Website sections
Editor's Choice:
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Signs, Diagnosis, Treatment - Online Diagnosis
- To whom and when is treatment with thrombolytics prescribed Thrombolytic system of the body
- Guillain-Barré syndrome: symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment
- Diagnosing scarlet fever in a child with a blood test, throat swab or rapid test
- Pulmonary hypertension in the new guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology (2015
- Examination of a patient with OX at the prehospital stage. Absolute contraindications for TLT.
- Immunohistochemical tests How the IHC study is performed
- Myxomatous degeneration of heart valves Treatment and preventive actions
- Modern standards of pharmacotherapy for stable angina pectoris Enteral routes of administration
- How does a pathological condition arise, and can it be cured?
Advertising
| Thrombolytic therapy of myocardial infarction. To whom and when is treatment with thrombolytics prescribed Thrombolytic system of the body |
|
Thrombus formation is one of the most common pathological phenomena in the human body, the fight against which must be timely. This process leads to many adverse consequences up to the death of a person. To get rid of it, doctors may prescribe thrombolysis. Overview of ThrombolysisA natural process of thrombolysis occurs in the body of every person. It is carried out with the help of special enzymes found in the blood. But these substances are not able to fully cope with large blood clots. They are only effective in the presence of small blood clots. As a result, the formed large clots block the lumen of the vessel completely or partially. Because of this, there is a failure of blood circulation, which leads to starvation of body cells and even their death. This phenomenon disrupts the functioning of internal organs. Therefore, the question arises, how to dissolve a blood clot? To solve this problem, artifactual thrombolysis is used. The essence of the technique lies in the fact that the doctor injects medications into the veins, which are designed to resorb blood clots. Thrombolytic treatment is carried out in two ways:
Which method to give preference in the implementation of thrombolytic treatment is decided by the attending physician for each patient individually. Where is thrombolytic therapy performed? Treatment can be carried out both at home and after hospitalization. Emergency thrombolytic treatment is most effective because it has a timing advantage. After all, the earlier you perform the procedure, the more chances you have to save a person. In this respect, hospital thrombolysis has a significant disadvantage. It is prescribed only after the patient has been fully examined. Therefore, the rate of therapy is lower, but it is possible to verify the presence of contraindications to the use of thrombolytics, which avoids many adverse complications. The use of thrombolysis for stroke and heart attackA cerebral stroke is a dangerous pathology that is often fatal. Even if a person survives, it is very difficult for him to recover. Indeed, with a disease, the blood supply to the brain cells is blocked, which leads to an acute violation of cerebral circulation (CVA) and tissue death. Thrombolysis for stroke helps prevent adverse events. It quickly dissolves a thrombus and prevents necrosis of brain cells. In this case, you need to have time to introduce the drug within 6 hours from the moment the signs of pathology appear. The same thing happens with a heart muscle infarction. The disease also occurs due to blockage of the lumen of the artery by a thrombus. This is often accompanied by thrombophlebitis. To prevent myocardial tissue from dying, thrombolytic treatment should be performed. It allows you to eliminate acute coronary syndrome (ACS), reduce the area of \u200b\u200bmuscle damage, preserve the function of the left ventricle, which pumps blood, as well as reduce the risk of complications and ensure stable heart function. When is thrombolytic treatment necessary?Indications for thrombolysis are various diseases of the heart and blood vessels, which are united by such a phenomenon as thrombus formation. Such diseases include:
The need for thrombolytic treatment is determined by the attending physician after examining the patient. Who should not be prescribed therapy?Doctors identify several factors, in the presence of which thrombolytic therapy is impossible. If treatment is prescribed without paying attention to contraindications, there is a high risk of complications.
