Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- Ingrown nail - causes, symptoms and treatment
- How to recognize by appearance?
- Inflammatory infections in the appendages are a serious danger.
- Categories of unfit for military service
- How to recognize tubular mushrooms
- Why do the pains of the fingers under the nails appear
- Determination of skin type and selection of cosmetics
- Summary of classes in fine arts in the older group with the use of non-traditional drawing techniques on the topic: Winter
- Materials for nail
- How to donate blood from a finger and why?
Advertising
| Gall mushroom edible or poisonous. How to recognize by appearance? Poisoning with boletus mushrooms |
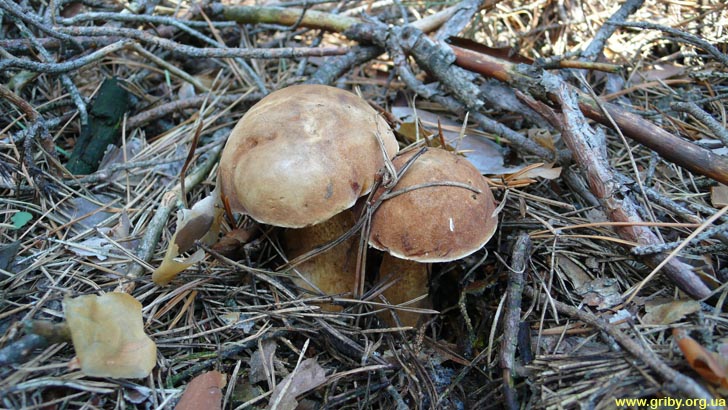
Poisoning with gall mushrooms can occur as a result of neglect of food or randomly. Therefore, one should not bring mushrooms from the forest or acquire from strangers, the appearance of which causes strong doubts in their edibility. Poisoning with gall mushrooms can occur as a result of neglect of food or randomly. Characteristics and propertiesMushrooms can be divided into edible, inedible and poisonous. Gall fungus - a typical and most common representative of the class of inedible.Much better known by the name of a bitter or false white fungus. It grows on the territory of Russia, mainly distributed in its middle zone. Can be found from June to October. The height of the mushroom varies in the range of 5-15 cm. The massive cap has a rounded shape with a spongy structure.
