal bleeding. Clinical symptoms of pain and light hemorrhagic shape are similar. In the clinical picture of the middle and heavy hemorrhagic (anemic) form of the apoplexy of the ovarian, the main symptoms are associated with intra-abdominal bleeding. The disease begins acutely, often associated with external causes (sexual intercourse, physical stress, injury, etc.). Pain in the lower sections of the abdomen often irradiates to the rear pass, leg, crushes, outdoor genitals, accompanied by weakness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, fainting. The severity of symptoms depends on the value of intra-abdominal blood loss. DIAGNOSTICS With an ultrasound of a small pelvis, a significant amount of free fine and medium-part fluid in the abdominal cavity is determined with the structures of irregular shape, increased echogenicity (blood clots). To diagnose the apoplexy of ovaries without pronounced disorders of general well-being, the puncture of the abdominal cavity through the rear arch of the vagina. However, the method of choice is optimally diagnostic laparoscopy. Treatment of apoplexy ovarianThe approach to the treatment of patients with apoplexy of the ovary depends on the form of the disease and severity of intra-painting bleeding. With pain and insignificant intra-abdominal blood loss (less than 150 ml) without signs of increments of bleeding, you can conduct conservative therapy. Medical treatment of the apoplexy of the ovary includes peace, ice to the bottom of the abdomen (contributes to the vessels of the vessels), the preparations of hemostatic action, antispasmodic agents, vitamins, physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis with calcium chloride, microwave therapy), especially during the rehabilitation period. Conservative therapy for the ovarian breaks is carried out in the hospital under round-the-clock supervision. With a positive dynamics from conservative therapy, the patient is issued under the supervision of the doctor a gynecologist of an outpatient institution for further treatment and prevention of relapses and complications. With hemorrhagic form, re-attack pain, deterioration of the general condition, instability of hemodynamics, increasing the amount of blood in the abdominal cavity clinically and when ultrasound of a small pelvis appear to indicate operational intervention(laparoscopy, laparotomy). At the same time, it is necessary to refund blood loss (repentance, transfusion of donor blood, blood substitutes), if necessary, administer cardiovascular drugs. The apoplexy of the ovary occurs infrequently, but its consequences and complications can stay in a woman for life. Therefore, it is essential in the preservation of women's health and reproductive function in particular, a reducing stage and recurrence prevention is given. Preventive measures are aimed at reducing the likelihood of repeated ovarian break. In order to prevent the repetition of the status and restoration of hormonal status, the patient is prescribed oral contraceptives. Women and girls gynecologists recommend avoiding the factors that provoke this condition, to pass inspections every six months and in time to contact a specialist for help. Timely treatment of diseases of the uterus and its appendages contributes to the healthy functioning of the entire sexual system. The site provides reference information solely to familiarize yourself. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases must be under the supervision of a specialist. All drugs have contraindications. Consultation of a specialist is obligatory! Apoplex ovarian (Apoplexia Ovarii) - an acute gynecological disease, as a result of which the vessels break occurs (it can be vessels both the ovary itself and the formed cyst), and a sudden hemorrhage in the ovarian fabric or in the abdominal cavity is developing.Anatomy and ovarian physiologyThe ovaries are a paired organ located on both sides of the uterus in a small pelvis. Their average length is 3 cm, 1 cm thickness, and width 2 cm. But these sizes are not constant, and change over the month depending on the menstrual cycle phase. The ovaries are women's sexual glands, sex hormones (progesterone and estrogens) are produced in them, and each month an egg generation is formed, which can give life to a new organism. The ovaries have their own bundles with which they join the uterus.Disease prevalenceThe apoplexy of the ovarian occurs at any age, but most often the gap occurs in women of the rootgeneric period (from 18 to 45 years), since the ovaries are actively working at this age. Among all gynecological diseases, the apoplexy of the ovary is about 1-3%. And if the ovary rupture occurred, the probability of repetition of the disease was very large - up to 70%. At the same time, the apoplexy of the right ovary is 3 times more often than the left. This is due to the fact that the right ovary is much more blood vessels.The reasonsI. Inflammatory diseases of the organs of the small pelvis (ovaries themselves, uterus, uterine pipes). As a result of inflammation, the ovarian fabric is modified and the blood vessels feeding it, which can cause their rupture.II. Varicose expansion of ovarian (ovarian) veins and their change in various diseases. III. Blood coagulation disorders (with congenital and acquired blood diseases, for example, with hemophilia) or the reception of drugs causing blood dilution. IV. Violation of the balance of sex hormones in the body. V. Diseases of the nervous system, stress, nervous overvoltage. Against the background of these reasons, there are external and internal factors that can provoke an apoplexy of the ovary. Internal factors:
Basic symptoms The most important symptom of the apoplexy of the ovarian is sharply appearing acute pain. The disease develops so suddenly that the patient with an accuracy of minutes can call the time of pain. The most important symptom of the apoplexy of the ovarian is sharply appearing acute pain. The disease develops so suddenly that the patient with an accuracy of minutes can call the time of pain. Pain syndrome during apoplexy is associated with blood intake in the abdominal cavity and irritation of peritoneum covering internal organs. In addition to pain, the patient will disturb weakness, dizziness. Nausea and vomiting may appear. And in the case of strong internal bleeding, loss of consciousness may occur. Forms of the diseaseManifestations of the apoplexy of the ovary depend on the clinical form of the disease.The painful form of apoplexy of the ovary is observed when hemorrhage occurs inside the ovary itself (when the egg leaving). The disease begins with a sharp pain at the bottom of the abdomen, sometimes may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting, but signs of internal bleeding (weakness, reduction of pressure, fainting) is not observed. Hemorrhagic, or anemic form. The disease is developing sharp, and is often associated with external provoking factors - sexual intercourse, exercise, trauma. The main symptoms at this form of apoplexy are associated with intra-painted bleeding. The pain is felt in the lower departments of the abdomen, often pulls out the rectum, exterior genitals, seats and back. There is almost always weakness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting. With severe internal bleeding, the pulse is increased, reduced pressure and loss of consciousness. Mixed form. Signs of apoplexy of the ovary in this form begin with pain syndrome, but with abundant bleeding, manifestations of anemic version of the apoplexy are joined. DiagnosticsThe diagnosis of the apoplexy of the ovarian is made on the basis of a consistent study of complaints, the history of the disease, examination of the patient, the results of the analyzes and additional instrumental methods of the survey.I. Complaints: Pain, nausea, vomiting, signs of internal bleeding. II. History of the disease. In 90-95% of women, the apoplexy of the ovary occurs in the middle or in the second phase of the menstrual cycle (after 14-21 days from the beginning of the monthly). These are the so-called "critical moments", because during the period of ovulation (exit of the egg) and before menstruation, the blood vessels become more permeable and crowded, which contributes to their rupture. III. Inspection of the patient. The general condition will depend on the form of apoplexy. With pain, the general condition will be satisfactory. The skin of the usual color, pulse and pressure will be located within the normal range. The stomach remains soft, painful above the pubic, more often on the right. In the hemorrhagic form of the apoplexy of the ovary, the pallor of the skin and mucous membranes will be observed, there may be a cold sticky sweat. Blood pressure in the patient will be lowered, and the pulse is rapidly. There is a bloating of the abdomen and sharp pain in the lower departments. IV. Generally clinical analyzes. In general blood test, the hemoglobin rate is reduced (but with acute strong blood loss due to blood thickening, it may remain normal), the level of leukocytes (inflammation cells) can be elevated. V. Instrumental research. The ultrasound during the apoplexy of the ovary will determine the liquid (blood) in the abdominal cavity. For accurate diagnosis of the character of the fluid, medical manipulation is performed - puncture (puncture) of the abdominal cavity through the vagina. This intervention is performed under anesthesia. If this study did not help to make a diagnosis, operation is carried out - diagnostic laparoscopy. Conservative treatmentTactics of treatment will depend on the form of the disease and the severity of the patient's condition.Conservative (non-state) treatment of apoplexy of the ovarian can be carried out with pain, when the patient feels satisfactorily, and there are no signs of internal bleeding. Conservative treatment includes: 1. Full peace. 2. The cold of the abdomen (this helps to reduce pain and narrowing vessels). 3. Hemostatic drugs (sodium ethalate, etc.). 4. Preparations, removing spasms (but-shpa, papaverine, etc.). 5. Vitaminotherapy: Vitamins in 1, in 6 and at 12 are prescribed. 6. Physiotherapeutic procedures: microwave treatment, electrophoresis with calcium chloride. Treatment should be carried out only in the hospital, under the clock observation of medical personnel. In the event of a repetition of a painful attack, with a worsening of the general condition and indicators of analyzes, the issue of conducting an operation. Surgery Operation during the apoplexy of the ovary can be carried out in two ways: laparotomically (through incision) and laparoscopically (through the pursuit of the abdominal wall). Operation during the apoplexy of the ovary can be carried out in two ways: laparotomically (through incision) and laparoscopically (through the pursuit of the abdominal wall). Indications for laparoscopy during the apoplexy of the ovary:
Differential diagnostics during the apoplexy of the ovaryDifferential diagnosis in apoplexy is carried out with the following diseases:1. Gynecological: the tip of the pipe with an ectopic pregnancy, the purulent formation of the fallopian tube, twisted the legs of the ovary cyst. 2. Surgical: appendicitis, acute intestinal obstruction, pancreatitis, intestinal colic, ulcerative stomach disease. Pregnancy after the apoplexy of the ovaryThe rupture of the ovary in itself does not affect the further possibility of conception, because During the operation, partial removal of the ovary is performed. But even if the ovary fabric is completely removed, the egg cell can be matured in the second, healthy ovary.Difficulties with conception may occur in the formation of adhesions in the abdominal cavity. To minimize the consequences of the apoplexy of the ovary, it is necessary to comply with all the recommendations of the doctor in the rehabilitation (recovery) period: Prevention is necessary for the patients who transferred the hemorrhagic form of the apoplexy, since they have resistant disorders of the hormonal background and the work of the central nervous system.
Apoplex ovarian - sudden damage to fabric and vessels ovarian, as a result of which bleeding in the abdominal cavity. This pathology is accompanied by painful sensations and blood loss of varying degrees. In the international classification of diseases of the tenth revision ( MKB-10) The apoplexy of the ovary is highlighted in two points. Point N83.0 corresponds to a hemorrhagic follicular ovarian cyst, and paragraph N83.1 is a hemorrhagic yellow body cycle. This pathology is usually characteristic of women in reproductive age. As a rule, women are suffering from this disease 25 to 40 years. The apoplexy of the ovary is more often observed in the second phase of the menstrual cycle or during the period of ovulation ( the process in which the mature egg leaving the ovary). Often, the rupture of the ovarian tissue can occur during pregnancy. Recurry ( re-exacerbation) Apoplexes of the ovary occurs in 40 - 70% of cases. Interesting Facts
Anatomy of ovarian The ovaries are a pair female organ. The average ovary size is 3- 4 cm in length, 2 - 2.5 cm wide and 1 - 1.5 cm in thickness. In the form of the ovary resembles a peach bone. The weight of the ovary of an adult woman is 5 - 7 g, an elderly woman has 3 g, and only a god-born girl is less than a gram. There are ovaries in a small pelvis, on both sides of the uterus. The ovarian urban uterine is connected using ligaments. The blood supply to the ovaries provide egg arteries. Right egg artery has a larger caliber, as it moves directly from the abdominal aorta. Left egg artery is a branch of the renal artery. Due to the fact that the right ovary is bloodtained a larger artery in size it is a little more left. The ovaries are a pair female organ. The average ovary size is 3- 4 cm in length, 2 - 2.5 cm wide and 1 - 1.5 cm in thickness. In the form of the ovary resembles a peach bone. The weight of the ovary of an adult woman is 5 - 7 g, an elderly woman has 3 g, and only a god-born girl is less than a gram. There are ovaries in a small pelvis, on both sides of the uterus. The ovarian urban uterine is connected using ligaments. The blood supply to the ovaries provide egg arteries. Right egg artery has a larger caliber, as it moves directly from the abdominal aorta. Left egg artery is a branch of the renal artery. Due to the fact that the right ovary is bloodtained a larger artery in size it is a little more left. In the structure of the ovary, the following components can be distinguished:
Non-epitheliumFrom above, the ovary is covered with a nuclear epithelium. In their form, it is a single-layer cubic epithelium. Its height is about 20 microns. This type of epithelium serves as a barrier and limits the ovary from other organs and tissues. Also, the numerical epithelium takes part in the synthesis of some substances.Skin shellImmediately under the kinderial epithelium there is a protein shell. The thickness of this shell is 100 μm. The protein shell contains a significant amount of collagen and elastin. Collagen is the main protein of the connective tissue and is responsible for strength. The elastin function is to give elasticity and flexibility to tissues. Also elastin promotes the regenerator function ( allows tissues to restore their structure after injuries). Along with collagen and elastin, a protein shell contains a