It is forbidden to do thrombolysis for such pathologies:
In addition to pathological conditions, it is not allowed to conduct thrombolytic therapy for women who are carrying a child, as well as for people taking anticoagulants, who have recently undergone surgery or have received a skull injury in the last 2 weeks. Thrombolysis is also contraindicated in patients over 75 years of age. How do blood clots dissolve?In medicine, there are a huge number of thrombolytic drugs. They are constantly improving. At the moment, there are the following types of medicines, differing in the nature of the effect:
Of all the groups, several thrombolytics can be distinguished, which are most often used for thrombolysis. These include:
In addition to thrombolytics, other agents are used for thrombosis, for example, diuretics (Fitolysin), anticoagulants (Heparin), antiplatelet agents (Aspirin). Also, to eliminate symptoms, improve blood circulation, it is allowed to additionally use folk remedies. In extreme cases, they resort to surgical intervention. The doctor is engaged in the appointment of surgical or drug treatment, taking into account the patient's condition, the degree of development of the pathology, the presence of concomitant diseases and other factors. Possible complicationsThrombolysis can not only save the patient, but also cause adverse consequences. These include:
The effectiveness of therapyThe effectiveness of thrombolytic tablets and injections depends primarily on how timely the therapy was carried out. The greatest effect is achieved if the drug was administered no later than 5 hours after the onset of symptoms of pathology. Unfortunately, it is far from always possible to carry out thrombolysis during this time. The problem lies in the fact that not all medical institutions have the opportunity to use this technique. How effective the therapy was, you can find out with the help of an examination. For this, magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography is performed in case of a stroke or coronary angiography in case of heart muscle infarction. Diagnosis after thrombolysis shows the expansion of the lumen of the vessel and the destruction of the blood clot. Thus, thrombolytic therapy is an effective way to eliminate blood clots. This technique gives us the answer to the question of how to absorb other parts of the body. It helps to quickly achieve resorption of the blood clot and avoid consequences that are dangerous to human life and health. The main goal of myocardial infarction treatment is to restore coronary blood flow in the infarcted artery. This is achieved by using thrombolytic agents: streptokinase, streptodecase, urokinase,tissue plasminogen activator(TAP). The use of thrombolytics is the standard of treatment for acute myocardial infarction. Indications for thrombolytic therapy: A typical anginal attack lasting more than 30 minutes and necessarily corresponding ECG changes: segment riseST, at least in 2 leads and / or the appearance of a "fresh" blockade of the left leg of the item of Gisa. The duration of the pain syndrome (myocardial infarction) is not more than 6 hours, but with the preservation of anginal pain and the acute stage of myocardial infarction by ECG and up to 12 hours. The best results are achieved within the first 4 hours. If thrombolytic therapy is carried out in the first hour, then 51% of the myocardium is saved, within the 2nd hour - 26%, within 3 hours - only 13%. Contraindications to thrombolytic therapy: Absolute: Bleeding, hemorrhagic syndrome. Cerebral hemorrhage, ischemic stroke (up to 3 months old). Allergy to thrombolytics. Peptic ulcer and 12 s / c. in the acute stage. Relative: Age 75 and older. Recent severe trauma, surgery, or "abdominal" biopsies. Uncontrolled hypertension BP\u003e 180/100. Tumor. Pregnancy or conditions after childbirth. Diabetic hemorrhagic retinopathy. Chronic or acute renal failure. Extraction of the tooth no earlier than 14 days. Long-term cardiopulmonary resuscitation. The use of thrombolytics in small-focal infarction and unstable angina pectoris is not for good reason, since their effectiveness in these conditions has not been proven. Thrombolytic drugs.
Before the introduction streptokinaseprednisolone 60 - 90 mg is introduced. Over three years, 21 systemic thrombolysis (ST) was performed with streptokinase at a dose of 1.5 million. Unfortunately, the amount of the drug is not enough, but there are more than 70% of patients with contraindications for CT. Complications of thrombolytic therapy.Allergic reactions. Hemorrhages: intracranial and systemic. With the introduction of streptokinase, their risk is 1%, with TAP(tissue plasminogen activator) - 1.3%. Prevention of bleeding:the correct choice of indications, do not carry out intramuscular injections, do not carry out catheterization of the central veins. Bleeding treatment: cryoprecipitate 10 units. (fibrinogen and factor VIII). The introduction of cryoprecipitate is indicated only in the first few hours after the use of thrombolytics. The introduction of fresh frozen plasma. Treatment with epsilonaminocaproic acid (AMA) is used only when all other measures have failed, as this can cause refractory thrombosis. AMK is administered at a loading dose of 5 g, then an infusion of 0.5 - 1 g / h is carried out until the bleeding stops. Blood transfusion with erythrocyte mass with a hematocrit of 25% and below. 