If poisoning with a gall fungus, you must call a doctor Its top is covered with a thick film, at the beginning of the growth of the gall fungus, it has a light brown color, and after a while it acquires a tinge of ocher. The leg of the bitter is large and thick, with a pronounced mesh. The color of the spores can be pink or pinkish brown. False white fungus prefers to grow on sandy or sandy-clay sedimentary soils. Coniferous forests and forest edges with rare plantings are suitable for its beneficial growth. Gorchak can often be found near tree stumps and tree trunks, and in dry weather - on rotters. Such mushrooms grow mainly in groups of 5-15 individuals, but they are found alone. The appearance of the gall fungus immediately attracts the attention of people, and insects and worms rarely attempt on it. The pulp of the bitchak has a white and fleshy, on the cut usually acquiring a red tint. The mushroom is odorless and bitter in taste. Spores of a young bitter do not have time to take the appropriate color. Therefore, it is often confused with boletus or boletus. Back to table of contents The main signs of intoxicationGall fungus contains tarry substances that cause poisoning. Even if they get a small amount on the tongue, a strong burning sensation appears. Resins are irritating to the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines. In medicine, this property of bitterness is used as a choleretic agent. In the course of research, components with immunostimulating and antitumor properties were isolated from the pulp.
As such, its taste is camouflaged with vinegar and spices.
Scientists still do not come to a common opinion regarding the toxicity of bitter. Some consider it unusable only because of the bitter taste that spoils the whole dish, while others believe that it represents a great danger and causes serious poisoning. They believe that there are toxins in the gall fungus that are chemically similar to those of plant origin. These poisons can enter the body through the pores of the skin and accumulate in the liver. And after a few days, the person will show signs of impaired bile production. The presence of a large concentration of poisons in the body causes the development of cirrhosis of the liver. Doctors attribute the bile fungus to the class of slightly poisonous. Symptoms of poisoning appear after 3 hours after entering the stomach as follows:
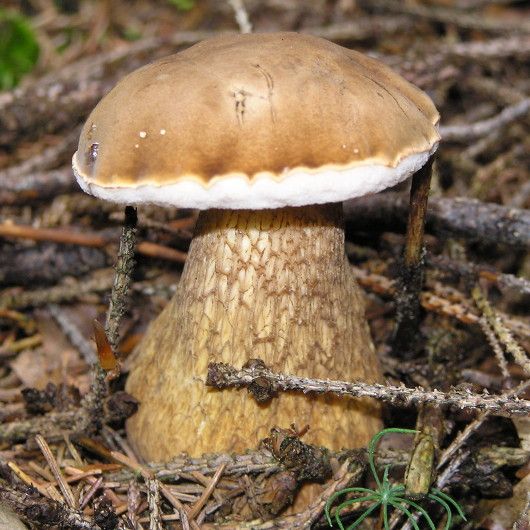
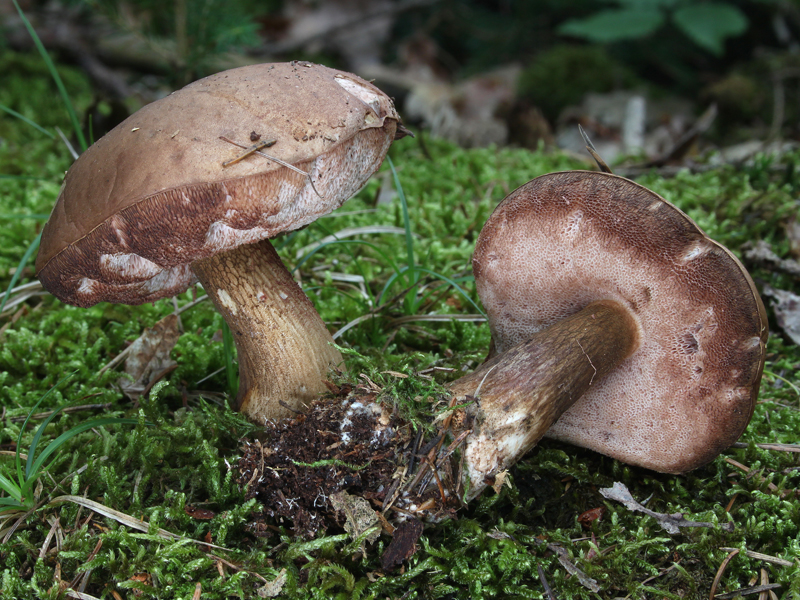
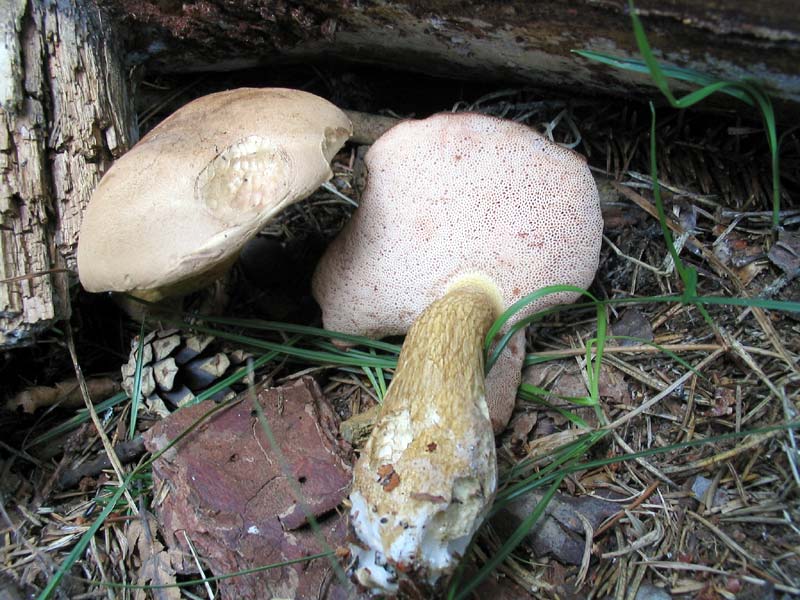
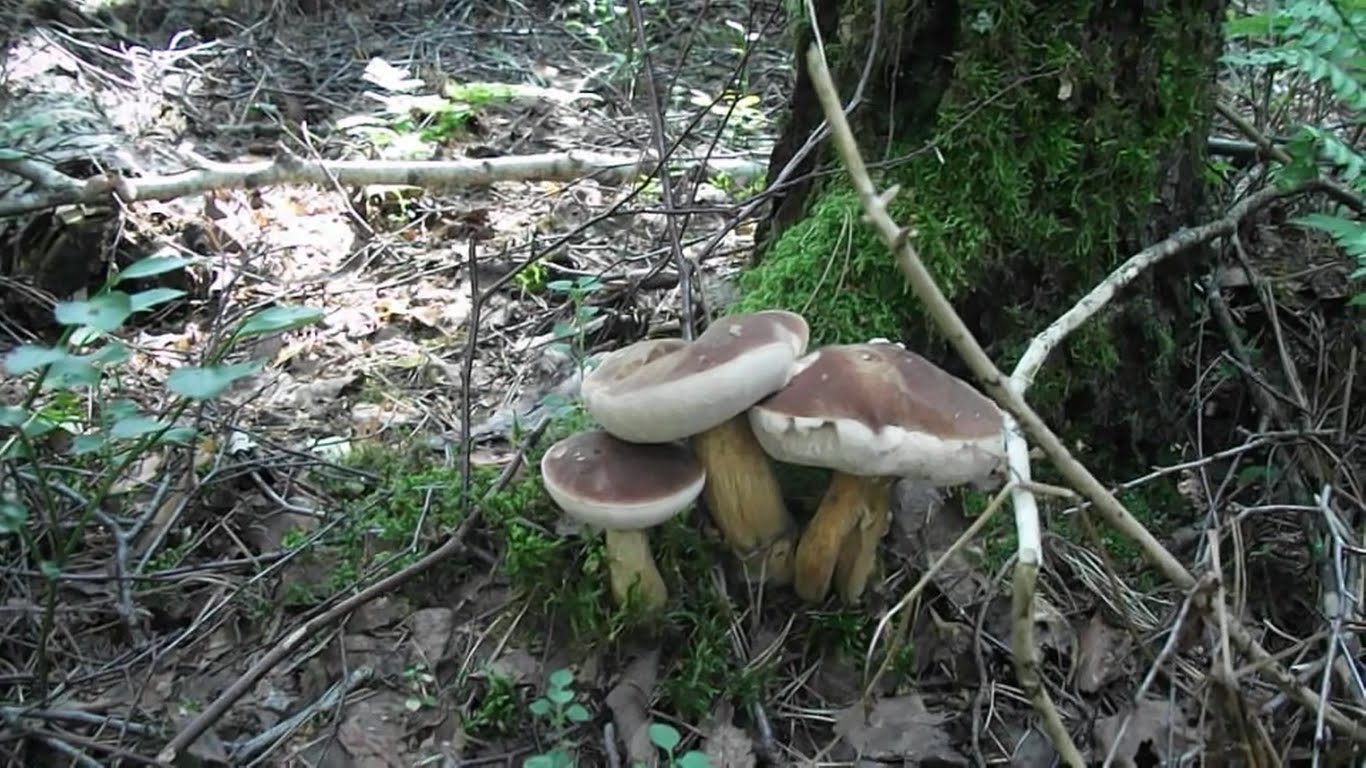
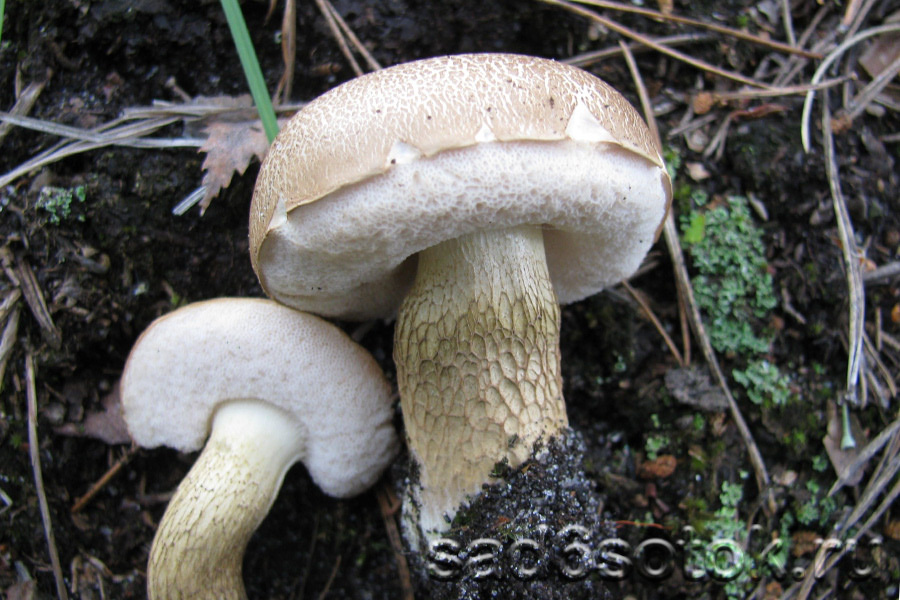
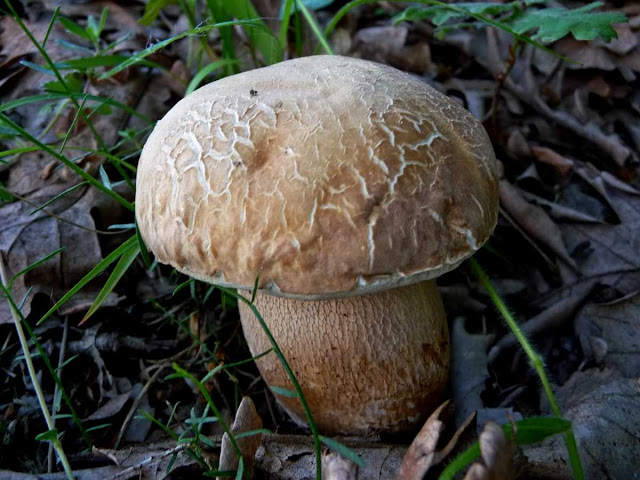
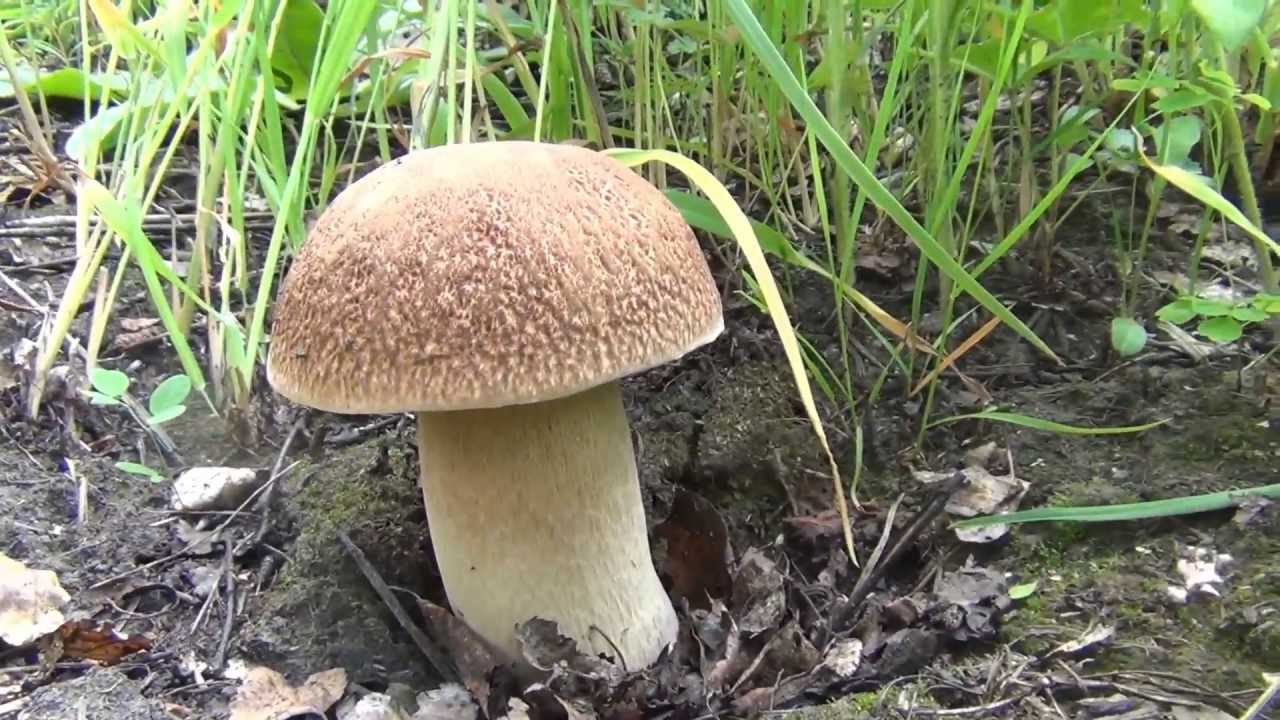
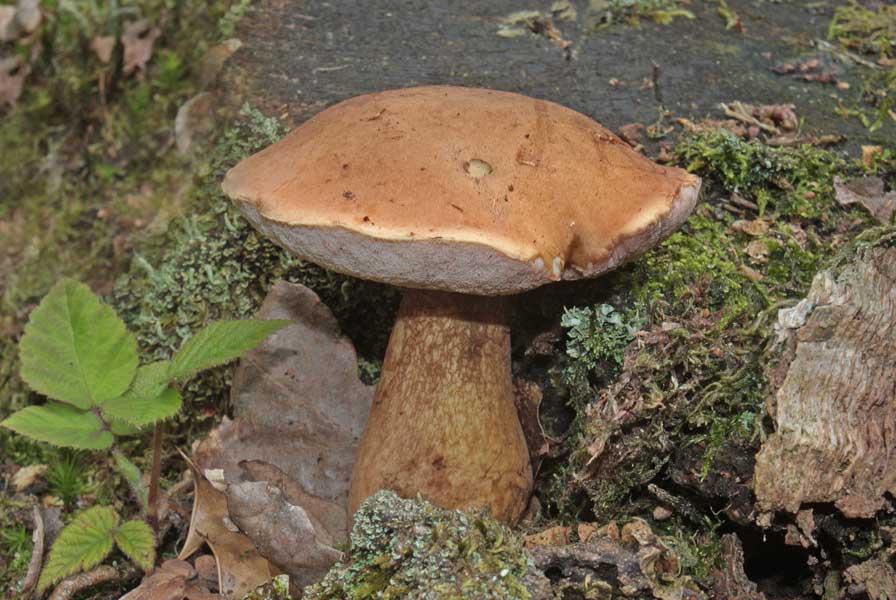
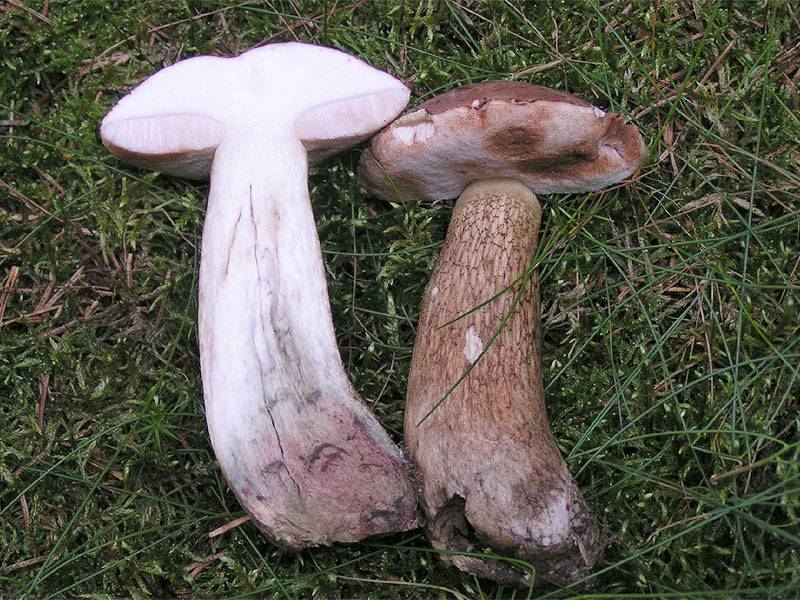
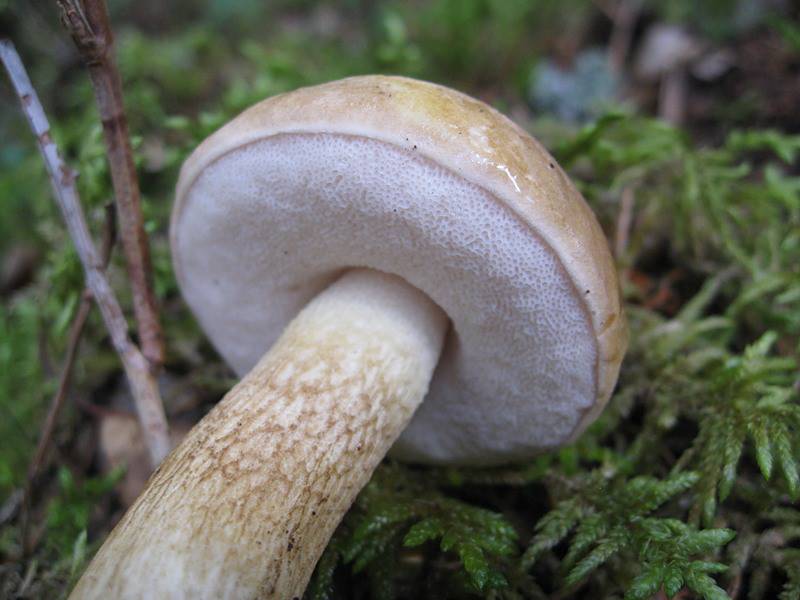
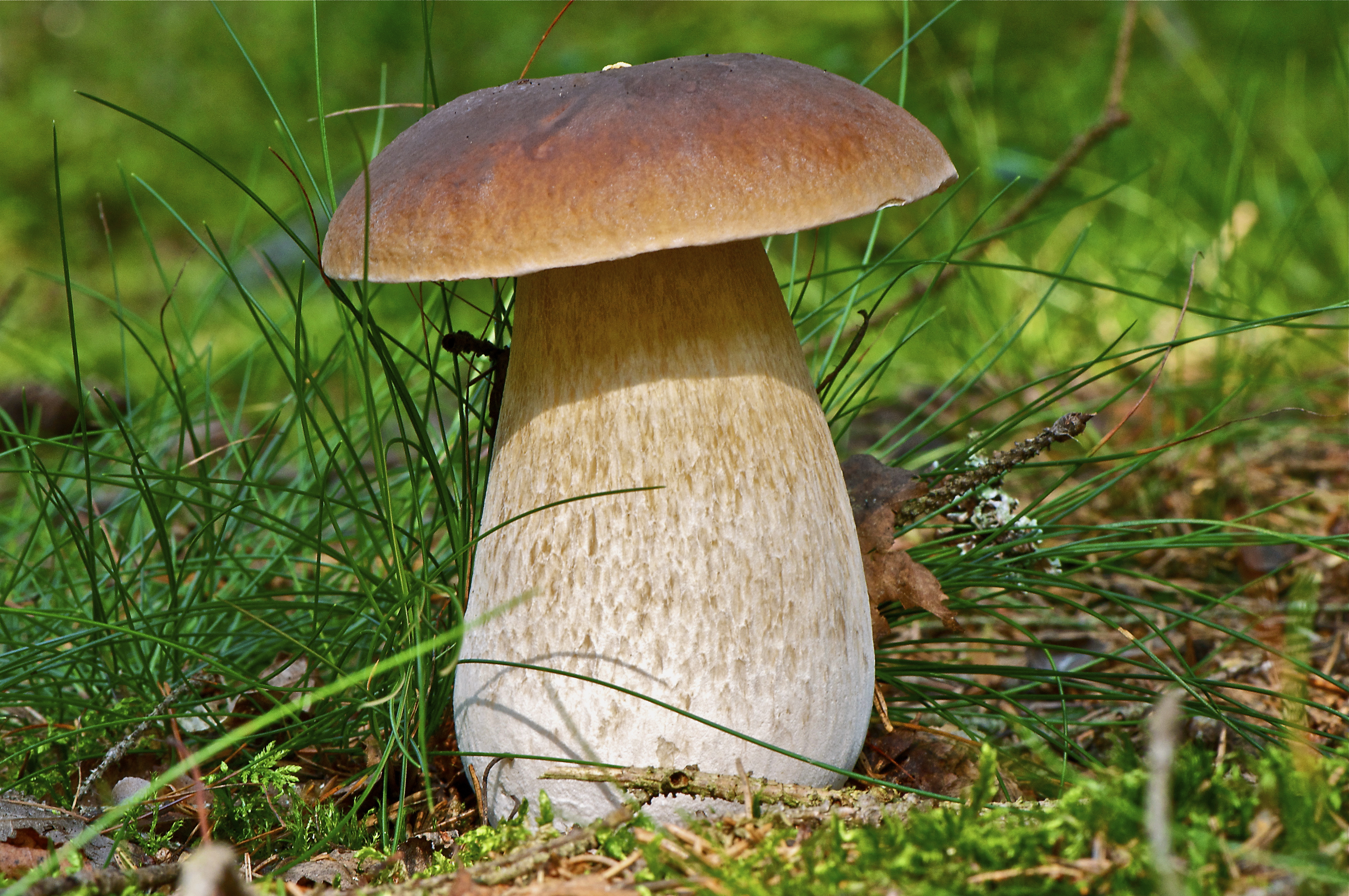