slight amount of smooth myocytes ( muscular cells). It is worth noting that the protein shell is formed on the fourth year of life.Cork substanceIn the cortical substance, two structures can be distinguished - stroma and parenchyma. Stroma is the basis of the organ, it is rich in a connective tissue, which gives the strength to this body. The sturge of the cortical substance contains a large amount of collagen. Also in stroma contain interstitial cells that perform the function of the synthesis of estrogen precursors ( female sex hormones). In the parenchyma, where the main functioning cells are located, follicles are distinguished ( special formations that contain egg cell) At different stages of development, yellow bodies, white bodies and atrethic bodies.The following stages of the development of the follicle are distinguished:
White body is a reborn yellow body. In the event that fertilization did not happen, the yellow body is reorganized in the form of a connective tissue. After some time, the white body of the ovary can completely disappear. BrainstuffThe brainstant consists of a connective tissue in which a large amount of elastine is located. Blood vessels and nerve fibers are located in the central part. More than 90% of women in the brainstant have a structure called the ovarian network. This network consists of heavy and epithelial tubes. It is formed from the remains of the tube tube.The reasons for the apoplexy of the ovarian The reasons for the apoplexy may become pathological modifications at the level of tissue structures and vessels of the cortical or brain substance of the ovary. The main causes of the apoplexy of the ovaries are the varicose expansion of the veins of the ovaries, the inflammatory process of the appendages of the uterus, polycystic, re-pregnancy. The reasons for the apoplexy may become pathological modifications at the level of tissue structures and vessels of the cortical or brain substance of the ovary. The main causes of the apoplexy of the ovaries are the varicose expansion of the veins of the ovaries, the inflammatory process of the appendages of the uterus, polycystic, re-pregnancy. To the most frequent reasons for the apoplexy of ovaries can be attributed:
Inflammation of the ovaryInflammation of the ovary or ooforite is an inflammatory disease of infectious nature. This pathology is in the first place among all diseases of the small pelvis organs. The ooforite can be one-sided and bilateral. Inflammation in the ovary in most cases is not isolated. An infection that causes an ooforitis is also able to cause an inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes ( salpingit). If the infection affects the ovary and the uterine tube, then this disease is called the salpingo-phorite, or adnexitis. The pathogens of this disease are capable of becoming trichomonas, gonococcus, mycoplasma, chlamydia, which are transmitted during sexual contact. In the case of a decrease in immunity to cause an ooforitis capable of a conditionally pathogenic microflora - intestinal chopstick, staphylococcus, streptococcus, candidates, and others. It is possible to cause an ooforita various surgical operations on genitals, menstruation, childbirth and even sometimes supercooling.The ooforite arises due to microorganisms in the shell of the mature follicle after ovulation. As in any inflammatory process, the ooforite is characterized by the emergence of the painful sensation, the appearance of hyperemia ( overflow of blood organ), the formation of the pathological secret ( exudate), the occurrence of the edema of the ovary. The same processes occur in the uterine tubes. The painful sensation is projected at the location of the ovary and the uterine tube, at the bottom of the abdomen. Often, SalpingOforite can lead to acute appendicitis. Varicose veins of ovarian veinsVaricose extension of the ovarian veins is a pathological condition that occurs with the difficulty of blood outflow from the venous network of the ovary. Most often, this is a consequence of partial or complete obstruction of one or several veins of the ovarian. This pathology should be considered in the context of the varicose veins of a small pelvis. The main reason for the emergence of varicose veins of a small pelvis is a violation in the structure of connective tissue, which is part of the venous walls. In these vessels there is a decrease in the number of collagen fibers. As a result, this leads to hypertension in the veins ( increased pressure), the diameter of the veins increases, as well as local expansions of venous walls appear.The reasons for the emergence of varicose extensions of the ovarian veins:
Medical stimulation ovulationMedical stimulation of ovulation is a method that helps to achieve pregnancy, due to the lack of ovulation in a woman. This method is suitable only when healthy follicles are formed in the cortical substance of the ovary, but the process of their development for some reason does not occur to the end. Drug stimulation is a way out of the situation in the event of an irregular ovulation or with ovarian polycystic disease.The use of various diagnostic stimulation schemes has a number of disadvantages. The side effects of this method include the cysts of ovarian, violation of the hormonal background, the apoplexy of the ovary. Polycystic ovarianPolycystic ovarian or polycystic ovarian syndrome - pathology in the structure and funnquences of the ovaries, which leads to a violation of the menstrual function and, as a result, to infertility. For polycystic ovarian syndrome characteristic of hyperandrode ( increased production of male genital hormones).With this pathology, the following modifications are allocated: a bilateral increase in ovaries at 2 - 6 times, stroma hyperplasia ( education in the excess of new structural elements), the presence of a large number of cystic follicles ( the cyst is formed from a mature follicle), thickening of the ovarian capsule. In the cortical matter, with polycystic ovaries, there are many cystic atretic follicles. These follicles are pathological formation, and the body seeks to reduce their number. When reorganized ( connective tissue) The major cystic atrethic follicles can occur their destruction, which will lead the tear of the ovarian tissue and the appearance of bleeding. Symptoms of apoplexy ovarian The symptoms of the apoplexy of the ovary are temporary or permanent. Symptoms, as a rule, depends on the amount of blood lost. The most frequent, and sometimes the only sign is the painful sensation in the pubic area. The symptoms of the apoplexy of the ovary are temporary or permanent. Symptoms, as a rule, depends on the amount of blood lost. The most frequent, and sometimes the only sign is the painful sensation in the pubic area. The apoplexy of the ovary is characterized by the following symptoms:
Pains at the bottom of the bellyPaints in the pubic area are the main sign of the apoplexy of the ovary. In the case of one-sided apoplexy of pain can be projected at the location of the affected ovary, and with bilateral apoplexy, the pain is spilled. Paints can begin sharply, sometimes they can be strong and unbearable. Pretty rare pain can occur at night, during sleep. Sometimes a day before the attack, a woman can feel muted pain in the lower abdomen. Pain occurs due to the fact that the generated hematoma ( blood accumulation) Produces pressure on the surrounding fabrics in which pain receptors are contained. Also, if the hematoma is formed in the ovary itself, it can squeeze the vessels and nerves in the cortical matter. In this case, the pains will be acute. If the pain becomes a major sign, and the bleeding was insignificant, then we are talking about pain or pseudo-apoplependicular form of the apoplexy of the ovary. A pronounced pain of acute character with one-sided apoplexy of the right ovary can resemble pain characteristic of acute appendicitis.Sharp reduction in blood pressure, pulseA sudden rupture of the ovarian tissue leads to bleeding into the abdominal cavity. Even if there was a small damage to the ovarian tissues, it can cause abundant bleeding. If internal bleeding prevails over pain syndrome, this form is called anemic. In the context of a anemic form, a number of symptoms are distinguished. As with any other bleeding, the reflexive decrease in blood pressure, the heart rate increases, the skin is pale. These features depend on the number of lost blood. Due to bleeding, the amount of blood delivered to the heart is reduced and, as a result, pressure in the arteries falls. Depending on the volume of blood loss, three severity of the anemic form of the apoplexy of the ovary can be distinguished. For apoplexy, the loss of blood does not exceed 150 ml of blood. If we are talking about the average severity, the amount of blood loss does not exceed 500 ml, and for severe degree - over 0.5 liters.Total weaknessThe general weakness is a consequence of blood loss. Since the volume of circulating blood during blood loss is reduced, it affects both in general condition. Blood performs transport function and delivers oxygen tissues and all the necessary nutrients. If the volume of circulating blood is reduced, then the tissues cease to receive the necessary substances in sufficient quantities. Some cells and tissues are extremely dependent on oxygen. Thus, the central nervous system consumes 20 - 25% of all inhaled oxygen. When bleeding, brain nerve cells are not able to function at the required level and, as a result, this is manifested in the form of quick fatigue, lethargy, and sometimes the appearance of apathy. Muscular fabric also needs a large amount of blood enriched and blood glucose. In case myocytes ( muscle tissue cells) Do not receive the necessary substances, it leads to muscle weakness.Disruption of menstrual cyclesThe apoplexy of the ovary may cause disorders in the menstrual cycle. For normal menstruation, bloody discharges are characterized, which occur every 21 - 35 days and continue to go for 3 to 7 days. Most often, the apoplexy of the ovary is characterized by the appearance of intermented bloody discharge from the vagina, which is not observed in the norm. Less often arise bleeding, which occur after menstruation delay. These phenomena are usually stopped