3. Reperfusion syndrome -syndrome of restoration of blood flow in the infarction-associated artery. Signs: Relief of pain syndrome. ECG-prizes: transition to the subacute stage. Rhythm and conduction disturbances up to ventricular fibrillation. Treatment: the use of antiarrhythmic drugs, depending on the type of arrhythmias, electric pulse therapy. Prevention:strict monitoring control, studying the effect of antioxidants, preductal. Among the thrombolysis performed in our department, apart from the reperfusion system, 2 patients (1.9%) had no other complications. With early (up to 3 hours) thrombolysis a similar effectiveness of the intracoronary method (done only in specialized cardiological departments) and the intravenous systemic method (carried out in an ambulance during the transportation period, in any department of an inpatient medical institution or at home) was noted. The latter has fewer side effects (less often causing CABG and dangerous arrhythmias). So, in England, 50% of all trombonises are performed at home (in 2/3 of cases - in the first 2 hours). In Western Europe at present for thrombolysis in myocardial infarction two time intervals are used: "bell-needle" (should not exceed 90 minutes) and "door-needle" (should not exceed 30 minutes). Thrombolysis is not indicated if the exact time of the onset of myocardial infarction is not known or if thrombolysis cannot be performed in the first 12-24 hours. With the held diagnosis of myocardial infarction it is advisable for the patient to prescribe thrombolysis during the first 6 hours, since MI of any type in most cases is caused by the development of thrombosis. The developing myocardial necrosis is accompanied by a large release of factors (adrenaline, ADP, pieces of the basement membrane) that cause the onset of clotting Usually, fibrinolysin proactivators streptokinase, urokinase are used for thrombolysis, forming a complex with plasminogen and converting it into an active form - plasmin - followed by cleavage of the fibrin component Indications for thrombolysisIndications for thrombolysis (old age is not a contraindication): First 6 h myocardial infarction... But if the pain persists, the ST segment elevation and the Q wave is absent (when the myocardium is still alive), the first 12 hours are also "suitable" if the myocardial infarction has not ended and there is a "mosaic" of the clinical picture. pictures, history and ECG Thrombolysis in ACS without persistent elevation of the ST segment (or with inversion of the T wave, or no changes in the ECG) Contraindications to thrombolysisContraindications to thrombolysis (usually associated with a risk of bleeding): relative:
Thrombolysis in ischemic stroke is the process of removing blood clots using special medications. In addition, the procedure helps to restore the functioning of the blood flow through the vessel, which was obviously blocked by a blood clot. Based on the moment at which treatment with thrombolysis begins, the methods of implementation are divided into two types:
By the type of access to the location of the blood clot, the procedure is divided into two types, such as:
What drugs have an effectThe thrombolytics used by healthcare professionals are improving from year to year. They are divided into four types according to the way they affect the body: Natural enzymes of natural origin. Such thrombolytics are also called systemic. They are prescribed accordingly in systemic therapy. They are divided into Streptokinase, Streptokinase, Urokinase. They have an effect aimed at resuming the process of fibrinolysis, they are able to transform plasminogen into plasmins. It should be noted that this action does not end with a blood clot. In addition, an allergy may appear, since the basis of the material is hemolytic streptococcus (if we are talking about streptokinases). Therefore, these drugs have limitations in their use.
Genetic engineering and biotechnological preparations. Their second name is selective fibrin. These include Alteplaza and Aktiliz. They selectively resume the work of fibrinogen in blood clots and their tissues. Have no general impact. An improved variety with a selective and prolonged effect. These include Reteplaza, Lanoteleplaza. Combined medications. These include Plasminogen and Urokinase. Unfortunately, it is impossible to determine exactly which drugs work best. One of the most studied and analyzed groups is the one that includes genetic engineering tools. Other groups differ in narrowly targeted action for specific cases. However, based on the rate of lysis, they have the highest rate than drugs of natural origin. Doctors treat them with extreme caution, as they cause multiple complications.
IndicationsLet's talk about general indications for thrombolysis. They are united by various vascular pathologies with the formation of blood clots, which lead to changes in internal organs. In order to save the patient's life, the most important diagnoses are:
In order to start thrombolysis in case of myocardial infarction at the stage when the patient has not yet been admitted to the hospital, there is only one solution - if there is a need for a long transportation of the patient.
Ischemic stroke is different:
Based on the instructions, it can be concluded that patients with PE and an increased risk of death have a mandatory indication for thrombolysis, despite the fact that, in fact, the procedure is contraindicated. We are talking about such situations as gastrointestinal bleeding, recent operations carried out within three weeks.