All these signs are not very pleasant and do not carry anything good for a person. When nausea develops into vomiting, and intestinal pain continues with diarrhea, this can cause severe dehydration. Then treatment will be required, but in general the outcome from poisoning is favorable. Within a few days the body is able to recover, and there should be no negative consequences. Spoil able. It is easily confused with boletus and boletus. We continue the description of mushrooms: what a gall mushroom looks like. Description of the mushroom as it looks and where it growsIt has a representative appearance, causing location. The mushroom has a hat, painted in light brown, chestnut or yellowish-gray shades. From age, it is covered with cracks and acquires a reddish-brown color. The bottom of the cap is white-pink, the old ones are distinguished by dirty-pink shades. Fungal pores are large, the flesh turns pink after cutting. The main sign that distinguishes the gall mushroom from edible is the pink tubular cap layer. It feels dry and velvety to the touch, has a small down. After the rain, being wetted, the cap becomes slightly sticky.
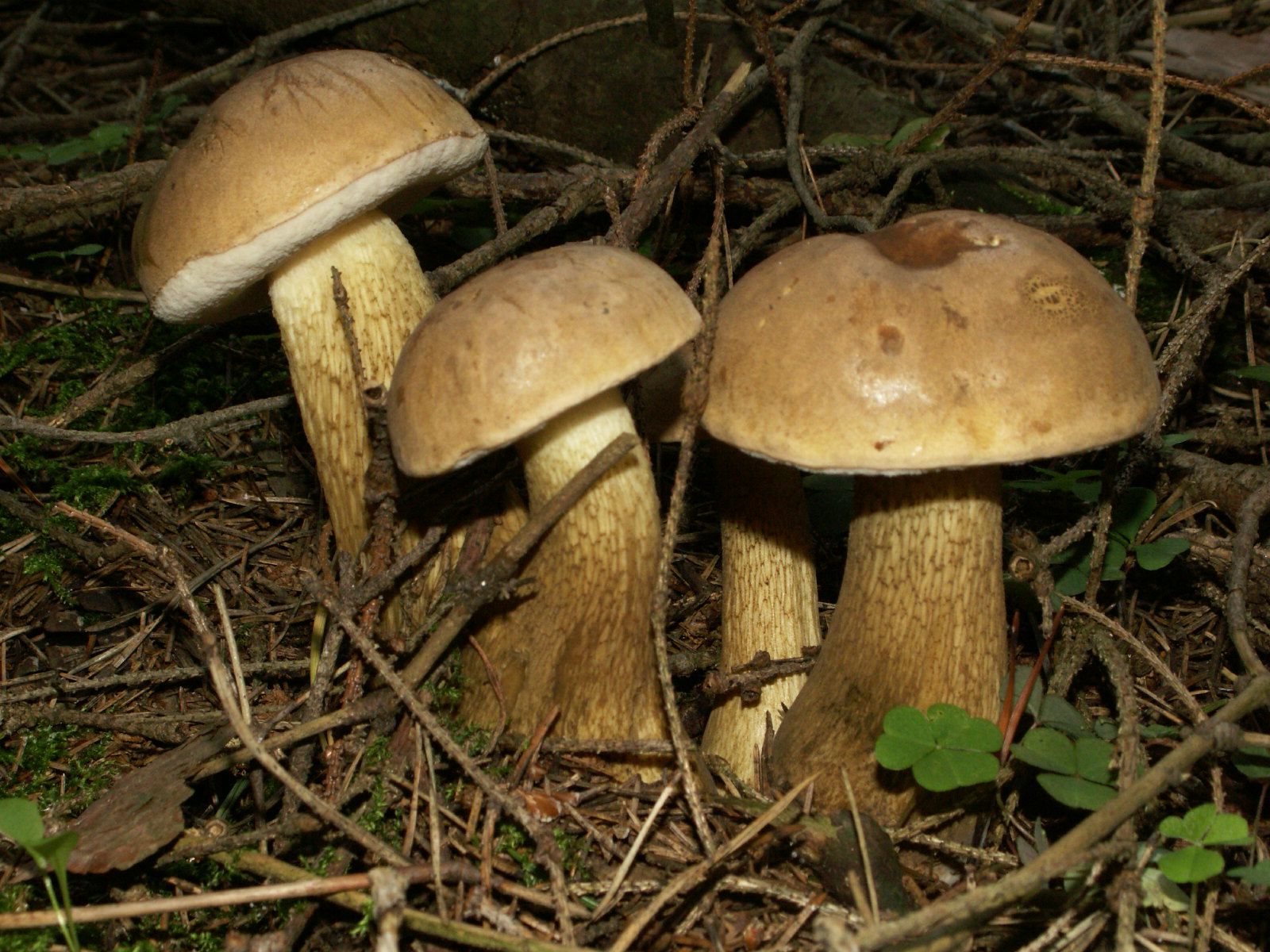
The mushroom pedicle is pinkish, in the upper part it has a dark-colored net. Additional vigilance can cause a mesh pattern of brown or blackish-brown outflow, located in the upper part of the leg. The shape of the legs is cylindrical, somewhat inflated towards the bottom.