quickly after the disappearance of pain. It is worth noting that disorders during the menstrual cycle are not mandatory and in some cases may be absent.Student urinationStudent urination is characterized by a visit to the toilet more than 10 times per day. Also taking some medicines ( diuretic) Or a large amount of drinking fluid contribute to this phenomenon.In some cases, the apoplexy of the ovary can cause a violation of the hormonal background. As a result, the impact of some hormones on the bladder can lead to the stretching of its wall. As a result of excessive stretching of the bladder wall, an increase in urination frequency increases. Also, the convergence of massive edema of the ovary can be accompanied by the participation of urination. Diagnosis of apoplections of ovarian In order to correctly make a diagnosis, it is necessary to carefully collect anamnesis ( patient poll), Inspection and use invasive or non-invasive diagnostic methods. In order to correctly make a diagnosis, it is necessary to carefully collect anamnesis ( patient poll), Inspection and use invasive or non-invasive diagnostic methods. To confirm the diagnosis of ovarian apoplexy, the following methods are used:
Gynecological examinationThis type of inspection begins with a survey of genitals. As a rule, it uses a special gynecological chair. The gynecologist consistently examines large and small sex lips. The examination of the outdoor genital organs by examining the legislation of the vagina.Next inspects the wall of the vagina. For this manipulation uses special gynecological mirrors ( a tool that is used to expand and reveal the vagina). Most often, the mucous vaginal remains ordinary color. If the apoplexy of the ovary leads to massive bleeding, characteristic of anemic form, then the mucous membrane of the vagina has a pale pink color. The next stage in the gynecological examination is bimanual ( two-handed) Vaginal research. This manipulation is necessary to determine the position, state and size of the uterus, as well as the appendages of the uterus ( ovaries and uterine pipes). Quite often, the bimanual study of the vagina reveals pain in the place of projection of one of the ovaries with one-sided apoplexy. Palpation of the affected ovary delivers painful sensations. The size of the ovary remains normal or slightly increased. Uzi small pelvis organsUltrasound examination is one of the main methods that are used in the diagnosis of apoplections of the ovary. This method is non-invasive ( does not damage the integrity of the skin) and is capable of confirming the alleged diagnosis in most cases.Ultrasound examination, as a rule, helps to see some structural changes in the ovary. The dimensions of the affected ovary can be slightly increased or located within the normal range. In apoplections, you can see the inhomogeneous structure in the cortical matter. This structure is a yellow body. In most cases, it is the yellow body that causes bleeding. If there are no accompanying gynecological diseases ( polycystic ovarian), In the follicles, no pathologies are detected. The main confirmation of the diagnosis of the anemic form of the apoplexy of the ovarian is the detection of free fluid in the abdominal cavity behind the uterus. It is worth noting that the assessment of the state of the affected ovary should be carried out in comparison with a healthy ovary, and the period of the menstrual cycle must also be taken into account. LaparoscopyLaparoscopy is a surgical way of diagnosing or treating certain abdominal diseases. The main advantage of laparoscopy is minimally invasion. Access to the abdominal organs is achieved through a small hole in the navel. The size of this hole on average does not exceed 1 - 2 cm. In the case of an apoplexy of the ovarian, laparoscopic diagnostics have almost 100% accuracy.With laparoscopic diagnostics, it is almost always possible to detect a certain amount of blood in a small pelvis. If the apoplexy occurred recently, the blood will be homogeneous consistency without a large number of clots. The presence of bunches suggests that the rupture of the ovarian tissue and hemorrhage occurred in a day or a few days before laparoscopy. In the future, these bunches can lead to the spike of the abdominal organs. When examining the uterus, its size and color remains normal. Quite often, it is possible to detect chronic inflammation of the uterine pipes, which is expressed in the presence of near-robber adhesions ( spikes around uterine pipes). When the yellow body is ruptured, the ovary, as a rule, retains normal sizes. An increase in the ovary is observed only when hemorrhage leads to the hematoma in the cavity of the ovary itself. If the apoplexy of the ovary is a consequence of the rupture of the cyst of the grappa of a bubble or a yellow body, then the affected ovary has a purple-crimson color. Also, the presence of cyst causes an increase in the size of the ovary. Vagina rear axlePencil of the rear vessel or cultocentsis - puncture of the rear wall of the vaginal arch in order to fence the liquid from the uterine-straight deepening ( Douglasovo space). This