ContraindicationsAfter the blood clots dissolve, new gastric bleeding, uterine bleeding and other bleeding that have occurred in the patient over the past six months may begin. Contraindications for thrombolysis:
Thrombolysis has no contraindications to thrombolysis according to criteria such as age. However, there is an upper limit, which is 75 years. If the patient is allergic to the proposed drugs, then this is the reason for the complete rejection of thrombolysis. There are special contraindications for pulmonary embolism. How to do?The technique is carried out in two ways: locally and systemically. Thrombolysis in stroke of a systemic type differs in that the medicine is used even when there is no exact data on the location of the blood clot. Together with the bloodstream, the medication spreads throughout the body and dissolves the blood clot at any point. But in such a situation, it is necessary to use an abundant dosage of the drug, which adds load to the blood flow system.
With a local technique, drugs are injected into the area of \u200b\u200blocalization of a blood clot. The drug is delivered through a catheter.
According to international standards, the length of time from the moment the patient is admitted to the hospital until the administration of the medication should be one hour. This is the longest time that doctors have for diagnosis and counseling. Only with well-coordinated work, doctors can meet this deadline.
The drug has its own optimal dose, which is calculated based on the patient's weight. Usually, about ten percent of the total dose is injected by the jet method, then, by drip, the remains of the drug are injected within one hour.
Patient monitoring is carried out throughout the day. The patient is monitored for such indicators as:
Possible complicationsThrombolytic therapy for ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction and pulmonary embolism gives some complications, we offer you a list of the most common of them:
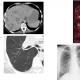
Evaluation of the effectiveness of treatmentThe result and effectiveness after treatment with thrombolysis is assessed based on the results of MRI and CT of the human brain, if we are talking about a stroke. After a heart attack, it is necessary to conduct a coronary angiogram and find out about the strength of the pain - it should go down. Coronary angiography is performed one and a half hours after thrombolysis. It makes it possible to slowly restore the throughput of the vessel through the blood clot. At the same time, the formation of a blood clot continues, but it is worth noting that disintegration also takes place. Doctors have developed a scale for the degree of treatment effectiveness: 0 - contrasts cannot pass through the place blocked by a blood clot. Now you know what thrombolysis is. The problem of thrombolytic treatment is one of the predominant problems in the field of modern healthcare. However, carrying out such a procedure, even taking into account limited conditions, makes it possible to reduce mortality from heart attacks by fifty percent (taking into account the provision of therapy in the first hour).
With the provision of treatment in the first three hours, the likelihood of death is reduced by twenty-five percent. This is why leading medical researchers around the world are puzzled to develop a tablet formulation that can be used at home. © Use of site materials only by agreement with the administration. Unfortunately, time does not make people younger. The body is aging, and with it the vessels are aging. In tissues, metabolism changes, blood clotting is impaired. Chronic illnesses accelerate these processes. As a result, blood clots form in the vessels that can block the blood flow. This disease is called. Depending on the localization, a person may develop myocardial infarction, stroke (cerebral infarction) and other equally formidable complications. Is it possible to help the victim? There is salvation - thrombolysis or thrombolytic therapy (TLT)! Undoubtedly, timely help will not only save a person's life, but also give hope for full rehabilitation. Not everyone knows about this, and therefore they lose precious time. But it is quite logical to assume that blood flow can be restored by removing the ill-fated thrombus in one way or another. This is the essence of TLT. Types of TLT:
Thrombolysis in cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke)
Acute (ACVA), which provoke severe neurological disorders, are called a stroke. Stroke diagnosis sounds like a sentence. In Russia. Half of the patients die, and most of them die within the first month. And the survivors cannot be envied - many remain helpless invalids until the end of their days. However, in countries that have been using TLT for many years, the statistics are different: no more than 20% of patients die. In many patients, neurological functions are fully restored. And this is thanks to thrombolysis - the most effective method of treating ischemic stroke. The TLT procedure is not very complicated - special enzymes are injected into the vessel that can dissolve a blood clot. However, there are contraindications:
The patient's age does not preclude thrombolytic therapy! Among the listed contraindications, some are absolute, others are relative. The most important absolute contraindication is bleeding. The implementation of thrombolysis can be hampered by the lack of necessary conditions: a computed tomograph, a laboratory, neuroresuscitation. And most importantly, there may simply not be enough time. Three (maximum six) hours from the onset of the disease - this period must be met during thrombolytic therapy. This is the case when time is not money, but life! Therefore, it is so important to pay attention to the first signs of a stroke:
You can ask the person to stretch out their arms and say something. If such a task turns out to be unbearable for him, urgently call an ambulance. Remember: the countdown has begun, but the patient has little! Heart and TLTAny vessel in the body, including the coronary one, can clog up. In this case, myocardial infarction develops. Of course, a blood clot is unlikely to appear in a healthy body. Usually this process is facilitated by general violations. Among them: a decrease in the amount of anticoagulant components in the blood: heparin and fibrinolysin, an increase in the content of clotting components. In addition, local disturbances appear in the vessel: the inner wall becomes rough, ulcerated, and blood flow slows down.