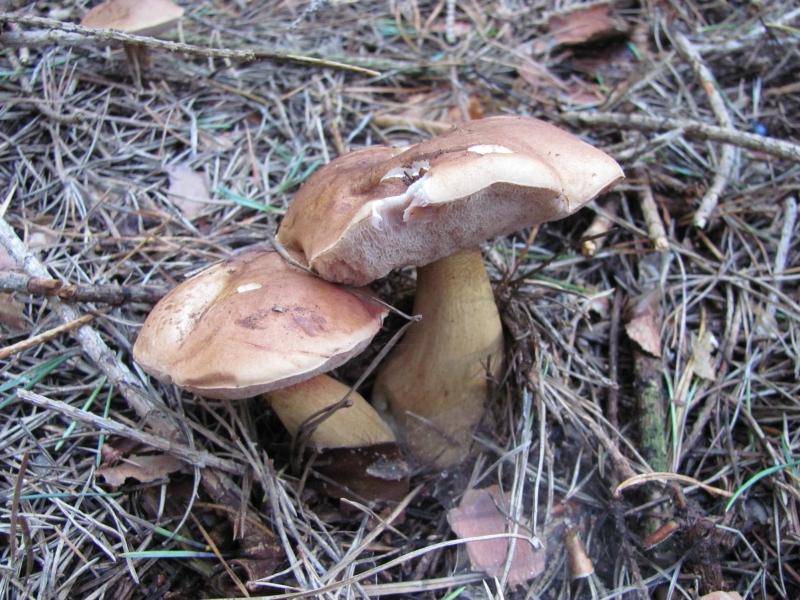
The fungus grows bile in mixed or coniferous forests, occurs rarely among deciduous trees, prefers acidic soil plots. He tries to be located among the serving root system of trees, on old stumps, fallen trunks. If you have found a gall mushroom - do not look for whites, they will not grow here. External signs of the mushroom look like white.
Especially for the species of boletus that grows in the southern oak forests. The greatest similarities are brown boletus. If you have doubts and do not find differences, pay attention to the leg of the fungus and the presence of scales on it.
They are absent in the gall fungus, which cannot be said about boletus mushrooms. The mesh on the leg of a boletus looks lighter.
Signs of poisoningRecall that the fungus bile poisonous is not considered - it is simply referred to as inedible species. Only one conclusion - the mushroom is not suitable for food because of its bitter taste.
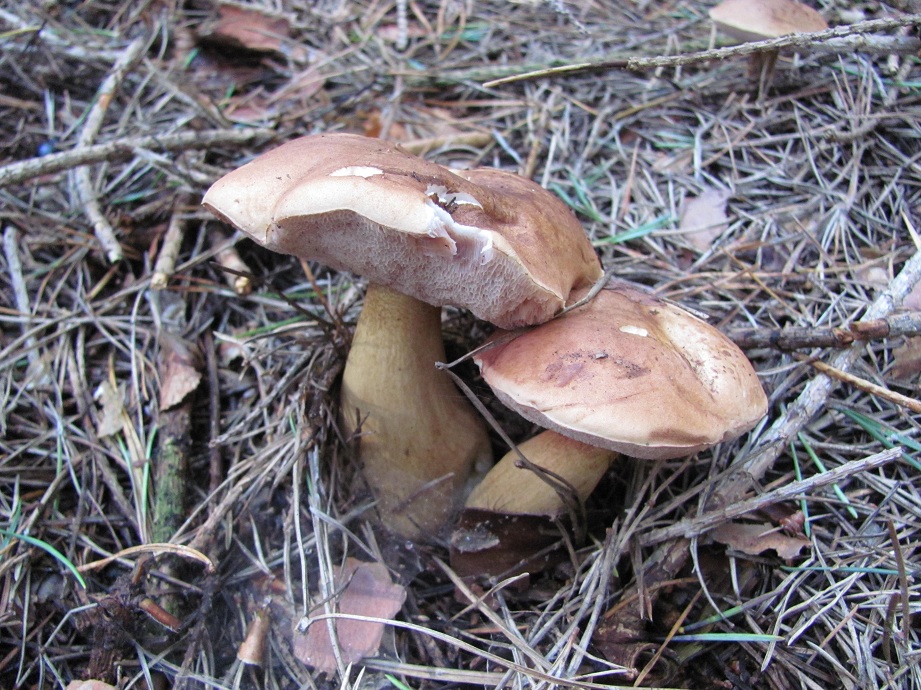
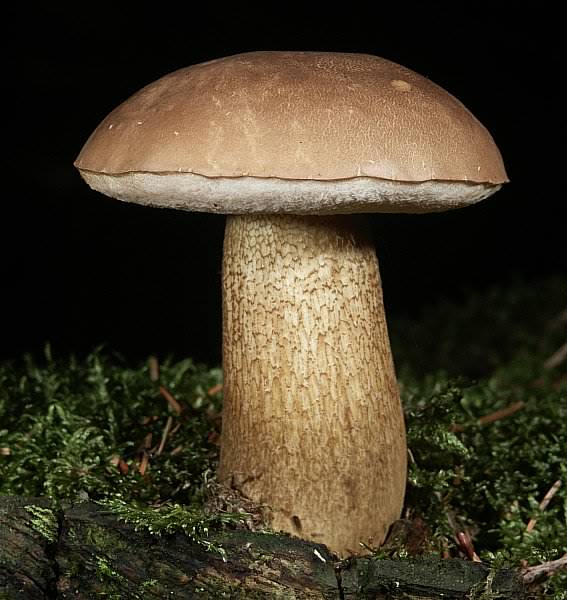
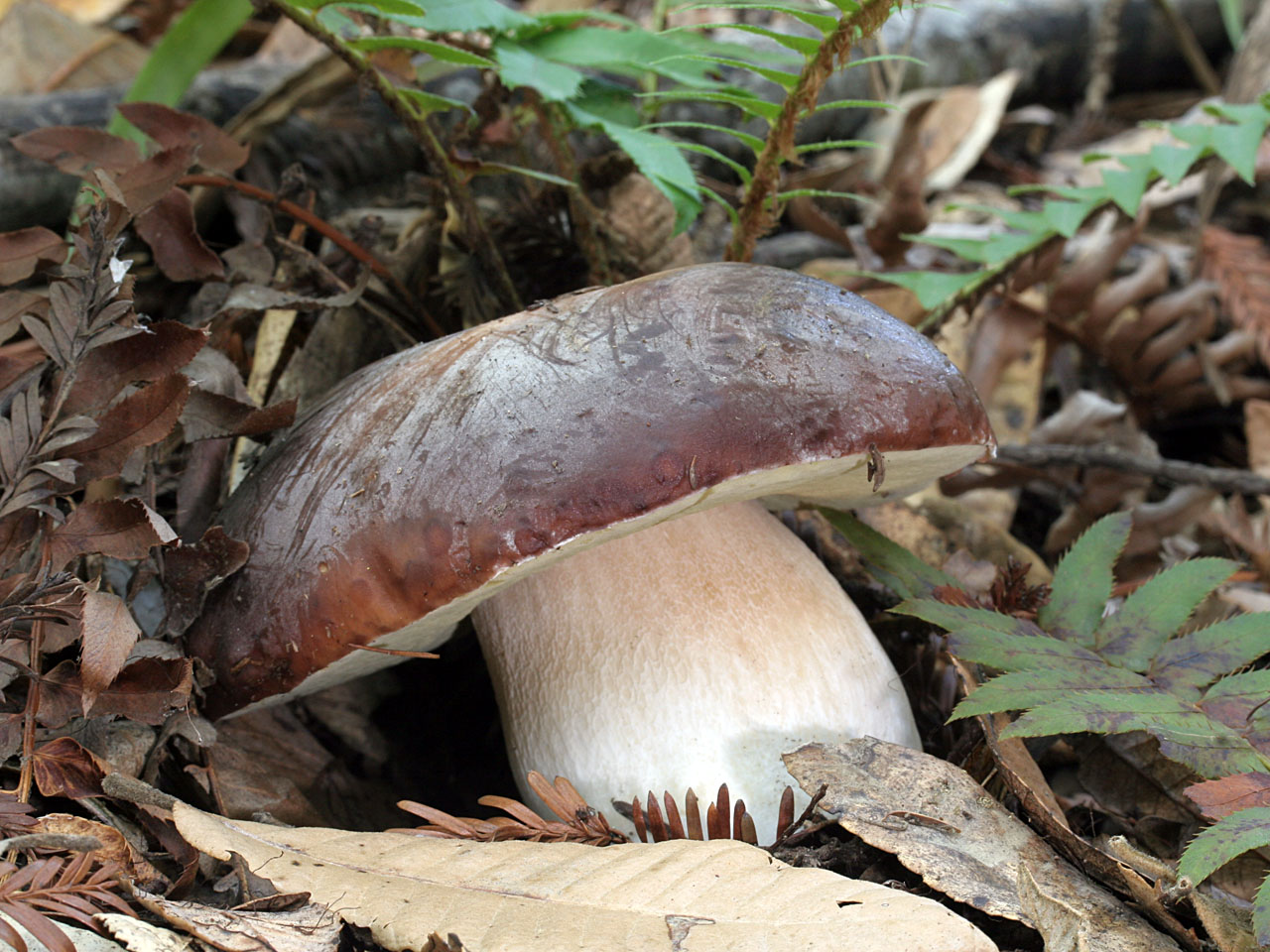
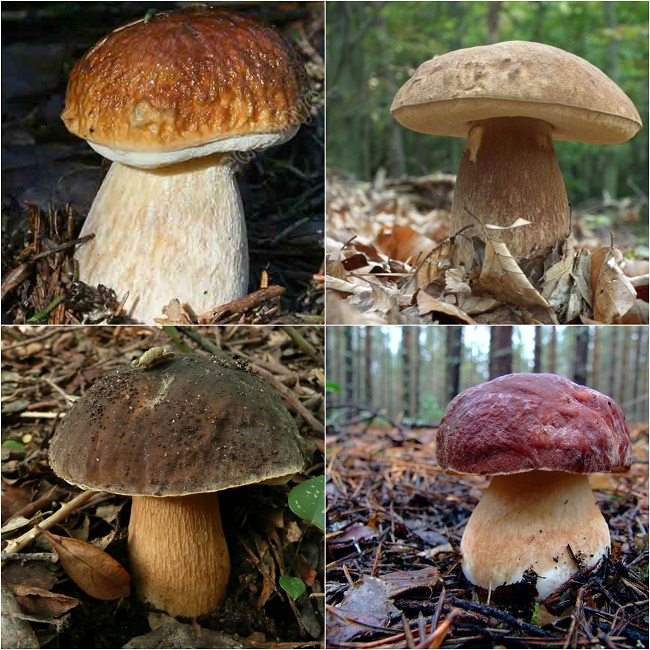
But scientists refute such a theory. They found that toxic elements are formed in the pulp of the gall fungus, which are distinguished by the ability to quickly penetrate into human blood even when touched to the fungus. Substances get into the liver, where they show destructive functions. Collecting the gall mushroom and checking it “on the tongue”, the person on the first day feels lightly spinning of the head and weakness. Further, the symptoms disappear. The first signs of poisoning come in a few weeks. After studying this information, you have the right to make a decision on your own - whether to pick up the gall mushroom and eat it, how edible it is. Please note that it is not eaten even by forest pests, which the fungus does not attract with its bitterness. In folk medicine: according to unconfirmed information, the bile fungus is used as a choleretic drug. The gall fungus (Tylorilus felleus) is an inedible tubular variety belonging to the genus Tilopil (Tylorilus) and the Boletov family (Bolytaseae). Mushroom cap with a size of not more than 14.0-15.0 cm, hemispherical, rounded-pillow or prostrate in shape, with a dry surface. The pulp is of a thin fibrous type. The surface is pubescent or slightly velvety, but at elevated moisture levels it may be slightly