manipulation helps determine the type of fluid that is accumulated in the uterine-recycling space. Depending on the disease, the point may be blood, exudate or pus. Douglasovo Space normally contains a slight amount of light yellow liquid. The main criterion for confirming the diagnosis is the detection of blood, which is not collapsed.Conservative ovarian apoplexy The choice of treatment depends on the result of hematological analyzes ( general blood analysis), degree of bleeding, as well as the presence or absence of peritoneal symptoms ( puritini's pains arising from irritation). Conservative treatment is produced in the hospital and is shown only when pain syndrome is not expressed, and the amount of lost blood is insignificant. The choice of treatment depends on the result of hematological analyzes ( general blood analysis), degree of bleeding, as well as the presence or absence of peritoneal symptoms ( puritini's pains arising from irritation). Conservative treatment is produced in the hospital and is shown only when pain syndrome is not expressed, and the amount of lost blood is insignificant. The main drugs in conservative treatment are coagulants ( heal standing drugs), antispasmodics and vitamins. Also needed a chamber ( semiating) Mode. To achieve a stop of bleeding, as a rule, use the applying of cold to the lower part of the abdomen. Medicia treatment includes:
SpasmolytikiAntispasmodics are a group of medical drugs that eliminates muscle spasm arising in smooth muscles. Antispasmodics are widely used in the relief of pains associated with the gastrointestinal tract, as well as in the occurrence of pain syndrome in gynecology. The main action of antispasmodics is based on blocking the transfer of nerve pulses in smooth muscles, which contributes to the relief of pain syndrome.Antispasmodics have a different form of release. In each case, it is precisely the doctor who must choose the necessary medical preparation, dosage, as well as the duration of the use of this medication. Antispasmodic drugs
Heal standing drugsHemostatic or hemostatic drugs are a group of medicines that contribute to stopping bleeding. Highlights of local and resorbative action. A group of hemostatic preparations of local action is used to stop bleeding from skin cover or mucous membranes. In the event of bleeding from internal organs, it is necessary to use blood suspension preparations of resorbative action. They directly enter the blood and are able to stop bleeding by strengthening the thrombosis process in damaged vessels.Hemostatic resorbative preparations
In the case of concomitant hematological diseases ( willebrand disease, autoimmune thrombocytopenia), conservative treatment can be carried out only after the consultation of the hematologist's doctor. VitaminsVitamins are a group of organic substances absolutely necessary for the normal life of the body. Two large groups of vitamins are distinguished - fat soluble and water soluble. Vitamins are part of various enzymes, and can also affect organs and fabrics by hormone type. When bleeding, the vitamins of the group B lead to strengthen the compensatory-restorative functions of the body and can reduce the degree of blood loss.Vitamins Group B.
It is worth noting that medication treatment has a number of shortcomings. Blood clots that cannot be removed without surgery in 80% of cases lead to the formation of adhesions. As a result of conservative treatment in 40% of cases, infertility is observed. In 15% of cases there is a recurrence of the apoplexy of the ovary. Such serious violations are forced to revise therapeutic tactics even with a light degree of apoplexy in favor of surgical treatment. Surgical treatment of apoplexy ovarian In the treatment of apoplexy of the ovary, preference is given to precisely surgical treatment. In the treatment of apoplexy of the ovary, preference is given to precisely surgical treatment. In most cases, a laparoscopic method is used to treat apoplexy of the ovarian. This method has a number of advantages over the usual bandwidth operation. In case there are contraindications for laparoscopy, the alternative is a laparotomic operation. Indications for the operationIn most cases, if a woman wants to preserve a childbearing function, or with a moderate or severe, surgical treatment is shown. Also, the testimony for the operation is the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, in which signs of internal hemorrhage appear, the overall state is deteriorating, and the indicators of the hemogram ( blood test) Fall sharply. The main indication for the operation is the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity, which is confirmed by an ultrasound study. In the case of increased pain syndrome, you should urgently resort to surgical intervention.ContraindicationsContraindications for a laparoscopic operation during apoplexy may be absolute or relative. Laparoscopic operation is absolutely contraindicated with severe cardiovascular diseases, pronounced hypertension ( elevated blood pressure), hemorrhagic shock ( acute blood loss), cachexia ( strong exhaustion of the organism), with