Just as in the case of a stroke with myocardial infarction, it is important to remove the clot in time and restore the blood supply to the heart muscle. However, doctors do not dare to carry out this procedure without a deep examination of the patient, fearing negative consequences. This examination includes duplex scanning, computed tomography,. All this allows you to most accurately determine the localization of the thrombus and inject the drug directly into the affected vessel. With this approach, the risk of complications is reduced many times. But nevertheless, sometimes, when the patient does not have time, even emergency doctors perform thrombolysis. Indeed, in such a case, delay is truly like death! Of course, this procedure should be carried out only by qualified specialists - the cardiological team. The duration of thrombolysis can vary from 10 minutes to two hours. Thrombolytic therapy for myocardial infarction, as well as for stroke, has contraindications. And also the main obstacle is bleeding of any localization.
Methods for performing thrombolysisThrombolysis is performed by two main methods:
The first method is advantageous in that the medicine can be injected into a vein without knowing where the thrombus is hiding. With the blood flow, the drug is carried throughout the entire circle of blood circulation, where it encounters an obstacle in the form of a blood clot on its way and dissolves it. But systemic thrombolysis has a significant drawback: an increased dose of the drug is required, and this is an additional load on the entire circulatory system. When conducting local thrombolysis, the drug is injected directly into the site of the thrombus. The drug is delivered through a catheter, which is why the method is called catheter thrombolysis. Nevertheless, this method is more difficult than the first one to execute and is fraught with certain danger. During the procedure, the doctor monitors the movement of the catheter using an X-ray. The advantage of this method is low invasiveness. It is used even if the patient has a large number of chronic diseases. How do blood clots dissolve?The main thrombolytics used in indications for thrombolysis:  Complications of TLT
TLT at the prehospital stageWhat are the signs of disturbances in the vessels of the brain:
Who is not familiar with these symptoms! At certain periods of life, they can appear in completely healthy people. However, these same signs are noted at an early stage of cerebrovascular accident. In order to exclude this possibility and not miss ACVA, every person who is in their fifties should have an ultrasound scan of the cerebral vessels, as well as duplex scanning of the carotid arteries, every year. It's also a good pass - the most informative research. It is especially indicated for patients at risk: suffering from diabetes mellitus, hypertension, obesity, heart disorders. A serious factor is physical inactivity and heredity (especially maternal). It is also helpful to do a coronary examination.
(infographic: "Health of Ukraine") If during the examination thrombosis of certain vessels is detected, thrombolysis will be the most correct solution. Stubborn statistics prove the effectiveness of this method. It has become an axiom that any disease is easier to prevent than to cure. Prehospital thrombolysis reduces deaths from strokes and heart attacks by up to 17%. Thrombolytic therapy is preferable precisely at the prehospital stage, subject to the availability of trained medical personnel, ambulance personnel, and on-site availability. In this case, TLT can begin as early as 30 minutes after the meeting with the patient. Panacea?The impressive list of contraindications and complications of thrombolytic therapy speaks of its careful use. This method should be used only in the most exceptional cases, when a person's life is at stake.
In the future, the death of the heart muscle or brain cells occurs. The use of thrombolysis in this case is not only useless, but more - extremely dangerous! Video: a story about the use of thrombolysis by doctors of the "Ambulance"
|
| Read: |
|---|
Popular:
New
- Cholera. Epidemiology. Cholera Vibrio Vibrio cholerae - the causative agent of cholera Cholera - anthroponous especially dangerous toxic infection, characterized by profuse watery diarrhea, - the presentation of Cholera as an especially dangerous infection is capable of
- Presentation "The structure of the cell of animals and plants. Tips on how to make a good report of a presentation or project
- How does a closed aquarium ecosystem work?
- Lymphatic system presentation
- Presentation on cancer The main direction of improving the oncological situation in Saratov
- Anatomy and physiology of the heart
- A presentation on appendicitis was done by a student of group f
- Presentation - the eye as an optical system
- Anatomy and physiology of the digestive system
- Spinal Cord Presentation