sticky. The color of the cap is yellowish-brownish, yellowish-brownish, light olive-brown, greyish-beige-ocher, grayish-brown, less often there are chestnut or brown-chocolate, dark brown hat. The flesh is usually white, reddening or not changing staining on the cut, with a very characteristic unpleasant, bitter taste, which has no particular smell and is almost never eaten by worms. The tubular layer growing to the leg, represented by white tubules with a pink or dirty pink tint. The pores are round or angular in shape, faceted type, small size, reddening or acquiring a brown color when pressed. The stem is cylindrical or club-shaped, with a characteristic swelling in the lower part, of a fibrous type, creamy-ocher, yellowish, ocher-yellow, or yellowish-brown-brown with a whitish or creamy-yellow upper part. A pronounced mesh, brownish, dark brown or slightly blackish pattern is necessarily present on the surface of the leg. Spore powder pinkish, pink or pinkish-brown coloring. The spore powder is represented by spindle-shaped ellipsoid spores in shape, with an absolutely smooth surface. Gall fungus is an inedible tubular variety belonging to the genus Tilopil and the Boletes family Other names of the bitterIn another way, this species is called Gorchak or white false mushroom. The name is due to the fact that the mushroom pulp has a very bitter taste, and the fruit bodies of this variety strongly resemble a noble white fungus in their appearance. Where does the gorchak mushroom grow?False white fungus is widely distributed almost everywhere in our country. This species is capable of forming resistant mycorrhiza with conifers and various deciduous tree species. Most often, bitters grow in coniferous forests, characterized by acidic fertile soils. Sometimes fruit bodies form on rotted stumps. Formed single fruit bodies or small groups from June to October. Gallery: Gorchak mushroom (25 photos)
Features of a bitch (video)Description of taste of bitterGall fungus is not poisonous - its flesh does not contain toxins. However, it is not possible to use the fruit bodies of this species for nutritional purposes, due to the presence of specific bitterness in the composition, which makes the taste very disgusting, pronounced bitter. Quite often, inexperienced mushroom pickers prepare dishes in which, in addition to edible species, a certain amount of false white mushroom is present.