serious violations in the rolling system of blood, in the presence of hernia with a white belly line ( passes through the middle line of the abdomen) And the diaphragms. Also, the contraindication is acute or chronic renal failure or liver failure. Of the diseases of the respiratory system, this operation is contraindicated in the presence of bronchial asthma. Relative contraindications include polyvalent medicinal allergies ( allergy to two or more medicine), malignant tumor of the ovarian and the uterine pipe, peritonitis ( inflammatory proceedings), late stage of pregnancy ( more than 16 weeks).Techniques for apoplexyFor the treatment of apoplexy of the ovary, you can use two surgical methods. We are talking about laparoscopic and laparotomic method. The surgical operation of the laparoscopic method is the gold standard in the treatment of apoplections of the ovary. Laparotomy is carried out only in the case of the detection of contraindications to the laparoscopic operation.Laparoscopic method
Laparoscopy during apoplexy of the ovary is extremely gentle. In most cases, only the exposure of the ovarian break site is produced. If the apoplexy occurred during pregnancy, it is not replaying for its preservation ( excision), and earsing the yellow body. The ignition of the region of bleeding of the protein shell is produced using an electrosurgical coagulator. This is due to the supply of high-frequency current, which heats the surrounding tissues. As a result of heating the protein, which is in the tissues, is coagulated, and bleeding stops. If massive bleeding is observed, a long coagulation is produced ( the use of electrosurgical coagulator). The removal of the ovary is a necessity only when the apoplexy is observed along with another disease of the uterus's appendages, such as, for example, when twisting the legs of the uterine tube. In any other cases, the exposure of the ovarian breakdown or the removal of the ovarian part of the ovary is to maintain a childbearing function, as well as not to break the hormonal background. During laparoscopy, it is extremely important to inspect both ovaries for the presence of bilateral apoplexy. It is also necessary to inspect the uterine pipes and a worm-shaped process ( appendix) Since apoplexy can proceed in combination with ectopic pregnancy or to meet with acute appendicitis. Endotracheal anesthesia is most often used for anesthesia. In the course of the operation, the abdominal cavity was washed and blood clots and all blood remove. Further, the abdominal cavity is in layers. In case of impossibility of holding a laparoscopic operation, resort to laparotomy. Laparotomic method
For anesthesia, endotracheal anesthesia is used. During the operation on the ovary it is necessary to remove all the bloodflow in the abdominal cavity. At the end of the operation, the abdominal cavity layers in layers. In the following days after the operation, it is necessary to carry out antibacterial therapy. Recovery after apoplexyWith an uncomplicated form of apoplexy, the average period of recovery after a laparoscopic operation lasts a week, and after laparotomy - two weeks. Already on the first day after the laparoscopic operation, it is allowed to get out of bed, as well as eating dietary broths.The dynamics produces an ultrasound study of the ovaries for the presence of recurrence of apoplexy. If various changes are revealed in the results of blood and urine test results, then their correction is carried out. In violation of the hormonal background, the attending physician individually selects the necessary treatment regimen. Antibiotic therapy is prescribed in the case of a laparotomic operation, as well as the indication. With laparotomy, it is necessary to wear compression linen, as well as various bandages on the belly for two months. The gentle nature of the laparoscopic operation allows in most cases to preserve the female function of the woman. Even when removing one ovarian, the chance to get pregnant remains extremely high. However, with ovariectomy ( oophorectomy) Risk of ectopic pregnancy increases. Natural pregnancy is not possible only with inflammatory and dystrophic changes at the level of both the uterine appendages or in the case of a tumor disease. It is worth noting that within 1 - 2 months after surgery, you must eliminate any sex contacts. Disability occurs after 30 - 50 days. In the event of various gynecological complications, it is necessary to urgently cause ambulance or contact the hospital. |
New
- Games where you can create, edit and customize the character what are called games where you can create a character
- The legendary fragrance in the new composition!
- Allods of the online spark of ae
- When Planet Saturn was opened
- Precious Stones in Blade & Soul Reservation Improvements
- Who opened the planet Saturn
- Eastern Elixir Youth of Garlic
- Dantalian Full Demon Description
- Lesson - Quiz for the initial classes "Erudite Competition" Questions for the Erudite Competition in elementary school
- ROC: The main temple of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation will embody the memory of the feud