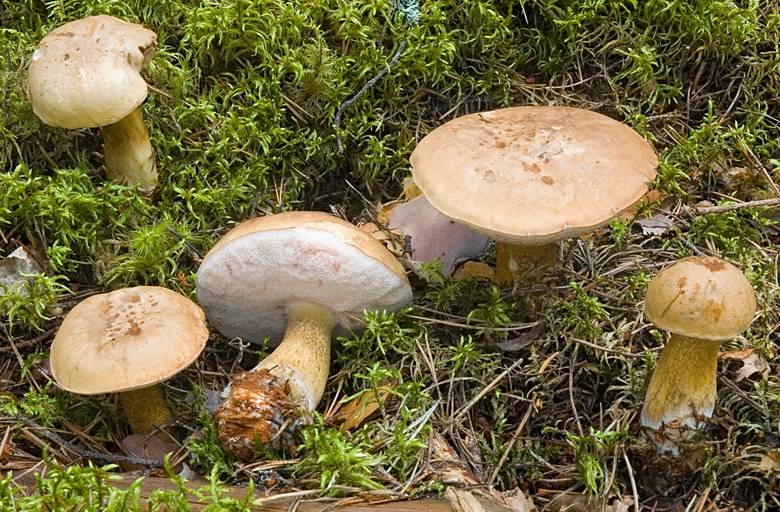
Gall fungus is not poisonous - its flesh does not contain toxins In this case, you have to recycle all the finished dish. It is for this reason that it is necessary to learn how to correctly distinguish a gall mushroom from edible varieties of similar appearance, which include almost all varieties of boletus, a true white mushroom or boletus, as well as some true boletus species. Where grows bitter (video)Similar types of mushroomsCurrently, there are several species similar to the false white fungus, which are classified as edible. White mushroomBoltus edulis is also known as the Boletus, and belongs to the Borovik genus. The cap is convex or flat-convex, sometimes prostrate, with a smooth or wrinkled, prone to cracking surface of a bare or thin-skinned type. With increased humidity, the surface is slightly mucous, in a dry - matte appearance or with shine. The skin of any shade of reddish-brown or almost white color, grown, not separated from strong and fleshy, sometimes fibrous, white flesh. The cut may be blue or a pinkish tint.
Boltus edulis is also known as the boletus, and belongs to the genus Borovik Mesh boletusVoletus tesisulatus belongs to the genus Borovik (Boletus) and the family of boletes (Botaceae). It has a hemispherical or strongly convex cap, covered with light brown, matte or velvety, dry, sometimes cracked skin. The dense and rather fleshy flesh of white color does not change on the cut; it has a pronounced mushroom aroma and a sweetish or slightly nutty taste. The stem is thick and fleshy, with a narrowed upper part, brownish or light brownish tinge, covered with a characteristic light-colored mesh pattern.
Mesh boletus Bronze boletusLetus aereus belongs to the Borovik genus. Hat of fleshy type, with high density, spherical, flat-convex or prostrate, covered with a smooth, velvety, sometimes grainy or cracked skin of dark, brown-brown, almost black color. Pulp of white coloring, not changing on a cut, having pleasant mushroom taste and aroma, characteristic of borovik. The foot is massive and rather hard, cylindrical in shape, with a thickening at the base, reddish-brown-brown coloring. . On the surface there is a convex mesh of light shades.
Bronze boletus BrownberryThe group of species belonging to the genus Obabok (Lessinum) is represented by:
The most poisonous mushrooms (video)Gall fungus belongs to the family Shishkogribribovyh. It is not edible mushroom. It can be eaten, but before that it must undergo thermal procedures in order to get rid of the poison. It tastes bitter, hence its second name “gorchak”. If you prepare edible mushrooms together with a gall mushroom, then it will transmit its bitterness to a normal mushroom, thereby spoiling the taste of the dish. CharacteristicOutwardly, the bitchak resembles a white mushroom and underbelly. In the people, because of its similarity with the white fungus, it is called "false white fungus." But there are features that distinguish it from other fruits:
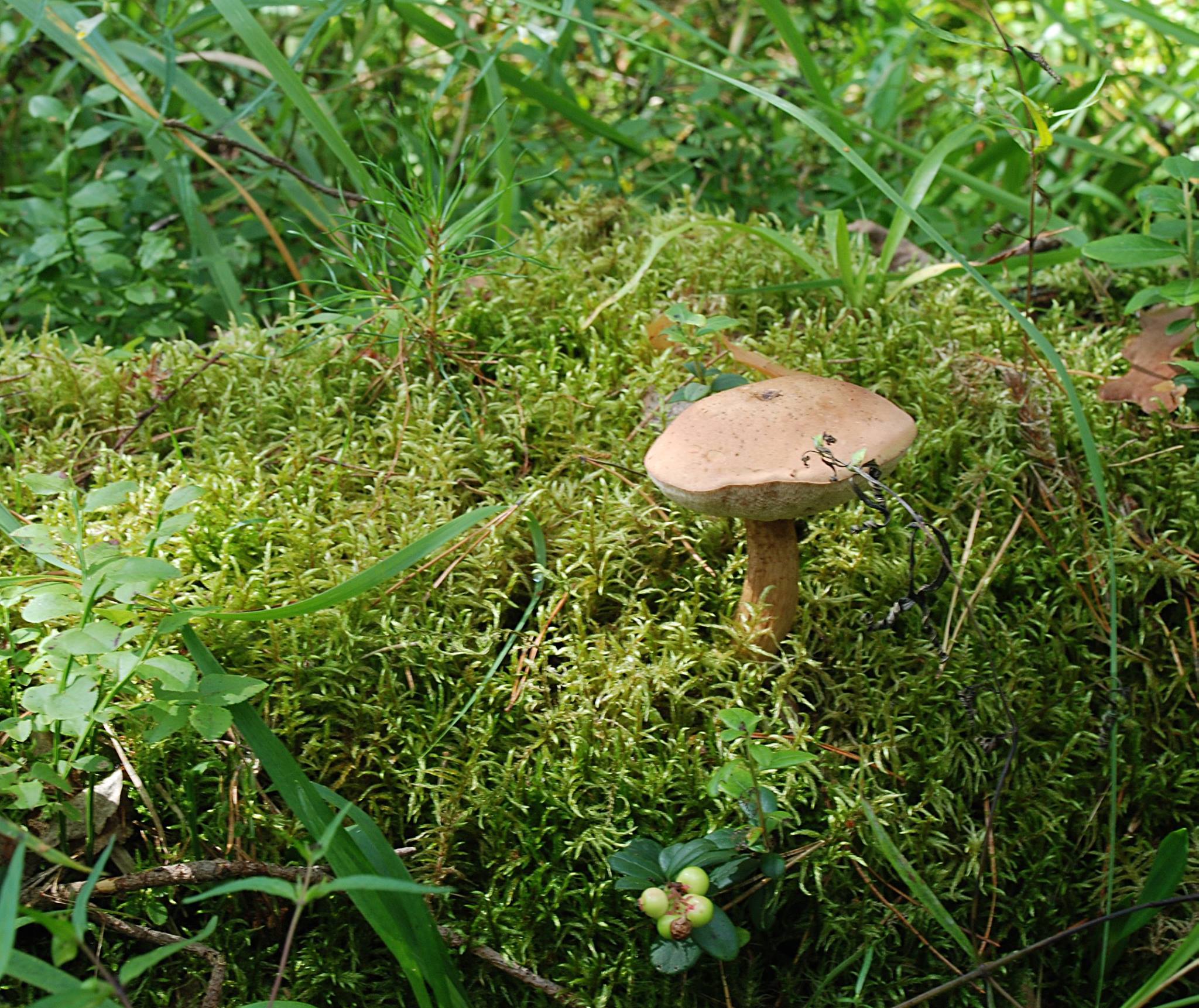
The cap of an inedible fetus can be of different sizes, from four to fifteen centimeters. Young fruits are hat-shaped closer to the globular, and already mature mushrooms, it is rounded and grows. The color of the cap itself can also vary, from yellow-brown to brown-light color. The most common white color, like a white fungus. Gorchak has pulp of fibrous structure, it has almost no smell or aroma, which all mushrooms have. The mustard plaster stem is cylinder-shaped with a slight decrease at the base. The size of the legs can also be different, in the aisles from three to thirteen centimeters, and its diameter is not large, about three centimeters. Over time, the leg of the bitter begins to hide with a mesh, a dense structure with white or gray fibers. Inedible bitter has round pores, in some cases they may become angular. The most important difference between a bit of gorchak is that a dark shade begins to appear in the place of breaking. And also the fact that insects such as worms are very rarely found in this type of mushroom. Most often, bitter can be found in coniferous areas. It grows in sandy soil. They grow both on some soil and on any stumps. He can live both in groups and by himself. The period of appearance of inedible bitterness is approximately in July and lasts till September. The activity of the emergence of a new crop depends on weather conditions. They grow most actively in the warm period of time. But a very large accumulation of them in one place can be seen rarely. The most favorable period for the appearance of gorchaka is the moment when heat comes after the rains. Signs for which you can distinguish from edible bitterGorchak is a fairly common species in temperate continental climates. Therefore, confusing it among other species is not difficult. In order to avoid getting an inedible fetus in the basket, it is recommended to know its features. The main differences are as follows:
Consequences of eating false white fungusGorchak belongs to the fruits that are not recommended to eat, but it does not contain poison in its composition. Since even worms and other insects avoid this fruit, it is understandable that it is not recommended for humans to be consumed. Its pulp contains toxic substances that contribute to the bitter taste. Since heat treatment increases bitter bitterness, it is very difficult for a person to eat a large amount of false white fungus at one time. It is from this cause that gall mushroom poisoning is very rare. The most common cases of food poisoning are observed if the fungus was confused with mushrooms similar to it and got into preservation. When canning these fruits are used, vinegar and various spices are used, and this hides the bitterness of the false white fungus, which increases the risk of poisoning. Some scientists argue that even with direct contact with him, you can get a toxic effect. If the toxic substances of gorchaka hit the human body, then they first begin to destroy his liver. The first symptoms that signal poisoning do not begin to appear immediately, but can only be felt after a week or even a month. The main symptoms of poisoning include the following:
Medicinal features of the gall fungusStrangely enough, but this completely inedible mushroom has medicinal features. From it were extracted some substances that are actively used in medicine. One such component is tilopilan. It is a substance that stimulates the immune system in humans. This substance improves the concentration of phagocytosis, which is a process that makes it possible for certain substances to look for and fight against foreign microorganisms in the body. In the nineteenth century, an inedible bitter was tested, and scientists proved that it can fight cancer cells. In addition to these advantages, it contains a component that is capable of over-harvesting bacterial cells. An interesting fact is that in ancient times, bitter was used as a ritual dish. This phenomenon was symbolic, because its round hats had a very bitter taste. They were a symbol of the bitterness of losing a loved one. At the same time, it was used in medicine as a choleretic agent. Due to the external similarity, inexperienced mushroom pickers often confuse a gall mushroom with porcini or boletus mushrooms. However, the benefits of such a trophy a little. Even a small piece of this mushroom, caught in the pan when frying with others, is able to make the dish completely unfit for consumption. The gall mushroom is not poisonous, but it is not worth eating. No wonder people call it bitter and bitter - the pulp of these mushrooms (especially young specimens) is very bitter, and during heat treatment the bitterness does not disappear, as happens with some mushrooms, but increases several times. Mushrooms like Gorchak, which for one reason or another are not eaten, are referred to as inedible. Why is bile mushroom inedible?There are a lot of reasons why mushrooms are not considered edible. As a rule, such mushrooms cannot be poisoned, but it is almost impossible for them to eat them. Some mushrooms have an unusually unpleasant odor, others are so tough that it is very difficult to chew, the third fruit bodies are covered with dense spikes and growths that prevent them from being eaten. Some mushroom pickers say that soaking the gall fungus in water helps to get rid of bitterness, and vinegar and other spices help mask the unpleasant taste of bitter in pickles. However, most fans of "quiet hunting" agree that the gall mushroom is simply not worth collecting. Interestingly, some people do not feel the strong bitterness of the gall fungus and can safely eat it. It turned out that the reason for this phenomenon is genetic - such people lack receptors of a certain type that allow them to distinguish bitter taste. But what compounds give the bitter taste of the mushrooms themselves, is still not known. Important unionThis species was first described by the French mycologist Pierre Bulliard in 1788. He attributed this mushroom to the genus Borovikov. Subsequently, changes occurred in the taxonomy of fungi, and experts recorded an inedible bitter in rodtilopilus. The gall mushroom prefers dry coniferous forests, grows close to old rotten trees, but is also found on the trunks themselves and collapsing stumps. Quite often you can find quite numerous clusters of gorchaks - under favorable conditions, they grow well and multiply. Gall mushrooms form mycorrhiza with roots of spruce and pine. Such cooperation between fungal hyphae and the roots of higher plants is beneficial for both members of the union. Mushrooms receive the amino acids and carbohydrates necessary for growth, and the tree has the ability to absorb phosphorus compounds and other mineral substances with water. Multicolored hatsIt is easy to spot a gall mushroom in the forest: strong bitters with rounded neat caps look quite attractive. They can be different shades: there are reddish-brown, yellowish and olive. Like most other mushrooms belonging to the family of boletes, in dry weather the hat of the gorchak seems velvety to the touch, and in rainy time it becomes slippery. Himenofor - the layer in which spores mature, the bile fungus has a tubular structure. It is located on the underside of the cap and is easily separated from it. In young mushrooms, the tubules are painted in a light pink color, while in older specimens they darken, acquiring a brownish tint. The leg of a bitter tree is rather dense, outside it is covered with a dark pattern resembling a grid. Double MushroomAnother name for the gall fungus is the false white fungus. It is not at all difficult to confuse a gorchak with a dense boletus, the white fungus and the bile appear in the forests at about the same time - they can be found from July to September. These mushrooms belong to the same family and are really quite similar. An important distinguishing feature is the color of the mesh on the leg: it is dark in bitter, and in a boletus and its fellows - a lighter shade. The white flesh of a grubka when cut becomes pinkish, and the light flesh of the white fungus does not change color. In order not to confuse a gall mushroom with a boletus, one should not forget that there are no characteristic scales for boletus on a leg of a gorchak. Some mushroom pickers just taste the pulp of the fungus - the sharp bitterness of the gall fungus is felt immediately. However, this is still not worth it - an unpleasant taste remains in the mouth for a long time. All gymnosperms and a large number of angiosperms form mycorrhiza. Pine trees, for example, cannot live without mycorrhiza at all, and only thanks to the mushrooms they get the necessary mineral compounds. Other plants can exist without the help of fungi, but mycorrhiza increases the ability of plants to absorb nutrients from the soil several dozen times. There is a subspecies of gall fungus, the raw flesh of which has a rather pleasant sweetish flavor. However, this mushroom, which looks different from the lighter coloring of the cap and leg, is not used in food. When it is cooked, the pulp also becomes unbearably bitter. a brief description ofKingdom: mushrooms.  
|
| Read: |
|---|
New
- Detection of pancreatitis with various tests
- How to rejuvenate your face at home
- Injection methods of rejuvenation
- Rowing purple edible
- Why does willow bloom early?
- What soap neutral pH
- Collective children's work on the theme: "Autumn bouquet
- Transport card "Wave"
- What period to get pregnant
- Blood. Blood type. Rh factor